Abstract
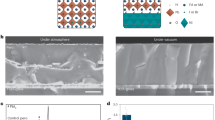
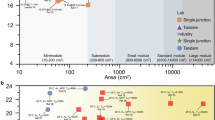
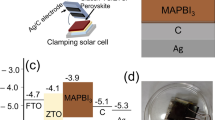
The power conversion efficiency (PCE) of perovskite solar cells (PSCs) has approached that of silicon-based counterparts, yet their limited long-term stability remains a critical obstacle to commercialization. In this study, laser scribing is identified as a crucial factor affecting the stability of perovskite solar modules (PSMs), as evidenced by the differing degradation rates observed between PSMs and PSCs. Detailed characterization reveals that the P1 scribe areas exhibit poor crystalline quality and accelerated degradation, primarily due to mismatched crystallization kinetics. Furthermore, the P2 and P3 scribing processes induce localized thermal damage, resulting in material decomposition that further undermines module stability. Therefore, we propose a strategy for regulation of perovskite crystallization kinetics by (E)-But-2-ene-1,4-diamine dihydrochloride, which promotes high-quality, preferentially oriented perovskite films to enhance their environmental tolerance. As a result, PSMs with aperture areas of 25 cm² and 100 cm² achieve impressive efficiencies of 24.70% and 23.89%, respectively. Notably, the 100 cm² PSM attains a certified record efficiency of 23.55%. Furthermore, unencapsulated PSMs retain 93% of their initial PCE after 3,120 hours of storage in ambient air (~15% RH), following the ISOS-D-1 standard. This work provides a module-level perspective for advancing the understanding and improvement of long-term stability in perovskite photovoltaics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the Article and its Supplementary Information files. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Lee, D. S. et al. Overcoming stability limitations of efficient, flexible perovskite solar modules. Joule 8, 1380–1393 (2024).
Zhang, X. et al. Advances in inverted perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photon. 18, 1243–1253 (2024).
Stranks, S. D. et al. Electron-hole diffusion lengths exceeding 1 micrometer in an organometal trihalide perovskite absorber. Science 342, 341–344 (2013).
Xing, G. et al. Long-range balanced electron- and hole-transport lengths in organic-inorganic CH3NH3PbI3. Science 342, 344–347 (2013).
Zhang, H. & Park, N.-G. Towards sustainability with self-healing and recyclable perovskite solar cells. eScience 2, 567–572 (2022).
National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Best research-cell efficiency chart. NREL. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html (2025).
Li, Z. et al. Scalable fabrication of perovskite solar cells. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3, 18017 (2018).
Cheng, Y. et al. Development and challenges of metal halide perovskite solar modules. Sol. RRL 6, 2100545 (2021).
Wang, H. et al. Impurity-healing interface engineering for efficient perovskite submodules. Nature 634, 1091–1095 (2024).
Yang, Y. et al. A thermotropic liquid crystal enables efficient and stable perovskite solar modules. Nat. Energy 9, 316–323 (2024).
Zhao, X. et al. Operationally stable perovskite solar modules enabled by vapor-phase fluoride treatment. Science 385, 433–438 (2024).
Xu, Y. et al. Printable oil-NiOX hole transport layer enables efficient n-i-p perovskite solar cells with a high thermal stability. Sci. China Chem. 67, 2335–2340 (2024).
Mei, A. et al. Stabilizing perovskite solar cells to IEC61215:2016 standards with over 9,000-h operational tracking. Joule 4, 2646–2660 (2020).
Qin, J. et al. Towards operation-stabilizing perovskite solar cells: fundamental materials, device designs, and commercial applications. InfoMat 6, e12522 (2024).
Ghazy, A. et al. Advances in upconversion enhanced solar cell performance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 230, 111234 (2021).
Ball, J. M. & Petrozza, A. Defects in perovskite-halides and their effects in solar cells. Nat. Energy 1, 16149 (2016).
Li, W. et al. Control of charge recombination in perovskites by oxidation state of halide vacancy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 15753–15763 (2018).
Azpiroz, J. et al. Defect migration in methylammonium lead iodide and its role in perovskite solar cell operation. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 2118–2127 (2015).
Gao, Y. et al. Elimination of unstable residual lead iodide near the buried interface for the stability improvement of perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 16, 2295–2303 (2023).
Tumen-Ulzii, G. et al. Detrimental effect of unreacted PbI2 on the long-term stability of perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 32, 1905035 (2020).
Hu, H. et al. Void-free buried interface for scalable processing of p-i-n-based FAPbI3 perovskite solar modules. Joule 7, 1574–1592 (2023).
Gong, C. et al. Printing-induced alignment network design of polymer matrix for stretchable perovskite solar cells with over 20% efficiency. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2301043 (2023).
He, J. et al. Organic crosslinked tin oxide mitigating buried interface defects for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202419957 (2025).
Park, J. et al. Controlled growth of perovskite layers with volatile alkylammonium chlorides. Nature 616, 724–730 (2023).
Luo, C. et al. Facet orientation tailoring via 2D-seed- induced growth enables highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Joule 6, 240–257 (2022).
Teale, S. et al. Molecular cation and low-dimensional perovskite surface passivation in perovskite solar cells. Nat. Energy 9, 779–792 (2024).
Zhang, J. et al. Elimination of interfacial lattice mismatch and detrimental reaction by self-assembled layer dual-passivation for efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 12, 2103674 (2022).
Tan, S. et al. Surface reconstruction of halide perovskites during post-treatment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 6781–6786 (2021).
Fan, B. et al. A bionic interface to suppress the coffee-ring effect for reliable and flexible perovskite modules with a near-90% yield rate. Adv. Mater. 34, 2201840 (2022).
Pininti, A. R. et al. Resolving scaling issues in self-assembled monolayer-based perovskite solar modules via additive engineering. Adv. Energy Mater. 15, 2403530 (2024).
Guo, S. et al. Preparation of perovskite solar cells in the air: degradation mechanism and prospects on large-area fabrication. Chin. J. Chem. 41, 599–617 (2023).
Castriotta, L. A. et al. Reducing losses in perovskite large area solar technology: laser design optimization for highly efficient modules and minipanels. Adv. Energy Mater. 12, 2103420 (2022).
Galagan, Y. Stability of perovskite PV modules. J. Phys. Energy 2, 021004 (2020).
Kosasih, F. U. et al. Electron microscopy characterization of P3 lines and laser scribing-induced perovskite decomposition in perovskite solar modules. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 45646–45655 (2019).
Yang, M. et al. Highly efficient perovskite solar modules by scalable fabrication and interconnection optimization. ACS Energy Lett. 3, 322–328 (2018).
Qiu, L. et al. Scalable fabrication of stable high efficiency perovskite solar cells and modules utilizing room temperature sputtered SnO2 electron transport layer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1806779 (2018).
Cheng, Y. et al. Revealing the degradation and self-healing mechanisms in perovskite solar cells by sub-bandgap external quantum efficiency spectroscopy. Adv. Mater. 33, 2006170 (2020).
Schultz, C. et al. Ablation mechanisms of nanosecond and picosecond laser scribing for metal halide perovskite module interconnection - An experimental and numerical analysis. Sol. Energy 198, 410–418 (2020).
Fenske, M. et al. Improved electrical performance of perovskite photovoltaic mini-modules through controlled PbI2 formation using nanosecond laser pulses for P3 patterning. Energy Technol. 9, 2000969 (2021).
Gao, Y. et al. Can nanosecond laser achieve high-performance perovskite solar modules with aperture area efficiency over 21%?. Adv. Energy Mater. 12, 2202287 (2022).
Bi, E. B. et al. Efficient perovskite solar cell modules with high stability enabled by iodide diffusion barriers. Joule 3, 2748–2760 (2019).
Dagar, J. et al. Efficient fully laser-patterned flexible perovskite modules and solar cells based on low-temperature solution-processed SnO2/mesoporous-TiO2 electron transport layers. Nano Res 11, 2669–2681 (2018).
Di Giacomo, F. et al. Up-scalable sheet-to-sheet production of high efficiency perovskite module and solar cells on 6-in. substrate using slot die coating. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 181, 53–59 (2018).
Chu, Z. et al. Laser annealing enables rapid, degradation-free ambient processing of perovskite solar modules. Science 390, 905–910 (2025).
Dong, Z. et al. Intermediate phase evolution for stable and oriented evaporated wide-bandgap perovskite solar cells. Nat. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02375-8 (2025).
Song, J. et al. Thermal instability originating from the interface between organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites and oxide electron transport layers. Energy Environ. Sci. 15, 4836–4849 (2022).
Talanquer, V. & Oxtoby, D. W. Nucleation in a slit pore. J. Chem. Phys. 114, 2793–2801 (2001).
Page, A. J. & Sear, R. P. Heterogeneous nucleation in and out of pores. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 065701 (2006).
Zhang, T. et al. Ion-modulated radical doping of spiro-OMeTAD for more efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Science 377, 495–501 (2022).
Chu, Z. et al. Synergistic macroscopic-microscopic regulation: dual constraints of the island effect and coffee-ring effect in printing efficient flexible perovskite photovoltaics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, 2424191 (2025).
Li, N. et al. Liquid medium annealing for fabricating durable perovskite solar cells with improved reproducibility. Science 373, 561–567 (2021).
Chen, S. et al. Stabilizing perovskite-substrate interfaces for high-performance perovskite modules. Science 373, 902–907 (2021).
Schultz, C. et al. Evidence of PbI2-containing debris upon P2 nanosecond laser patterning of perovskite solar cells. IEEE J. Photovolt. 8, 1244–1251 (2018).
Bayer, L. et al. Studies on perovskite film ablation and scribing with ns-, ps- and fs-laser pulses. Appl. Phys. A 123, 619 (2017).
Jeong, Y. et al. Laser scribing for perovskite solar modules of long-term stability. Sol. RRL 8, 2301040 (2024).
Luo, C. et al. Self-induced type-I band alignment at surface grain boundaries for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 33, 2103231 (2021).
Liu, F. et al. Is excess PbI2 beneficial for perovskite solar cell performance?. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1502206 (2016).
Gao, Y. et al. Efficient and stable perovskite solar modules enabled by inhibited escape of volatile species. Adv. Mater. 36, 2309310 (2023).
Cheng, Q. et al. Green solvent processable, asymmetric dopant-free hole transport layer material for efficient and stable n-i-p perovskite solar cells and modules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202312231 (2023).
Li, J. et al. Homogeneous coverage of the low-dimensional perovskite passivation layer for formamidinium-caesium perovskite solar modules. Nat. Energy 9, 1540–1550 (2024).
Liu, P. et al. Ambient scalable fabrication of high-performance flexible perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 17, 7069–7080 (2024).
Huang, C. et al. Effect of laser scribing on coating, drying, and crystallization of absorber layer of perovskite solar cells. Sol. RRL 7, 2200945 (2022).
Brooks, K. G. & Nazeeruddin, M. K. Laser processing methods for perovskite solar cells and modules. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2101149 (2021).
Chen, S. S. et al. Crystallization in one-step solution deposition of perovskite films: upward or downward?. Sci. Adv. 7, eabb2412 (2021).
Jiang, X. et al. Top-down induced crystallization orientation toward highly efficient p-i-n perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 36, 2313524 (2024).
Lin, Y. et al. Unveiling the operation mechanism of layered perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 10, 1008 (2019).
Gao, H. et al. Homogeneous crystallization and buried interface passivation for perovskite tandem solar modules. Science 383, 855–859 (2024).
Lee, J. W. et al. Control of crystal growth toward scalable fabrication of perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1807047 (2019).
Xing, Z. et al. Multi-environment phase stabilization by lattice reinforcement for efficient perovskite solar cells. Sci. China Mater. 66, 2573–2581 (2023).
Meng, Y. et al. Epitaxial growth of α-FAPbI3 at a well-matched heterointerface for efficient perovskite solar cells and solar modules. Adv. Mater. 36, 2309208 (2023).
Sidhik, S. et al. Two-dimensional perovskite templates for durable, efficient formamidinium perovskite solar cells. Science 384, 1227–1235 (2024).
Huang, Y. et al. Low-temperature phase-transition for compositional-pure α-FAPbI3 solar cells with low residual-stress and high crystal-orientation. Small Methods 6, 2200933 (2022).
Acknowledgements
The authors thanks for support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2024YFF1401100 and 2024YFB3815200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (52527804, 22461142139, 52573277, 52263027, 22379060 and 52463021) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20242BAB24002 and 20231ZDH04036). Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (JCYJ20241202124937050). A portion of this work is based on the data obtained at Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (BSRF) and Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF). We thank the 1W1A-Diffuse X-ray Scattering Beamline of BSRF and BL16B1, BL02U2 and BL03HB of SSRF for providing technical support and assistance in GIWAXS data collection. We acknowledge the supports from Wilson Tang Brilliant Energy Science and Technology Lab (BEST Lab) and Materials Characterization & Preparation Facility (MCPF) at HKUST (Guangzhou). The author expresses gratitude to the Center of Analytical and Testing Nanchang University for its valuable assistance in Micro-FTIR testing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.X., B.F. and H.L. contribute equally to this work. Y.C., X.H., Y.Z., S.Z., Z.C., C.G., H.L., B.F. and Y.X. conceive of the concept, design the experiments, analyse the data for this work and write the manuscript. Y.X., B.F. and Z.C. fabricate and characterize the various photoelectric properties for the perovskite solar cells and films. B.F. and C.G. conduct the stability characterization and application demonstration experiments. Y.X., S.Z. and B.F. analyse and measure the defect density and morphology of perovskite films. Y.X., H.L. and B.F. complete nucleation and crystallization analysis for the perovskite films. B.F. and Y.X. fabricate the large-area PSMs. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the writing of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Y., Fan, B., Li, H. et al. Regulating perovskite crystallization kinetics at laser scribe lines for efficient and stable perovskite modules. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69685-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69685-6