Abstract
Objective
To understand intraocular pressure (IOP) response after switching from intravitreal bevacizumab (IVB) and/or ranibizumab (IVR) to intravitreal aflibercept (IVA) for treatment-resistant neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) in patients with and without coexisting glaucoma-related diagnoses.
Methods
Retrospective, cross-sectional comparative case series of 62 eyes of 58 patients treated with intravitreal injection for nAMD from March 2010 to April 2018. Patients with glaucoma-related diagnoses, defined here as open-angle glaucoma or suspicion of open-angle glaucoma, ocular hypertension, and/or narrow-angle glaucoma, were compared to those without glaucoma. IOP data were collected at baseline, at the three visits where patients received loading doses of IVB/IVR, and at all of the visits following the switch to IVA through the end of follow-up.
Results
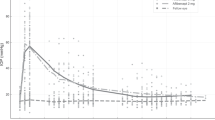
19 eyes with pre-existing glaucoma-related diagnoses were compared to 43 eyes without such diagnoses. Baseline IOP was similar for glaucoma and non-glaucoma patients. The loading doses of IVB/IVR did not impact IOP; however, a small, sustained rise in IOP was noted among patients with glaucoma-related diagnoses by the final IVB/IVR injections before the switch to IVA (∆IOP 1.61 ± 0.52 mmHg, P < 0.002). After conversion to IVA, pre-injection IOP declined in eyes both with (−1.59 ± 0.54 mmHg, P < 0.001) and without (−0.99 ± 0.28 mmHg, P < 0.001) glaucoma-related diagnoses.
Conclusions
IOP in patients with glaucoma-related diagnoses appears to be more sensitive to intravitreal injections than it is in patients without glaucoma-related diagnoses. It rises with IVB/IVR and declines after the switch to IVA. Switching patients with nAMD to IVA may present an opportunity to lower IOP in patients with glaucoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bressler NM, Doan QV, Varma R, Lee PP, Suner IJ, Dolan C, et al. Estimated cases of legal blindness and visual impairment avoided using ranibizumab for choroidal neovascularization: non-Hispanic white population in the United States with age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011;129:709–17.
Haddock LJ, Ramsey DJ, Young LH. Complications of subspecialty ophthalmic care: endophthalmitis after intravitreal injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor medications. Semin Ophthalmol. 2014;29:257–62.
Ramsey DJ, Haddock LJ, Young LH, Elliott D. Complications of subspecialty ophthalmic care: systemic complications from the intravitreal administration of agents that target the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway. Semin Ophthalmol. 2014;29:263–75.
Brown DM, Kaiser PK, Michels M, Soubrane G, Heier JS, Kim RY, et al. Ranibizumab versus verteporfin for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1432–44.
Bakri SJ, Pulido JS, McCannel CA, Hodge DO, Diehl N, Hillemeier J. Immediate intraocular pressure changes following intravitreal injections of triamcinolone, pegaptanib, and bevacizumab. Eye. 2009;23:181–5.
Mojica G, Hariprasad SM, Jager RD, Mieler WF. Short-term intraocular pressure trends following intravitreal injections of ranibizumab (Lucentis) for the treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008;92:584.
Foss AJ, Scott LJ, Rogers CA, Reeves BC, Ghanchi F, Gibson J, et al. Changes in intraocular pressure in study and fellow eyes in the IVAN trial. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016;100:1662–7.
Bakri SJ, McCannel CA, Edwards AO, Moshfeghi DM. Persistent ocular hypertension following intravitreal ranibizumab. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008;246:955–8.
Kahook MY, Kimura AE, Wong LJ, Ammar DA, Maycotte MA, Mandava N. Sustained elevation in intraocular pressure associated with intravitreal bevacizumab injections. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2009;40:293–5.
Good TJ, Kimura AE, Mandava N, Kahook MY. Sustained elevation of intraocular pressure after intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF agents. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011;95:1111–4.
Hoang QV, Mendonca LS, Della Torre KE, Jung JJ, Tsuang AJ, Freund KB. Effect on intraocular pressure in patients receiving unilateral intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor injections. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:321–6.
Tseng JJ, Vance SK, Della Torre KE, Mendonca LS, Cooney MJ, Klancnik JM, et al. Sustained increased intraocular pressure related to intravitreal antivascular endothelial growth factor therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. J Glaucoma. 2012;21:241–7.
Hoang QV, Tsuang AJ, Gelman R, Mendonca LS, Della Torre KE, Jung JJ, et al. Clinical predictors of sustained intraocular pressure elevation due to intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Retina. 2013;33:179–87.
Pershing S, Bakri SJ, Moshfeghi DM. Ocular hypertension and intraocular pressure asymmetry after intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retin. 2013;44:460–4.
Bakri SJ, Moshfeghi DM, Francom S, Rundle AC, Reshef DS, Lee PP, et al. Intraocular pressure in eyes receiving monthly ranibizumab in 2 pivotal age-related macular degeneration clinical trials. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:1102–8.
Solomon SD, Lindsley K, Vedula SS, Krzystolik MG, Hawkins BS. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;8:CD005139.
Freund KB, Hoang QV, Saroj N, Thompson D. Intraocular pressure in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration receiving intravitreal aflibercept or ranibizumab. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:1802–10.
Eadie BD, Etminan M, Carleton BC, Maberley DA, Mikelberg FS. Association of repeated intravitreous bevacizumab injections with risk for glaucoma surgery. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017;135:363–8.
Atchison EA, Wood KM, Mattox CG, Barry CN, Lum F, MacCumber MW. The real-world effect of intravitreous anti-vascular endothelial growth factor drugs on intraocular pressure: an analysis using the IRIS registry. Ophthalmology. 2018;125:676–82.
Bilgic A, Kodjikian L, Chhablani J, Sudhalkar A, Trivedi M, Vasavada V, et al. Sustained intraocular pressure rise after the treat and extend regimen at 3 years: aflibercept versus ranibizumab. J Ophthalmol. 2020;2020:7462098.
Rosenfeld PJ, Brown DM, Heier JS, Boyer DS, Kaiser PK, Chung CY, et al. Ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1419–31.
CATT Research Group, Martin DF, Maguire MG, Ying GS, Grunwald JE, Fine SL, et al. Ranibizumab and bevacizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1897–908.
Heier JS, Brown DM, Chong V, Korobelnik JF, Kaiser PK, Nguyen QD, et al. Intravitreal aflibercept (VEGF trap-eye) in wet age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:2537–48.
Rusu IM, Deobhakta A, Yoon D, Lee M, Slakter JS, Klancnik JM, et al. Intraocular pressure in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration switched to aflibercept injection after previous anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatments. Retina. 2014;34:2161–6.
Gabrielle PH, Nguyen V, Wolff B, Essex R, Young S, Hunt A, et al. Intraocular pressure changes and vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor use in various retinal diseases: long-term outcomes in routine clinical practice: data from the Fight Retinal Blindness! Registry. Ophthalmol Retin. 2020;4:861–70.
Unsal E, Cubuk MO. The outcomes of aflibercept therapy in patients with age-related macular degeneration resistant to bevacizumab or ranibizumab. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2018;30:337–42.
Cui QN, Gray IN, Yu Y, VanderBeek BL. Repeated intravitreal injections of antivascular endothelial growth factors and risk of intraocular pressure medication use. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019;257:1931–9.
Zlateva GP, Javitt JC, Shah SN, Zhou Z, Murphy JG. Comparison of comorbid conditions between neovascular age-related macular degeneration patients and a control cohort in the Medicare population. Retina. 2007;27:1292–9.
Zhou Y, Zhou M, Xia S, Jing Q, Gao L. Sustained elevation of intraocular pressure associated with intravitreal administration of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39301.
Schmidt-Erfurth U, Kaiser PK, Korobelnik JF, Brown DM, Chong V, Nguyen QD, et al. Intravitreal aflibercept injection for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: ninety-six-week results of the VIEW studies. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:193–201.
Dugel PU, Koh A, Ogura Y, Jaffe GJ, Schmidt-Erfurth U, Brown DM, et al. HAWK and HARRIER: phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-masked trials of brolucizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2020;127:72–84.
Mansberger SL, Gordon MO, Jampel H, Bhorade A, Brandt JD, Wilson B, et al. Reduction in intraocular pressure after cataract extraction: the Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:1826–31.
Hahn P, Kim JE, Stinnett S, Chung MM, Dugel PU, Flynn HW Jr, et al. Aflibercept-related sterile inflammation. Ophthalmology. 2013;120:1100–1.
Mergen B, Ramsey DJ. Underdiagnosis of glaucoma in patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration. Eye. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-021-01417-0.
Hu CC, Ho JD, Lin HC, Kao LT. Association between open-angle glaucoma and neovascular age-related macular degeneration: a case-control study. Eye. 2017;31:872–7.
Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T, Cheng CY. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:2081–90.
Shaikh Y, Yu F, Coleman AL. Burden of undetected and untreated glaucoma in the United States. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014;158:1121–9. e1
Leske MC, Heijl A, Hussein M, Bengtsson B, Hyman L, Komaroff E, et al. Factors for glaucoma progression and the effect of treatment: the early manifest glaucoma trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121:48–56.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Jeffrey L. Marx, Dr. Megan Nichols, Christine Gould, Jamie Ramos, and Miranda D. Prosniewski, as well as Carol Spencer, Lahey Hospital Librarian, for research support. DJR is the Harry N. Lee Family Chair in Innovation at the Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Beth Israel Lahey Health.
Funding
DJR: Supported by the Harry N. Lee Family Chair in Innovation at the Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Beth Israel Lahey Health. JCM: Supported by a grant from Office of Medical Education, Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Beth Israel Lahey Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DJR was responsible for the study hypothesis and design, the development of electronic medical record reporting tools, reviewing and analyzing the data, interpreting the results, and writing of the manuscript. JCM was responsible for the chart review, extracting and analyzing the data, figure development, and writing of the manuscript. EES was responsible for the chart review, extracting and analyzing the data, and writing of the manuscript. YZ was responsible for the chart review, extracting and analyzing the data, figure development, and writing of the manuscript. AMA was responsible for analyzing the data and writing of the manuscript. MLC was responsible for interpreting the data, figure development, and writing of the manuscript. SR was responsible for interpreting the data and writing of the manuscript. PRC was responsible for interpreting the data and writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Meeting Presentation: Annual meeting of the American Glaucoma Society, San Diego, California, March 17, 2019.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramsey, D.J., McCullum, J.C., Steinberger, E.E. et al. Intraocular pressure decreases in eyes with glaucoma-related diagnoses after conversion to aflibercept for treatment-resistant age-related macular degeneration. Eye 36, 1813–1819 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-021-01729-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-021-01729-1
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of intraocular pressure changes in Japanese patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration treated with aflibercept or faricimab
Japanese Journal of Ophthalmology (2025)
-
Intraocular pressure changes during intravitreal aflibercept injection based on treat-and-extend regimen in Japanese patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration and glaucoma
Japanese Journal of Ophthalmology (2024)