Abstract
Background
Multiple meta-analyses (MAs) have demonstrated that six pharmacotherapies, including orlistat, liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, semaglutide, and tirzepatide, improve weight loss and weight maintenance. However, few studies have synthesized and evaluated the quality of this evidence.
Objective
To identify the relevant MAs of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that explored the association between the six pharmacotherapies and obesity-related health outcomes and adverse events (AEs).
Methods
A comprehensive search was conducted across PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science from database inception up to January 2024. We calculated the effect size as the mean difference and risk ratio using the random-effects model. The quality of MAs was evaluated using “A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews 2”.
Results
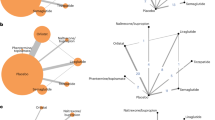
Sixteen MAs comprising 235 RCTs that described 115 unique associations between the six pharmacotherapies and various health outcomes were included. Overall, 101 statistically significant associations (88%) had beneficial outcomes on body weight, weight loss, waist circumference, body mass index, total cholesterol, triglycerides, both low-density and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, blood pressure, and glycemic profile. The pharmacotherapies were associated with significant weight loss and partial improvements in the lipid profile, blood pressure, and glycemic control among individuals with overweight or obesity. Notable AEs were associated with liraglutide, naltrexone/bupropion, semaglutide, and orlistat. The methodological quality of the included MAs requires improvement.
Conclusions
This umbrella review identified significant beneficial associations between pharmacotherapies and anthropometric measures, lipid profile, blood pressure, glycemic profile, and quality-of-life outcomes in individuals with overweight or obesity. In addition, the umbrella review highlighted safety considerations. The findings affirm the efficacy of the six pharmacotherapies in promoting weight loss in this demographic. Further clinical trials with long-term follow-up are essential to evaluate the effects of these pharmacotherapies on clinical outcomes, including cancer, cardiovascular events, and mortality.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data for this article can be found in the Appendix.
References
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387:1377–96..
Gadde KM, Martin CK, Berthoud HR, Heymsfield SB. Obesity: pathophysiology and management. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:69–84.
Garvey WT, Mechanick JI, Brett EM, Garber AJ, Hurley DL, Jastreboff AM, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for medical care of patients with obesity. Endocr Pract. 2016;22:1–203.
Bray GA, Fruhbeck G, Ryan DH, Wilding JP. Management of obesity. Lancet. 2016;387:1947–56.
The GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators, Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, Sur P, Estep K, Lee A, et al. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:13–27.
Wharton S, Lau DCW, Vallis M, Sharma AM, Biertho L, Campbell-Scherer D, et al. Obesity in adults: a clinical practice guideline. CMAJ. 2020;192:e875–91.
Arterburn DE, Telem DA, Kushner RF, Courcoulas AP. Benefits and risks of bariatric surgery in adults: a review. JAMA. 2020;324:879–87.
Ikramuddin S, Korner J, Lee WJ, Connett JE, Inabnet WB, Billington CJ, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs intensive medical management for the control of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia: the Diabetes Surgery Study randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;309:2240–9.
Food and Drug Administration. Accessed 11/26/2024, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014.
Food and Drug Administration. Accessed 11/26/2024, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-medication-chronic-weight-management.
Jobanputra R, Sargeant JA, Almaqhawi A, Ahmad E, Arsenyadis F, Webb DR, et al. The effects of weight-lowering pharmacotherapies on physical activity, function and fitness: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. 2023;24:e13553.
Lei XG, Ruan JQ, Lai C, Sun Z, Yang X. Efficacy and safety of phentermine/topiramate in adults with overweight or obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2021;29:985–94.
Patikorn C, Roubal K, Veettil SK, Chandran V, Pham T, Lee YY. Intermittent fasting and obesity-related health outcomes: an umbrella review of meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2139558.
Rozga M, Handu D. Nutrition interventions for pediatric obesity prevention: an umbrella review of systematic reviews. Nutrients. 2023;15:5097.
Kermansaravi M, Vitiello A, Valizadeh R, Shahmiri SS, Musella M. Comparing the safety and efficacy of sleeve gastrectomy versus Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in elderly (>60 years) with severe obesity: an umbrella systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2023;109:3541–54.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017;358:j4008.
Lu TT, Lu CC, Li MX, Ke LX, Cai H, Yang KH. Reporting and methodological quality of meta-analyses of acupuncture for patients with migraine: a methodological investigation with evidence map. J Integr Med. 2022;20:213–20.
Lu CC, Ke LX, Li JY, Zhao HT, Lu TT, Mentis AFA, et al. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and health outcomes: a meta-research review of meta-analyses and an evidence mapping study. Phytomedicine. 2021;91:153699.
Thorlund K, Walter SD, Johnston BC, Furukawa TA, Guyatt GH. Pooling health-related quality of life outcomes in meta-analysis-a tutorial and review of methods for enhancing interpretability. Res Synth Methods. 2011;2:188–203.
Nikniaz Z, Nikniaz L, Farhangi MA, Mehralizadeh H, Salekzamani S. Effect of Orlistat on anthropometrics and metabolic indices in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023;23:142.
Rohani P, Malekpour Alamdari N, Bagheri SE, Hekmatdoost A, Sohouli MH. The effects of subcutaneous Tirzepatide on obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1230206.
Konwar M, Bose D, Jaiswal SK, Maurya MK, Ravi R. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide 3.0 mg in patients with overweight and obese with or without diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2022;2022:1201977.
Barboza JJ, Huamán MR, Melgar B, Diaz-Arocutipa C, Valenzuela-Rodriguez G, Hernandez AV. Efficacy of liraglutide in non-diabetic obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Med. 2022;11:2998.
Gao X, Hua X, Wang X, Xu W, Zhang Y, Shi C, et al. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide on weight loss in obese or overweight patients without diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:935823.
Tan HC, Dampil OA, Marquez MM. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide for weight loss in obesity without diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2022;37:65–72.
Singh AK, Singh R. Pharmacotherapy in obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of anti-obesity drugs. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2020;13:53–64.
Onakpoya IJ, Lee JJ, Mahtani KR, Aronson JK, Heneghan CJ. Naltrexone-bupropion (Mysimba) in management of obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of unpublished clinical study reports. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;86:646–67.
Zhang P, Liu Y, Ren Y, Bai J, Zhang G, Cui Y. The efficacy and safety of liraglutide in the obese, non-diabetic individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Afr Health Sci. 2019;19:2591–9.
Sahebkar A, Simental-Mendía LE, Reiner Ž, Kovanen PT, Simental-Mendía M, Bianconi V, et al. Effect of orlistat on plasma lipids and body weight: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 33 randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol Res. 2017;122:53–65.
Rucker D, Padwal R, Li SK, Curioni C, Lau DC. Long term pharmacotherapy for obesity and overweight: updated meta-analysis. BMJ. 2007;335:1194–9.
O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G. A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness of orlistat used for the management of obesity. Obes Rev. 2004;5:51–68.
Hutton B, Fergusson D. Changes in body weight and serum lipid profile in obese patients treated with orlistat in addition to a hypocaloric diet: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80:1461–8.
O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G. A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of orlistat in the management of obesity. Health Technol Assess. 2001;5:1–81.
Ryan DH. Next generation antiobesity medications: setmelanotide, semaglutide, tirzepatide and bimagrumab: what do they mean for clinical practice? J Obesity Metabol Syndrome. 2021;30:196–208.
Wharton S, Calanna S, Davies M, Dicker D, Goldman B, Lingvay I, et al. Gastrointestinal tolerability of once-weekly semaglutide 2.4 mg in adults with overweight or obesity, and the relationship between gastrointestinal adverse events and weight loss. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022;24:94–105.
Khera R, Murad MH, Chandar AK, Dulai PS, Wang Z, Prokop LJ, et al. Association of pharmacological treatments for obesity with weight loss and adverse events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016;315:2424–34.
Shi Q, Wang Y, Hao Q, Vandvik PO, Guyatt G, Li J, et al. Pharmacotherapy for adults with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 2024;403:e21–31.
Davies MJ, Bergenstal R, Bode B, Kushner RF, Lewin A, Skjøth TV, et al. NN8022-1922 Study Group. Efficacy of liraglutide for weight loss among patients with type 2 diabetes: the SCALE diabetes randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314:687–99.
Ge L, Tian JH, Li YN, Pan JX, Li G, Wei D, et al. Association between prospective registration and overall reporting and methodological quality of systematic reviews: a meta-epidemiological study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;93:45–55.
Lu TT, Liu B, Lu CC, Du ZX, Yang KH, Ge L, et al. Reporting quality of acupuncture overviews: a methodological investigation based on the PRIOR statement. Complement Ther Med. 2024;82:103034.
US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for obesity in adults: recommendations and rationale. Am Fam Physician. 2004;69:1973–6.
Yanovski SZ, Yanovski JA. Long-term drug treatment for obesity: a systematic and clinical review. JAMA. 2014;311:74–86.
Camilleri M, Acosta A. Gastrointestinal traits: individualizing therapy for obesity with drugs and devices. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83:48–56.
Funding
This research was funded by the Gansu Provincial Youth Science and Technology Fund Program (No. 22JR5RA706), the 2022 Master/Doctor/Postdoctoral program of NHC Key Laboratory of Diagnosis and Therapy of Gastrointestinal Tumor (No. NHCDP2022017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TTL and YL contributed to the conception and design. TTL and BL contributed to the acquisition of data. YLL and LG contributed to the analysis and interpretation of data; TTL and BL drafted the manuscript; YL revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Tt., Liu, B., Ge, L. et al. Association of long-term weight management pharmacotherapy with multiple health outcomes: an umbrella review and evidence map. Int J Obes 49, 464–477 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01719-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01719-3