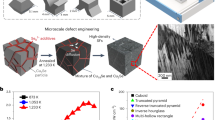
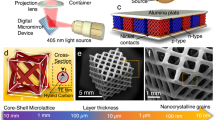
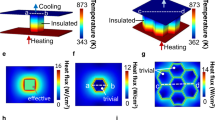
Abstract
Thermoelectric generators offer a promising approach for harvesting waste heat from both natural and human-made sources, enabling sustainable electricity generation. While geometric design plays a crucial role in optimizing device performance, conventional approaches remain confined to simple configurations, limiting efficiency improvements. This constraint arises from the complex interplay of multiphysical interactions and diverse thermal environments, which complicates structural optimization. Here, we introduce a universal design framework that integrates topology optimization (TO) with additive manufacturing to systematically derive high-efficiency thermoelectric 3D architectures. By formulating an optimization problem to maximize power generation efficiency, our approach explores an unprecedentedly large design space, optimizing the geometries of thermoelectric materials across diverse thermal boundary conditions and material properties. The resulting TO-derived geometries consistently outperform conventional cuboids, demonstrating significant efficiency gains. Beyond in-silico studies, we provide theoretical insights and experimental validation, confirming the feasibility of our design approach. Our study offers a transformative way for enhancing thermoelectric power generation, with broad implications for next-generation sustainable energy technologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the published article and its Supplementary Information. The source data underlying the figures of the Main Text are provided within the “Source Data” file. Source data are provided with this paper.
Code availability
The COMSOL Multiphysics codes generated for this work have been uploaded to a public repository at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.18410821.
References
Munch, E. et al. Tough, bio-inspired hybrid materials. Science 322, 1516–1520 (2008).
Tian, Y. et al. Adhesion and friction in gecko toe attachment and detachment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 19320–19325 (2006).
Berger, J., Wadley, H. & McMeeking, R. Mechanical metamaterials at the theoretical limit of isotropic elastic stiffness. Nature 543, 533–537 (2017).
Baba, T. Slow light in photonic crystals. Nat. Photonics 2, 465–473 (2008).
Ahmed, H. E., Salman, B. H., Kherbeet, A. S. & Ahmed, M. Optimization of thermal design of heat sinks: a review. Int. J. Heat. Mass Transf. 118, 129–153 (2018).
Bendsøe, M. P. & Sigmund, O. Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods, and Applications (Springer, 2013).
Bendsøe, M. P. & Kikuchi, N. Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 71, 197–224 (1988).
Aage, N., Andreassen, E., Lazarov, B. S. & Sigmund, O. Giga-voxel computational morphogenesis for structural design. Nature 550, 84–86 (2017).
Cavazzuti, M. et al. High performance automotive chassis design: a topology optimization based approach. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 44, 45–56 (2011).
Chen, C.-T., Chrzan, D. C. & Gu, G. X. Nano-topology optimization for materials design with atom-by-atom control. Nat. Commun. 11, 3745 (2020).
Liu, Y. et al. Ultrastiff metamaterials generated through a multilayer strategy and topology optimization. Nat. Commun. 15, 2984 (2024).
Kobayashi, H. et al. Computational synthesis of locomotive soft robots by topology optimization. Sci. Adv. 10, eadn6129 (2024).
Sundaram, S., Skouras, M., Kim, D. S., van den Heuvel, L. & Matusik, W. Topology optimization and 3D printing of multimaterial magnetic actuators and displays. Sci. Adv. 5, eaaw1160 (2019).
DiSalvo, F. J. Thermoelectric cooling and power generation. Science 285, 703–706 (1999).
Bell, L. E. Cooling, heating, generating power, and recovering waste heat with thermoelectric systems. Science 321, 1457–1461 (2008).
Snyder, G. J. & Toberer, E. S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nat. Mater. 7, 105–114 (2008).
He, J. & Tritt, T. M. Advances in thermoelectric materials research: looking back and moving forward. Science 357, eaak9997 (2017).
Biswas, K. et al. High-performance bulk thermoelectrics with all-scale hierarchical architectures. Nature 489, 414–418 (2012).
Choo, S. et al. Geometric design of Cu2Se-based thermoelectric materials for enhancing power generation. Nat. Energy 9, 1105–1116 (2024).
Kim, K. et al. Heat-dissipation design and 3D printing of ternary silver chalcogenide-based thermoelectric legs for enhancing power generation performance. Adv. Sci. 11, 2402934 (2024).
Lee, J. et al. Doping-induced viscoelasticity in PbTe thermoelectric inks for 3D printing of power-generating tubes. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2100190 (2021).
Karthikeyan, V. et al. Three dimensional architected thermoelectric devices with high toughness and power conversion efficiency. Nat. Commun. 14, 2069 (2023).
Choo, S. et al. Cu2Se-based thermoelectric cellular architectures for efficient and durable power generation. Nat. Commun. 12, 3550 (2021).
Fabián-Mijangos, A., Min, G. & Alvarez-Quintana, J. Enhanced performance thermoelectric module having asymmetrical legs. Energy Convers. Manag. 148, 1372–1381 (2017).
Zhang, Q. et al. Realizing a thermoelectric conversion efficiency of 12% in bismuth telluride/skutterudite segmented modules through full-parameter optimization and energy-loss minimized integration. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 956–963 (2017).
Qiu, P. et al. High-efficiency and stable thermoelectric module based on liquid-like materials. Joule 3, 1538–1548 (2019).
He, Z.-Z. A coupled electrical-thermal impedance matching model for design optimization of thermoelectric generator. Appl. Energy 269, 115037 (2020).
Yang, W. et al. Performance improvement and thermomechanical analysis of a novel asymmetrical annular thermoelectric generator. Appl. Therm. Eng. 237, 121804 (2024).
Weng, Z. et al. Performance improvement of variable-angle annular thermoelectric generators considering different boundary conditions. Appl. Energy 306, 118005 (2022).
Zhu, W. et al. Theoretical analysis of shape factor on performance of annular thermoelectric generators under different thermal boundary conditions. Energy 239, 122285 (2022).
Yang, S. E. et al. Composition-segmented BiSbTe thermoelectric generator fabricated by multimaterial 3D printing. Nano Energy 81, 105638 (2021).
Van Erp, R., Soleimanzadeh, R., Nela, L., Kampitsis, G. & Matioli, E. Co-designing electronics with microfluidics for more sustainable cooling. Nature 585, 211–216 (2020).
Zou, K. et al. Electronic cooling and energy harvesting using ferroelectric polymer composites. Nat. Commun. 15, 6670 (2024).
Gebrael, T. et al. High-efficiency cooling via the monolithic integration of copper on electronic devices. Nat. Electron. 5, 394–402 (2022).
Kraemer, D. et al. High-performance flat-panel solar thermoelectric generators with high thermal concentration. Nat. Mater. 10, 532–538 (2011).
Kang, J. S. et al. Integration of boron arsenide cooling substrates into gallium nitride devices. Nat. Electron. 4, 416–423 (2021).
Baranowski, L. L., Snyder, G. J. & Toberer, E. S. Concentrated solar thermoelectric generators. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 9055–9067 (2012).
Liu, Z. et al. Maximizing the performance of n-type Mg3Bi2-based materials for room-temperature power generation and thermoelectric cooling. Nat. Commun. 13, 1120 (2022).
El Oualid, S. et al. Innovative design of bismuth-telluride-based thermoelectric micro-generators with high output power. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 3579–3591 (2020).
Jiang, J. et al. Achieving high room-temperature thermoelectric performance in cubic AgCuTe. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 4790–4799 (2020).
Zhang, X. et al. High-performance MgAgSb/Mg3(Sb, Bi)2-based thermoelectrics with η = 12% at T ≤ 583 K. Joule 8, 3324–3335 (2024).
Perumal, S. et al. Realization of high thermoelectric figure of merit in GeTe by complementary co-doping of Bi and In. Joule 3, 2565–2580 (2019).
Zhao, L.-D. et al. Ultrahigh power factor and thermoelectric performance in hole-doped single-crystal SnSe. Science 351, 141–144 (2016).
Yang, X. et al. Enhancement in thermoelectric properties of ZrNiSn-based alloys by Ta doping and Hf substitution. Acta Mater. 233, 117976 (2022).
Fu, C. et al. Realizing high figure of merit in heavy-band p-type half-Heusler thermoelectric materials. Nat. Commun. 6, 8144 (2015).
TE Technology, Inc. Thermoelectric module (TEM) peltier element mounting procedure. https://tetech.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/tem_thermoelectric_module_mounting_procedure.pdf (2025).
Bendsøe, M. P. Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct. Optim. 1, 193–202 (1989).
Rozvany, G. I., Zhou, M. & Birker, T. Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct. Optim. 4, 250–252 (1992).
Lazarov, B. S. & Sigmund, O. Filters in topology optimization based on Helmholtz‐type differential equations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 86, 765–781 (2011).
Guest, J. K., Prévost, J. H. & Belytschko, T. Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 61, 238–254 (2004).
Svanberg, K. The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 24, 359–373 (1987).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Mid-Career Researcher Program (RS-2022-NR070604) and Nano & Material Technology Development Program (RS-2024-00449743) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L., S.E.Y., and S.C. contributed equally to this work. J.L., S.E.Y., S.C., H.C., and J.S.S. designed the experiments, analysed the data, and wrote the paper. J.L., H.L., and H.C. performed the topology optimization studies. J.L., S.E.Y., S.C., H.H., K.K., and Y.E.P. carried out the fabrication and measurement of the devices. J.L., H.H.L., and D.W.S. performed the mechanical durability tests and analysed the results. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Yang, S.E., Choo, S. et al. Topology optimization of thermoelectric generator for maximum power efficiency. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69901-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69901-3