Abstract
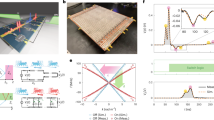
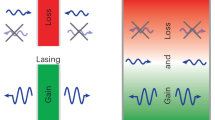
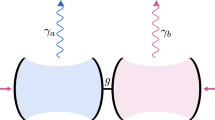
In many linear and nonlinear systems, time-reversal symmetry makes it possible to control the output waves by appropriately shaping the input waves. However, time-reversal symmetry is broken in systems with energy dissipation, necessitating a different approach for relating the input and output fields. We theoretically consider a saturated multimode fibre amplifier in which light generates a heat flow and suffers thermo-optical nonlinearity, thus breaking time-reversal symmetry. We identify a spacetime symmetry that maps the target output back to an input field. This spacetime symmetry mapping applies phase conjugation, gain and absorption substitution but not time reversal, and it holds in a steady state and for slowly varying inputs. Our approach enables coherent wavefront control of nonlinear dissipative systems.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available via Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14190653 (ref. 51).
Code availability
The codes are available at https://github.com/joe851642001/MWAT.
References
Fink, M. Time reversal in acoustics. Contemp. Phys. 37, 95–109 (1996).
Potton, R. J. Reciprocity in optics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 67, 717 (2004).
Przadka, A. et al. Time reversal of water waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 064501 (2012).
Fink, M. Time-reversal mirrors. J. Phys. D 26, 1333 (1993).
Fink, M. & Prada, C. Acoustic time-reversal mirrors. Inverse Probl. https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/17/1/201 (2001).
Kuperman, W. et al. Phase conjugation in the ocean: experimental demonstration of an acoustic time-reversal mirror. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103, 25–40 (1998).
Mounaix, M. et al. Time reversed optical waves by arbitrary vector spatiotemporal field generation. Nat. Commun. 11, 5813 (2020).
Zel’Dovich, B. Y., Popovichev, V., Ragul’Skii, V. & Faizullov, F. in Landmark Papers on Photorefractive Nonlinear Optics (eds Yeh, P. & Gu, C.) 303–306 (World Scientific, 1995).
Bloom, D. M. & Bjorklund, G. C. Conjugate wave-front generation and image reconstruction by four-wave mixing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 31, 592–594 (1977).
Yariv, A. & Pepper, D. M. Amplified reflection, phase conjugation, and oscillation in degenerate four-wave mixing. Opt. Lett. 1, 16–18 (1977).
Nosach, O. Y., Popovichev, V. I., Ragul’Skii, V. & Faizullov, F. Cancellation of phase distortions in an amplifying medium with a ‘Brillouin mirror’. ZhETF Pis ma Redaktsiiu 16, 617 (1972).
Wang, V. & Giuliano, C. R. Correction of phase aberrations via stimulated Brillouin scattering. Opt. Lett. 2, 4–6 (1978).
Agarwal, G., Friberg, A. T. & Wolf, E. Scattering theory of distortion correction by phase conjugation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 73, 529–538 (1983).
Yariv, A., Fekete, D. & Pepper, D. M. Compensation for channel dispersion by nonlinear optical phase conjugation. Opt. Lett. 4, 52–54 (1979).
Lerosey, G., De Rosny, J., Tourin, A. & Fink, M. Focusing beyond the diffraction limit with far-field time reversal. Science 315, 1120–1122 (2007).
Yaqoob, Z., Psaltis, D., Feld, M. S. & Yang, C. Optical phase conjugation for turbidity suppression in biological samples. Nat. Photonics 2, 110–115 (2008).
Papadopoulos, I. N., Farahi, S., Moser, C. & Psaltis, D. Focusing and scanning light through a multimode optical fiber using digital phase conjugation. Opt. Express 20, 10583–10590 (2012).
Dezfooliyan, A. & Weiner, A. M. Spatiotemporal focusing of phase compensation and time reversal in ultrawideband systems with limited rate feedback. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 65, 1998–2006 (2015).
Feldkhun, D., Tzang, O., Wagner, K. H. & Piestun, R. Focusing and scanning through scattering media in microseconds. Optica 6, 72–75 (2019).
Baek, Y., de Aguiar, H. B. & Gigan, S. Phase conjugation with spatially incoherent light in complex media. Nat. Photonics 17, 1114–1119 (2023).
Cheng, Z., Li, C., Khadria, A., Zhang, Y. & Wang, L. V. High-gain and high-speed wavefront shaping through scattering media. Nat. Photonics 17, 299–305 (2023).
Bureau, F. et al. Three-dimensional ultrasound matrix imaging. Nat. Commun. 14, 6793 (2023).
Yariv, A. Phase conjugate optics and real-time holography. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 14, 650–660 (1978).
Pepper, D. M. Nonlinear optical phase conjugation. Opt. Eng. 21, 212156 (1982).
Rouseff, D. et al. Underwater acoustic communication by passive-phase conjugation: theory and experimental results. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 26, 821–831 (2001).
Popoff, S., Lerosey, G., Fink, M., Boccara, A. C. & Gigan, S. Image transmission through an opaque material. Nat. Commun. 1, 81 (2010).
Fisher, R. A. (ed.) Optical Phase Conjugation (Academic, 2012).
Mosk, A. P., Lagendijk, A., Lerosey, G. & Fink, M. Controlling waves in space and time for imaging and focusing in complex media. Nat. Photonics 6, 283–292 (2012).
Alexandropoulos, G. C. et al. Time reversal for 6G spatiotemporal focusing: recent experiments, opportunities, and challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 17, 74–82 (2022).
Tanter, M., Thomas, J.-L., Coulouvrat, F. & Fink, M. Breaking of time reversal invariance in nonlinear acoustics. Phys. Rev. E 64, 016602 (2001).
Ducrozet, G., Fink, M. & Chabchoub, A. Time-reversal of nonlinear waves: applicability and limitations. Phys. Rev. Fluids 1, 054302 (2016).
Fernandes, D. E. & Silveirinha, M. G. Role of time-reversal symmetry in the dynamical response of one-way nonlinear devices. Phys. Rev. Appl. 18, 024002 (2022).
Pepper, D. M. & Yariv, A. Compensation for phase distortions in nonlinear media by phase conjugation. Opt. Lett. 5, 59–60 (1980).
Fisher, R. A., Suydam, B. & Yevick, D. Optical phase conjugation for time-domain undoing of dispersive self-phase-modulation effects. Opt. Lett. 8, 611–613 (1983).
Chabchoub, A. & Fink, M. Time-reversal generation of rogue waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 124101 (2014).
Ducrozet, G., Bonnefoy, F., Mori, N., Fink, M. & Chabchoub, A. Experimental reconstruction of extreme sea waves by time reversal principle. J. Fluid Mech. 884, A20 (2020).
Chong, Y., Ge, L., Cao, H. & Stone, A. D. Coherent perfect absorbers: time-reversed lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 053901 (2010).
Pichler, K. et al. Random anti-lasing through coherent perfect absorption in a disordered medium. Nature 567, 351–355 (2019).
Longhi, S. Time-reversed optical parametric oscillation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 033901 (2011).
Suwunnarat, S. et al. Non-linear coherent perfect absorption in the proximity of exceptional points. Commun. Phys. 5, 5 (2022).
Cheng, M.-Y. et al. High-energy and high-peak-power nanosecond pulse generation with beam quality control in 200-μm core highly multimode yb-doped fiber amplifiers. Opt. Lett. 30, 358–360 (2005).
Jauregui, C., Limpert, J. & Tünnermann, A. High-power fibre lasers. Nat. Photonics 7, 861–867 (2013).
Zervas, M. N. & Codemard, C. A. High power fiber lasers: a review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 20, 219–241 (2014).
Jauregui, C., Stihler, C. & Limpert, J. Transverse mode instability. Adv. Opt. Photonics 12, 429–484 (2020).
Chen, C.-W., Wisal, K., Eliezer, Y., Stone, A. D. & Cao, H. Suppressing transverse mode instability through multimode excitation in a fiber amplifier. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2217735120 (2023).
Wisal, K., Chen, C.-W., Cao, H. & Stone, A. D. Theory of transverse mode instability in fiber amplifiers with multimode excitations. APL Photonics 9, 066114 (2024).
Florentin, R. et al. Shaping the light amplified in a multimode fiber. Light Sci. Appl 6, e16208 (2017).
Florentin, R., Kermene, V., Desfarges-Berthelemot, A. & Barthelemy, A. Shaping of amplified beam from a highly multimode Yb-doped fiber using transmission matrix. Opt. Express 27, 32638–32648 (2019).
Chen, C.-W. et al. Mitigating stimulated Brillouin scattering in multimode fibers with focused output via wavefront shaping. Nat. Commun. 14, 7343 (2023).
Wisal, K., Warren-Smith, S. C., Chen, C.-W., Cao, H. & Stone, A. D. Theory of stimulated Brillouin scattering in fibers for highly multimode excitations. Phys. Rev. X 14, 031053 (2024).
Chen, C.-W. et al. Dataset for ‘Output control of dissipative nonlinear multimode amplifiers via spacetime symmetry mapping’. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14190653 (2024).
Acknowledgements
We thank Y. Eliezer for assisting in establishing the time-domain simulation code. We also thank A. Yamilov, O. D. Miller and S. Fan for fruitful discussions. This work is supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (Grant No. FA9550-24-1-0182 to H.C. and A.D.S.) and by the Simons Foundation (A.D.S. and M.F.). We acknowledge the computational resources provided by the Yale High Performance Computing Cluster.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.C. proposed the idea and initiated this project. C.-W.C. performed the numerical simulations under the supervision of H.C. K.W. performed the theoretical analysis under the supervision of A.D.S. M.F. provided key insights that shaped the scope of this study. C.-W.C., K.W., A.D.S. and H.C. wrote the paper with input from M.F.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Physics thanks Mario Ferraro and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Sections I–VIII and Figs. 1–3.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CW., Wisal, K., Fink, M. et al. Output control of dissipative nonlinear multimode amplifiers using spacetime symmetry mapping. Nat. Phys. 21, 839–845 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-02853-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-02853-5