Abstract
Background/objectives
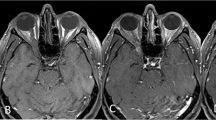
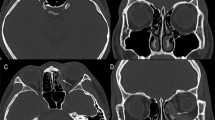
This study aims to identify radiologically the position of the optic foramen in relation to the anterior face of the sphenoid sinus, to aid surgeons in their planning for orbital decompression.
Methods
CT scans of 100 orbits from 50 adult patients without any abnormality were assessed. Primary outcome measures included: position and measurement of the distance from the optic foramen to the anterior face of the sphenoid sinus. Secondary outcomes included: medial orbital wall length, distance from the optic foramen and the anterior face of the sphenoid sinus to the carotid prominence in the sphenoid sinus, and the thickness of bone anterior to the optic foramen.
Results
The mean location of the optic foramen was just posterior to the position of the anterior face of sphenoid sinus, with an average distance of +0.4 +/− 3.5 mm. In 54% of orbits the optic foramen was positioned posterior to the anterior face of the sphenoid sinus. The finding was symmetrical in 80% of patients.
Conclusions
Our study identifies that the optic foramen lies posterior to the anterior face of sphenoid sinus in approximately half of cases. The position may be asymmetric in 20% of individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Cornelius CP, Mayer P, Ehrenfeld M, Metzger MC. The orbits-anatomical features in view of innovative surgical methods. Facial Plast Surg. 2014;30:487–508.
Singh S, Curragh DS, Selva D. Augmented endoscopic orbital apex decompression in dysthyroid optic neuropathy. Eye. 2019;33:1613–8.
Wu W, Selva D, Bian Y, Wang X, Sun MT, Kong Q, et al. Endoscopic medial orbital fat decompression for proptosis in type 1 graves orbitopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015;159:277–84.
Stokken J, Gumber D, Antisdel J, Sindwani R. Endoscopic surgery of the orbital apex: outcomes and emerging techniques. Laryngoscope. 2016;126:20–4.
Lund VJ, Larkin G, Fells P, Adams G. Orbital decompression for thyroid eye disease: a comparison of external and endoscopic techniques. J Laryngol Otol. 1997;111:1051–5.
Stammberger HR, Kennedy DW, Anatomic Terminology G. Paranasal sinuses:anatomic terminology and nomenclature. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1995;167:7–16.
Chmielik LP, Chmielik A. The prevalence of the Onodi cell—most suitable method of CT evaluation in its detection. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;97:202–5.
Ozdemir A, Bayar Muluk N, Asal N, Sahan MH, Inal M. Is there a relationship between Onodi cell and optic canal? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;276:1057–64.
Wada K, Moriyama H, Edamatsu H, Hama T, Arai C, Kojima H, et al. Identification of Onodi cell and new classification of sphenoid sinus for endoscopic sinus surgery. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015;5:1068–76.
Enatsu K, Takasaki K, Kase K, Jinnouchi S, Kumagami H, Nakamura T, et al. Surgical anatomy of the sphenoid sinus on the CT using multiplanar reconstruction technique. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;138:182–6.
Bansberg SF, Harner SG, Forbes G. Relationship of the optic nerve to the paranasal sinuses as shown by computed tomography. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1987;96:331–5.
DeLano MC, Fun FY, Zinreich SJ. Relationship of the optic nerve to the posterior paranasal sinuses: a CT anatomic study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996;17:669–75.
Akdemir G, Tekdemir I, Altin L. Transethmoidal approach to the optic canal: surgical and radiological microanatomy. Surg Neurol. 2004;62:268–74.
Abed SF, Shams P, Shen S, Adds PJ, Uddin JM. A cadaveric study of the morphometric and geometric relationships of the orbital apex. Orbit. 2011;30:72–6.
Karakas P, Bozkir MG, Oguz O. Morphometric measurements from various reference points in the orbit of male Caucasians. Surg Radio Anat. 2003;24:358–62.
Singh J, Rahman RA, Rajion ZA, Abdullah J, Mohamad I. Orbital morphometry: a computed tomography analysis. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28:e64–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aujla, J.S., Curragh, D.S., Patel, S. et al. Orbital apex anatomy: relationship between the optic foramen and anterior face of sphenoid sinus — a radiological study. Eye 35, 2613–2618 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-020-01289-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-020-01289-w