Abstract
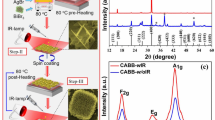
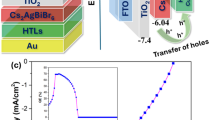
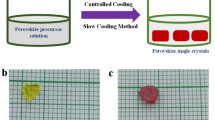
Efficient carrier injection at metal–semiconductor interfaces is essential for probing intrinsic electronic properties and enabling high-performance devices. Thinning the Schottky barrier via contact doping is a cornerstone strategy in semiconductor technology for minimizing contact resistance (Rc). However, carrier doping in halide perovskites has remained elusive, and selective contact doping has not been achieved, resulting in excessive Rc that far exceeds the intrinsic material resistance. Here we report an effective contact-doping strategy by transferring Ag/Au electrodes onto single-crystal CsPbBr3 thin films using a low-energy van der Waals integration process. Moderate annealing (80–180 °C) during transfer enables silver diffusion into CsPbBr3, followed by its transformation into Ag2O clusters upon ultraviolet treatment, forming an Ag2O/CsPbBr3 bulk heterojunction. The Ag2O clusters embedded in CsPbBr3 act as interfacial electron acceptors, inducing a local hole density of ∼5 × 1017 cm−3 in the contact region. This markedly shrinks the Schottky barrier and enhances carrier injection, yielding a substantially reduced Rc of 26–70 Ω cm and a notably high two-terminal sheet conductance exceeding 225 µS at 190 K.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available in the main text or the supplementary information. Source data for Figs. 1d, 2b–d,f, 3a–e and 4a–f are available from Figshare via https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.30957728 (ref. 55). Source data for Fig. 3f are listed in Supplementary Table 1. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Cao, Y. et al. Perovskite light-emitting diodes based on spontaneously formed submicrometre-scale structures. Nature 562, 249–253 (2018).
Zou, C. et al. Electrically driven lasing from a dual-cavity perovskite device. Nature 645, 369–374 (2025).
Liu, S. W. et al. Buried interface molecular hybrid for inverted perovskite solar cells. Nature 632, 536–542 (2024).
Chen, H. et al. Improved charge extraction in inverted perovskite solar cells with dual-site-binding ligands. Science 384, 189–193 (2024).
Li, M. M. et al. Acceleration of radiative recombination for efficient perovskite LEDs. Nature 630, 631–635 (2024).
Lei, Y. et al. A fabrication process for flexible single-crystal perovskite devices. Nature 583, 790–795 (2020).
Yuan, S. et al. Efficient blue electroluminescence from reduced-dimensional perovskites. Nat. Photon. 18, 425–431 (2024).
Qian, Q. et al. Photocarrier-induced persistent structural polarization in soft-lattice lead halide perovskites. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 357–364 (2023).
Senanayak, S. P. et al. Charge transport in mixed metal halide perovskite semiconductors. Nat. Mater. 22, 216–224 (2023).
Lin, Y. et al. Metallic surface doping of metal halide perovskites. Nat. Commun. 12, 7 (2021).
Younis, A. et al. Enhancing resistive switching performance and ambient stability of hybrid perovskite single crystals via embedding colloidal quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2002948 (2020).
Zhou, S. et al. Ag-doped halide perovskite nanocrystals for tunable band structure and efficient charge transport. ACS Energy Lett 4, 534–541 (2019).
Wang, Y. et al. Probing photoelectrical transport in lead halide perovskites with van der Waals contacts. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 768–775 (2020).
Wang, J. et al. Investigation of electrode electrochemical reactions in CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite single-crystal field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 31, 1902618 (2019).
Chin, X. Y., Cortecchia, D., Yin, J., Bruno, A. & Soci, C. Lead iodide perovskite light-emitting field-effect transistor. Nat. Commun. 6, 7383 (2015).
Li, F. et al. Ambipolar solution-processed hybrid perovskite phototransistors. Nat. Commun. 6, 8238 (2015).
Jana, S., Carlos, E., Panigrahi, S., Martins, R. & Fortunato, E. Toward stable solution-processed high-mobility p-type thin film transistors based on halide perovskites. ACS Nano 14, 14790–14797 (2020).
Fu, Y. et al. Metal halide perovskite nanostructures for optoelectronic applications and the study of physical properties. Nat. Rev. Mater. 4, 169–188 (2019).
Senanayak, S. P. et al. A general approach for hysteresis-free, operationally stable metal halide perovskite field-effect transistors. Sci. Adv. 6, eaaz4948 (2020).
Wang, L. et al. A general one-step plug-and-probe approach to top-gated transistors for rapidly probing delicate electronic materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 1206–1213 (2022).
Chen, B., Rudd, P. N., Yang, S., Yuan, Y. & Huang, J. Imperfections and their passivation in halide perovskite solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48, 3842–3867 (2019).
Kovalenko, M. V. et al. Properties and potential optoelectronic applications of lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. Science 358, 745–750 (2017).
Euvrard, J., Yan, Y. & Mitzi, D. B. Electrical doping in halide perovskites. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 531–549 (2021).
Li, Z. hen et al. Extrinsic ion migration in perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 1234–1242 (2017).
Li, D. et al. Gate-induced insulator to band-like transport transition in organolead halide perovskite. J. Phy. Chem. Lett. 8, 429–434 (2017).
Jiang, J. et al. Synergistic strain engineering of perovskite single crystals for highly stable and sensitive X-ray detectors with low-bias imaging and monitoring. Nat. Photon. 16, 575–581 (2022).
Xiao, J. W. et al. Contact engineering: electrode materials for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Sol. RRL 1, 1700082 (2017).
Svanstrom, S. et al. Degradation mechanism of silver metal deposited on lead halide perovskites. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 12, 7212–7221 (2020).
Boyd, C. C. et al. Barrier design to prevent metal-induced degradation and improve thermal stability in perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett 3, 1772–1778 (2018).
Ju, Y. Y. et al. The interactions between halide perovskites and oxygen: from stages to strategies. Matter 7, 3756–3785 (2024).
Xiao, X. et al. A facile way to synthesize Ag@AgBr cubic cages with efficient visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B 163, 564–572 (2015).
Waterhouse, G., Bowmaker, G. & Metson, J. Oxidation of a polycrystalline silver foil by reaction with ozone. Appl. Surf. Sci. 183, 191–204 (2001).
He, Z., Su, J., Chen, R. & Tang, B. Fabrication of novel p-Ag2O/n-PbBiO2Br heterojunction photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible-light irradiation. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El 30, 20870–20880 (2019).
Jin, N. et al. Ag nanodot/Mg/Al reflective ohmic contacts simultaneously suitable for n-type and p-type GaN. J. Phy. D-Appl. Phy. 56, 215101 (2023).
Jayadevan, K., Kumar, N., Mallya, R. & Jacob, K. Use of metastable, dissociated and charged gas species in synthesis: a low pressure analogue of the high pressure technique. J. Mater. Sci. 35, 2429–2434 (2000).
Gronbeck, H. et al. Mechanism for reversed photoemission core-level shifts of oxidized Ag. Phys. Rev. B 85, 115445 (2012).
Gaarenstroom, S. W. & Winograd, N. Initial and final state effects in the ESCA spectra of cadmium and silver oxides. J. Chem. Phys. 67, 3500–3506 (1977).
Han, Y. et al. Effect of oxidation on surface-enhanced Raman scattering activity of silver nanoparticles: a quantitative correlation. Anal. Chem. 83, 5873–5880 (2011).
Walsh, L. A. et al. Hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and electrical characterization study of the surface potential in metal/Al2O3/GaAs(100) metal-oxide-semiconductor structures. Phys. Rev. B 88, 045322 (2013).
Yang, L. M. et al. Chloride molecular doping technique on 2D materials: WS2 and MoS2. Nano Lett 14, 6275–6280 (2014).
Zhou, Y., Chen, J., Bakr, O. M. & Sun, H.-T. Metal-doped lead halide perovskites: synthesis, properties, and optoelectronic applications. Chem. Mater. 30, 6589–6613 (2018).
Muñoz, M. et al. Burstein–Moss shift of n-doped In0.53Ga0.47As/InP. Phy. Rev. B 63, 233302 (2001).
Jiang, Q. et al. Electrochemical lithium doping induced property changes in halide perovskite CsPbBr3 crystal. ACS Energy Lett 3, 264–269 (2017).
Mathieson, A., Feldmann, S. & De Volder, M. Solid-state lithium-ion batteries as a method for doping halide perovskites with an in situ optical readout of dopant concentration. JACS Au 2, 1313–1317 (2022).
Li, D. et al. Electronic and ionic transport dynamics in organolead halide perovskites. ACS Nano 10, 6933–6941 (2016).
Thiesbrummel, J. et al. Ion-induced field screening as a dominant factor in perovskite solar cell operational stability. Nat. Energy 9, 664–676 (2024).
Sze, S. M., Li, Y. & Ng, K. K. Physics of Semiconductor Devices (John Wiley, 2021).
Liu, A. et al. High-performance metal halide perovskite transistors. Nat. Electron. 6, 559–571 (2023).
Zhu, H. et al. Fabrication of high-performance tin halide perovskite thin-film transistors via chemical solution-based composition engineering. Nat. Protoc. 20, 1915–1929 (2025).
Tsarev, S. et al. Vertically stacked monolithic perovskite colour photodetectors. Nature 642, 592–598 (2025).
Wang, Y. et al. Large-area synthesis and patterning of all-inorganic lead halide perovskite thin films and heterostructures. Nano Lett. 21, 1454–1460 (2021).
Wang, Y. L. et al. Chemical vapor deposition growth of single-crystalline cesium lead halide microplatelets and heterostructures for optoelectronic applications. Nano Res. 10, 1223–1233 (2017).
Guan, Z. et al. Perovskite photocatalyst CsPbBr3−xIx with a bandgap funnel structure for H2 evolution under visible light. Appl. Catal. B 245, 522–527 (2019).
Lee, T.-H. & Dickson, R. M. Discrete two-terminal single nanocluster quantum optoelectronic logic operations at room temperature. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 3043–3046 (2003).
Wang, L. et al. Data for ‘Bulk-heterojunction doping in halide perovskites for low-resistance metal contacts’. Figshare https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.30957728 (2025).
Acknowledgements
X.D. acknowledges support from the National Science Foundation through grant DMR 2324943. H.W. acknowledges the use of Bridges-2 at the Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center for DFT calculations through allocation PHY230112 from the Advanced Cyberinfrastructure Coordination Ecosystem: Services & Support (ACCESS) programme, which is supported by US National Science Foundation grants number 2138259, 2138286, 2138307, 2137603 and 2138296.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.D. conceived the research. L.W. and B.Z. performed device fabrication, characterization and data analysis. B.Z. also carried out the optical characterizations and device simulations. B.H. and Y.Y. assisted with the device fabrication and testing. H.W. carried out the DFT calculations. A.Z. and S.Z. performed the XPS measurements. Q.Q., Z.W., Y.W. and Y.Y. prepared the materials. P.W., D.Z., K.B., A.S., J.Z. and Y.H. discussed the data. L.W., B.Z. and X.D. co-wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Materials thanks Max Lemme, Maryam Mohammadi, Yong-Young Noh and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–25, Table 1 and References.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Calculated differential charge distribution.
Source Data Fig. 2
Characterizations of the p-doping effect.
Source Data Fig. 3
Electrical performance of the LHP device with doped contacts.
Source Data Fig. 4
Analysis of the local carrier density, injection mechanism, and contact resistance at the doped contacts.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhou, B., Qian, Q. et al. Bulk-heterojunction doping in lead halide perovskites for low-resistance metal contacts. Nat. Mater. (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-026-02485-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-026-02485-x