Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the early real-world clinical outcomes regarding safety and efficacy after administering the aflibercept 2 mg biosimilar (Tyalia, Cinnagen, Tehran, Iran).
Methods
A retrospective, uncontrolled observational study was conducted with a total of 499 Tyalia injections given in 189 eyes of 148 patients for variable indications. All patients were treated with at least one intravitreal injection of Tyalia 2 mg; 102 eyes with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (n-AMD), 67 eyes with diabetic macular oedema (DMO), and 20 eyes with retinal vein occlusion (RVO) associated with macular oedema were included in the analysis.
Results
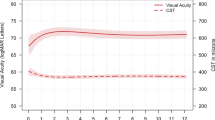
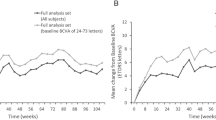
The mean central subfield thickness (CST) of the overall group improved from baseline to the last follow-up from 408.8 ± 155.1 µ to 353.4 ± 142.4 µ (p < 0.001). Best corrected visual acuity was found to be stable in the total cohort. The total number of adverse events (AEs) was (0.4%).
Conclusions
The preliminary real-world data from this limited early series suggest that Tyalia appears to have similar clinical efficacy and safety as aflibercept 2 mg innovator across the approved indications. However, long-term data with a larger population are needed to further strengthen the findings of this study.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 18 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $14.39 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are not openly available due to reasons of sensitivity and are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Data are located in controlled access data storage at Lotus Eye Hospital and Institute.
References
Finger RP, Daien V, Eldem BM, Talks JS, Korobelnik JF, Mitchell P, et al. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor in neovascular age-related macular degeneration - a systematic review of the impact of anti-VEGF on patient outcomes and healthcare systems. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020;20:294.
Kaiser PK, Schmitz-Valckenberg MS, Holz FG. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor biosimilars in ophthalmology. Retina 2022;42:2243–50.
Kelkar A, Webers C, Shetty R, Kelkar J, Labhsetwar N, Pandit A, et al. Factors affecting compliance to intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in Indian patients with retinal vein occlusion, age-related macular degeneration, and diabetic macular edema. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2143–7.
Sharma A, Kumar N, Parachuri N, Bandello F, Kuppermann BD, Loewenstein A. Biosimilars for retinal diseases: an update. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021;224:36–42.
Sharma A, Kondo M, Iwahashi C, Parachuri N, Kumar N, Bandello F, et al. Approved biosimilar ranibizumab-a global update. Eye (Lond). 2023;37:200–2.
Sharma A, Kumar N, Parachuri N, Loewenstein A, Bandello F, Kuppermann BD. Preparing for the next decade of anti-VEGF biosimilars for retinal diseases: a focus on South Asia. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023;23:689–92.
Sharma A, Holz FG, Regillo CD, Freund KB, Sarraf D, Khanani AM, et al. Biosimilars for retinal diseases: United States-Europe awareness survey (Bio-USER - survey). Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023;23:851–9.
Sharma A, Kaiser PK, Tadayoni R, Holz FG, Nicholson L, Vazquez-Alfageme C, et al. Anti-VEGF Biosimilars for Retinal Diseases Survey 2023- India (Bio-INDAS) by the International Retina Biosimilar Study Group (Inter-BIOS Group) in collaboration with the Vitreo-Retinal Society of India (VRSI). Eye (Lond). 2024;38:3392–95.
Ueda-Consolvo T, Ishida M, Nakamura T, Yanagisawa S, Tsuboi K, Wakabayashi T, et al. Biosimilar ranibizumab (BS1) - early experience from Japan (BRIJ study). Eye (Lond). 2024;38:3193–96.
Sharma A, Holz FG, Kumar N, Sarraf D, Ayachit S, Mishra C, et al. Biosimilar Ranibizumab (Ranieyes) Safety and Efficacy in the Real World: BRESER Study. J Vitreoretin Dis. 2025;24741264251322213 https://doi.org/10.1177/24741264251322213.
FDA Approves Amgen’s Pavblu™ as Fifth Aflibercept Biosimilar. https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=e930ee60-d2a7-4e8c-9d41-42adb9897a7f#:~:text=Pavblu%E2%84%A2%20is%20the%20fifth,Yesafili%E2%84%A2%20(May%202024). Accessed November 19, 2024
Karkhaneh R, Faghihi H, Riazi-Esfahani H, Abrishami M, Bazvand F, Ebrahimiadib N, et al. Evaluating the efficacy and safety of aflibercept biosimilar (P041) compared with originator product in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmol Retin. 2024;8:744–53.
Sharma A, Kumar N, Kuppermann BD, Bandello F, Loewenstein A. Biotherapeutics and immunogenicity: ophthalmic perspective. Eye (Lond). 2019;33:1359–61.
Sharma A, Kumar N, Parachuri N, Sharma R, Bandello F, Kuppermann BD, et al. Brolucizumab and immunogenicity. Eye (Lond). 2020;34:1726–8.
FDA rejects first DARPin https://www.nature.com/articles/d41573-020-00127-8. Accessed November 19, 2024.
ASRS reports six cases of occlusive retinal vasculitis linked to pegcetacoplan injection. https://www.ophthalmologytimes.com/view/asrs-reports-six-cases-of-occlusive-retinal-vasculitis-linked-to-pegcetacoplan-injection. Accessed November 19, 2024.
Sharma A, Kumar N, Kuppermann BD, Bandello F, Loewenstein A. Ophthalmic biosimilars and biologics-role of endotoxins. Eye (Lond). 2020;34:614–5.
Sharma S, Khan MA, Chaturvedi A, RE-ENACT Study Investigators Group. Real-Life clinical effectiveness of Razumab® (the world’s first biosimilar of ranibizumab) in retinal vein occlusion: a subgroup analysis of the pooled retrospective RE-ENACT study. Ophthalmologica. 2019;241:24–31.
Sharma S, Khan MA, Chaturvedi A, RE-ENACT Study Investigators Group. Real life clinical effectiveness of Razumab® (world’s first biosimilar ranibizumab) in wet age-related macular degeneration: a subgroup analysis of pooled retrospective RE-ENACT study. Int J Ophthalmol Eye Res. 2018;6:368–73.
Sharma A, Hafeez Faridi M, Kumar N, Parachuri N, Sharma R, Kuppermann BD, et al. Immunogenicity and efficacy after switching from original Ranibizumab to a Ranibizumab biosimilar: real-world data. Eye (Lond). 2020;34:1008–9.
Sharma A, Loewenstein A, Parachuri N, Kumar N, Kuppermann BD. Biosimilar to biosimilar. Anti-VEGF switching for retinal diseases. J VitreoRetinal Dis. 2023;0(0). https://doi.org/10.1177/24741264231202080.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
KGF: conception, analysis, drafting, integrity check, final approval. SA, AS, MMP: data, drafting, revision, analysis, integrity check.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
KGF: Consultant for CinnaGen. Ashish Sharma: Consultant for Bayer, Lupin, Novartis, Allergan, Roche and Intas. SA and MMP: None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Avadzadeh, S., Sharma, A., Parvaresh, M.M. et al. Aflibercept 2 mg biosimilar (Tyalia)—real-world experience from IRAN (ATRIA study). Eye 39, 2159–2163 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-025-03813-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-025-03813-2