Abstract
Objectives
Major ocular diseases share common risk factors and pathogeneses with stroke. This study aimed to evaluate the relation between stroke and ocular diseases including visual impairment (VI).
Methods
The cross-sectional study investigated the prevalence and associations of VI and major eye diseases with stroke among 4570 participants in the 2005–2008 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The association of VI and major ocular diseases with stroke were estimated using univariate and multivariate logistic regression crude models and models adjusted for demographics and clinical factors. We also conducted stratified analyses by diabetes and hypertension status.
Results
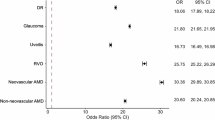
VI was associated with stroke, and the odds ratios (ORs) for mild and moderate and severe visual impairment (MSVI) were 6.79 (95% confidence interval (CI): 2.44–18.88) and 9.46 (95% CI: 2.19–40.94) after adjusting for age and gender (all P < 0.05). Ocular disease was associated with stroke with OR reaching 5.54 (95% CI: 1.83–16.74), and the OR was 9.61 (95% CI: 3.05–30.23) for stroke patients suffering DR after adjusting for age and gender (all P < 0.05). After multivariable adjustment, the associations were limited to mild VI (OR = 10.00, 95% CI: 3.16–30.58), MSVI (OR = 8.57, 95% CI: 1.58–43.36), and any ocular disease (OR = 5.18, 95% CI: 1.46–18.42) (all P < 0.05). Significant associations between stroke and any ocular disease and DR were observed among diabetic participants, and significant relation between stroke and MSVI was found among hypertension patients.
Conclusions
The sample of the US population demonstrates significant associations between VI and major ocular disease with stroke.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Data availability
Data supporting the findings of this study are available from https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm.
References
Rajsic S, Gothe H, Borba HH, Sroczynski G, Vujicic J, Toell T, et al. Economic burden of stroke: a systematic review on post-stroke care. Eur J Heal Econ. 2019;20:107–34.
Feigin VL, Krishnamurthi RV, Theadom AM, Abajobir AA, Mishra SR, Ahmed MB, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol 2017;16:877–97.
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP, Bruno A, Connors JJB, Demaerschalk BM, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013;44:870–947.
In S. Causes and prevalence of visual impairment among adults in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:477–85.
Nashine S, Liu Y, Kim BJ, Clark AF, Pang IH. Role of C/EBP homologous protein in retinal ganglion cell death after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:221–31.
Osborne NN, Casson RJ, Wood JPM, Chidlow G, Graham M, Melena J. Retinal ischemia: mechanisms of damage and potential therapeutic strategies. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004;23:91–147.
Solomon SD, Chew E, Duh EJ, Sobrin L, Sun JK, VanderBeek BL, et al. Diabetic retinopathy: a position statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:412–8.
Rowe FJ. Stroke survivors’ views and experiences on impact of visual impairment. Brain Behav. 2017;7:1–9.
Zhang LY, Zhang J, Kim RK, Matthews JL, Rudich DS, Greer DM, et al. Risk of acute ischemic stroke in patients with monocular vision loss of vascular etiology. J Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2018;38:328–33.
Cheung CYL, Tay WT, Ikram MK, Ong YT, De Silva DA, Chow KY, et al. Retinal microvascular changes and risk of stroke: The Singapore Malay eye study. Stroke 2013;44:2402–8.
CDC. About the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (Introduction) 2019. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about_nhanes.htm.
Zipf G, Chiappa M, Porter KS, Lewis BG, Ostchega Y, Dostal J. National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey: Plan and operations, 1999–2010. Vital Heal Stat Ser 1 Programs Collect Proced. 2013;56:1–37
https://hso.research.uiowa.edu/studies-are-not-human-subjects-research.
Sommer A. Prevalence of visual impairment in the United States. Ophthalmology 2006;295:28–9.
Lundström M, Goh PP, Henry Y, Salowi MA, Barry P, Manning S, et al. The changing pattern of cataract surgery indications: A 5-year study of 2 cataract surgery databases. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:31–8.
Grading Diabetic Retinopathy from Stereoscopic Color Fundus Photographs — An Extension of the Modified Airlie House Classification: ETDRS Report Number 10. Ophthalmology. 2020;127:S99–119.
Klein R, Davis MD, Magli YL, Segal P, Klein BEK, Hubbard L. The Wisconsin Age-related Maculopathy Grading System. Ophthalmology. 1991;98:1128–34.
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure Kurt. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16:606–13.
Ko F, Boland MV, Gupta P, Gadkaree SK, Vitale S, Guallar E, et al. Diabetes, triglyceride levels, and other risk factors for glaucoma in the national health and nutrition examination survey 2005-2008. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57:2152–7.
Wang YX, Wei WBin, Xu L, Jonas JB. Prevalence, risk factors and associated ocular diseases of cerebral stroke: The population-based Beijing Eye Study. BMJ Open. 2020;10:1–7.
Petitti DBBH. Retinopathy as a risk factor for nonembolic stroke in diabetic subjects. Stroke. 1995;26:593–6.
Wieberdink RG, Ho L, Ikram MK, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, De Jong PTVM, et al. Age-related macular degeneration and the risk of stroke: The rotterdam study. Stroke 2011;42:2138–42.
Der HoJ, Hu CC, Lin HC. Open-angle glaucoma and the risk of stroke development: a 5-year population-based follow-up study. Stroke 2009;40:2685–90.
Lotery AJ, Wiggam MI, Jackson AJ, Silvestri G, Refson K, Fullerton KJ, et al. Correctable visual impairment in stroke rehabilitation patients. Age Ageing. 2000;29:221–2.
Jones SA, Shinton RA. Improving outcome in stroke patients with visual problems. Age Ageing. 2006;35:560–5.
Wong KH, Hu K, Peterson C, Sheibani N, Tsivgoulis G, Majersik JJ, et al. Diabetic retinopathy and risk of stroke: a secondary analysis of the ACCORD eye study. Stroke. 2020;51:3733–6.
Rowe FJ, Wright D, Brand D, Maan T, Peel S, Akerman N, et al. Vision in stroke cohort: profile overview of visual impairment. Brain Behav. 2017;7:e00771.
Klein R, Klein BEK, Moss SE, Davis MD, DeMets DL. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy: IV. Diabetic Macular Edema. Ophthalmology 1984;91:1464–74.
Klein R, Sharrett AR, Klein BEK, Moss SE, Folsom AR, Wong TY, et al. The association of atherosclerosis, vascular risk factors, and retinopathy in adults with diabetes: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Ophthalmology 2002;109:1225–34.
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82141128); The Capital Health Research and Development of Special (2020–1–2052); Science & Technology Project of Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (Z201100005520045, Z181100001818003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.B. Wei, H.Y Li and Q. Yang designed the study, H.Y Li, L. Dong and Q. Yang wrote the manuscript. H.Y Li, W.D Zhou, H.T Wu, Y.F Li, and R. H Zhang collected the data and conducted the analyses, W.B. Wei edited and revised the manuscript. All authors have approved the submitted version and agreed with the contributions declarations.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, HY., Yang, Q., Dong, L. et al. Visual impairment and major eye diseases in stroke: a national cross-sectional study. Eye 37, 1850–1855 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-022-02238-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-022-02238-5