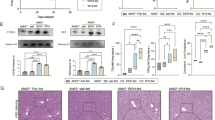
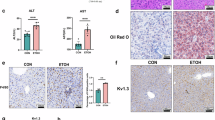
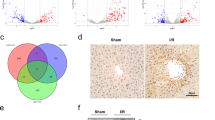
Abstract
Alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) remains a predominant cause of chronic hepatic pathology, and effective therapeutic strategies are needed. Krüppel-like factor 15 (KLF15) is a member of the KLF family of zinc-finger transcription factors and is ubiquitously expressed in metabolically active tissues, with a particularly high abundance in the liver. KLF15 has been implicated in various hepatic disorders. In this study, we investigated the pathophysiological role of KLF15 in ALD. We established a National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) model in mice by feeding them an ethanol Lieber–DeCarli liquid diet containing 5% (vol/vol) ethanol for 10 days. EtOH-fed mice were administered binge ethanol gavage (5 g/kg, body weight) on D11. We observed that the expression levels of KLF15 were significantly decreased in the livers of ALD patients and model mice. Overexpression of KLF15 conferred substantial protective effects in EtOH-fed mice, as evidenced by attenuated hepatic injury, apoptosis, steatosis and inflammation. In ethanol-treated AML-12 cells, overexpression of KLF15 reduced apoptosis and steatosis, whereas KLF15 knockdown exacerbated these pathological features. By performing RNA-seq and bioinformatics analyses, we observed that KLF15 regulated the AKT pathway by directly binding to the PFKFB3 promoter (−128 to −121). The physical interaction between PFKFB3 and AKT1 was further verified by Co-IP and molecular docking. These results suggest that KLF15 is a pivotal regulator of ALD pathogenesis through modulation of the PFKFB3/AKT axis, highlighting its potential as a novel therapeutic target for ALD intervention.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seitz HK, Bataller R, Cortez-Pinto H, Gao B, Gual A, Lackner C, et al. Alcoholic liver disease. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2018;4:16.
Bajaj JS. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:235–46.
Parker R, Kim SJ, Gao B. Alcohol, adipose tissue and liver disease: mechanistic links and clinical considerations. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:50–9.
Tacke F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2017;66:1300–12.
Liu K, Wang FS, Xu R. Neutrophils in liver diseases: pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18:38–44.
Rogal S, Youk A, Zhang H, Gellad WF, Fine MJ, Good CB, et al. Impact of alcohol use disorder treatment on clinical outcomes among patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2020;71:2080–92.
Chen H, Li LL, Du Y. Kruppel-like factor 15 in liver diseases: insights into metabolic reprogramming. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1115226.
Anzai K, Tsuruya K, Ida K, Kagawa T, Inagaki Y, Kamiya A. Kruppel-like factor 15 induces the development of mature hepatocyte-like cells from hepatoblasts. Sci Rep. 2021;11:18551.
Zhou L, Li Q, Chen A, Liu N, Chen N, Chen X, et al. KLF15-activating Twist2 ameliorated hepatic steatosis by inhibiting inflammation and improving mitochondrial dysfunction via NF-kappaB-FGF21 or SREBP1c-FGF21 pathway. FASEB J. 2019;33:14254–69.
Wang G, Wu B, Cui Y, Zhang B, Jiang C, Wang H. Teneligliptin promotes bile acid synthesis and attenuates lipid accumulation in obese mice by targeting the KLF15-Fgf15 pathway. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020;33:2164–71.
Hou W, Huo KG, Guo X, Xu M, Yang Y, Shi Z, et al. KLF15-Cyp3a11 axis regulates rifampicin-induced liver injury. Drug Metab Dispos. 2024;52:606–13.
Bertola A, Mathews S, Ki SH, Wang H, Gao B. Mouse model of chronic and binge ethanol feeding (the NIAAA model). Nat Protoc. 2013;8:627–37.
Song Q, Chen Y, Wang J, Hao L, Huang C, Griffiths A, et al. ER stress-induced upregulation of NNMT contributes to alcohol-related fatty liver development. J Hepatol. 2020;73:783–93.
Sun LJ, Chen X, Zhu S, Xu JJ, Li XF, Diao SX, et al. Hesperetin derivative 2a inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury in mice via downregulation of circDcbld2. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024;45:354–65.
Jung DY, Chalasani U, Pan N, Friedline RH, Prosdocimo DA, Nam M, et al. KLF15 is a molecular link between endoplasmic reticulum stress and insulin resistance. PLoS One. 2013;8:e77851.
Gao X, Huang L, Grosjean F, Esposito V, Wu J, Fu L, et al. Low-protein diet supplemented with ketoacids reduces the severity of renal disease in 5/6 nephrectomized rats: a role for KLF15. Kidney Int. 2011;79:987–96.
Yang K, Qiu T, Zhou J, Gong X, Zhang X, Lan Y, et al. Blockage of glycolysis by targeting PFKFB3 suppresses the development of infantile hemangioma. J Transl Med. 2023;21:85.
Shi WK, Zhu XD, Wang CH, Zhang YY, Cai H, Li XL, et al. PFKFB3 blockade inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by impairing DNA repair through AKT. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:428.
Dou Q, Grant AK, Callahan C, Coutinho de Souza P, Mwin D, Booth AL, et al. PFKFB3-mediated pro-glycolytic shift in hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;15:61–75.
Mejias M, Gallego J, Naranjo-Suarez S, Ramirez M, Pell N, Manzano A, et al. CPEB4 increases expression of PFKFB3 to induce glycolysis and activate mouse and human hepatic stellate cells, promoting liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:273–88.
Wang C, Chu X, Deng Y, Wang J, Qiu T, Zhu J, et al. PA and OA induce abnormal glucose metabolism by inhibiting KLF15 in adipocytes. Nutr Metab. 2021;18:100.
Takeuchi Y, Murayama Y, Aita Y, Mehrazad Saber Z, Karkoutly S, Tao D, et al. GR-KLF15 pathway controls hepatic lipogenesis during fasting. FEBS J. 2024;291:259–71.
Fan L, Hsieh PN, Sweet DR, Jain MK. Kruppel-like factor 15: regulator of BCAA metabolism and circadian protein rhythmicity. Pharmacol Res. 2018;130:123–6.
Zhang X, Tian X, Wang Y, Yan Y, Wang Y, Su M, et al. Application of lipopolysaccharide in establishing inflammatory models. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;279:135371.
Prosdocimo DA, John JE, Zhang L, Efraim ES, Zhang R, Liao X, et al. KLF15 and PPARalpha cooperate to regulate cardiomyocyte lipid gene expression and oxidation. PPAR Res. 2015;2015:201625.
Hu Y, Xu J, Gao R, Xu Y, Huangfu B, Asakiya C, et al. Diallyl trisulfide prevents adipogenesis and lipogenesis by regulating the transcriptional activation function of KLF15 on PPARgamma to ameliorate obesity. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022;66:e2200173.
Xiao J, Xiang H, Xiang H, Sun Z, Xu J, Ren H, et al. GW9662 ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting the PPARgamma/CD36 pathway and altering the gut microbiota. Eur J Pharmocol. 2023;960:176113.
Lin H, Wang L, Liu Z, Long K, Kong M, Ye D, et al. Hepatic MDM2 causes metabolic associated fatty liver disease by blocking triglyceride-VLDL secretion via ApoB degradation. Adv Sci. 2022;9:e2200742.
Saltiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature. 2001;414:799–806.
Arab HH, Salama SA, Eid AH, Kabel AM, Shahin NN. Targeting MAPKs, NF-kappaB, and PI3K/AKT pathways by methyl palmitate ameliorates ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:22424–38.
Han S, Liang CP, Westerterp M, Senokuchi T, Welch CL, Wang Q, et al. Hepatic insulin signaling regulates VLDL secretion and atherogenesis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:1029–41.
Song L, Huang Y, Liu L, Chang X, Hu L, Wang G, et al. Meteorin-like alleviates hepatic steatosis by regulating hepatic triglyceride secretion and fatty acid oxidation. Cell Rep. 2025;44:115246.
Sun YY, Zhao YX, Li XF, Huang C, Meng XM, Li J. beta-Arrestin 2 promotes hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting Akt pathway in alcoholic liver disease. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1031.
Zheng H, Ye W, Huang K, Chen Q, Yang J, Luo L. KLF15 alleviates oxidative stress and apoptosis of H/R-induced trophoblast cells to improve invasion and migration capacity via the activation of IGF1R. Tissue Cell. 2024;90:102485.
Yecies JL, Zhang HH, Menon S, Liu S, Yecies D, Lipovsky AI, et al. Akt stimulates hepatic SREBP1c and lipogenesis through parallel mTORC1-dependent and independent pathways. Cell Metab. 2011;14:21–32.
Bijl N, Sokolovic M, Vrins C, Langeveld M, Moerland PD, Ottenhoff R, et al. Modulation of glycosphingolipid metabolism significantly improves hepatic insulin sensitivity and reverses hepatic steatosis in mice. Hepatology. 2009;50:1431–41.
Song ZK, Zhao L, Liu DS, Zhao LN, Peng QB, Li ZY, et al. Macrophage KLF15 prevents foam cell formation and atherosclerosis via transcriptional suppression of OLR-1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024;186:57–70.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82400205), the Pharmaceutical Innovative Fund of Anhui Medical University (YXCX202210) and the Natural Science Projects for Colleges and Universities in Anhui Province (2022AH051163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HC, LY and XFL designed and performed this research, performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript; SYH, QZ and RCX participated in data processing; ZYO analysed the software data and methodology; LF and YD supervised the experiments. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
41401_2025_1651_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S1
41401_2025_1651_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S2
41401_2025_1651_MOESM3_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S3
41401_2025_1651_MOESM4_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S4
41401_2025_1651_MOESM5_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S5
41401_2025_1651_MOESM6_ESM.docx
Supplementary Table S1
41401_2025_1651_MOESM7_ESM.docx
Supplementary Table S2
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Yang, L., Li, Xf. et al. Krüppel-like factor 15 ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury in mice via regulation of the PFKFB3/AKT axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01651-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01651-2