Abstract
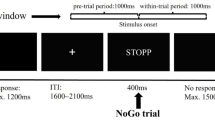
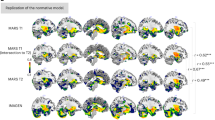
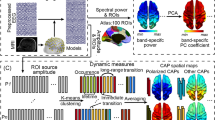
The neurophysiological mechanisms supporting brain maturation are fundamental to attention and memory capacity across the lifespan. Human brain regions develop at different rates, with many regions developing into the third and fourth decades of life. Here, in this preregistered study (https://osf.io/gsru7), we analysed intracranial electroencephalography recordings from widespread brain regions in a large developmental cohort. Using task-based (that is, attention to to-be-remembered visual stimuli) and task-free (resting-state) data from 101 children and adults (5.93–54.00 years, 63 males; n electrodes = 5,691), we mapped aperiodic (1/ƒ-like) activity, a proxy of neural noise, where steeper slopes indicate less noise and flatter slopes indicate more noise. We reveal that aperiodic slopes flatten with age into young adulthood in both association and sensorimotor cortices, challenging models of early sensorimotor development based on brain structure. In the prefrontal cortex (PFC), attentional state modulated age effects, revealing steeper task-based than task-free slopes in adults and the opposite in children, consistent with the development of cognitive control. Age-related differences in task-based slopes also explained age-related gains in memory performance, linking the development of PFC cognitive control to the development of memory. Last, with additional structural imaging measures, we reveal that age-related differences in grey matter volume are similarly associated with aperiodic slopes in association and sensorimotor cortices. Our findings establish developmental trajectories of aperiodic activity in localized brain regions and illuminate the development of PFC control during adolescence in the development of attention and memory.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and code are available at https://tinyurl.com/m5yfc9ny.
References
Bethlehem, R. A. I. et al. Brain charts for the human lifespan. Nature 604, 525–533 (2022).
Gogtay, N. et al. Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 8174–8179 (2004).
Grydeland, H. et al. Waves of maturation and senescence in micro-structural MRI markers of human cortical myelination over the lifespan. Cereb. Cortex 29, 1369–1381 (2019).
Favaro, J. et al. The maturation of aperiodic EEG activity across development reveals a progressive differentiation of wakefulness from sleep. NeuroImage 277, 120264 (2023).
Hill, A. T., Clark, G. M., Bigelow, F. J., Lum, J. A. G. & Enticott, P. G. Periodic and aperiodic neural activity displays age-dependent changes across early-to-middle childhood. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 54, 101076 (2022).
Schaworonkow, N. & Voytek, B. Longitudinal changes in aperiodic and periodic activity in electrophysiological recordings in the first seven months of life. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 47, 100895 (2021).
Tröndle, M., Popov, T., Dziemian, S. & Langer, N. Decomposing the role of alpha oscillations during brain maturation. eLife 11, e77571 (2022).
Donoghue, T. et al. Parameterizing neural power spectra into periodic and aperiodic components. Nat. Neurosci. 23, 1655–1665 (2020).
Wen, H. & Liu, Z. Separating fractal and oscillatory components in the power spectrum of neurophysiological signal. Brain Topogr. 29, 13–26 (2016).
Ahmad, J. et al. From mechanisms to markers: novel noninvasive EEG proxy markers of the neural excitation and inhibition system in humans. Transl. Psychiatry 12, 467 (2022).
van Nifterick, A. M. et al. Resting-state oscillations reveal disturbed excitation–inhibition ratio in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Sci. Rep. 13, 7419 (2023).
Manning, J. R., Jacobs, J., Fried, I. & Kahana, M. J. Broadband shifts in local field potential power spectra are correlated with single-neuron spiking in humans. J. Neurosci. 29, 13613–13620 (2009).
Miller, K. J. et al. Human motor cortical activity is selectively phase-entrained on underlying rhythms. PLoS Comput. Biol. 9, e1002655 (2012).
Kramer, M. A. & Chu, C. J. A general, noise-driven mechanism for the 1/f-like behavior of neural field spectra. Neural Comput. 36, 1643–1668 (2024).
Voytek, B. & Knight, R. T. Dynamic network communication as a unifying neural basis for cognition, development, aging, and disease. Biol. Psychiatry 77, 1089–1097 (2015).
Voytek, B. et al. Age-related changes in 1/f neural electrophysiological noise. J. Neurosci. 35, 13257–13265 (2015).
Buzsáki, G., Anastassiou, C. A. & Koch, C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents—EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 407–420 (2012).
Bédard, C. & Destexhe, A. Macroscopic models of local field potentials and the apparent 1/f noise in brain activity. Biophys. J. 96, 2589–2603 (2009).
Evertz, R., Hicks, D. G. & Liley, D. T. Alpha blocking and 1/fβ spectral scaling in resting EEG can be accounted for by a sum of damped alpha band oscillatory processes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 18, e1010012 (2022).
Martínez‐Cañada, P. et al. Combining aperiodic 1/f slopes and brain simulation: an EEG/MEG proxy marker of excitation/inhibition imbalance in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 15, e12477 (2023).
Wiest, C. et al. The aperiodic exponent of subthalamic field potentials reflects excitation/inhibition balance in Parkinsonism. eLife 12, e82467 (2023).
Turrigiano, G. G. & Nelson, S. B. Homeostatic plasticity in the developing nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 97–107 (2004).
Earl, R. J., Ford, T. C., Lum, J. A. G., Enticott, P. G. & Hill, A. T. Exploring aperiodic activity in first episode schizophrenia spectrum psychosis: a resting-state EEG analysis. Brain Res. 1840, 149052 (2024).
Pani, S. M., Saba, L. & Fraschini, M. Clinical applications of EEG power spectra aperiodic component analysis: a mini-review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 143, 1–13 (2022).
Shuffrey, L. C. et al. Aperiodic electrophysiological activity in preterm infants is linked to subsequent autism risk. Dev. Psychobiol. 64, e22271 (2022).
Fernandez, F. & Garner, C. C. Over-inhibition: a model for developmental intellectual disability. Trends Neurosci. 30, 497–503 (2007).
Merkin, A. et al. Do age-related differences in aperiodic neural activity explain differences in resting EEG alpha? Neurobiol. Aging 121, 78–87 (2023).
Waschke, L., Wöstmann, M. & Obleser, J. States and traits of neural irregularity in the age-varying human brain. Sci. Rep. 7, 17381 (2017).
Tran, T. T., Rolle, C. E., Gazzaley, A. & Voytek, B. Linked sources of neural noise contribute to age-related cognitive decline. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 32, 1813–1822 (2020).
Cross, Z. R., Corcoran, A. W., Schlesewsky, M., Kohler, M. J. & Bornkessel-Schlesewsky, I. Oscillatory and aperiodic neural activity jointly predict language learning. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 34, 1630–1649 (2022).
Lendner, J. D. et al. Oscillatory and aperiodic neuronal activity in working memory following anesthesia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 150, 79–88 (2023).
Cellier, D., Riddle, J., Petersen, I. & Hwang, K. The development of theta and alpha neural oscillations from ages 3 to 24 years. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 50, 100969 (2021).
Ofen, N., Tang, L., Yu, Q. & Johnson, E. L. Memory and the developing brain: from description to explanation with innovation in methods. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 36, 100613 (2019).
Musall, S., von Pföstl, V., Rauch, A., Logothetis, N. K. & Whittingstall, K. Effects of neural synchrony on surface EEG. Cereb. Cortex 24, 1045–1053 (2014).
Palva, J. M. et al. Ghost interactions in MEG/EEG source space: a note of caution on inter-areal coupling measures. NeuroImage 173, 632–643 (2018).
Johnson, E. L., Kam, J. W., Tzovara, A. & Knight, R. T. Insights into human cognition from intracranial EEG: a review of audition, memory, internal cognition, and causality. J. Neural Eng. 17, 051001 (2020).
Johnson, E. L. & Knight, R. T. Intracranial recordings and human memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 31, 18–25 (2015).
Parvizi, J. & Kastner, S. Promises and limitations of human intracranial electroencephalography. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 474–483 (2018).
Johnson, E. L., Tang, L., Yin, Q., Asano, E. & Ofen, N. Direct brain recordings reveal prefrontal cortex dynamics of memory development. Sci. Adv. 4, eaat3702 (2018).
Johnson, E. L. et al. Dissociable oscillatory theta signatures of memory formation in the developing brain. Curr. Biol. 32, 1457–1469.e4 (2022).
Johnson, E. L. & Knight, R. T. How can iEEG be used to study inter-individual and developmental differences? in Intracranial EEG: A Guide for Cognitive Neuroscientists (ed Axmacher, N.) 143–154 (Springer, 2023).
Rau, E. M. B. et al. Reinstatement and transformation of memory traces for recognition. Sci. Adv. 11, eadp9336 (2025).
Yin, Q. et al. Direct brain recordings reveal occipital cortex involvement in memory development. Neuropsychologia 148, 107625 (2020).
Yin, Q., Johnson, E. L. & Ofen, N. Neurophysiological mechanisms of cognition in the developing brain: Insights from intracranial EEG studies. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 64, 101312 (2023).
Leszczyński, M. et al. Dissociation of broadband high-frequency activity and neuronal firing in the neocortex. Sci. Adv. 6, eabb0977 (2020).
Nir, Y. et al. Coupling between neuronal firing rate, gamma LFP, and BOLD fMRI is related to interneuronal correlations. Curr. Biol. 17, 1275–1285 (2007).
Ray, S., Crone, N. E., Niebur, E., Franaszczuk, P. J. & Hsiao, S. S. Neural correlates of high-gamma oscillations (60–200 Hz) in macaque local field potentials and their potential implications in electrocorticography. J. Neurosci. 28, 11526–11536 (2008).
Rich, E. L. & Wallis, J. D. Spatiotemporal dynamics of information encoding revealed in orbitofrontal high-gamma. Nat. Commun. 8, 1139 (2017).
Watson, B. O., Ding, M. & Buzsáki, G. Temporal coupling of field potentials and action potentials in the neocortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 48, 2482–2497 (2018).
Hunt, B. A. et al. Relationships between cortical myeloarchitecture and electrophysiological networks. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 13510–13515 (2016).
Schölvinck, M. L., Leopold, D. A., Brookes, M. J. & Khader, P. H. The contribution of electrophysiology to functional connectivity mapping. NeuroImage 80, 297–306 (2013).
Doval, S. et al. When maturation is not linear: brain oscillatory activity in the process of aging as measured by electrophysiology. Brain Topogr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-024-01064-0 (2024).
Overbye, K., Huster, R. J., Walhovd, K. B., Fjell, A. M. & Tamnes, C. K. Development of the P300 from childhood to adulthood: a multimodal EEG and MRI study. Brain Struct. Funct. 223, 4337–4349 (2018).
Sui, J., Huster, R., Yu, Q., Segall, J. & Calhoun, V. Function–structure associations of the brain: evidence from multimodal connectivity and covariance studies. NeuroImage 102, 11–23 (2014).
Whitford, T. J. et al. Brain maturation in adolescence: concurrent changes in neuroanatomy and neurophysiology. Hum. Brain Mapp. 28, 228–237 (2007).
Groeschel, S., Vollmer, B., King, M. & Connelly, A. Developmental changes in cerebral grey and white matter volume from infancy to adulthood. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 28, 481–489 (2010).
Finley, A. J., Angus, D. J., Van Reekum, C. M., Davidson, R. J. & Schaefer, S. M. Periodic and aperiodic contributions to theta‐beta ratios across adulthood. Psychophysiology 59, e14113 (2022).
Thuwal, K., Banerjee, A. & Roy, D. Aperiodic and periodic components of ongoing oscillatory brain dynamics link distinct functional aspects of cognition across adult lifespan. eNeuro https://doi.org/10.1523/eneuro.0224-21.2021 (2021).
Hill, J. et al. Similar patterns of cortical expansion during human development and evolution. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 13135–13140 (2010).
Sydnor, V. J. et al. Neurodevelopment of the association cortices: patterns, mechanisms, and implications for psychopathology. Neuron 109, 2820–2846 (2021).
Ofen, N. et al. Development of the declarative memory system in the human brain. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 1198–1205 (2007).
Wilke, M., Krägeloh-Mann, I. & Holland, S. K. Global and local development of gray and white matter volume in normal children and adolescents. Exp. Brain Res. 178, 296–307 (2007).
Hill, P. F., King, D. R., Lega, B. C. & Rugg, M. D. Comparison of fMRI correlates of successful episodic memory encoding in temporal lobe epilepsy patients and healthy controls. NeuroImage 207, 116397 (2020).
Klein, A. & Tourville, J. 101 labeled brain images and a consistent human cortical labeling protocol. Front. Neurosci. 6, (2012).
Fotiadis, P. et al. Myelination and excitation–inhibition balance synergistically shape structure-function coupling across the human cortex. Nat. Commun. 14, 6115 (2023).
Mahjoory, K., Schoffelen, J.-M., Keitel, A. & Gross, J. The frequency gradient of human resting-state brain oscillations follows cortical hierarchies. eLife 9, e53715 (2020).
Keller, A. S. et al. Hierarchical functional system development supports executive function. Trends Cogn. Sci. 27, 160–174 (2023).
Larsen, B., Sydnor, V. J., Keller, A. S., Yeo, B. T. T. & Satterthwaite, T. D. A critical period plasticity framework for the sensorimotor–association axis of cortical neurodevelopment. Trends Neurosci. 46, 847–862 (2023).
Sydnor, V. J. et al. Intrinsic activity development unfolds along a sensorimotor–association cortical axis in youth. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 638–649 (2023).
Tervo-Clemmens, B. et al. A canonical trajectory of executive function maturation from adolescence to adulthood. Nat. Commun. 14, 6922 (2023).
Momi, D. et al. Stimulation mapping and whole-brain modeling reveal gradients of excitability and recurrence in cortical networks. Nat. Commun. 16, 3222 (2025).
Bornkessel-Schlesewsky, I. et al. Effects of neural noise on predictive model updating across the adult lifespan. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.14.520501 (2022).
McSweeney, M. et al. Age-related trends in aperiodic EEG activity and alpha oscillations during early- to middle-childhood. NeuroImage 269, 119925 (2023).
Ouyang, G., Hildebrandt, A., Schmitz, F. & Herrmann, C. S. Decomposing alpha and 1/f brain activities reveals their differential associations with cognitive processing speed. NeuroImage 205, 116304 (2020).
Gazit, T. et al. The role of mPFC and MTL neurons in human choice under goal-conflict. Nat. Commun. 11, 3192 (2020).
Miller, E. K. & Cohen, J. D. An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 167–202 (2001).
Noudoost, B. & Moore, T. Control of visual cortical signals by prefrontal dopamine. Nature 474, 372–375 (2011).
Dave, S., Brothers, T. A. & Swaab, T. Y. 1/f neural noise and electrophysiological indices of contextual prediction in aging. Brain Res. 1691, 34–43 (2018).
Sheehan, T. C., Sreekumar, V., Inati, S. K. & Zaghloul, K. A. Signal complexity of human intracranial EEG tracks successful associative-memory formation across individuals. J. Neurosci. 38, 1744 (2018).
Immink, M. A. et al. Resting-state aperiodic neural dynamics predict individual differences in visuomotor performance and learning. Hum. Mov. Sci. 78, 102829 (2021).
Dziego, C. A. et al. Neural and cognitive correlates of performance in dynamic multi-modal settings. Neuropsychologia 180, 108483 (2023).
Fuster, J. M. Frontal lobe and cognitive development. J. Neurocytol. 31, 373–385 (2002).
Ridderinkhof, K. R., Ullsperger, M., Crone, E. A. & Nieuwenhuis, S. The role of the medial frontal cortex in cognitive control. Science 306, 443–447 (2004).
Robertson, M. M. et al. EEG power spectral slope differs by ADHD status and stimulant medication exposure in early childhood. J. Neurophysiol. 122, 2427–2437 (2019).
Molina, J. L. et al. Memantine effects on electroencephalographic measures of putative excitatory/inhibitory balance in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimag. 5, 562–568 (2020).
Peterson, E. J., Rosen, B. Q., Belger, A., Voytek, B. & Campbell, A. M. Aperiodic neural activity is a better predictor of schizophrenia than neural oscillations. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 54, 434–445 (2023).
Kolk, S. M. & Rakic, P. Development of prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 47, 41–57 (2022).
McKeon, S. D. et al. Aperiodic EEG and 7T MRSI evidence for maturation of E/I balance supporting the development of working memory through adolescence. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 66, 101373 (2024).
Sukenik, N. et al. Neuronal circuits overcome imbalance in excitation and inhibition by adjusting connection numbers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118, e2018459118 (2021).
Bornkessel-Schlesewsky, I. et al. Rapid adaptation of predictive models during language comprehension: aperiodic EEG slope, individual alpha frequency and idea density modulate individual differences in real-time model updating. Front. Psychol. 13, 817516 (2022).
Braver, T. S., Paxton, J. L., Locke, H. S. & Barch, D. M. Flexible neural mechanisms of cognitive control within human prefrontal cortex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 7351–7356 (2009).
Cabeza, R. et al. Maintenance, reserve and compensation: the cognitive neuroscience of healthy ageing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 19, 701–710 (2018).
Spreng, R. N. & Turner, G. R. The shifting architecture of cognition and brain function in older adulthood. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 14, 523–542 (2019).
Buzsaki, G. Rhythms of the Brain (Oxford Univ. Press, 2006).
Nunez, P. L. & Srinivasan, R. Recording strategies, reference issues, and dipole localization. Nunez PL Srinivasan R. Electr. Fields Brain Neurophys. EEG Ed. 2, 275–312 (2006).
Euler, M. J. et al. Associations between the resting EEG aperiodic slope and broad domains of cognitive ability. Psychophysiology 61, e14543 (2024).
Montemurro, S. et al. Aperiodic component of EEG power spectrum and cognitive performance are modulated by education in aging. Sci. Rep. 14, 15111 (2024).
Pi, Y. et al. Interindividual aperiodic resting-state EEG activity predicts cognitive-control styles. Psychophysiology 61, e14576 (2024).
Larsen, B. et al. A developmental reduction of the excitation:inhibition ratio in association cortex during adolescence. Sci. Adv. 8, eabj8750 (2022).
Miller, K. J., Sorensen, L. B., Ojemann, J. G. & den Nijs, M. Power-law scaling in the brain surface electric potential. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5, e1000609 (2009).
Herweg, N. A., Solomon, E. A. & Kahana, M. J. Theta oscillations in human memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 24, 208–227 (2020).
Lega, B. C., Jacobs, J. & Kahana, M. Human hippocampal theta oscillations and the formation of episodic memories. Hippocampus 22, 748–761 (2012).
Josefsson, M. et al. Memory profiles predict dementia over 23–28 years in normal but not successful aging. Int. Psychogeriatr. 35, 351–359 (2023).
Riley, K. P. et al. Prediction of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: longitudinal rates of change in cognition. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 25, 707–717 (2011).
Chai, X. J., Ofen, N., Jacobs, L. F. & Gabrieli, J. D. Scene complexity: influence on perception, memory, and development in the medial temporal lobe. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 4, 1021 (2010).
Ofen, N., Chai, X. J., Schuil, K. D., Whitfield-Gabrieli, S. & Gabrieli, J. D. The development of brain systems associated with successful memory retrieval of scenes. J. Neurosci. 32, 10012–10020 (2012).
Tang, L., Shafer, A. T. & Ofen, N. Prefrontal cortex contributions to the development of memory formation. Cereb. Cortex 28, 3295–3308 (2018).
Davoudi, S., Parto Dezfouli, M., Knight, R. T., Daliri, M. R. & Johnson, E. L. Prefrontal lesions disrupt posterior alpha–gamma coordination of visual working memory representations. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 33, 1798–1810 (2021).
Dezfouli, M. P., Davoudi, S., Knight, R. T., Daliri, M. R. & Johnson, E. L. Prefrontal lesions disrupt oscillatory signatures of spatiotemporal integration in working memory. Cortex 138, 113–126 (2021).
Johnson, E. L. et al. Dynamic frontotemporal systems process space and time in working memory. PLoS Biol. 16, e2004274 (2018).
Johnson, E. L. et al. Orbitofrontal cortex governs working memory for temporal order. Curr. Biol. 32, R410–R411 (2022).
Johnson, E. L. et al. Bidirectional frontoparietal oscillatory systems support working memory. Curr. Biol. 27, 1829–1835 (2017).
Johnson, E. L. et al. Spectral imprints of working memory for everyday associations in the frontoparietal network. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 12, 65 (2019).
Mercier, M. R. et al. Advances in human intracranial electroencephalography research, guidelines and good practices. NeuroImage 260, 119438 (2022).
Oostenveld, R., Fries, P., Maris, E. & Schoffelen, J.-M. FieldTrip: open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 1–9 (2011).
Rossini, L. et al. Seizure activity per se does not induce tissue damage markers in human neocortical focal epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 82, 331–341 (2017).
Vallat, R. & Walker, M. P. An open-source, high-performance tool for automated sleep staging. Elife 10, e70092 (2021).
Stolk, A. et al. Integrated analysis of anatomical and electrophysiological human intracranial data. Nat. Protoc. 13, 1699–1723 (2018).
Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. NeuroImage 62, 774–781 (2012).
Groppe, D. M. et al. iELVis: An open source MATLAB toolbox for localizing and visualizing human intracranial electrode data. J. Neurosci. Methods 281, 40–48 (2017).
Adamek, M., Swift, J. R. & Brunner, P. VERA-Versatile electrode localization Framework. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7486841 (2022).
Wickham, H. et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 4, 1686 (2019).
Kuznetsova, A., Brockhoff, P. B. & Christensen, R. H. lmerTest package: tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 82, 1–26 (2017).
Fox, J. et al. The car package. R. Found. Stat. Comput. 1109, 1431 (2007).
Lüdecke, D. ggeffects: Tidy data frames of marginal effects from regression models. J. Open Source Softw. 3, 772 (2018).
Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (Springer-Verlag, 2016).
Brehm, L. & Alday, P. M. Contrast coding choices in a decade of mixed models. J. Mem. Lang. 125, 104334 (2022).
Austin, P. C. & Hux, J. E. A brief note on overlapping confidence intervals. J. Vasc. Surg. 36, 194–195 (2002).
MacGregor-Fors, I. & Payton, M. E. Contrasting diversity values: statistical inferences based on overlapping confidence intervals. PLoS ONE 8, e56794 (2013).
Tukey, J. W. Exploratory Data Analysis Vol. 2 131–160 (Addison-Wesley, 1977).
Mowinckel, A. M. & Vidal-Piñeiro, D. Visualization of brain statistics with R packages ggseg and ggseg3d. Adv. Methods Pract. Psychol. Sci. 3, 466–483 (2020).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part through the computational resources and staff contributions provided for the Quest high-performance computing facility at Northwestern University, which is jointly supported by the Office of the Provost, the Office for Research and Northwestern University Information Technology. We thank P. M. Alday for helpful discussions regarding statistical modelling and K. I. Auguste for assistance with patient recruitment. Funding was provided by R00NS115918 (E.L.J.), R01MH107512 (N.O.), R01NS21135 (R.T.K.), R00MH117226, P30AG013854, DGE-2234667 (Y.M.R.), T32MH067564 (Y.M.R. and C.C.), T32NS047987 (A.M.H.) and P41EB018783. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.R.C., N.O. and E.L.J. designed the study. S.M.G., A.J.O.D., Y.M.R., C.R., A.M.H., E.A., J.J.L., O.K.M., S.S., I.S., F.G., D.K.-S., P.B.W., K.D.L., S.U.S., J.M.R., J.Y.W., S.K.L., J.S.R., E.F.C., A.S., P.B., J.L.R., R.M.B. and E.L.J. recruited patients and/or collected data. Z.R.C., S.M.G., Q.Y., P.V., E.M.B.R., C.C., A.M.H., R.T.K., N.O. and E.L.J. preprocessed data. Z.R.C. and A.J.O.D. analysed data. Z.R.C. visualized results. Z.R.C. and E.L.J. interpreted data. Z.R.C. drafted the manuscript. Z.R.C. and E.L.J. revised the manuscript. E.L.J. supervised the study. All authors provided feedback on the completed manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Human Behaviour thanks Aron Hill, Ezequiel Mikulan and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cross, Z.R., Gray, S.M., Dede, A.J.O. et al. The development of aperiodic neural activity in the human brain. Nat Hum Behav 9, 2548–2563 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-025-02270-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-025-02270-x