Abstract
Purpose
To examine the association between smoking and idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH).
Methods
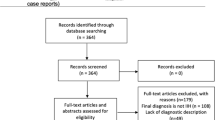
A systematic literature search was conducted on Ovid MEDLINE, Embase, and the Cochrane Library from inception to March 12th, 2025, to identify eligible observational studies evaluating the association between smoking and IIH in adult populations. A random-effects meta-analysis using the Mantel-Haenszel method was conducted to calculate pooled odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Leave-one-out sensitivity analyses and subgroup analyses stratified by study continent were performed to assess the robustness of findings. Study quality was appraised using the ROBINS-E tool and the certainty of evidence was evaluated through the GRADE framework. Publication bias was assessed using Egger’s test.
Results
Eleven observational studies comprising 8,098 IIH patients and 90,381 non-IIH controls were included. Patients with IIH exhibited higher odds of current smoking status compared to controls (OR = 1.46, 95%CI = [1.39–1.54], p < 0.001, I2 = 0%). This association remained consistent in the leave-one-out sensitivity analysis and across geographical subgroups: European studies (OR = 1.45, 95%CI = [1.33–1.59], p < 0.001, I2 = 24%) and North American studies (OR = 1.42, 95%CI = [1.21–1.67], p < 0.001, I2 = 0%). Additionally, IIH patients had higher odds of former smoking status compared to controls (OR = 1.13, 95%CI = [1.05–1.21], p < 0.001, I2 = 0%). Quality assessments ranged from some concerns to low risk of bias, with no publication bias (p = 0.59).
Conclusions
Low certainty of evidence suggests that current and former smoking status are associated with IIH. Clinicians should consider smoking history as part of risk assessment in patients with suspected IIH. Further prospective studies with detailed exposure metrics are needed to confirm causality and explore dose-dependent relationships.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 18 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $14.39 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Wall M. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurol Clin. 2010;28:593–617.
Curry WT Jr., Butler WE, Barker FG II. Rapidly Rising Incidence of Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunting Procedures for Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in the United States, 1988–2002. Neurosurgery. 2005;57:97–108.
Raoof N, Hoffmann J. Diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia. 2021;41:472–8.
Shaia JK, Sharma N, Kumar M, Chu J, Maatouk C, Talcott K, et al. Changes in Prevalence of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in the United States Between 2015 and 2022, Stratified by Sex, Race, and Ethnicity. Neurology. 2024;102:e208036.
Chen J, Wall M. Epidemiology and risk factors for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2014;54:1–11.
Ghaffari-Rafi A, Mehdizadeh R, Ko AWK, Ghaffari-Rafi S, Leon-Rojas J. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in the United States: Demographic and Socioeconomic Disparities. Front Neurol. 2020;11:869.
Friedman DI, Liu GT, Digre KB. Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Neurology. 2013;81:1159–65.
Subramaniam S, Fletcher WA. Obesity and Weight Loss in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Narrative Review. J Neuroophthalmol. 2017;37:197–205.
Passi SF, Butcher R, Orme DR, Warner JEA, Stoddard GJ, Crum AV, et al. Increased Incidence of Pseudotumor Cerebri Syndrome Among Users of Tetracycline Antibiotics. J Neuroophthalmol. 2022;42:323–7.
Adderley NJ, Subramanian A, Nirantharakumar K, Yiangou A, Gokhale KM, Mollan SP, et al. Association Between Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Women in the United Kingdom. JAMA Neurol. 2019;76:1088–98.
Riise T, Nortvedt MW, Ascherio A. Smoking is a risk factor for multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2003;61:1122–4.
Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB, Kannel WB, Bonita R, Belanger AJ. Cigarette smoking as a risk factor for stroke. The Framingham Study. Jama. 1988;259:1025–9.
Messner B, Bernhard D. Smoking and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction and early atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:509–15.
Cao L, Wang H, Kwapong WR, Wan J, Yan Y, Liu G, et al. Macular exudate in idiopathic intracranial hypertension affects outer retina and visual acuity. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2024;9:e001810.
Barke M, Castro HM, Adesina OO, Chuang AZ, Do T, Patel RP, et al. Thinning of the Skull Base and Calvarial Thickness in Patients With Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. J Neuroophthalmol. 2022;42:192–8.
Deveci Ş, Kabeloğlu V. The Relationship between Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Is Obesity the Only Mediating Factor between the Two? Duzce Med J. 2024;26:122–8.
Sander K, Poppert H, Etgen T, Hemmer B, Sander D. Dynamics of intracranial venous flow patterns in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Eur Neurol. 2011;66:334–8.
Brooke BS, Schwartz TA, Pawlik TM. MOOSE Reporting Guidelines for Meta-analyses of Observational Studies. JAMA Surg. 2021;156:787–8.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj. 2021;372:n71.
Higgins JPT, Morgan RL, Rooney AA, Taylor KW, Thayer KA, Silva RA, et al. A tool to assess risk of bias in non-randomized follow-up studies of exposure effects (ROBINS-E). Environ Int. 2024;186:108602.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. Bmj. 2008;336:924–6.
Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959;22:719–48.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Bmj. 2003;327:557–60.
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Bmj. 1997;315:629–34.
Amikam U, Baghlaf H, Badeghiesh A, Brown R, Dahan MH. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and obstetric and neonatal outcomes: A 1:20 matched study from a population database. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2024;166:1040–6.
Youssef M, Sundaram ANE, Veitch M, Aziz A, Gurges P, Bingeliene A, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea in those with idiopathic intracranial hypertension undergoing diagnostic in-laboratory polysomnography. Sleep Med. 2024;114:279–89.
Mollan SP, Subramanian A, Perrins M, Nirantharakumar K, Adderley NJ, Sinclair AJ. Depression and anxiety in women with idiopathic intracranial hypertension compared to migraine: A matched controlled cohort study. Headache. 2023;63:290–8.
Samancı B, Samancı Y, Şen C, Şahin E, Sezgin M, Kocasoy Orhan E, et al. Assessment of the Olfactory Function in Patients With Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Using the Sniffin’ Sticks Test: A Case-Control Study. Headache. 2019;59:848–57.
Wallentin T, Linnet J, Lichtenstein MB, Hansen NS, Korsbæk JJ, Høgedal L, et al. The impact of eating disorders on idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia. 2024;44:3331024241237237.
Ireland B, Corbett JJ, Wallace RB. The search for causes of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. A preliminary case-control study. Arch Neurol. 1990;47:315–20.
Puranik R, Celermajer DS. Smoking and endothelial function. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2003;45:443–58.
Tanriverdi H, Evrengul H, Kuru O, Tanriverdi S, Seleci D, Enli Y, et al. Cigarette smoking induced oxidative stress may impair endothelial function and coronary blood flow in angiographically normal coronary arteries. Circ J. 2006;70:593–9.
Sunyer J, Forastiere F, Pekkanen J, Plana E, Kolz M, Pistelli R, et al. Interaction between smoking and the interleukin-6 gene affects systemic levels of inflammatory biomarkers. Nicotine Tob Res. 2009;11:1347–53.
Churg A, Dai J, Tai H, Xie C, Wright JL. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is central to acute cigarette smoke-induced inflammation and connective tissue breakdown. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:849–54.
Tapson VF. The role of smoking in coagulation and thromboembolism in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2:71–7.
Nielsen VG, Hafner DT, Steinbrenner EB. Tobacco smoke-induced hypercoagulation in human plasma: role of carbon monoxide. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2013;24:405–10.
Masood S, Cappelli C, Li Y, Tanenbaum H, Chou CP, Spruijt-Metz D, et al. Cigarette smoking is associated with unhealthy patterns of food consumption, physical activity, sleep impairment, and alcohol drinking in Chinese male adults. Int J Public Health. 2015;60:891–9.
Eshtiaghi A, Margolin EA, Micieli JA. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension and Socioeconomic Status in the Greater Toronto Area, Canada. J Neuroophthalmol. 2023;43:197–201.
Hornby C, Mollan SP, Botfield H, OʼReilly MW, Sinclair AJ. Metabolic Concepts in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension and Their Potential for Therapeutic Intervention. J Neuroophthalmol. 2018;38:522–30.
Abbott S, Chan F, Tahrani AA, Wong SH, Campbell FEJ, Parmar C, et al. Weight Management Interventions for Adults With Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Practice Recommendations. Neurology. 2023;101:e2138–e50.
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ryan S. Huang: Conceptualisation, Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualisation, Writing – Original draft preparation, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. Andrew Mihalache: Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualisation, Writing – Original draft preparation, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. Brendan K. Tao: Conceptualisation, Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Writing – Original draft preparation, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. Jim S. Xie: Conceptualisation, Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Writing – Original draft preparation, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. Jonathan A. Micieli: Conceptualisation, Methodology, Supervision, Project administration, Resources, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. Edward A. Margolin: Conceptualisation, Methodology, Supervision, Project administration, Validation, Resources, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. All authors have equally fulfilled the authorship criteria and contributions outlined by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) and approved the current version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
41433_2026_4282_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplemental Figure S2. Summary of risk of bias evaluation using the ROBINS-E (Risk of Bias in Non-randomized Studies – of Exposures) tool
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, R.S., Mihalache, A., Tao, B.K. et al. Smoking and idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a meta-analysis. Eye (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-026-04282-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-026-04282-x