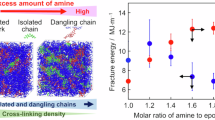
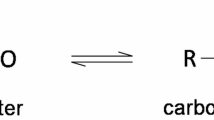
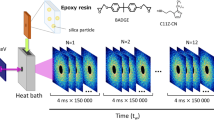
Abstract
A better understanding of the degradation mechanism of epoxy resins is crucial for the design and fabrication of materials with long-term durability. However, the understanding of this process has remained limited because the contributions of both heat and water must be considered simultaneously. In this study, we investigated the degradation mechanism of an amine-cured epoxy resin under hygrothermal conditions. Although the glass transition temperature (Tg) decreased with increasing hygrothermal aging time, this decrease was independent of the amount of sorbed water, indicating that plasticization was not the dominant factor. Instead, the reduction in the Tg was attributed to a decrease in the cross-linking density arising from C−O bond scission. Importantly, this scission was not based on acid-catalyzed cleavage but on radical-mediated cleavage. This process was induced by thermal decomposition followed by hydrogen donation from sorbed water. The insights obtained here provide molecular-level guidelines for designing epoxy resins with increased durability in hygrothermal environments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
St John NA, George GA. Diglycidyl amine epoxy-resin networks—kinetics and mechanisms of cure. Prog Polym Sci. 1994;19:755–95.
Jin FL, Li X, Park SJ. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: a review. J Ind Eng Chem. 2015;29:1–11.
Oliveux G, Dandy LO, Leeke GA. Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties. Prog Mater Sci. 2015;72:61–99.
Hsissou R, Seghiri R, Benzekri Z, Hilali M, Rafik M, Elharfi A. Polymer composite materials: a comprehensive review. Compos Struct. 2021;262:113640–54.
Shundo A, Yamamoto S, Tanaka K. Network formation and physical properties of epoxy resins for future practical applications. JACS Au. 2022;2:1522–42.
Browning CE. The mechanisms of elevated temperature property losses in high-performance structural epoxy resin matrix materials after exposure to high-humidity environments. Polym Eng Sci. 1978;1:16–24.
Feraboli P, Masini A. Development of carbon/epoxy structural components for a high-performance vehicle. Compos Part B. 2004;35:323–30.
Lahive CW, Dempsey SH, Reiber SE, Pal A, Stevenson KR, Michener WE, Alt HM, Ramirez KJ, Rognerud EG, Lincoln CL, Clarke RW, DesVeaux JS, Uekert T, Rorrer NA, Knauer KM, Beckham GT. Acetolysis for epoxy-amine carbon fibre-reinforced polymer recycling. Nature. 2025;642:605–12.
Harada M, Yokoyama Y. Effect of the ordered network polymer structure of cyclic-siloxane-type liquid crystalline epoxy thermosets on their fracture toughness and thermal conductivity. Polym J. 2025;57:395–405.
Gledhill RA, Kinloch AJ, Yamini S, Young RJ. Relationship between mechanical properties and crack progogation in epoxy resin adhesives. Polymer. 1978;19:574–82.
Van Lijsebetten F, Maiheu T, Winne JM, Du Prez FE. Epoxy adhesives with reversible hardeners: controllable thermal debonding in bulk and at interfaces. Adv Mater. 2023;35:2300802–1-11.
Obayashi K, Kojio K. Adhesive properties of low-cross-linking density cured epoxy resin. Polym J. 2025;57:679–87.
Tanizaki S, Kubo S, Bito Y, Mori S, Aoki H, Satoh K. Development of a bio-based adhesive by polymerization of boc-protected vinyl catechol derived from caffeic acid. RSC Sustain. 2025;3:1714–20.
Wang K, Chen L, Wu JS, Toh ML, He CB, Yee AF. Epoxy nanocomposites with highly exfoliated clay: mechanical properties and fracture mechanisms. Macromolecules. 2005;38:788–800.
Woodcock JW, Sheridan RJ, Beams R, Stranick SJ, Mitchell WF, Brinson LC, Gudapati V, Hartman D, Vaidya A, Gilman JW, Holmes GA. Damage sensing using a mechanophore crosslinked epoxy resin in single-fiber composites. Compos Sci Technol. 2020;192:108074–1-8.
Nguyen HK, Shundo A, Liang X, Yamamoto S, Tanaka K, Nakajima K. Unraveling nanoscale elastic and adhesive properties at the nanoparticle/epoxy interface using bimodal atomic force microscopy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14:42713–22.
Aoki N, Yamazaki J, Matsumoto T, Totani M, Shundo A, Tanaka K, Nishino T. Analyses and control of interphase structures and adhesion properties of epoxy resin/epoxy resin for development of CFRP adhesion systems. Compos Part A. 2024;187:108511–20.
Kobayashi T, Ogawa K, Maeda R, Wang P, Kubozono T, Yoshihara D, Yamamoto S, Yamada S, Tanaka K, Omiya M. Quantitative evaluation of crack arrest mechanisms in epoxy/silica nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol. 2025;261:111028–36.
Yamamoto S, Tanaka K. Molecular dynamics simulation of cross-linked epoxy resins: past and future. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2025;46:2400978–1-20.
Zhou JM, Lucas JP. Hygrothermal effects of epoxy resin. Part I: the nature of water in epoxy. Polymer. 1999;40:5505–12.
Yamamoto S, Kuwahara R, Tanaka K. Dynamic behaviour of water molecules in heterogeneous free space formed in an epoxy resin. Soft Matter. 2021;17:6073–80.
Nakamura S, Tsuji Y, Yoshizawa K. Molecular dynamics study on the thermal aspects of the effect of water molecules at the adhesive interface on an adhesive structure. Langmuir. 2021;37:14724–32.
Karuth A, Alesadi A, Vashisth A, Xia WJ, Rasulev B. Reactive molecular dynamics study of hygrothermal degradation of crosslinked epoxy polymers. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2022;4:4411–23.
Liu Y, Miyata N, Miyazaki T, Shundo A, Kawaguchi D, Tanaka K, Aoki H. Neutron reflectometry analysis of condensed water layer formation at a solid interface of epoxy resins under high humidity. Langmuir. 2023;39:10154–62.
Jiang Z, Ding Y, Chen Z, Zuo B. Quantitative characterization of the interfacial failure of metallic coatings on epoxy substrates in salty atmospheres. Polym J. 2025;57:1015–23.
Xiao GZ, Shanahan MER. Water absorption and desorption in an epoxy resin with degradation. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys. 1997;35:2659–70.
Musto P, Ragosta G, Abbate M, Scarinzi G. Photo-oxidation of high-performance epoxy networks: correlation between the molecular mechanisms of degradation and the viscoelastic and mechanical response. Macromolecules. 2008;41:5729–43.
Le Gac PY, Choqueuse D, Melot D. Description and modeling of polyurethane hydrolysis used as thermal insulation in oil offshore conditions. Polym Test. 2013;32:1588–93.
Zahra Y, Djouani F, Fayolle B, Kuntz M, Verdu J. Thermo-oxidative aging of epoxy coating systems. Prog Org Coat. 2014;77:380–7.
Richaud E, Derue I, Gilormini P, Verdu J, Vaulot C, Coquillat M, Desgardin N, Vandenbrouke A. Plasticizer effect on network structure and hydrolytic degradation. Eur Polym J. 2015;69:232–46.
Capiel G, Miccio LA, Montemartini PE, Schwartz GA. Water diffusion and hydrolysis effect on the structure and dynamics of epoxy-anhydride networks. Polym Degrad Stab. 2017;143:57–63.
Wu J, Dong J, Wang Y, Gond BK. Thermal oxidation ageing effects on silicone rubber sealing performance. Polym Degrad Stab. 2017;135:43–53.
Sousa J, Correia JR, Gabral-Fonseca S. Some permanent effects of hygrothermal and outdoor ageing on a structural polyurethane adhesive used in civil engineering applications. Int J Adhes Adhes. 2018;84:406–19.
Xie F, Zhang T, Bryant P, Kurusingal V, Colwell JM, Laycock B. Degradation and stabilization of polyurethane elastomers. Prog Polym Sci. 2019;90:211–68.
Rezig N, Bellahcene T, Aberkane M, Abdelaziz MN. Thermo‑oxidative ageing of an SBR rubber: effects on mechanical and chemical properties. J Polym Res. 2020;27:339–1-13.
Wang X, Yang K, Zhang P. Evaluation of the aging coefficient and the aging lifetime of carbon black-filled styrene-isoprene-butadiene rubber after thermal-oxidative aging. Compos Sci Technol. 2022;220:109258–1-8.
Lou W, Xie C, Guan X. Thermal-aging constitutive model for a silicone rubber foam under compression. Polym Degrad Stab. 2022;198:109873–1-9.
Mwafy EA, Gaafar MS. Dynamic mechanical characteristics of aged silicone rubber blend. Polym Bull. 2023;80:9015–32.
Luo Z, Wang L, Zhao B, Yin F, Li J, Cui B, Liu HY. Hygrothermal aging mechanism of epoxy composites used for medium-frequency transformers. Polym Degrad Stab. 2024;228:110913–1-10.
Yang D, Edgar AS, Billow BS, Brett JK. Hydrolysis of poly(ester urethane): in-depth mechanistic pathway determination through thermal and chemical characterization. Polym Degrad Stab. 2025;231:111084–1-14.
Russell GA. Fundamental processes of autoxidation. J Chem Educ. 1959;36:111–8.
Levchik SV, Camino G, Luda MP, Costa L, Muller G, Costes B. Epoxy resins cured with aminophenylmethylphosphine oxide–II. mechanism of thermal decomposition. Polym Degrad Stab. 1998;60:169–83.
Mailhot B, Morlat-Thérias S, Ouahioune M, Gardette JL. Study of the degradation of an epoxy/amine resin, 1 photo- and thermo-chemical mechanisms. Macromol Chem Phys. 2005;206:575–84.
Delozanne J, Desgardin N, Cuvillier N, Richaud E. Thermal oxidation of aromatic epoxy-diamine networks. Polym Degrad Stab. 2019;166:174–87.
Karuth A, Alesadi A, Vashisth A, Xia W, Rasulev B. Reactive molecular dynamics study of hygrothermal degradation of crosslinked epoxy polymers. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2022;4:4411.
Marshall WL, Franck EU. Ion product of water substance, 0–1000 °C, 1–10,000 bars, new international formulation and its background. J Phys Chem Ref Data. 1981;10:295–304.
Pitzer KS. Self-ionization of water at high temperature and the thermodynamic properties of the ions. J Phys Chem. 1982;86:4704–8.
Liu YY, Wei HG, Wu SQ, Guo ZH. Decomposition of epoxy model compounds in near-critical water. Chem Eng Technol. 2013;36:2117–24.
Gong XY, Liu YY, Wu SQ, Ding DW, Wie H, Guo Z. Decomposition mechanisms of cured epoxy resins in near-critical water. J Appl Polym Sci. 2014;132:41648–1-11.
Yamamoto S, Phan NT, Kihara K, Shundo A, Tanaka K. Off-stoichiometry effect on the physical properties of epoxy resins. Polym J. 2025;57:357–66.
Rubinstein M, Colby RH. Polymer Physics. Canada: Oxford University Press; 2003.
Yamaguchi K, Kawaguchi D, Miyata N, Miyazaki T, Aoki H, Yamamoto S, Tanaka K. Kinetics of the interfacial curing reaction for an epoxy–amine mixture. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2022;24:21578–82.
Shundo A, Phan NT, Aoki M, Tokunaga A, Kuwahara R, Yamamoto S, Tanaka K. Exploring the impact of molecular structure on curing kinetics: a comparative study of diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A and F epoxy resins. J Phys Chem B. 2024;128:4846–52.
Kumamoto K, Shundo A, Yamamoto S, Tanaka K. One-time network rearrangement for homogenization of epoxy resin structures. Macromolecules. 2025;58:9636–44.
Li K, Wang K, Zhan MS, Xu W. The change of thermal-mechanical properties and chemical structure of ambient-cured DGEBA/TEPA under accelerated thermo-oxidative aging. Polym Degrad Stab. 2013;98:2340–6.
Belec L, Nguyen TH, Nguyen DL, Chailan JF. Comparative effects of humid tropical weathering and artificial ageing on a model composite's properties from nano- to macro-scale. Compos Part A. 2015;68:235–41.
Ernault E, Dirrenberger J, Richaud E, Fayolle B. Prediction of stress induced by heterogeneous oxidation: case of epoxy/amine networks. Polym Degrad Stab. 2019;162:112–21.
Ishida T, Kitagaki R, Elakneswaran Y, Mizukado J, Shinzawa H, Sato H, Hagihara H, Watanabe R. Network degradation assessed by evolved gas analysis–mass spectrometry combined with principal component analysis (EGA–MS–PCA): a case of thermo-oxidized epoxy/amine network. Macromolecules. 2023;56:883–91.
Balabanovich AI, Hornung A, Merz D, Seffert H. The effect of a curing agent on the thermal degradation of fire retardant brominated epoxy resins. Polym Degrad Stab. 2004;85:713–23.
Poljansek I, Krajnc M. Characterization of phenol-formaldehyde prepolymer resins by in-line FT-IR spectroscopy. Acta Chim Slov. 2005;52:238–44.
Sideridou ID, Vouvoudi EC, Papadopoulos GD. Epoxy polymer Hxtal NYL-1™ used in restoration and conservation: irradiation with short and long wavelengths and study of photo-oxidation by FT-IR spectroscopy. J Cult Herit. 2016;18:279–89.
Pike PR, Sworan PA, Cabaniss SE. Quantitative aqueous attenuated total reflectance fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: Part II. Integrated molar absorptivities of alkyl carboxylates. Anal Chim Acta. 1993;280:253–61.
Hay MB, Myneni SCB. Structural environments of carboxyl groups in natural organic molecules from terrestrial systems. Part 1: infrared spectroscopy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2007;71:3518–32.
Galant C, Fayolle B, Kuntz M, Verdu J. Thermal and radio-oxidation of epoxy coatings. Prog Org Coat. 2010;69:322–29.
Shimokawaji T, Sudo A. Synthesis of partially bio-based triepoxides from naturally occurring myo-inositol and their polyadditions. J Polym Sci. 2020;58:1229–35.
Tokunaga A, Shundo A, Kuwahara R, Yamamoto S, Tanaka K. Effect of number density of epoxy functional groups on reaction kinetics for epoxy resin. Macromolecules. 2024;57:10530–8.
Marui R, Maeda H, Hatakeyama-Sato K, Nabae Y, Hayakawa T. Ortho-, meta-, versus para-substituted mesogens inducing higher-order structures for highly thermal-conductive cured epoxy resins. Macromolecules. 2024;57:11221–8.
Peyser P, Bascom WD. The anomalous lowering of the glass-transition of epoxy resin by plasticization with water. J Mater Sci. 1981;16:75–83.
Khan LA, Nesbitt A, Day RJ. Hygrothermal degradation of 977-2A carbon/epoxy composite laminates cured in autoclave and quickstep. Compos Part A. 2010;41:942–53.
Nogueira P, Ramírez C, Torres A, Abad MJ, Cano J, López J, López-bueno I, Barral L. Effect of water sorption on the structure and mechanical properties of an epoxy resin system. J Appl Polym Sci. 2001;80:71–80.
Mckague EL, Reynolds JD, Halkias JE. Swelling and glass-transition relations for epoxy matrix material in humid environments. J Appl Polym Sci. 1978;22:1643–54.
Maggana C, Pissis P. Water sorption and diffusion studies in an epoxy resin system. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys. 1998;37:1165–82.
Xiao GZ, Shanahan MER. Irreversible effects of hygrothermal aging on DGEBA/DDA epoxy resin. J Appl Polym Sci. 1998;69:363–9.
Wang M, Xu X, Ji J, Yang Y, Shen J, Ye M. The hygrothermal aging process and mechanism of the novolac epoxy resin. Compos Part B. 2016;107:1–8.
Xu K, Chen W, Zhu X, Liu L, Zhao Z, Luo G. Chemical, mechanical and morphological investigation on the hygrothermal aging mechanism of a toughened epoxy. Polym Test. 2022;110:107548–1-11.
Pedersen SN, Lindholst C. Quantification of the xenoestrogens 4-tert-octylphenol and bisphenol A in water and in fish tissue based on microwave-assisted extraction, solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 1999;864:17–24.
Gallart-Ayala H, Moyano E. Multiple-stage mass spectrometry analysis of bisphenol A diglycidyl ether, bisphenol F diglycidyl ether and their derivatives. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2010;24:3469–77.
Longiéras N, Sebban M, Palmas P, Rivaton A, Gardette JL. Multiscale approach to investigate the radiochemical degradation of epoxy resins under high-energy electron-ream irradiation. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem. 2006;44:865–87.
Yan H, Lu CX, Jing DQ, Hou XL. Chemical degradation of amine-cured DGEBA epoxy resin in supercritical 1-propanol for recycling carbon fiber from composites. Chin J Polym Sci. 2014;32:1550–63.
Gong XY, Kang HJ, Liu YY, Wu SQ. Decomposition mechanisms and kinetics of amine/anhydride-cured DGEBA epoxy resin in near-critical water. RSC Adv. 2015;5:40269–82.
Urata K, Takaishi N. The Alkyl glycidyl ether as synthetic building blocks. Fresenius J Anal Chem. 1994;71:1027–33.
Paseiro-Losada P, Simal-Lozano J, Paz-Abuín S, López-Mahía P, Simal-Gándara J. Kinetics of the hydrolysis of bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE) in water-based food simulants - implications for legislation on the migration of BADGE-type epoxy resins into foodstuffs. Fresenius J Anal Chem. 1993;345:527–32.
Hanif M, Zahoor AF, Saif MJ, Nazeer U, Ali KG, Parveen B, Mansha A, Chaudhry AR, Irfan A. Exploring the synthetic potential of epoxide ring opening reactions toward the synthesis of alkaloids and terpenoids: a review. RSC Adv. 2024;14:13100–28.
Gassman PG, Guggenheim TL. Opening of epoxides with trimethylsilyl cyanide to produce β-hydroxy isonitriles. A general synthesis of oxazolines and β-amino alcohols. J Am Chem Soc. 1982;104:5849–50.
Cole BM, Shimizu KD, Krueger CA, Harrity JP, Snapper ML, Hoveyda AH. Discovery of chiral catalysts through ligand diversity: Ti-catalyzed enantioselective addition of TMSCN to meso epoxides. Angew Chem Int Ed. 1996;35:1668–71.
Nugent WA. Desymmetrization of meso epoxides with halides: a new catalytic reaction based on mechanistic insight. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;120:7139–40.
Burwell RL. The cleavage of ethers. Chem Rev. 1954;54:615–85.
Klein E, Lukeš V. DFT/B3LYP study of O–H bond dissociation enthalpies of Para and Meta substituted phenols: correlation with the phenolic C–O bond length. J Mol Struct. 2006;767:43–50.
Atifi A, Talipov M, Mountacer H, Ryan MD, Sarakha MA. Density functional theory and laser flash photolysis investigation of carbofuran photodegradation in aqueous medium. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem. 2012;235:1–6.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI for Scientific Research (B) (No. 23K26707) to KT, Scientific Research (B) (No. 25K01836) to AS and Scientific Research (B) (No. 25K01825) to DK from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan, and was in part supported by CERI Proposed Cooperative Research (KT). We are also thankful for the support of the JST-Mirai Program (JPMJMI18A2) (KT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, K., Shundo, A., Taguchi, H. et al. Hygrothermal degradation mechanism of amine-cured epoxy resin. Polym J (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-026-01150-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-026-01150-z