Abstract
Purpose
To describe a modified technique of endoscopic orbital decompression for dysthyroid optic neuropathy nonresponsive to pulsed corticosteroids.
Methods
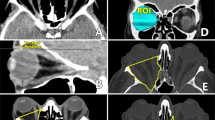
Retrospective, interventional single centre case series included 17 consecutive patients with dysthyroid optic neuropathy (DON) who were refractory to pulse corticosteroids. Removal of the posteromedial floor and the orbital process of palatine bone (OPPB) was performed in addition to the endoscopic transethmoidal medial orbital wall decompression (ETMOWD), to achieve maximal orbital apex decompression. Main outcome measures were change in visual acuity (VA), color vision, degree of proptosis reduction, incidence of new-onset diplopia, and any complications.
Results
Seventeen eyes (100%) had a statistically significant improvement in VA from 1.0 ± 0.44 LogMAR to 0.0 ± 0.15, with an average improvement of 0.41 ± 0.30 LogMAR (p 0.05, paired t-test). Fourteen out of 16 eyes had a complete improvement in color vision and two eyes had partial recovery. Afferent pupillary defect (76.5%) resolved in all cases. Five out of 10 cases with preoperative visual field defects demonstrated no residual field defects following surgery. The range of proptosis reduction was 0–5 mm (mean 2.7 ± 1.3 mm). No patients with diplopia (12/17) had worsening or developed new-onset diplopia following surgery.
Conclusion
Combined removal of the posterior medial floor including the OPPB with ETMOWD may be a viable alternative in the surgical management of DON.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Neigel JM, Rootman J, Belkin RI, et al. Dysthyroid optic neuropathy: the crowded orbital apex syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1988;95:1515–21.
Saeed P, Tavakoli Rad S, Bisschop PHLT. Dysthyroid optic neuropathy. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;34:S60–S67.
Kazim M, Trokel SL, Acaroglu G, et al. Reversal of dysthyroid optic neuropathy following orbital fat decompression. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000;84:600–5.
Korkmaz S, Konuk O. Surgical treatment of dysthyroid optic neuropathy: long-term visual outcomes with comparison of 2-wall versus 3-wall orbital decompression. Curr Eye Res. 2016;41:159–64.
Kennedy DW, Goldstein ML, Miller NL, et al. Endoscopic transnasal orbital decompression. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990;116:275–82.
Michel O, Oberlander N, Neugebauer P, et al. Follow-up of transnasal orbital decompression in severe Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Ophthalmology. 2001;108:400–4.
Metson R, Dallow RL, Shore JW. Endoscopic orbital decompression. Laryngoscope. 1994;104:950–7.
Schaefer SD, Soliemanzadeh P, Della Rocca DA, Yoo GP, Maher EA, Milite JP, et al. Endoscopic and transconjunctival orbital decompression for thyroid-related orbital apex compression. Laryngoscope. 2003;113:508–13.
Lund VJ, Larkin G, Fells P, et al. Orbital decompression for thyroid eye disease: a comparison of external and endoscopic techniques. J Laryngol Otol. 1997;111:1051–5.
Goldberg RA, Shorr N, Cohen MS. The medial orbital strut in the prevention of postdecompression dystopia in dysthyroid ophthalmopathy. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992;8:32–34.
Metson R, Samaha M. Reduction of diplopia following endoscopic orbital decompression: the orbital sling technique. Laryngoscope. 2002;112:1753–7.
Lv Z, Selva D, Yan W, Daniel P, Tu Y, Wu W. Endoscopical orbital fat decompression with medial orbital wall decompression for dysthyroid optic neuropathy. Curr Eye Res. 2016;41:150–8.
Martins C, Costa E, Silva IE, Campero A, Yasuda A, Aguiar LR, Tatagiba M, Rhoton A Jr. Microsurgical anatomy of the orbit: the rule of seven. Anat Res Int. 2011;2011:468727.
Wu W, Selva D, Bian Y, Wang X, Sun MT, Kong Q, Yan W. Endoscopic medial orbital fat decompression for proptosis in type 1 graves orbitopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015;159:277–84.
Tyler MA, Zhang CC, Saini AT, Yao WC. Cutting-edge endonasal surgical approaches to thyroid ophthalmopathy. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2018;3:100–4.
Chu EA, Miller NR, Grant MP, Merbs S, Tufano RP, Lane AP. Surgical treatment of dysthyroid orbitopathy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;141:39–45.
Garrity JA, Fatourechi V, Bergstralh EJ, et al. Results of transantral orbital decompression in 428 patients with severe Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993;116:533–47.
Perry JD, Kadakia A, Foster JA. Transcaruncular orbital decompression for dysthyroid optic neuropathy. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;19:353–8.
Liao SL, Chang TC, Lin LL. Transcaruncular orbital decompression: an alternate procedure for Graves ophthalmopathy with compressive optic neuropathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;141:810–8.
Chu EA, Miller NR, Lane AP. Selective endoscopic decompression of the orbital apex for dysthyroid optic neuropathy. Laryngoscope. 2009;119:1236–40.
Kingdom TT, Davies BW, Durairaj VD. Orbital decompression for the management of thyroid eye disease: an analysis of outcomes and complications. Laryngoscope. 2015;125:2034–40.
Luxenberger W, Stammberger H, Jebeles JA, Walch C. Endoscopic optic nerve decompression: the Graz experience. Laryngoscope. 1998;108:873–82.
Dallan I, Castelnuovo P, de Notaris M, Sellari-Franceschini S, Lenzi R, Turri-Zanoni M, Battaglia P, Prats-Galino A. Endoscopic endonasal anatomy of superior orbital fissure and orbital apex regions: critical considerations for clinical applications. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;270:1643–9.
Mueller SK, Freitag SK, Bleier BS. Morphometric analysis of the orbital process of the palatine bone and its relationship to endoscopic orbital apex surgery. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;34:254–7.
Sowerby LJ, Rajakumar C, Allen L, Rotenberg BW. Urgent endoscopic orbital decompression for vision deterioration in dysthyroid optic neuropathy. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2018;S1879-7296(18)30125-X.
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge help of Luke Halladay in archiving skull model images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Curragh, D. & Selva, D. Augmented endoscopic orbital apex decompression in dysthyroid optic neuropathy. Eye 33, 1613–1618 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-019-0464-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-019-0464-5
This article is cited by
-
Comparative effectiveness of various orbital decompression techniques in treating thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
BMC Ophthalmology (2024)
-
Dysthyroid optic neuropathy: emerging treatment strategies
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2023)
-
Modified endoscopic transnasal orbital apex decompression in dysthyroid optic neuropathy
Eye and Vision (2021)
-
Orbital apex anatomy: relationship between the optic foramen and anterior face of sphenoid sinus — a radiological study
Eye (2021)
-
Orbital wall decompression in the management of Graves’ orbitopathy: a systematic review with meta-analysis
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology (2021)