Abstract
Therapsids were a dominant component of middle–late Permian terrestrial ecosystems worldwide, eventually giving rise to mammals during the early Mesozoic. However, little is currently known about the time and place of origin of Therapsida. Here we describe a definitive therapsid from the lower–?middle Permian palaeotropics, a partial skeleton of a gorgonopsian from the island of Mallorca, western Mediterranean. This specimen represents, to our knowledge, the oldest gorgonopsian record worldwide, and possibly the oldest known therapsid. Using emerging relaxed clock models, we provide a quantitative timeline for the origin and early diversification of therapsids, indicating a long ghost lineage leading to the evolutionary radiation of all major therapsid clades within less than 10 Myr, in the aftermath of Olson’s Extinction. Our findings place this unambiguous early therapsid in an ancient summer wet biome of equatorial Pangaea, thus suggesting that the group originated in tropical rather than temperate regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Therapsida is a clade of diverse and ecologically successful tetrapods, with mammals as their modern representatives1. The roots of the clade extend back to the late Palaeozoic, when non-mammalian therapsids were important components of terrestrial ecosystems. Until now, the oldest known unequivocal therapsid was Raranimus dashankouensis, from probable Roadian (lower middle Permian) deposits of central-east Asia2. Yet, phylogenetic analyses consistently suggest that therapsids are the sister group of sphenacodontid ‘pelycosaur’-grade synapsids, which originated in the Pennsylvanian (ca. 320 Ma)3,4. This implies a long therapsid ghost lineage spanning about 40 million years.
This vast knowledge gap likely stems from the uneven geographic sampling of Permian tetrapods worldwide. The best-known early Permian tetrapod-bearing formations in North America (southwestern ‘Red Beds’) and in Europe (Central European Basin) correspond to palaeotropical ecosystems and have not yet yielded any definitive therapsid fossils1,5. By contrast, the sites with the most diverse and abundant middle to upper Permian therapsid records are in the Cis-Urals of Russia and in southern Africa, preserving ecosystems of northern and southern palaeotemperate latitudes, respectively6,7. The historical lack of a spatiotemporal link between these regions has obscured the early history of therapsid evolution and diversification. Furthermore, the exact timing for the origin of the major groups of therapsids has always relied on a literal reading of the fossil record8, without implementation of statistical modelling.
Here we describe the earliest unequivocal therapsid from equatorial Pangaea, collected in the upper Cisuralian (lower Permian)–?lowermost Guadalupian (middle Permian) of Mallorca (Balearic Islands, western Mediterranean)9 (Figs. 1, 2). We discuss its identity, age and palaeobiogeographical implications, revealing that it is the oldest known gorgonopsian to our knowledge (Fig. 1c), and very likely the oldest therapsid worldwide. The presence of a derived therapsid at this age and location is unexpected, indicates that the diversification of the major therapsid subclades may not have been restricted to high palaeolatitudes as previously thought, and provides insight on the timing and phylogenetic structure of the therapsid evolutionary radiation. Olson’s Extinction, which happened in the early–middle Permian transition10,11,12, may have provided the necessary ecological opportunity for this previously inconspicuous group to diversify into varied phenotypes and distinct ecological roles.
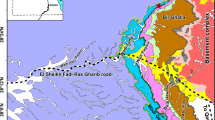
a World map showing the location of the island of Mallorca, and map of the Balearic Islands with indication of the study area. b Composite stratigraphic log for the Racó de s’Algar-Pedra de s’Ase section (simplified from Matamales-Andreu et al.9), indicating the beds that contain tetrapod tracks, spores and pollen, and the gorgonopsian. c, Magneto- and biostratigraphic criteria used to date the Permian formations of Mallorca (modified from Matamales-Andreu et al.9, with additional data from Marchetti et al.36).
a Detailed stratigraphic log of the Torrent de na Nadala fossil site with indication of the lithology, palaeoenvironment and location of fossiliferous horizons16. b Site map of the Torrent de na Nadala horizon 2, with all the bones attributed to the gorgonopsian. astr = astragalus, bcr = basicranium, calc = calcaneum, can = canine, d = dentary, ept = ectopterygoid, f = femur, fi = fibula, inc = incisor, (L) = left element, mt = metatarsal, mx = maxilla, n = nasal, ph = phalanx, pt = pterygoid, (R) = right element, smx = septomaxilla, t = tibia, tar = tarsal, ung = ungual, vert = vertebra.
Results and discussion
Systematic palaeontology
Synapsida Osborn, 190313
Therapsida Broom, 190514
Gorgonopsia Seeley, 189415
Gorgonopsia indet.
(Figure 3, Supplementary Figs. 1–5)
a Snout fragment. b Pterygoid. c Basicranium. d Incisors. e Canine. f1-3 Left dentary. g Cervical? vertebra. h Proximal caudal vertebrae. i Distal caudal vertebrae. j Right dorsal rib. k Left femur. l Left fibula. m Left tibia. n Left astragalus. o Left calcaneum. p Ungual. q First metatarsal (below) and first phalanx of right digit I (above). r Penultimate phalanx. s Distal tarsal (below) and metatarsal (above) of left digit III. t First (below) and second (above) phalanges of right digit IV. u Left fourth tarsal. v First phalanx of right digit V. w Right fifth metatarsal. azg = prezygapophysis, bo = basioccipital, bt = basal tuber, ca = alveolus of canine, cnc = cnemial crest, fcr = fused caudal ribs, ina = alveoli of incisors, lpf = lateral pterygoid flange, mprp = median palatal ramus of the pterygoid, mx = maxilla, n = nasal, ns = neural spine, pca = alveoli of postcanines, pop = paroccipital process (opisthotic), pqrp = pterygoid posterior quadrate rami, pro = prootic, pt = pterygoid, pzg = postzygapophysis, smx = septomaxilla, tp = transverse process, fn = fibular notch, gt = greater trochanter. (L) and (R) next to the elements refer to the left and right sides of the skeleton, respectively.
Studied material
DA21/17-01-01 (see the full list of institution acronyms in Supplementary Note 1), a disarticulated, partial skeleton consisting of partial snout roof, partial basicranium, pterygoid, ectopterygoid?, hyoid?, left dentary, one upper canine, four lower? incisors, four presacral vertebrae, two proximal caudal vertebrae, eight distal caudal vertebrae, two right dorsal ribs and fragments of others, left femur, left tibia, left fibula, left calcaneum, left astragalus, possible left distal tarsal 3, left metatarsals 3 and 4, right metatarsals 1 and 5, first phalanges of right digits I, IV and V, second phalanx of right digit IV, one penultimate phalanx of digit III, IV or V, and one ungual phalanx. All the bones were found near the base of bed NA2 (Torrent de na Nadala 2, Banyalbufar, Mallorca, western Mediterranean16; see Fig. 2) except for one of the presacral vertebrae, which was extracted from the upper part of the same bed (ca. 4 cm above), in a conglomerate horizon (Fig. 2b).
Description and comparative anatomy
DA21/17-01-01 represents a small gorgonopsian (estimated skull length ~18 cm) known from various cranial fragments, several sections of the axial column (including a large portion of the tail), and most of the left hind limb. See Supplementary Figs. 1–5 and Supplementary Note 2 for a detailed description and illustration of all the elements.
Cranial elements consist of a highly-flattened dorsal portion of the snout, fused basicranium incorporating at least the basioccipital, opisthotic, and prootic, and an isolated pterygoid. The fused pterygoid exhibits prominently ‘wing’-shaped, backswept transverse processes (seen in other early gorgonopsians, such as Eriphostoma and Gorgonops17) and bears anterior articular facets for the ectopterygoids. The left dentary is preserved almost in its entirety, with alveoli indicating a tooth count of i4/c1/pc5 (incisor/canine/postcanine). The dentary has a prominent mentum at the ventral edge of the symphysis and a clear inflection point dorsally where the incisor roots would have been housed. Several serrated, weakly spatulate teeth probably represent the lower incisors. A much larger, laterally compressed, blade-like tooth represents a canine, probably an upper based on size.
Preserved axial elements include two probable cervical vertebrae, two intact dorsal ribs and fragments of additional ribs, two isolated anterior caudal vertebrae, and an articulated caudal series including evidence for 14 vertebrae. The vertebrae are similar to those known in other gorgonopsians18. The left hind limb includes the femur, tibia, fibula, astragalus, calcaneum, and several metatarsals and phalanges, including one ungual. The tibia and fibula are both bowed, indicating the presence of a large interosseous space. The femur is weakly curved with a notably offset head, which is the typical morphology of small gorgonopsians19. In general, the postcranial anatomy of the gorgonopsian from Mallorca is very consistent with that of other small-bodied members of the group (e.g., Cyonosaurus), with no clear autapomorphies.
A suite of characters clearly demonstrates that specimen DA21/17-01-01 represents a gorgonopsian therapsid. The dentary is characteristic for this clade, showing the combination of a steeply inclined mandibular symphysis, canine-postcanine diastema, relatively short postcanine tooth row, and anterodorsally-to-posteroventrally angled postcanine tooth row. Together, this combination of characters is only known in Gorgonopsia among Permian synapsids19. A steep mandibular symphysis is also present in anteosaurs20, and some biarmosuchians and therocephalians (e.g., Hipposaurus19, Moschorhinus21), but in these taxa no diastema exists between the lower canine and the (usually extensive) postcanine tooth row. In most therocephalians and some biarmosuchians (e.g., Herpetoskylax22), the symphysis is generally weakly sloping, with a low, convex anterior face23. Anterodorsal-to-posteroventral angulation of the postcanine tooth row is typical of biarmosuchians and therocephalians in addition to gorgonopsians, but this character excludes identification as a dinocephalian or a non-therapsid synapsid (‘pelycosaur’). Furthermore, the triangular anterodorsal projection housing the incisor tooth row is seen in almost all small gorgonopsians (Sigogneau24: fig. 206). The canine is mesiodistally serrated and very compressed labiolingually (although this may be exaggerated by taphonomic distortion). This tooth is more circular in cross-section in other early synapsid groups with serrated canines (biarmosuchians, anteosaurs, and early therocephalians; also the caniniforms of some sphenacodontids)25. The pterygoid shows a backswept ‘wing’-like morphology of the transverse processes, which is frequently observed in early gorgonopsians and differs strongly from the more robust-edged transverse processes of biarmosuchians and dinocephalians, which lack attenuate tips. Some early therocephalians also have backswept transverse processes of the pterygoid23, but in therocephalians the ectopterygoid is located lateral to this process, such that there is not an anterior facet for the ectopterygoid as in DA21/17-01-01. The general morphology of the femur (sinuous with the head sharply offset from the shaft; low, rounded fourth trochanter; and greatly expanded distal end) is characteristically gorgonopsian, and the fibula and especially the tibia bow strongly away from one another (indicating a large interosseous space), a morphology unique to gorgonopsians among therapsids26.
Because of the incompleteness of the specimen, it is difficult to identify it more precisely than Gorgonopsia, especially considering the notorious morphological conservatism of the clade. Some types of gorgonopsians can clearly be excluded as possibilities, however. The morphology of the pterygoids is unlike that of Rubidgeinae and related taxa (e.g., Arctops), in which the transverse processes are generally swollen towards their tips and not backswept27,28. The presence of five lower postcanines also excludes several rubidgeine taxa (e.g., Clelandina, Rubidgea) as well as various other gorgonopsians with absent (e.g., Inostrancevia) or reduced (e.g., Eriphostoma) lower postcanine tooth rows17. However, the same tooth count is known in small gorgonopsians such as Aelurosaurus felinus24. A variety of other features distinguish this specimen from rubidgeines and Inostrancevia, but these may be more size-related than strictly phylogenetic. For example, the inflected anterior face of the mandibular symphysis and the sinuous femoral shape differ from the straight, massive symphysis and nearly-straight femur of large gorgonopsians, but they are known in most small-bodied members of the clade regardless of relationships24. Ontogenetic variation in these features is poorly understood, and whether they change with increasing body size during the life of an individual is currently unknown. However, this specimen likely represents an osteologically mature individual, based on the very well-ossified limb and ankle elements and fused basicranium (Fig. 3, Supplementary Fig. 1), instead of a juvenile of one of the larger species (those with skull length 40 cm or greater). Although the exact size of the animal is hard to determine given the paucity of elements and limited basis for postcranial comparisons in the group, based on dentary length, and assuming comparable proportions to Gorgonops, this individual would have had a skull length of ~18 cm (Fig. 3).
Presence of a steep mandibular symphysis suggests that the specimen from Mallorca is more derived than the current earliest-diverging gorgonopsian, Nochnitsa (following the character polarity of Kammerer & Masyutin29), but otherwise its cranial characters are generally plesiomorphic. The elongate, backswept transverse processes of the pterygoids are seen in Eriphostoma, Gorgonops and Cynariops17,30 among African taxa, but also in the earlier-diverging Viatkogorgon29, suggesting that this morphology is ancestral for Gorgonopsia. The relatively anterior position of the divergence between the quadrate rami of the pterygoids is also observed in Gorgonops, Aelurosaurus, and Cyonosaurus, and the close proximity between the basal tubera and the occipital condyle is comparable to that of Gorgonops, Suchogorgon, and Sauroctonus (Kammerer, pers. obs.). Overall, the gorgonopsian from Mallorca shows features most consistent with early-diverging members of the ‘African clade’ (sensu Kammerer & Masyutin29), but, as these are plesiomorphic, it could also fall outside of this subclade as either an early-diverging member of the ‘Russian clade’ (like Suchogorgon) or outside of the major divergence altogether (like Viatkogorgon). Given its stratigraphic and geographic separation from other members of the group, this specimen likely represents a new taxon, but in the absence of any uniquely diagnostic features in the preserved material, we do not erect a new species for it here.
Age of the oldest known therapsids
The bone-bearing beds containing the gorgonopsian described here have been argued to belong to the Artinskian or Kungurian stages of the Cisuralian series (lower Permian)9, based on four lines of evidence. First, magnetostratigraphic analysis showed that the uppermost levels of the succession, 250 m stratigraphically above the bone-bearing levels, belong to the Kiaman Reverse Superchron, which dates from the middle Bashkirian to middle Wordian (early Pennsylvanian to middle Permian)31. This indicates that the gorgonopsian from Mallorca must be older than middle Wordian. A pre-Wordian age for the specimen is very likely considering the thick overlying sequence of mudstones with carbonate palaeosols (Fig. 1b)9, a type of rock with low sedimentation rates32. Second, palynoassemblages from the upper part of the overlying Pedra de s’Ase Formation provided additional evidence for a Guadalupian (middle Permian) age for the uppermost part of the section (Fig. 1b, c). Third, the tetrapod tracks stratigraphically bracketing the gorgonopsian site (Fig. 1b, c) possess the typical components of Cisuralian ichnoassemblages elsewhere (Fig. 1c), including the ichnogenus Dimetropus, which is unknown from rocks younger than the Kungurian (upper part of the lower Permian)33. ‘Pelycosaur’ body fossils are known from the Kungurian to the Roadian of Russia34, North America5, and Sardinia35, raising the possibility that this ichnogenus could be found in Guadalupian rocks, but the abundance of ‘pelycosaur’-dominated ichnoassemblages in the Port des Canonge Formation is more typical of the Cisuralian worldwide, regardless of the sedimentary palaeoenvironment33. Fourth, these ichnoassemblages lack the ichnogenera Erpetopus (middle Artinskian–middle Wuchiapingian) and Brontopus (Roadian–middle Capitanian), which commonly appear in younger strata in palaeogeographically proximate basins33,36,37.
Based on these arguments, the Mallorcan gorgonopsian is certainly older than middle Wordian (early Guadalupian, middle Permian), and it may be as old as Artinskian (late Cisuralian, early Permian) (Fig. 1c). The minimum age places it among the oldest known gorgonopsians worldwide, rivalled only by an indeterminate gorgonopsian from the Wordian Eodicynodon Assemblage Zone of South Africa38. Because the stratigraphic position of the specimen from Mallorca is 250 m below the last bed of the section, which is still part of the Kiaman Reverse Superchron (Fig. 1c), it is very likely to be older than Wordian, therefore making it the oldest record of gorgonopsians worldwide, to our knowledge. A Roadian age for the Mallorca specimen would make it a contemporary of the oldest therapsids (e.g., Raranimus, Biseridens) currently known from the Dashankou assemblage of China2, whereas a Kungurian or Artinskian age, which best accords with the magnetostratigraphic and ichnological data, would make it the oldest definitive therapsid discovered to date.
Phylogeny and a detailed timeline for the origin and early radiation of therapsids
Currently, no definitive early Permian therapsids are known, despite widespread agreement that the divergence between therapsids and other synapsids must have happened by that time (and possibly as early as the Pennsylvanian4,39). The unusual Artinskian synapsid Tetraceratops has been proposed to partially fill this gap40,41, but more recent research suggests that it is a non-therapsid eupelycosaur42, which is supported by our phylogenetic results (Fig. 4, Supplementary Fig. 6). This important fossil gap in the early history of therapsids has historically obscured our understanding regarding the time of origin of Therapsida and its major clades. Furthermore, discussions of therapsid origins have mostly been conducted by qualitative assessments and literal readings of the therapsid fossil record, which have been used to argue for an explosive radiation of the clade in the middle Permian8.
Maximum compatible tree from relaxed morphological clock Bayesian inference analysis under the skyline fossilised birth-death tree model (SFBD) using tip-dating and the best fitting clock model (see Methods and Supplementary Table 1). All the major therapsid groups originated much later than ‘total group’ therapsids, but radiated in a relatively short time span of only ca. 10 Myr. Red star indicates single node calibration based on new Mallorca specimen (see Supplementary Fig. 6 for variance in divergence time estimates with and without new data from the Mallorcan site). Node values represent posterior probabilities (top) and median ages (bottom, in bold). Node violin plots (cyan) represent the distribution of the 95% highest posterior density (HPD) intervals. All silhouettes produced by TRS.
To advance our knowledge on this topic, we used, for the first time, mechanistic models of evolution to estimate divergence times for the origin of the major therapsid clades; namely Bayesian relaxed morphological clock analyses. We used the skyline fossilised birth-death tree model (SFBD)43 in combination with new relaxed clock models recently implemented in the software Mr. Bayes44 — see Methods. We updated and expanded the phylogenetic data matrix of Brink et al.45 to create the most comprehensive available dataset sampling the major early therapsid clades at the species level. We implemented tip-dated calibrations followed by a tip + node-dating. In the latter, we applied a node calibration for the age of Gorgonopsia informed by the range of potential ages of the Mallorcan specimen to see its impact on divergence time estimates.
The results of this analysis provide an updated temporal framework for the therapsid diversification (Fig. 4, Supplementary Fig. 6). We infer the split between therapsids and ‘pelycosaurs’ (represented here by non-therapsid sphenacodonts) to have occurred at ~294 Ma (95% HPD = 290.5–298.0 Ma) in the earliest Permian (Asselian), rather than in the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian), as previously hypothesised39. We confirm the traditional understanding that there was a relatively long ghost lineage of about 15 Myr between the origin of ‘total-group’ therapsids and the radiation of the major therapsid clades (dinocephalians, anomodonts, biarmosuchians, gorgonopsians, therocephalians) at ~278 Ma in the late Cisuralian. Our results support Raranimus as the only known member of this early (‘stem’) stock of therapsids before the origin of the major therapsid clades. Despite its incompleteness and relatively young age (early Guadalupian; coeval with dinocephalians and anomodonts), Raranimus preserves several morphological characters that would support this phylogenetic interpretation, including two upper caniniform tooth positions and an elongate caudal alveolar portion of the maxillary canal2.
Interestingly, despite the long ghost lineage in the early history of therapsids, our results support previous qualitative interpretations of the fossil record indicating that major therapsid clades originated over a relatively short span of time, which we infer here to be only 10 Myr, between ~278–268 Ma (late Cisuralian–early Guadalupian, or early–middle Permian transition). This time range encompasses the period of heightened tetrapod turnover known as Olson’s Extinction at ca. 273 Ma10,11,12, which marked the extinction of important components of terrestrial tetrapod faunas at the time, including other synapsids (Ophiacodontidae, Edaphosauridae) and early tetrapods (Molgophidae, Trimerorhachidae), besides major drops in diversity for Sphenacodontidae and Eryopidae (i.e., ‘dead clades walking’). After this event, the emergence of robust herbivorous lineages, such as pareiasaurs, appears to have prompted a dramatic shift in jaw morphofunctionality of carnivorous synapsids (mostly therapsids) towards injuring and subduing the prey, instead of the optimisation for grasping and holding smaller prey seen in ‘pelycosaurs’46. The loss of potential competitors and the evolution of novel morphotypes in terrestrial animals may have provided ecological opportunity for emerging therapsid clades, catalysing their evolutionary radiation in the middle Permian.
The Bayesian clock results also inform our expectations for the structure of the early therapsid fossil record. Based on divergence times of the major therapsid clades, we predict that morphologically diagnosable members of these clades could be found in rocks as old as the Kungurian (273–283 Ma). As a diagnostic member of Gorgonopsia whose potential age falls in this range, the Mallorcan specimen corroborates this prediction (Fig. 4, Supplementary Fig. 6). Our revised understanding of the therapsid fossil record also makes it unlikely that we will find diagnostic members of major therapsid clades in rocks older than the Artinskian (~285 Ma). Instead, we predict that therapsids from this time interval would be ‘stem’ members of the group, lacking many diagnostic characters found in the later clades, and likely difficult to differentiate from contemporaneous ‘pelycosaurs’. Critical re-appraisal of previously collected fossils (e.g., Spindler42), and collecting efforts in under-sampled regions from the continental northwestern Tethyan domain, are important areas of ongoing work in the search for the currently missing ‘stem’ therapsids.
Biogeographic origin of therapsids
A long-established pattern in the biogeography of early synapsids is that early Permian ‘pelycosaurs’ occur in lower palaeolatitudes and middle–late Permian therapsids in higher palaeolatitudes. This geographically disjunct distribution has obscured the biogeographic centre of origin of therapsids1. Kemp8, for instance, hypothesised that the first therapsids would have evolved from sphenacodont ‘pelycosaurs’ during the late part of the early Permian, acquiring a unique combination of traits that facilitated their occurrence in the seasonally arid tropical biomes of Pangaea. There, they would have persisted as medium-sized carnivores until the middle Permian, when the tropical and temperate biomes became connected, allowing therapsids to diversify and colonise higher latitudes. However, until now, tropical therapsids were rare and only known with certainty from the late Permian (Lopingian), represented by a poor fossil record consisting of fragmentary gorgonopsian remains from central Africa47 and derived dicynodonts from Laos48. Unfortunately, those records provide no relevant information about the time or place of origin of therapsids. Richer therapsid assemblages are known from northern China, but the complex geological history and conflicting palaeogeographic reconstructions for this region complicates confident palaeolatitudinal assignments. Although current evidence indicates that the North China Block was within the tropics during the Permian49, the portion of Gansu yielding middle Permian therapsids (the possibly Roadian Dashankou assemblage) was part of a distinct land mass (the Alashan Terrane) that did not amalgamate with the North China Block until the Mesozoic and was situated north of it (though at least in the subtropics)50.
The gorgonopsian from Mallorca provides the first unequivocal evidence that therapsids were indeed present in the summer wet biomes of equatorial Pangaea during the early–middle Permian transition, suggesting that the group may have originated in lower, tropical latitudes, rather than in the higher latitudes where nearly all of their fossils are known (Fig. 5). The Mallorcan specimen represents a specialised form that, based on the fossil track record of its locality—dominated by moradisaurine captorhinids and small-sized ‘pelycosaurs’9,16, was probably the apex predator of its ecosystem. However, contra Kemp’s hypothesis8 that the diversification of therapsids into their major subclades was driven by expansion into seasonally cool temperate regions, the presence of a definitive gorgonopsian (a clade deeply nested in therapsid phylogeny; Fig. 4) in equatorial Pangaea implies that this radiation was underway prior to synapsid dispersal to higher latitudes.
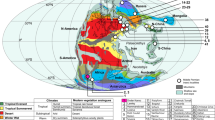
Note a dominant tropical distribution of ‘pelycosaur’-grade synapsids during the early and early part of the middle Permian, and a trans-Pangaean distribution of non-mammalian therapsids during the middle and late Permian. The specimen studied herein has been displayed on the early Permian map because that is its most probable age, although it could also be from the earliest middle Permian. Maps after Scotese72, and climate zones after Rees et al.73 for the early and middle Permian, and Smith et al.60 for the late Permian. Synapsid distribution after Laurin et al.5, Bernardi et al.6, Olroyd & Sidor7, Marchetti et al33,36, Romano et al.35 and De Jaime-Soguero et al.37.
If therapsids originated in the tropics, this has implications for metabolic evolution in the clade. Although recent evidence indicates that mammal-like endothermy in synapsids did not originate until the Triassic51, the expansion of early therapsids in higher latitudes8 suggests that, following Olson’s Extinction, the members of this clade were more eurythermal due to some rudimentary form of thermoregulation. The palaeotropical gorgonopsian presented here implies that this early thermal niche relaxation was probably the result of an exaptive process, in which early therapsids first developed their revolutionary new suite of morphological and physiological traits (more efficient locomotion, respiration, food manipulation, and elevated growth rates, among others) in the ancestral synapsid equatorial belt, which later facilitated their colonisation of cooler climates. Given that the earliest therapsids were all faunivorous52, an additional selective force operating on the therapsid body plan may have been the appearance of larger prey that required novel methods to subdue46. Large moradisaurine captorhinids became abundant in the Kungurian–Roadian53,54, with one of these species and large tracks correlated to this clade found in the same formation as the Mallorcan gorgonopsian9,55, and geographically proximate beds of similar age in Menorca, Sardinia and southern France have yielded enormous moradisaurine captorhinids56 and caseid ‘pelycosaurs’57. Possibly, the traits selected to prey upon these animals also benefitted therapsids as they expanded into new environments inhabited by other large tetrapods.
This discovery underscores the need for more sampling in poorly studied areas of northern Africa and southern Europe that preserve Permian tropical ecosystems. Available data suggest that, at least during the late Permian, tropical tetrapod assemblages consisted of an ‘atypical’ mixture of classical middle–late Permian taxa (pareiasaurs and therapsids) and relict groups otherwise widespread during the late Carboniferous and early Permian (cochleosaurid temnospondyls, diplocaulid lepospondyls, moradisaurine captorhinids)6,7,58,59. The assemblage from Mallorca is also unique but in a different sense, as in this case it shows a mixture of typically early Permian tetrapods (‘pelycosaurs’ and moradisaurine captorhinids) and therapsids. These observations hint at a complex tetrapod palaeobiogeographical history in the tropical regions of Pangaea, with therapsids constituting a key component.
Our findings demonstrate that therapsids inhabited equatorial Pangaea during the early–middle Permian. Specifically, we provide, to our knowledge, the first record of Gorgonopsia in western Europe, represented by a relatively small taxon (Figs. 3, 6). Several independent lines of evidence (palaeomagnetism, palynoassemblages, tetrapod ichnoassemblages) point to a late Cisuralian/?earliest Guadalupian age. This implies that the specimen is the oldest (albeit not earliest-diverging) gorgonopsian worldwide, and is among the oldest therapsids, if not the oldest member of the clade discovered to date. Our Bayesian evolutionary analyses indicate that diversification of the major therapsid clades was underway by the Kungurian, potentially in association with Olson’s Extinction. After a long ghost lineage in the early history of Therapsida, its major clades originated in a relatively short span of time of less than 10 Myr between the late Cisuralian and the early Guadalupian (280–270 Ma). Prior to that time, we are likely to only find stem therapsids that had undergone less phylogenetic and morphological diversification. This discovery opens the door for findings that may fill in the early therapsid fossil gap in the lower Permian (Fig. 4), not in high latitude sites as traditionally thought, but in the so far poorly explored lower–middle Permian areas of palaeoequatorial Pangaea. Those locations hold the potential to elucidate the early evolution of therapsids and the origins of mammalian features.
Methods
Permits
Collection and preparation were carried out with the permission of the Comissió Insular de Patrimoni Històric of the Consell Insular de Mallorca (excavations with file numbers 306/2019 and 75/2021, preparation with file numbers 374/2020 and 295/2021).
Data collection and curation
The specimen DA21/17-01-01 was collected from the Torrent de na Nadala site (Port des Canonge Formation, Mallorca, Balearic Islands, western Mediterranean)9,16 (Figs. 1, 2). The tetrapod bones are very brittle and were collected in the matrix and subsequently prepared using air scribes. The bones glow under UV light (wavelength of 365 nm), which made it possible to distinguish them from the surrounding matrix, which is usually of almost the same colour. All the outcrops of this formation are located at the base of coastal cliffs in the northwestern margin of the Serra de Tramuntana, the main mountain range of the island, and have been interpreted as meandering river systems and associated floodplains deposited under a semi-arid, seasonal climate9. The horizon where the gorgonopsian fossil was collected (Figs. 1b, 2) consists of silty, very fine-grained, red sandstones with carbonate nodules and rhizocretions (indicating the formation of carbonate palaeosols), and fragments of coalified plant remains. Bones were scattered with no preferential orientation nor selection of elements (Fig. 2b), indicating a relatively prolonged exposure and a late stage of decay without (major) transportation of the remains60. In outcrop view, the fossil site corresponds to the infill of a depressed part of the floodplain, wedging laterally16. Considering this morphology, the very fine grain size, and the abundance of tetrapod bones (five semi-complete, partially disarticulated adult and juvenile skeletons found so far, four of them corresponding to the moradisaurine captorhinid Tramuntanasaurus tiai16 and one to the gorgonopsian studied here), this deposit probably corresponded to a shrinking waterhole, similar to those grouped under the taphonomical class B1 of Smith et al.61. In the Karoo Basin of South Africa, waterhole deposits (corresponding to abandoned chute channels or floodplain depressions) contain abundant and well-preserved tetrapod skeletons that probably accumulated because of increased predation in such environments62 and transportation of mummified carcasses by sheet flows61. In the case of Torrent de na Nadala 2, another important cause of death might have been dehydration when the waterhole dried out, based on the joint presence of juvenile and adult carcasses with no apparent signs of prolonged transport or predation.
Morphological phylogenetic dataset
To test the evolutionary hypotheses of this study, we used the only available morphological phylogenetic dataset sampling the major early therapsid clades at the species level, which was last updated by Brink et al.45. We modified scorings for several taxa because of differences in character interpretation from previous work. Further, we added eight species to the dataset based on personal observations of the relevant specimens and data from the literature, to provide a larger, species-level sample of the earliest known species of the major therapsid clades. The new taxa are: early sphenacodonts Palaeohatteria longicaudata, Pantelosaurus saxonicus, and Cutleria wilmarthi, the dinocephalians Archaeosyodon praeventor and Tapinocaninus pamelae, the anomodont Ulemica efremovi, the gorgonopsians Viatkogorgon ivakhnenkoi, Suchogorgon golubevi, Eriphostoma microdon, and Arctops willistoni, and the eutheriodont Lycosuchus vanderrieti. The final dataset includes a total of 39 taxa and 78 characters; the full list of changes to the dataset can be found in Supplementary Note 3. Specimen DA21/17-01-01 was not included in the analysed version of the data matrix, as it could only be coded for one character (Character 50: Dentary height in canine versus anterior postcanine regions: state 1, shows pronounced difference) and its inclusion resulted in collapse of the tree into an unresolved polytomy.
Character evolution model
We used the Mk(v) model of character evolution63 for morphological characters, implementing assortment bias correction for the inclusion of variable characters only. We allowed for among character rate variation by using a gamma distribution with four rate categories and with shape (alpha) sampled from an exponential distribution with mean = 1.0.
Clock models
We assessed the fit of various clock models to our data, including a new suite of clock models available in the developer’s version of Mr. Bayes (future Mr. Bayes 3.2.8 release)64 compiled from source code available at https://github.com/NBISweden/MrBayes. These models include the continuous autocorrelated clock model (TK02)65 and three uncorrelated clock models: the white noise model (former IGR model up to version 3.2.7a of Mr. Bayes)66, and the new independent gamma rate (IGR) and independent lognormal clock (ILN) models44. These models represent radically different interpretations of how and where in the tree evolutionary rates are allowed to change across lineages, which can substantially impact divergence time estimates using morphological and/or molecular data44,67.
We tested model fit using the stepping-stone sampling strategy to assess the marginal model likelihoods68 and calculated Bayes Factors (BF) — 30 steps (+5 as burn in) for 250 million generations. Using the significance thresholds of Kass & Raftery69, we found a strong support (BF > 10) for the IGR and ILN models relative to the autocorrelated (TK02) and the WN model (Supplementary Table 1), with a minor advantage for them IGR over the ILN model.
The starting value for the prior on the clock rate was given an informative prior as per previous non-clock analysis — the median value for tree height in substitutions from posterior trees divided by the age of the tree based on the median of the distribution for the root prior (5.89/307 = 0.02). The mean of the lognormal distribution was given the value based on the non-clock tree estimate in natural log scale: ln(0.02) = − 3.9535. Finally, we chose a broad standard deviation around the mean (σ = 1.0).
Tree model and age calibrations
The age of the root was given a hard minimum age of 303.7 Ma based on minimum possible age for outgroup Haptodus, and a conservative soft maximum age based on the maximum estimated divergence for all Sphenacodontia at ca. 310 Ma4 (Supplementary Data S1). We used an offset exponential distribution for the prior on root age, which gives a higher sampling probability for values closer to the minimum age and a relatively low (but nonzero) probability of age values higher than 310 Ma.
A first, analysis was conducted with tip dating only—in which all fossil calibrations (apart from the root node) were based on tip calibrations. Additionally, we avoided the strong biases that can be introduced by point age calibrations on the age of the fossils70 by using a uniform prior distribution on the age range of the stratigraphic occurrence of the fossils (Supplementary Data S1). We implemented the skyline FBD (SFBD) process for the tree model with a flat prior (uniform distribution: samples ∈ U[0,1]) on the parameters of relative extinction (= turnover) and probability of sampling fossils, whereas the net diversification rate was sampled from an exponential distribution with mean = 1.0. These parameters were allowed to change across the Guadalupian–Lopingian boundary at 259.51 Ma, which is associated with a mass extinction, and thus provides reasonable expectation for a major shift in diversification dynamics.
In a second set of analyses, we repeated the same protocol described above, but placed a node calibration on the age of Gorgonopsia informed by the new findings reported here. This calibration implies a minimum age of 265 Ma (middle Wordian) and a maximum age of 290 Ma (Artinskian), which is the potential stratigraphic range of the beds where it was found. This node age was sampled from a uniform distribution.
MCMC and Diagnostic parameters
All analyses were conducted using the developer’s version of Mr. Bayes (future Mr. Bayes 3.2.8 release)64 compiled from source code available at https://github.com/NBISweden/MrBayes using the Della cluster at Princeton University. Convergence of independent runs was assessed using: average standard deviation of split frequencies (ASDSF ~ 0.01), potential scale reduction factors [PSRF ≈ 1 for all parameters], and effective sample size (ESS) for each parameter greater than 200, and analysed using Tracer v. 1.7.171.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
All data generated and analysed are freely available online as Supplementary Data at: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/9RNJAE. It contains the following: SD 1: List of changes to previous version of synapsid dataset (.doc). SD 2: Data table with list of sampled taxa including their age ranges used for time calibration in Bayesian clock analyses. SD 3: All input and output files necessary to replicate all phylogenetic analysis conducted. Input files include Mr. Bayes command block with all Bayesian inference commands with explanatory comments. The original fossil material has been deposited at the Museu de Mallorca (Palma, Spain), and, together with casts of all the elements, is now housed at the MUCBO | Museu Balear de Ciències Naturals (Sóller, Spain). The curator is Dr. Rafel Matamales-Andreu, first author of the present paper. Casts have also been deposited at the Institut Català de Paleontologia Miquel Crusafont (Sabadell, Spain). The collection manager is Dr. Josep Robles: josep.robles@icp.cat.
Code availability
All code is freely available online as Supplementary Data at: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/9RNJAE.
References
Angielczyk, K. & Kammerer, C. in Mammalian Evolution, Diversity and Systematics Non-Mammalian Synapsids: the Deep Roots of the Mammalian Family Tree (eds Zachos, F. & Asher, R.) 117–198 (De Gruyter, 2018).
Duhamel, A., Benoit, J., Rubidge, B. S. & Liu, J. A re-assessment of the oldest therapsid Raranimus confirms its status as a basal member of the clade and fills Olson’s gap. Sci. Nat. 108, 26 (2021).
Ford, D. P. & Benson, R. B. The phylogeny of early amniotes and the affinities of Parareptilia and Varanopidae. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 4, 57–65 (2020).
Simões, T. R., Kammerer, C. F., Caldwell, M. W. & Pierce, S. E. Successive climate crises in the deep past drove the early evolution and radiation of reptiles. Sci. Adv. 8, eabq1898 (2022).
Laurin, M. & Hook, R. W. The age of North America’s youngest Paleozoic continental vertebrates: a review of data from the Middle Permian Pease River (Texas) and El Reno (Oklahoma) Groups. BSGF — Earth Sci. Bull. 193, 10 (2022).
Bernardi, M. et al. Late Permian (Lopingian) terrestrial ecosystems: a global comparison with new data from the low-latitude Bletterbach Biota. Earth-Sci. Rev. 175, 18–43 (2017).
Olroyd, S. L. & Sidor, C. A. A review of the Guadalupian (middle Permian) global tetrapod fossil record. Earth-Sci. Rev. 171, 583–597 (2017).
Kemp, T. S. The origin and early radiation of the therapsid mammal-like reptiles: a palaeobiological hypothesis. J. Evol. Biol. 19, 1231–1247 (2006).
Matamales-Andreu, R. et al. Early–middle Permian ecosystems of equatorial Pangaea: Integrated multi-stratigraphic and palaeontological review of the Permian of Mallorca (Balearic Islands, western Mediterranean). Earth-Sci. Rev. 228, 103948 (2022).
Sahney, S. & Benton, M. J. Recovery from the most profound mass extinction of all time. Proc. R. Soc. B 275, 759–765 (2008).
Brocklehurst, N. Olson’s Gap or Olson’s Extinction? A Bayesian tip-dating approach to resolving stratigraphic uncertainty. Proc. R. Soc. B 287, 20200154 (2020).
Didier, G. & Laurin, M. Distributions of extinction times from fossil ages and tree topologies: the example of mid-Permian synapsid extinctions. PeerJ 9, e12577 (2021).
Osborn, H. F. On the primary division of the Reptilia into two sub-classes, Synapsida and Diapsida. Science 17, 275–276 (1903).
Broom, R. On the use of the term Anomodontia. Rec. Albany Mus. 1, 266–269 (1905).
Seeley, H. G. Researches on the structure, organisation, and classification of the fossil reptilia. — Part IX., Section 1. On the Therosuchia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 185, 987–1018 (1894).
Matamales-Andreu, R., Mujal, E., Galobart, À. & Fortuny, J. A new medium-sized moradisaurine captorhinid eureptile from the Permian of Mallorca (Balearic Islands, western Mediterranean) and correlation with the co-occurring ichnogenus Hyloidichnus. Pap. Palaeontol. 9, e1498 (2023).
Kammerer, C. H., Smith, R. M. H., Day, M. O. & Rubidge, B. S. New information on the morphology and stratigraphic range of the mid-Permian gorgonopsian Eriphostoma microdon Broom, 1911. Pap. Palaeontol. 1, 201–221 (2015).
Gebauer, E. V. I. in Early Evolutionary History of the Synapsida (eds Kammerer, C. F., Angielczyk, K. D. & Fröbisch, J.) 185–207 (Springer, 2014).
Sigogneau-Russell, D. Handbuch der Paläoherpetologie/Encyclopedia of Paleoherpetology. Teil 17 B/I / Part 17 B/I: Theriodontia I. Phthinosuchia, Biarmosuchia, Eotitanosuchia, Gorgonopsia (Gustav Fischer Verlag, 1989).
Kammerer, C. F. Systematics of the Anteosauria (Therapsida: Dinocephalia). J. Syst. Palaeo 9, 261–304 (2011).
Durand, J. F. A revised description of the skull of Moschorhinus (Therapsida, Therocephalia). Ann. South Afr. Mus. 99, 381–413 (1991).
van den Heever, J. A. The cranial anatomy of the early Therocephalia (Amniota: Therapsida). Universiteit van. Stellenbosch Ann. 1, 1–59 (1994).
Sidor, C. A. & Rubidge, B. S. in Amniote Paleobiology: Perspectives on the Evolution of Mammals, Birds, and Reptiles (eds Carrano, M. T., Gaudin, T. J., Blob, R. W. & Wible, J. R.) 76–113 (University of Chicago Press, 2006).
Sigogneau, D. Révision Systématique des Gorgonopsiens Sud-Africains (Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, 1970).
Whitney, M. R., LeBlanc, A. R. H., Reynold, A. R. & Brink, K. S. Convergent dental adaptations in the serrations of hypercarnivorous synapsids and dinosaurs. Bio Lett. 16, 20200750 (2020).
Colbert, E. H. The mammal-like reptile Lycaenops. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 89, 353–404 (1948).
Kammerer, C. F. Systematics of the Rubidgeinae (Therapsida: Gorgonopsia). PeerJ 4, e1608 (2016).
Kammerer, C. F. Anatomy and relationships of the South African gorgonopsian Arctops (Therapsida, Theriodontia). Pap. Palaeontol. 3, 583–611 (2017).
Kammerer, C. F. & Masyutin, V. Gorgonopsian therapsids (Nochnitsa gen. nov. and Viatkogorgon) from the Permian Kotelnich locality of Russia. PeerJ 6, e4954 (2018).
Bendel, E.-M., Kammerer, C. F., Kardjilov, N., Fernandez, V. & Fröbisch, J. Cranial anatomy of the gorgonopsian Cynariops robustus based on CT-reconstruction. PLoS ONE 13, e0207367 (2018).
Gradstein, F. M., Ogg, J. G., Schmitz, M. D. & Ogg, G. M.Geologic Time Scale 2020 (Elsevier, 2020).
Kraus, M. J. Paleosols in clastic sedimentary rocks: their geologic applications. Earth-Sci. Rev. 47, 41–70 (1999).
Marchetti, L. et al. Tetrapod ichnotaxonomy in eolian paleoenvironments (Coconino and De Chelly formations, Arizona) and late Cisuralian (Permian) sauropsid radiation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 190, 148–170 (2019).
Sennikov, A. G. & Golubev, V. K. Sequence of Permian tetrapod faunas of Eastern Europe and the Permian–Triassic ecological crisis. Paleontol. J. 51, 600–611 (2017).
Romano, M. et al. New basal synapsid discovery at the Permian outcrop of Torre del Porticciolo (Alghero, Italy). Geol. J. 54, 1554–1566 (2019).
Marchetti, L. et al. Vertebrate tracks from the Permian of Gonfaron (Provence, Southern France) and their implications for the late Capitanian terrestrial extinction event. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 599, 111043 (2022).
De Jaime-Soguero, C., Mujal, E., Oms, O., Bolet, A., Dinarès-Turell, J., Ibáñez-Ansa, J. & Fortuny, J. Palaeoenvironmental reconstruction of a lower to middle Permian terrestrial composite succession from the Catalan Pyrenees: Implications for the evolution of tetrapod ecosystems in equatorial Pangaea. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 632, 111837 (2023).
Kammerer, C. F. & Rubidge, B. S. The earliest gorgonopsians from the Karoo Basin of South Africa. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 194, 104631 (2022).
Huttenlocker, A. H., Singh, S. A., Henrici, A. C. & Sumida, S. S. A Carboniferous synapsid with caniniform teeth and a reappraisal of mandibular size-shape heterodonty in the origin of mammals. R. Soc. Open Sci. 8, 211237 (2021).
Laurin, M. & Reisz, R. R. Tetraceratops is the oldest known therapsid. Nature 345, 249–250 (1990).
Amson, E. & Laurin, M. On the affinities of Tetraceratops insignis, an Early Permian synapsid. Acta Palaeontol. Pol. 56, 301–312 (2011).
Spindler, F. The skull of Tetraceratops insignis (Synapsida, Sphenacodontia). Palaeovertebrata 43, 1–11 (2020).
Zhang, C., Stadler, T., Klopfstein, S., Heath, T. A. & Ronquist, F. Total-evidence dating under the fossilized birth–death process. Syst. Biol. 65, 228–249 (2016).
Zhang, C. Selecting and averaging relaxed clock models in Bayesian tip dating of Mesozoic birds. Paleobiology 48, 340–352 (2021).
Brink, K. S., Maddin, H. C., Evans, D. C. & Reisz, R. R. Re-evaluation of the historic Canadian fossil Bathygnathus borealis from the Early Permian of Prince Edward Island. Can. J. Earth Sci. 52, 1109–1120 (2015).
Singh, S. A., Elsler, A., Stubbs, T. L., Rayfield, E. J. & Benton, M. J. Predatory synapsid ecomorphology signals growing dynamism of late Palaeozoic terrestrial ecosystems. Comm. Biol. 7, 201 (2024).
Smiley, T. M., Sidor, C. A., Maga, A. & Ide, O. The vertebrate fauna of the upper Permian of Niger. VI. First evidence of a gorgonopsian therapsid. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 28, 543–547 (2008).
Olivier, C. et al. New dicynodonts (Therapsida, Anomodontia) from near the Permo-Triassic boundary of Laos: implications for dicynodont survivorship across the Permo-Triassic mass extinction and the paleobiogeography of Southeast Asian blocks. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 39, e1584745 (2019).
Shen, B. et al. Quantitative palaeogeographical reconstruction of the North China Block during the Carboniferous and Permian transition: Implications for coal accumulation and source rock development. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 640, 112102 (2024).
Yuan, W. & Yang, Z. The Alashan Terrane did not amalgamate with North China block by the Late Permian: Evidence from Carboniferous and Permian paleomagnetic results. J. Asian Earth Sci. 104, 145–159 (2015).
Araújo, R. et al. Inner ear biomechanics reveals a Late Triassic origin for mammalian endothermy. Nature 607, 726–731 (2022).
Hellert, S. M., Grossnickle, D. M., Lloyd, G. T., Kammerer, C. F. & Angielczyk, K. D. Derived faunivores are the forerunners of major synapsid radiations. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 7, 1903–1913 (2023).
Olson, E. C. Late Permian terrestrial vertebrates, U.S.A. and U.S.S.R. Trans. Am. Philos. Soc. 52, 1–224 (1962).
Dodick, J. T. & Modesto, S. P. The cranial anatomy of the captorhinid reptile Labidosaurikos meachami from the lower Permian of Oklahoma. Palaeontology 38, 687–711 (1995).
Liebrecht, T., Fortuny, J., Galobart, À., Müller, J. & Sander, P. M. A large, multiple-tooth-rowed captorhinid reptile (Amniota: Eureptilia) from the Upper Permian of Mallorca (Balearic Islands, Western Mediterranean). J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 37, e1251936 (2017).
Matamales-Andreu, R., Roig-Munar, F. X., Oms, O., Galobart, À. & Fortuny, J. A captorhinid-dominated assemblage from the palaeoequatorial Permian of Menorca (Balearic Islands, western Mediterranean). Earth Environ Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 112, 125–145 (2021).
Werneburg, R. et al. A new caseid synapsid from the Permian (Guadalupian) of the Lodève basin (Occitanie, France). Palaeovertebrata 45, e2 (2022).
Smith, R. M. H., Sidor, C. A., Tabor, N. J. & Steyer, J. S. Sedimentology and vertebrate taphonomy of the Moradi Formation of northern Niger: A Permian wet desert in the tropics of Pangaea. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 440, 128–141 (2015).
Sidor, C. A. et al. Permian tetrapods from the Sahara show climate-controlled endemism in Pangaea. Nature 434, 886–889 (2005).
Behrensmeyer, A. K. Taphonomic and ecologic information from bone weathering. Paleobiology 4, 150–162 (1978).
Smith, R. M., Botha, J. & Viglietti, P. A. Taphonomy of drought afflicted tetrapods in the Early Triassic Karoo Basin, South Africa. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 604, 111207 (2022).
Smith, R. M. Vertebrate taphonomy of Late Permian floodplain deposits in the southwestern Karoo Basin of South Africa. PALAIOS 8, 45–67 (1993).
Lewis, P. O. A likelihood approach to estimating phylogeny from discrete morphological character data. Syst. Biol. 50, 913–925 (2001).
Ronquist, F. et al. MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 61, 539–542 (2012).
Thorne, J. L. & Kishino, H. Divergence time and evolutionary rate estimation with multilocus data. Syst. Biol. 51, 689–702 (2002).
Lepage, T., Bryant, D., Philippe, H. & Lartillot, N. A general comparison of relaxed molecular clock models. Molec Biol. Evol. 24, 2669–2680 (2007).
Simões, T. R., Caldwell, M. W. & Pierce, S. E. Sphenodontian phylogeny and the impact of model choice in Bayesian morphological clock estimates of divergence times and evolutionary rates. BMC Biol. 18, 191 (2020).
Xie, W., Lewis, P. O., Fan, Y., Kuo, L. & Chen, M.-H. Improving marginal likelihood estimation for Bayesian phylogenetic model selection. Syst. Biol. 60, 150–160 (2011).
Kass, R. E. & Raftery, A. E. Bayes factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 90, 773–795 (1995).
Barido-Sottani, J. et al. Ignoring fossil age uncertainty leads to inaccurate topology and divergence time estimates in time calibrated tree inference. Front. Ecol. Evol. 8, 1–13 (2020).
Rambaut, A., Suchard, M. A., Xie, D. & Drummond, A. J. Tracer v1.7. http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer (2018).
Scotese, C. R. Atlas of Middle & Late Permian and Triassic Paleogeographic Maps, maps 43 – 48 from Volume 3 of the PALEOMAP Atlas for ArcGIS (Jurassic and Triassic) and maps 49 – 52 from Volume 4 of the PALEOMAP Atlas for ArcGIS (Late Paleozoic), Mollweide Projection (PALEOMAP Project, 2014)
Rees, P. M. et al. Permian phytogeographic patterns and climate data/model comparisons. J. Geol. 110, 1–31 (2002).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Sebastià Matamalas and Chabier De Jaime for aid in fieldwork; Marina Rull and Xènia Aymerich (ICP, Cerdanyola del Vallès) for preparation of the specimen; Enric Vicens (UAB, Cerdanyola del Vallès) for granting us access to the photographic equipment of the Palaeontology Unit of the UAB; the Comissió de Patrimoni Històric del Consell Insular de Mallorca for granting us the excavation permits and funding for preparation. R.M.A. was supported by a predoctoral grant FPU17/01922 (Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades) and the grant Synthesys+ DE-TAF-23 (European Commission). The project was further supported by the Generalitat de Catalunya (CERCA Programme and consolidated research groups 2021 SGR 01184 to J.F. and 2021 SGR 01192 to À.G.). This work is part of the Ramon y Cajal grant to J.F. [RYC2021-032857-I] financed by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and the European Union ‘NextGenerationEU’/PRTR. We acknowledge support from the project ‘Mallorca abans dels dinosaures: estudi dels ecosistemes continentals del Permià i Triàsic amb especial èmfasi en les restes de vertebrats’ (ref15,619.), based at the Institut Català de Paleontologia Miquel Crusafont and funded by the Departament de Cultura, Patrimoni i Política Lingüística (Consell Insular de Mallorca).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization R.M.A., C.F.K., K.D.A.; Data Curation T.R.S., J.F.; Formal Analysis C.F.K., K.D.A., T.R.S.; Funding Acquisition R.M.A., À.G., J.F.; Investigation R.M.A., C.F.K., K.D.A., T.R.S.; Methodology R.M.A., C.F.K., K.D.A., T.R.S., À.G., J.F.; Project Administration J.F.; Resources À.G., J.F.; Visualisation R.M.A., T.R.S., E.M.; Writing — Original Draft Preparation R.M.A., C.F.K., T.R.S.; Writing — Review & Editing R.M.A., C.F.K., K.D.A., T.R.S., E.M., À.G., J.F.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Alfio Chiarenza, Jun Liu and Suresh Singh for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Matamales-Andreu, R., Kammerer, C.F., Angielczyk, K.D. et al. Early–middle Permian Mediterranean gorgonopsian suggests an equatorial origin of therapsids. Nat Commun 15, 10346 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-54425-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-54425-5