Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the clinical features and treatment outcomes of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease (IgG4-ROD) among idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease (IOID) patients.
Methods
The medical records of 165 biopsy-proven IOID patients were retrospectively reviewed. Biopsy specimens were immunostained to detect IgG4 and IgG, and data regarding the clinicopathologic features, treatment outcomes, and recurrence were analyzed.
Results
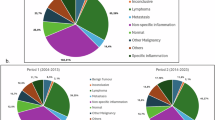
Among the 165 IOID patients enrolled, 100 (60.6%) were histopathologically IgG4-positive. The IgG4-positive patients had a lower rate of painful swelling or mass (17.0% versus 33.8%, p = 0.013), a longer symptom duration (p = 0.070), and a lower proportion of eyelid hyperemia (39.0% versus 58.5%, p = 0.014) than the IgG4-negative patients. Increased Ki-67 expression (15.02 ± 6.86%, p < 0.001) was observed in the IgG4-positive patients with characteristic pathological manifestations (more lymphocyte infiltration, nodular plasma cell infiltration, and follicular hyperplasia). IgG4-positive group had a higher recurrence rate in the subgroup of patients treated with surgery plus oral glucocorticoids (p = 0.046), and combined radiotherapy group has a higher cumulative proportion with recurrence (p = 0.011).
Conclusion
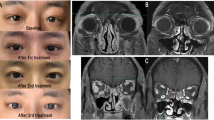
Over 60% of biopsy-proven IOID were classified as IgG4-ROD with a stronger proliferation potential. Additional radiotherapy after surgical debulking with oral corticosteroids still has a higher relapse rate, and more effective treatments are needed to prevent recurrence.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(6):539–51.
Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015;385(9976):1460–71.
Plaza JA, Garrity JA, Dogan A, Ananthamurthy A, Witzig TE, Salomao DR. Orbital inflammation with IgG4-positive plasma cells: manifestation of IgG4 systemic disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011;129(4):421–8.
Wah C, Yuen HKL, Chan JKC. Chronic sclerosing dacryoadenitis: part of the spectrum of IgG4-related Sclerosing disease? Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31(4):643–5.
Mahajan VS, Mattoo H, Deshpande V, Pillai SS, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:315–47.
Nicholas A, Daniel K, Dinesh S. IgG4-related orbital disease: a meta-analysis and review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2013;91(8):694–700.
Sa HS, Lee JH, Woo KI, Kim YD. IgG4-related disease in idiopathic sclerosing orbital inflammation. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015;99(11):1493–7.
Deschamps R, Deschamps L, Depaz R, Coffin-Pichonnet S, Belange G, Jacomet PV, et al. High prevalence of IgG4-related lymphoplasmacytic infiltrative disorder in 25 patients with orbital inflammation: a retrospective case series. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013;97(8):999–1004.
Hisanori U, Kazuichi O, Yasufumi M, Mitsuhiro K, Motohisa Y, Takako S, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22(1):21–30.
Andrew NH, Sladden N, Kearney DJ, Selva D. An analysis of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) among idiopathic orbital inflammations and benign lymphoid hyperplasias using two consensus-based diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015;99(3):376–81.
Sato Y, Ohshima K, Ichimura K, Sato M, Yamadori I, Tanaka T, et al. Ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease has uniform clinicopathology. Pathol Int. 2008;58(8):465–70.
Kubota T, Moritani S, Katayama M, Terasaki H. Ocular adnexal IgG4-related lymphoplasmacytic infiltrative disorder. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128(5):577–84.
Takahira M, Ozawa Y, Kawano M, Zen Y, Hamaoka S, Yamada K, et al. Clinical aspects of IgG4-related orbital inflammation in a case series of ocular adnexal lymphoproliferative disorders. Int J Rheumatol. 2012;2012:635473.
Abad S, Martin A, Heran F, Cucherousset N, Mouriaux F, Heron E, et al. IgG4-related disease in patients with idiopathic orbital inflammation syndrome: data from the French SIOI prospective cohort. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019;97:e648–56.
Yamamoto M, Harada S, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, et al. Clinical and pathological differences between Mikulicz’s disease and Sjogren’s syndrome. Rheumatology 2005;44(2):227–34.
Nishimori I, Tamakoshi A, Otsuki M, Research Committee on Intractable Diseases of the Pancreas, Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan. Prevalence of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan from a nationwide survey in 2002. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42(18):6–8.
Kanno A, Masamune A, Okazaki K, Kamisawa T, Kawa S, Nishimori I, et al. Nationwide epidemiological survey of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan in 2011. Pancreas. 2015;44(4):535–9.
Origuchi T, Yano H, Nakamura H, Hirano A, Kawakami A. Three cases of IgG4-related orbital inflammation presented as unilateral pseudotumor and review of the literature. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33(11):2931–6.
Pasquali T, Schoenfield L, Spalding SJ, Singh AD. Orbital inflammation in IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Orbit. 2011;30(5):258–60.
Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Ravdin PM, Hayes MM, Gelmon KA. Ki67 in breast cancer: prognostic and predictive potential. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(2):174–83.
Igawa T, Hayashi T, Ishiguro K, Maruyama Y, Takeuchi M, Takata K, et al. IgG4-producing lymphoma arising in a patient with IgG4-related disease. Med Mol Morphol. 2016;49(4):243–9.
Poo SX, Tham CSW, Smith C, Lee J, Cairns T, Galliford J, et al. IgG4-related disease in a multi-ethnic community: clinical characteristics and association with malignancy. QJM. 2019;112:763–9.
Lin YH, Yen SH, Tsai CC, Kao SC, Lee FL. Adjunctive orbital radiotherapy for ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease: preliminary experience in patients refractory or intolerant to corticosteroid therapy. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2015;23(2):162–7.
Detiger SE, Karim AF, Verdijk RM, van Hagen PM, van Laar JAM, Paridaens D. The treatment outcomes in IgG4-related orbital disease: a systematic review of the literature. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019;97(5):451–9.
Aouidad I, Schneider P, Zmuda M, Gottlieb J, Viguier M. IgG4-related disease with orbital pseudotumors treated with rituximab combined with palpebral surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(3):355–6.
Ebbo M, Grados A, Samson M, Groh M, Loundou A, Rigolet A, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of rituximab in IgG4-related disease: data from a French nationwide study of thirty-three patients. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0183844.
Lin W, Zhang P, Chen H, Chen Y, Yang H, Zheng W, et al. Circulating plasmablasts/plasma cells: a potential biomarker for IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):25.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81700875, 81670887, and 81870689).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the collection, analysis, interpretation, and preparation of the data, as well as the review and approval of the manuscript and the final decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Zhang, P., Ye, H. et al. Clinical features and outcomes of IgG4-related idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease: from a large southern China-based cohort. Eye 35, 1248–1255 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-020-1083-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-020-1083-x
This article is cited by
-
Local recurrence as extraocular muscle lymphoma after 6 years of chronic myositis: a case report
BMC Ophthalmology (2022)