Abstract
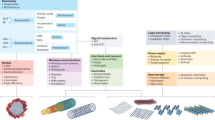
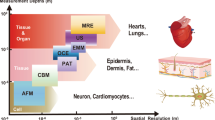
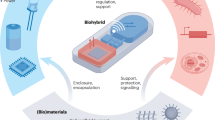
Spatiotemporal resolution is a cornerstone of bioelectronics, enabling precise observation and control of biological events at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels. In this Review, we analyse recent advancements in spatiotemporal resolution essential for applications such as neuroprosthetics, cardiac monitoring and biosensing, with a focus on devices utilizing electrical, electrochemical and optoelectronic signal transduction. We define the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of spatial and temporal resolution and highlight high-performance materials and device architectures — including electrodes, transistors and optoelectronic interfaces — that drive these capabilities. Strategies such as device miniaturization, 3D fabrication and multifunctional integration are evaluated for their capacity to improve resolution, particularly within the complex microenvironments of biological tissues. However, challenges persist, including signal interference, device stability and the demand for reliable long-term operation. Overcoming these obstacles requires continuous innovation in materials science, device engineering and computational approaches. Enhanced spatiotemporal resolution holds promise for advancing diagnostic precision, therapeutic responsiveness and our understanding of dynamic biological systems across biomedical disciplines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong, G. S. & Lieber, C. M. Novel electrode technologies for neural recordings. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 20, 330–345 (2019).
Bouchez, D., Uyttewaal, M. & Pastuglia, M. Spatiotemporal regulation of plant cell division. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 79, 102530 (2024).
Ren, J. Y., Luo, S. C., Shi, H. L. & Wang, X. Spatial omics advances for in situ RNA biology. Mol. Cell 84, 3737–3757 (2024).
Velten, B. & Stegle, O. Principles and challenges of modeling temporal and spatial omics data. Nat. Methods 20, 1462–1474 (2023).
Bassett, D. S. & Sporns, O. Network neuroscience. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 353–364 (2017).
Choi, J., Ghaffari, R., Baker, L. B. & Rogers, J. A. Skin-interfaced systems for sweat collection and analytics. Sci. Adv. 4, eaar3921 (2018).
Shaltout, A. M., Shalaev, V. M. & Brongersma, M. L. Spatiotemporal light control with active metasurfaces. Science 364, 648 (2019).
Ham, D., Park, H., Hwang, S. & Kim, K. Neuromorphic electronics based on copying and pasting the brain. Nat. Electron. 4, 635–644 (2021).
Zhao, Y. L. et al. Scalable ultrasmall three-dimensional nanowire transistor probes for intracellular recording. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 783–790 (2019).
Duan, X. J. et al. Intracellular recordings of action potentials by an extracellular nanoscale field-effect transistor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 174–179 (2012).
Tian, B. Z. et al. Three-dimensional, flexible nanoscale field-effect transistors as localized bioprobes. Science 329, 830–834 (2010).
Tian, B. Z. & Lieber, C. M. Synthetic nanoelectronic probes for biological cells and tissues. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 6, 31–51 (2013).
Gu, Y. et al. Three-dimensional transistor arrays for intra- and inter-cellular recording. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 292–300 (2022).
Jayant, K. et al. Targeted intracellular voltage recordings from dendritic spines using quantum-dot-coated nanopipettes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 335–342 (2017).
Feng, J. D. et al. Identification of single nucleotides in MoS2 nanopores. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 1070 (2015).
Lee, Y. H. et al. Carbon-nanotube field-effect transistors for resolving single-molecule aptamer-ligand binding kinetics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 660–667 (2024).
Laborde, C. et al. Real-time imaging of microparticles and living cells with CMOS nanocapacitor arrays. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 791–795 (2015).
Abbott, J. et al. A nanoelectrode array for obtaining intracellular recordings from thousands of connected neurons. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 4, 232–241 (2020).
Abbott, J. et al. CMOS nanoelectrode array for all-electrical intracellular electrophysiological imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 460–466 (2017).
Dipalo, M. et al. Plasmonic meta-electrodes allow intracellular recordings at network level on high-density CMOS-multi-electrode arrays. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 965–971 (2018).
Spira, M. E. & Hai, A. Multi-electrode array technologies for neuroscience and cardiology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 83–94 (2013).
Xie, C., Lin, Z. L., Hanson, L., Cui, Y. & Cui, B. X. Intracellular recording of action potentials by nanopillar electroporation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 185–190 (2012).
Taal, A. J. et al. Optogenetic stimulation probes with single-neuron resolution based on organic LEDs monolithically integrated on CMOS. Nat. Electron. 6, 669–679 (2023).
Tsai, D., Sawyer, D., Bradd, A., Yuste, R. & Shepard, K. L. A very large-scale microelectrode array for cellular-resolution electrophysiology. Nat. Commun. 8, 1802 (2017).
Shekar, S. et al. A miniaturized multi-clamp CMOS amplifier for intracellular neural recording. Nat. Electron. 2, 343–350 (2019).
Bellin, D. L. et al. Integrated circuit-based electrochemical sensor for spatially resolved detection of redox-active metabolites in biofilms. Nat. Commun. 5, 3256 (2014).
Nakatsuka, N. et al. Aptamer-field-effect transistors overcome Debye length limitations for small-molecule sensing. Science 362, 319–324 (2018).
Stern, E. et al. Label-free immunodetection with CMOS-compatible semiconducting nanowires. Nature 445, 519–522 (2007).
Zheng, G. F., Patolsky, F., Cui, Y., Wang, W. U. & Lieber, C. M. Multiplexed electrical detection of cancer markers with nanowire sensor arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 23, 1294–1301 (2005).
Huffman, B. L., Bredar, A. R. C. & Dempsey, J. L. Origins of non-ideal behaviour in voltammetric analysis of redox-active monolayers. Nat. Rev. Chem. 8, 628–643 (2024).
Sorgenfrei, S. et al. Label-free single-molecule detection of DNA-hybridization kinetics with a carbon nanotube field-effect transistor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6, 125–131 (2011).
Xie, P., Xiong, Q. H., Fang, Y., Qing, Q. & Lieber, C. M. Local electrical potential detection of DNA by nanowire-nanopore sensors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 119–125 (2012).
Rosenstein, J. K., Wanunu, M., Merchant, C. A., Drndic, M. & Shepard, K. L. Integrated nanopore sensing platform with sub-microsecond temporal resolution. Nat. Methods 9, 487–492 (2012).
Li, P. J. et al. Monolithic silicon for high spatiotemporal translational photostimulation. Nature 626, 990–998 (2024).
Luo, Y. F. et al. Technology roadmap for flexible sensors. ACS Nano 17, 5211–5295 (2023).
Tang, X., Shen, H., Zhao, S. Y., Li, N. & Liu, J. Flexible brain-computer interfaces. Nat. Electron. 6, 109–118 (2023).
Abiri, R., Borhani, S., Sellers, E. W., Jiang, Y. & Zhao, X. P. A comprehensive review of EEG-based brain-computer interface paradigms. J. Neural Eng. 16, 011001 (2019).
Chaudhary, U., Birbaumer, N. & Ramos-Murguialday, A. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and rehabilitation. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 12, 513–525 (2016).
Zhang, M. L., Tang, Z. J., Liu, X. L. & van der Spiegel, J. Electronic neural interfaces. Nat. Electron. 3, 191–200 (2020).
Nussinovitch, U. & Gepstein, L. Optogenetics for in vivo cardiac pacing and resynchronization therapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 750–754 (2015).
Vernooy, K., van Deursen, C. J. M., Strik, M. & Prinzen, F. W. Strategies to improve cardiac resynchronization therapy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 11, 481–493 (2014).
Lorach, H. et al. Photovoltaic restoration of sight with high visual acuity. Nat. Med. 21, 476–482 (2015).
Mahato, K. et al. Hybrid multimodal wearable sensors for comprehensive health monitoring. Nat. Electron. 7, 735–750 (2024).
Sempionatto, J. R., Lasalde-Ramírez, J. A., Mahato, K., Wang, J. & Gao, W. Wearable chemical sensors for biomarker discovery in the omics era. Nat. Rev. Chem. 6, 899–915 (2022).
Goh, G. D. et al. Machine learning for bioelectronics on wearable and implantable devices: challenges and potential. Tissue Eng. A 29, 20–46 (2023).
Wang, M. et al. Fusing stretchable sensing technology with machine learning for human-machine interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2008807 (2021).
Cheong, W. F., Prahl, S. A. & Welch, A. J. A review of the optical-properties of biological tissues. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 26, 2166–2185 (1990).
Deisseroth, K. Optogenetics: 10 years of microbial opsins in neuroscience. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 1213–1225 (2015).
Jahed, Z. et al. Nanocrown electrodes for parallel and robust intracellular recording of cardiomyocytes. Nat. Commun. 13, 2253 (2022).
Wang, M. et al. Printable molecule-selective core–shell nanoparticles for wearable and implantable sensing. Nat. Mater. 24, 589–598 (2025).
Heng, W. et al. A smart mask for exhaled breath condensate harvesting and analysis. Science 385, 954–961 (2024).
Wang, Y., Jia, K. & Suo, Z. Non-faradaic junction sensing. Nat. Rev. Mater. 10, 176–190 (2024).
Tian, B. Z. & Lieber, C. M. Nanowired bioelectric interfaces. Chem. Rev. 119, 9136–9152 (2019).
Zhang, A. Q. & Lieber, C. M. Nano-bioelectronics. Chem. Rev. 116, 215–257 (2016).
Wang, B. et al. High-k gate dielectrics for emerging flexible and stretchable electronics. Chem. Rev. 118, 5690–5754 (2018).
Wang, S. S. et al. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 1, 41 (2021).
Yu, N. et al. Near‐infrared‐light activatable nanoparticles for deep‐tissue‐penetrating wireless optogenetics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 8, 1801132 (2019).
Sze, S. M. & Lee, M.-K. Semiconductor Devices: Physics and Technology 3rd edn (2012).
Fabbri, L. et al. How to achieve high spatial resolution in organic optobioelectronic devices? Adv. Mater. Interfaces https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202400822 (2025).
Pan, L. F. et al. High carrier mobility along the 111 orientation in Cu2O photoelectrodes. Nature 628, 765–770 (2024).
Xia, Y. et al. Thickness — independent capacitance of vertically aligned liquid-crystalline MXenes. Nature 557, 409–412 (2018).
Cea, C. et al. Enhancement-mode ion-based transistor as a comprehensive interface and real-time processing unit for in vivo electrophysiology. Nat. Mater. 19, 679–686 (2020).
Cheema, S. S. et al. Ultrathin ferroic HfO2-ZrO2 superlattice gate stack for advanced transistors. Nature 604, 65–71 (2022).
Fuentes-Hernandez, C. et al. Large-area low-noise flexible organic photodiodes for detecting faint visible light. Science 370, 698–701 (2020).
Liu, Y. et al. Approaching the Schottky-Mott limit in van der Waals metal-semiconductor junctions. Nature 557, 696–700 (2018).
Cobb, S. J. et al. Fast CO2 hydration kinetics impair heterogeneous but improve enzymatic CO2 reduction catalysis. Nat. Chem. 14, 417–424 (2022).
Costentin, C., Di Giovanni, C., Giraud, M., Savéant, J. M. & Tard, C. Nanodiffusion in electrocatalytic films. Nat. Mater. 16, 1016–1021 (2017).
Graniel, O., Weber, M., Balme, S., Miele, P. & Bechelany, M. Atomic layer deposition for biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 122, 147–159 (2018).
Jeong, J. et al. Conformal hermetic sealing of wireless microelectronic implantable chiplets by multilayered atomic layer deposition (ALD). Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1806440 (2019).
Prominski, A. et al. Porosity-based heterojunctions enable leadless optoelectronic modulation of tissues. Nat. Mater. 21, 647–655 (2022).
Jiang, Y. W. et al. Topological supramolecular network enabled high-conductivity, stretchable organic bioelectronics. Science 375, 1411–1417 (2022).
Viana, D. et al. Nanoporous graphene-based thin-film microelectrodes for in vivo high-resolution neural recording and stimulation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 514–523 (2024).
Dong, C. Q. et al. Electrochemically actuated microelectrodes for minimally invasive peripheral nerve interfaces. Nat. Mater. 23, 969–976 (2024).
Liu, Y. X. et al. Soft and elastic hydrogel-based microelectronics for localized low-voltage neuromodulation. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 3, 58–68 (2019).
Ledesma, H. A. et al. An atlas of nano-enabled neural interfaces. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 645–657 (2019).
Köhler, M. et al. A silicon carbide-based highly transparent passivating contact for crystalline silicon solar cells approaching efficiencies of 24%. Nat. Energy 6, 529–537 (2021).
Yu, Y. H. et al. Enhanced photoelectrochemical efficiency and stability using a conformal TiO2 film on a black silicon photoanode. Nat. Energy 2, 17045 (2017).
Jiang, Y. et al. Rational design of silicon structures for optically controlled multiscale biointerfaces. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2, 508–521 (2018).
Dai, Y. et al. Soft hydrogel semiconductors with augmented biointeractive functions. Science 386, 431–439 (2024).
Jiang, Y. et al. A universal interface for plug-and-play assembly of stretchable devices. Nature 614, 456–462 (2023).
Lacour, S. P., Courtine, G. & Guck, J. Materials and technologies for soft implantable neuroprostheses. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 16063 (2016).
Nair, V. et al. Laser writing of nitrogen-doped silicon carbide for biological modulation. Sci. Adv. 6, eaaz2743 (2020).
Yang, C. W. et al. A bioinspired permeable junction approach for sustainable device microfabrication. Nat. Sustain. 7, 1190–1203 (2024).
Yang, Y. R. et al. A laser-engraved wearable sensor for sensitive detection of uric acid and tyrosine in sweat. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 217–224 (2020).
Zeng, M. X. et al. High-throughput printing of combinatorial materials from aerosols. Nature 617, 292–298 (2023).
Parameswaran, R. et al. Photoelectrochemical modulation of neuronal activity with free-standing coaxial silicon nanowires. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 260 (2018).
Chung, W. G. et al. Liquid-metal-based three-dimensional microelectrode arrays integrated with implantable ultrathin retinal prosthesis for vision restoration. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 688–697 (2024).
Wang, Y. Y., Fedin, I., Zhang, H. & Talapin, D. V. Direct optical lithography of functional inorganic nanomaterials. Science 357, 385–388 (2017).
Jung, D. et al. Highly conductive and elastic nanomembrane for skin electronics. Science 373, 1022–1026 (2021).
Feng, H. B. et al. Optimized design of block copolymers with covarying properties for nanolithography. Nat. Mater. 21, 1426–1433 (2022).
Fang, Y. et al. Micelle-enabled self-assembly of porous and monolithic carbon membranes for bioelectronic interfaces. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 206–213 (2021).
Capel, A. J., Rimington, R. P., Lewis, M. P. & Christie, S. D. R. 3D printing for chemical, pharmaceutical and biological applications. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2, 422–436 (2018).
MacDonald, E. & Wicker, R. Multiprocess 3D printing for increasing component functionality. Science 353, eaaf2093 (2016).
Zhu, Z. J., Ng, D. W. H., Park, H. S. & McAlpine, M. C. 3D-printed multifunctional materials enabled by artificial-intelligence-assisted fabrication technologies. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 27–47 (2021).
Yuk, H. et al. 3D printing of conducting polymers. Nat. Commun. 11, 1604 (2020).
Wang, F. et al. 3D printed implantable hydrogel bioelectronics for electrophysiological monitoring and electrical modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34. 2314471 (2023).
Tay, R. Y., Song, Y., Yao, D. R. & Gao, W. Direct-ink-writing 3D-printed bioelectronics. Mater. Today 71, 135–151 (2023).
Kim, S. et al. Three-dimensional electrodes of liquid metals for long-term, wireless cardiac analysis and modulation. ACS Nano 18, 24364–24378 (2024).
Fumeaux, N. & Briand, D. 3D printing of customizable transient bioelectronics and sensors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 10, 2400058 (2024).
Dominguez‐Alfaro, A. et al. Light‐based 3D multi-material printing of micro-structured bio-shaped, conducting and dry adhesive electrodes for bioelectronics. Adv. Sci. 11, 2306424 (2024).
Zhou, T. et al. 3D printable high-performance conducting polymer hydrogel for all-hydrogel bioelectronic interfaces. Nat. Mater. 22, 895–902 (2023).
Lee, A. et al. 3D bioprinting of collagen to rebuild components of the human heart. Science 365, 482–487 (2019).
Kolesky, D. B., Homan, K. A., Skylar-Scott, M. A. & Lewis, J. A. Three-dimensional bioprinting of thick vascularized tissues. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 3179–3184 (2016).
Kang, H.-W. et al. A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity. Nat. Biotechnol. 34, 312–319 (2016).
Rodrigo-Navarro, A., Sankaran, S., Dalby, M. J., del Campo, A. & Salmeron-Sanchez, M. Engineered living biomaterials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 1175–1190 (2021).
Ershad, F., Patel, S. & Yu, C. Wearable bioelectronics fabricated in situ on skins. npj Flex. Electron. 7, 32 (2023).
Freedman, B. R. et al. Enhanced tendon healing by a tough hydrogel with an adhesive side and high drug-loading capacity. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 6, 1167–1179 (2022).
Chaudhuri, O., Cooper-White, J., Janmey, P. A., Mooney, D. J. & Shenoy, V. B. Effects of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity on cellular behaviour. Nature 584, 535–546 (2020).
Liu, X., Inda, M. E., Lai, Y., Lu, T. K. & Zhao, X. Engineered living hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 34, 2201326 (2022).
Jiang, Y. W. & Tian, B. Z. Inorganic semiconductor biointerfaces. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3, 473–490 (2018).
He, F. et al. Multimodal mapping of neural activity and cerebral blood flow reveals long-lasting neurovascular dissociations after small-scale strokes. Sci. Adv. 6, eaba1933 (2020).
Luan, L. et al. Ultraflexible nanoelectronic probes form reliable, glial scar-free neural integration. Sci. Adv. 3, e1601966 (2017).
Zhang, A. et al. Ultraflexible endovascular probes for brain recording through micrometer-scale vasculature. Science 381, 306–312 (2023).
Han, F. et al. Three-dimensional nanofabrication via ultrafast laser patterning and kinetically regulated material assembly. Science 378, 1325–1331 (2022).
Zheng, Y. Q. et al. Monolithic optical microlithography of high-density elastic circuits. Science 373, 88–94 (2021).
Wang, W. C. et al. Strain-insensitive intrinsically stretchable transistors and circuits. Nat. Electron. 4, 143–150 (2021).
Xu, J. et al. Multi-scale ordering in highly stretchable polymer semiconducting films. Nat. Mater. 18, 594–601 (2019).
Diao, Y. et al. Solution coating of large-area organic semiconductor thin films with aligned single-crystalline domains. Nat. Mater. 12, 665–671 (2013).
Wang, C. et al. Biomimetic olfactory chips based on large-scale monolithically integrated nanotube sensor arrays. Nat. Electron. 7, 157–167 (2024).
Yin, J., Wang, S., Tat, T. & Chen, J. Motion artefact management for soft bioelectronics. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2, 541–558 (2024).
Nair, V. et al. Miniature battery-free bioelectronics. Science 382, eabn4732 (2023).
Topalovic, U. et al. A wearable platform for closed-loop stimulation and recording of single-neuron and local field potential activity in freely moving humans. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 517–527 (2023).
Khodagholy, D. et al. NeuroGrid: recording action potentials from the surface of the brain. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 310–315 (2015).
Liu, Y. et al. A high-density 1,024-channel probe for brain-wide recordings in non-human primates. Nat. Neurosci. 27, 1620–1631 (2024).
Wei, S. et al. Shape-changing electrode array for minimally invasive large-scale intracranial brain activity mapping. Nat. Commun. 15, 715 (2024).
Kauvar, I. V. et al. Cortical observation by synchronous multifocal optical sampling reveals widespread population encoding of actions. Neuron 107, 351–367.e19 (2020).
Zhao, Z. T. et al. Ultraflexible electrode arrays for months-long high-density electrophysiological mapping of thousands of neurons in rodents. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 7, 520–532 (2023).
Li, J. et al. A tissue-like neurotransmitter sensor for the brain and gut. Nature 606, 94–101 (2022).
van Erp, R., Soleimanzadeh, R., Nela, L., Kampitsis, G. & Matioli, E. Co-designing electronics with microfluidics for more sustainable cooling. Nature 585, 211–216 (2020).
Yang, Z. Y., Albrow-Owen, T., Cai, W. W. & Hasan, T. Miniaturization of optical spectrometers. Science 371, 480–532 (2021).
Kim, K., Choi, J. Y., Kim, T., Cho, S. H. & Chung, H. J. A role for graphene in silicon-based semiconductor devices. Nature 479, 338–344 (2011).
Manzeli, S., Ovchinnikov, D., Pasquier, D., Yazyev, O. V. & Kis, A. 2D transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 17033 (2017).
Wang, H. M. et al. Graphene nanoribbons for quantum electronics. Nat. Rev. Phys. 3, 791–802 (2021).
Kim, D. et al. A CMOS-integrated quantum sensor based on nitrogen-vacancy centres. Nat. Electron. 2, 284–289 (2019).
Kim, B. H. et al. Three-dimensional electronic microfliers inspired by wind-dispersed seeds. Nature 597, 503–510 (2021).
Park, Y., Chung, T. S. & Rogers, J. A. Three dimensional bioelectronic interfaces to small-scale. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 72, 1–7 (2021).
Park, Y. et al. Three-dimensional, multifunctional neural interfaces for cortical spheroids and engineered assembloids. Sci. Adv. 7, eabf9153 (2021).
Xu, S. et al. Assembly of micro/nanomaterials into complex, three-dimensional architectures by compressive buckling. Science 347, 154–159 (2015).
Yan, Z. et al. Three-dimensional mesostructures as high-temperature growth templates, electronic cellular scaffolds, and self-propelled microrobots. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, E9455–E9464 (2017).
Huang, Z. L. et al. Three-dimensional integrated stretchable electronics. Nat. Electron. 1, 473–480 (2018).
Lee, H. et al. An endoscope with integrated transparent bioelectronics and theranostic nanoparticles for colon cancer treatment. Nat. Commun. 6, 10059 (2015).
Yang, R. X. et al. Multimodal sensors with decoupled sensing mechanisms. Adv. Sci. 9, 2202470 (2022).
Bai, H. D., Hu, Z. Y. & Rogers, J. A. Hybrid materials approaches for bioelectronics. MRS Bull. 48, 1125–1139 (2023).
Grajales-Reyes, J. G. et al. Surgical implantation of wireless, battery-free optoelectronic epidural implants for optogenetic manipulation of spinal cord circuits in mice. Nat. Protoc. 16, 3072–3088 (2021).
Gutruf, P. et al. Wireless, battery-free, fully implantable multimodal and multisite pacemakers for applications in small animal models. Nat. Commun. 10, 5742 (2019).
Mickle, A. D. et al. A wireless closed-loop system for optogenetic peripheral neuromodulation. Nature 565, 361–365 (2019).
Yang, Y. Y. et al. Wireless multilateral devices for optogenetic studies of individual and social behaviors. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 1035–1045 (2021).
Gebrael, T. et al. High-efficiency cooling via the monolithic integration of copper on electronic devices. Nat. Electron. 5, 394–402 (2022).
Ray, T. R. et al. Bio-integrated wearable systems: a comprehensive review. Chem. Rev. 119, 5461–5533 (2019).
Ding, S. C. et al. A fingertip-wearable microgrid system for autonomous energy management and metabolic monitoring. Nat. Electron. 7, 788–799 (2024).
Lin, M. Y. et al. A fully integrated wearable ultrasound system to monitor deep tissues in moving subjects. Nat. Biotechnol. 42, 448–457 (2024).
Yin, L. et al. A stretchable epidermal sweat sensing platform with an integrated printed battery and electrochromic display. Nat. Electron. 5, 694–705 (2022).
Jiang, Y. W. et al. Wireless, closed-loop, smart bandage with integrated sensors and stimulators for advanced wound care and accelerated healing. Nat. Biotechnol. 41, 652–662 (2023).
Matsuhisa, N. et al. High-frequency and intrinsically stretchable polymer diodes. Nature 600, 246–252 (2021).
Zhang, Z. T. et al. High-brightness all-polymer stretchable LED with charge-trapping dilution. Nature 603, 624–630 (2022).
Shi, J. Y. et al. Active biointegrated living electronics for managing inflammation. Science 384, 1023–1030 (2024).
Zhang, Y. et al. Millimetre-scale bioresorbable optoelectronic systems for electrotherapy. Nature 640, 77–86 (2025).
Zheng, Y., Zhang, S., Tok, J. B. H. & Bao, Z. N. Molecular design of stretchable polymer semiconductors: current progress and future directions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 4699–4715 (2022).
Li, N. et al. Bioadhesive polymer semiconductors and transistors for intimate biointerfaces. Science 381, 686–693 (2023).
Park, S. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat. Commun. 12, 3435 (2021).
Zhao, C., Park, J., Root, S. E. & Bao, Z. Skin-inspired soft bioelectronic materials, devices and systems. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2, 671–690 (2024).
Yuk, H., Wu, J. & Zhao, X. Hydrogel interfaces for merging humans and machines. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 935–952 (2022).
Yang, C. & Suo, Z. Hydrogel ionotronics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3, 125–142 (2018).
Rousche, P. J. & Normann, R. A. Chronic recording capability of the Utah Intracortical Electrode Array in cat sensory cortex. J. Neurosci. Methods 82, 1–15 (1998).
Abidian, M. R. & Martin, D. C. Multifunctional nanobiomaterials for neural interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 573–585 (2009).
Jun, J. J. et al. Fully integrated silicon probes for high-density recording of neural activity. Nature 551, 232–236 (2017).
Chiang, C.-H. et al. Development of a neural interface for high-definition, long-term recording in rodents and nonhuman primates. Sci. Transl Med. 12, eaay4682 (2020).
Zhao, S. Y. et al. Tracking neural activity from the same cells during the entire adult life of mice. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 696–710 (2023).
Yang, X. et al. Bioinspired neuron-like electronics. Nat. Mater. 18, 510–517 (2019).
Yu, K. J. et al. Bioresorbable silicon electronics for transient spatiotemporal mapping of electrical activity from the cerebral cortex. Nat. Mater. 15, 782–791 (2016).
Yang, X. et al. Laminin-coated electronic scaffolds with vascular topography for tracking and promoting the migration of brain cells after injury. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 7, 1282–1292 (2023).
Robinson, J. T. et al. Vertical nanowire electrode arrays as a scalable platform for intracellular interfacing to neuronal circuits. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 180–184 (2012).
Yan, L., Fang, Q., Zhang, X. & Huang, B. Optimal pipette resistance, seal resistance, and zero-current membrane potential for loose patch or breakthrough whole-cell recording in vivo. Front. Neural Circuits 14, 34 (2020).
Kyndiah, A. et al. Direct recording of action potentials of cardiomyocytes through solution processed planar electrolyte-gated field-effect transistors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 393, 134227 (2023).
Hai, A., Shappir, J. & Spira, M. E. In-cell recordings by extracellular microelectrodes. Nat. Methods 7, 200–202 (2010).
Terrell, J. L. et al. Bioelectronic control of a microbial community using surface-assembled electrogenetic cells to route signals. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 688–697 (2021).
Liu, J. et al. Genetically targeted chemical assembly of functional materials in living cells, tissues, and animals. Science 367, 1372–1376 (2020).
Zhang, A. Q. et al. Genetically targeted chemical assembly of polymers specifically localized extracellularly to surface membranes of living neurons. Sci. Adv. 9, eadi1870 (2023).
Zhang, A. Q., Zhao, S., Tyson, J., Deisseroth, K. & Bao, Z. N. Applications of synthetic polymers directed toward living cells. Nat. Synth. 3, 943–957 (2024).
Gu, Y. Q. et al. Structure of Geobacter pili reveals secretory rather than nanowire behaviour. Nature 597, 430–434 (2021).
Li, Q. et al. Multimodal charting of molecular and functional cell states via in situ electro-sequencing. Cell 186, 2002–2017.e21 (2023).
Strakosas, X. et al. Metabolite-induced in vivo fabrication of substrate-free organic bioelectronics. Science 379, 795–802 (2023).
Gu, L. L. et al. A biomimetic eye with a hemispherical perovskite nanowire array retina. Nature 581, 278–282 (2020).
Liu, J. et al. Syringe-injectable electronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 629–636 (2015).
Patel, S. R. & Lieber, C. M. Precision electronic medicine in the brain. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 1007–1012 (2019).
Tian, B. Z. et al. Macroporous nanowire nanoelectronic scaffolds for synthetic tissues. Nat. Mater. 11, 986–994 (2012).
Xie, C. et al. Three-dimensional macroporous nanoelectronic networks as minimally invasive brain probes. Nat. Mater. 14, 1286–1292 (2015).
Park, B. et al. Cuticular pad-inspired selective frequency damper for nearly dynamic noise-free bioelectronics. Science 376, 624–629 (2022).
Nahon, D. M. et al. Standardizing designed and emergent quantitative features in microphysiological systems. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 8, 941–962 (2024).
Yang, X. et al. Kirigami electronics for long-term electrophysiological recording of human neural organoids and assembloids. Nat. Biotechnol. 42, 1836–1843 (2024).
Tang, J. et al. Flexible CMOS integrated circuits based on carbon nanotubes with sub-10 ns stage delays. Nat. Electron. 1, 191–196 (2018).
Hussain, A. M. & Hussain, M. M. CMOS‐technology‐enabled flexible and stretchable electronics for internet of everything applications. Adv. Mater. 28, 4219–4249 (2016).
Allen, M. E., Hindley, J. W., Baxani, D. K., Ces, O. & Elan, Y. Hydrogels as functional components in artificial cell systems. Nat. Rev. Chem. 6, 562–578 (2022).
Ganewatta, M. S., Wang, Z. K. & Tang, C. B. Chemical syntheses of bioinspired and biomimetic polymers toward biobased materials. Nat. Rev. Chem. 5, 753–772 (2021).
Shi, J. Y. et al. Monolithic-to-focal evolving biointerfaces in tissue regeneration and bioelectronics. Nat. Chem. Eng. 1, 73–86 (2024).
Krauhausen, I., Coen, C. T., Spolaor, S., Gkoupidenis, P. & van de Burgt, Y. Brain-inspired organic electronics: merging neuromorphic computing and bioelectronics using conductive polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34, 2307729 (2024).
Zhao, X. et al. Conformal neuromorphic bioelectronics for sense digitalization. Adv. Mat. 36. 2403444 (2024).
Gkoupidenis, P. et al. Organic mixed conductors for bioinspired electronics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 9, 134–149 (2024).
Harikesh, P. C., Tu, D. Y. & Fabiano, S. Organic electrochemical neurons for neuromorphic perception. Nat. Electron. 7, 525–536 (2024).
Liang, X. P. et al. Physical reservoir computing with emerging electronics. Nat. Electron. 7, 193–206 (2024).
Luo, J. L., Geng, Y. F., Rana, F. & Fuchs, G. D. Room temperature optically detected magnetic resonance of single spins in GaN. Nat. Mater. 23, 512–518 (2024).
Miller, B. S. et al. Spin-enhanced nanodiamond biosensing for ultrasensitive diagnostics. Nature 587, 588–593 (2020).
Aslam, N. et al. Quantum sensors for biomedical applications. Nat. Rev. Phys. 5, 157–169 (2023).
Kucsko, G. et al. Nanometre-scale thermometry in a living cell. Nature 500, 54–58 (2013).
Lovchinsky, I. et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of an atomically thin material using a single-spin qubit. Science 355, 503 (2017).
Lovchinsky, I. et al. Applied physics nuclear magnetic resonance detection and spectroscopy of single proteins using quantum logic. Science 351, 836–841 (2016).
Stas, P. J. et al. Robust multi-qubit quantum network node with integrated error detection. Science 378, 557–560 (2022).
Chatterjee, S., Thakur, R. S., Yadav, R. N., Gupta, L. & Raghuvanshi, D. K. Review of noise removal techniques in ECG signals. IET Signal Process. 14, 569–590 (2020).
He, Y. T. et al. Brain-machine interfaces for controlling lower-limb powered robotic systems. J. Neural Eng. 15, 021004 (2018).
Tian, C. W. et al. Deep learning on image denoising: an overview. Neural Netw. 131, 251–275 (2020).
Barbastathis, G., Ozcan, A. & Situ, G. On the use of deep learning for computational imaging. Optica 6, 921–943 (2019).
Alzubaidi, L. et al. Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 8, 53 (2021).
Biamonte, J. et al. Quantum machine learning. Nature 549, 195–202 (2017).
Ching, T. et al. Opportunities and obstacles for deep learning in biology and medicine. J. R. Soc. Interface 15, 20170387 (2018).
Gong, S., Lu, Y., Yin, J. L., Levin, A. & Cheng, W. L. Materials-driven soft wearable bioelectronics for connected healthcare. Chem. Rev. 124, 455–553 (2024).
Xia, X. X., Spadaccini, C. M. & Greer, J. R. Responsive materials architected in space and time. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 683–701 (2022).
Chen, Y. T. et al. All-analog photoelectronic chip for high-speed vision tasks. Nature 623, 48–57 (2023).
Kang, I., Zhang, Q. R., Yu, S. X. & Ji, N. Coordinate-based neural representations for computational adaptive optics in widefield microscopy. Nat. Mach. Intell. 6, 714–725 (2024).
Temma, K. et al. Selective-plane-activation structured illumination microscopy. Nat. Methods 21, 889–896 (2024).
Fang, X. et al. Programmable gear-based mechanical metamaterials. Nat. Mater. 21, 869–876 (2022).
Fu, H. R. et al. Morphable 3D mesostructures and microelectronic devices by multistable buckling mechanics. Nat. Mater. 17, 268–276 (2018).
Ou, Z. H. et al. Achieving optical transparency in live animals with absorbing molecules. Science 385, eadm6869 (2024).
Shemetov, A. A., Nabiev, I. & Sukhanova, A. Molecular interaction of proteins and peptides with nanoparticles. ACS Nano 6, 4585–4602 (2012).
Waduge, P. et al. Nanopore-based measurements of protein size, fluctuations, and conformational changes. ACS Nano 11, 5706–5716 (2017).
Wei, S. et al. Control of protein conformation and orientation on graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 20335–20343 (2019).
Medintz, I. L. et al. A fluorescence resonance energy transfer-derived structure of a quantum dot-protein bioconjugate nanoassembly. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 9612–9617 (2004).
López‐Andarias, J. et al. Toward bioelectronic nanomaterials: photoconductivity in protein–porphyrin hybrids wrapped around SWCNT. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1704031 (2018).
Elnathan, R. et al. Biointerface design for vertical nanoprobes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 953–973 (2022).
Morales-Narváez, E. & Dincer, C. The impact of biosensing in a pandemic outbreak: COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 163, 112274 (2020).
Kabay, G. et al. Emerging biosensing technologies for the diagnostics of viral infectious diseases. Adv. Mater. 34, 2201085 (2022).
Chen, K.-I., Li, B.-R. & Chen, Y.-T. Silicon nanowire field-effect transistor-based biosensors for biomedical diagnosis and cellular recording investigation. Nano Today 6, 131–154 (2011).
Lerner, M. B. et al. Hybrids of a genetically engineered antibody and a carbon nanotube transistor for detection of prostate cancer biomarkers. Acs Nano 6, 5143–5149 (2012).
Venturelli, E. et al. Antibody covalent immobilization on carbon nanotubes and assessment of antigen binding. Small 7, 2179–2187 (2011).
Aftab, S. et al. Nanomaterials-based field-effect transistor for protein sensing: new advances. ACS Sens. 9, 9–22 (2023).
Callaghan, N. I. et al. Harnessing conserved signaling and metabolic pathways to enhance the maturation of functional engineered tissues. npj Regener. Med. 7, 44 (2022).
Liu, H. et al. Bioenergetic-active materials enhance tissue regeneration by modulating cellular metabolic state. Sci. Adv. 6, eaay7608 (2020).
Ren, C., Hu, X. & Zhou, Q. Graphene oxide quantum dots reduce oxidative stress and inhibit neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo through catalase‐like activity and metabolic regulation. Adv. Sci. 5, 1700595 (2018).
Hu, X., Lu, K., Mu, L., Kang, J. & Zhou, Q. Interactions between graphene oxide and plant cells: regulation of cell morphology, uptake, organelle damage, oxidative effects and metabolic disorders. Carbon 80, 665–676 (2014).
Xu, S. & Minteer, S. D. Enzymatic biofuel cell for oxidation of glucose to CO2. ACS Catal. 2, 91–94 (2012).
Wu, J., Liu, H., Chen, W., Ma, B. & Ju, H. Device integration of electrochemical biosensors. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 1, 346–360 (2023).
Rivnay, J. et al. Integrating bioelectronics with cell-based synthetic biology. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 3, 317–332 (2025).
Huang, J., Xue, S., Buchmann, P., Teixeira, A. P. & Fussenegger, M. An electrogenetic interface to program mammalian gene expression by direct current. Nat. Metab. 5, 1395–1407 (2023).
Li, S., Duan, Y., Zhu, W., Cheng, S. & Hu, W. Sensing interfaces engineering for organic thin film transistors-based biosensors: opportunities and challenges. Adv. Mater. 36, 2412379 (2024).
Milias-Argeitis, A., Rullan, M., Aoki, S. K., Buchmann, P. & Khammash, M. Automated optogenetic feedback control for precise and robust regulation of gene expression and cell growth. Nat. Commun. 7, 12546 (2016).
Ochoa-Fernandez, R. et al. Optogenetic control of gene expression in plants in the presence of ambient white light. Nat. Methods 17, 717–725 (2020).
Rajabi, A. H., Jaffe, M. & Arinzeh, T. L. Piezoelectric materials for tissue regeneration: a review. Acta Biomater. 24, 12–23 (2015).
Abramson, A. et al. A flexible electronic strain sensor for the real-time monitoring of tumor regression. Sci. Adv. 8, eabn6550 (2022).
Boutry, C. M. et al. A stretchable and biodegradable strain and pressure sensor for orthopaedic application. Nat. Electron. 1, 314–321 (2018).
Nguyen, T. D. et al. Piezoelectric nanoribbons for monitoring cellular deformations. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 587–593 (2012).
Kapat, K., Shubhra, Q. T., Zhou, M. & Leeuwenburgh, S. Piezoelectric nano‐biomaterials for biomedicine and tissue regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1909045 (2020).
Qin, J. et al. Flexible and stretchable capacitive sensors with different microstructures. Adv. Mater. 33, 2008267 (2021).
Frank, J. A., Antonini, M. J. & Anikeeva, P. Next-generation interfaces for studying neural function. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 1013–1023 (2019).
Xu, Y.-T. et al. A nanofluidic spiking synapse. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 121, e2403143121 (2024).
Jayant, K. et al. Flexible nanopipettes for minimally invasive intracellular electrophysiology in vivo. Cell Rep. 26, 266–278.e5 (2019).
Huffman, M. L. & Venton, B. J. Carbon-fiber microelectrodes for in vivo applications. Analyst 134, 18–24 (2009).
Kim, S. et al. Modulating synaptic plasticity with metal–organic framework for information-filterable artificial retina. Nat. Commun. 16, 162 (2025).
Lewis, C. M. et al. Electrochemically driven photosynthetic electron transport in cyanobacteria lacking photosystem II. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 2933–2942 (2022).
Du, Z. et al. Plasmonic effect with tailored Au@TiO2 nanorods in photoanode for quantum dot sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 5917–5924 (2019).
Yu, S. & Jain, P. K. Plasmonic photosynthesis of C1–C3 hydrocarbons from carbon dioxide assisted by an ionic liquid. Nat. Commun. 10, 2022 (2019).
Park, J. et al. Electrically conductive hydrogel nerve guidance conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2003759 (2020).
Namhongsa, M. et al. Surface-modified polypyrrole-coated PLCL and PLGA nerve guide conduits fabricated by 3D printing and electrospinning. Biomacromolecules 23, 4532–4546 (2022).
Jia, M. & Rolandi, M. Soft and ion-conducting materials in bioelectronics: from conducting polymers to hydrogels. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9, 1901372 (2020).
Wang, T. et al. A dual‐mode, scalable, machine‐learning‐enhanced wearable sensing system for synergetic muscular activity monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 10, 2400857 (2024).
Tang, H. et al. In situ forming epidermal bioelectronics for daily monitoring and comprehensive exercise. ACS Nano 16, 17931–17947 (2022).
Yang, S. et al. Stretchable surface electromyography electrode array patch for tendon location and muscle injury prevention. Nat. Commun. 14, 6494 (2023).
Yoon, H. et al. Decoding tissue biomechanics using conformable electronic devices. Nat. Rev. Mater. 10, 4–27 (2025).
Stoyanov, H., Kollosche, M., Risse, S., Waché, R. & Kofod, G. Soft conductive elastomer materials for stretchable electronics and voltage controlled artificial muscles. Adv. Mater. 25, 578–583 (2013).
Dong, R., Ma, P. X. & Guo, B. Conductive biomaterials for muscle tissue engineering. Biomaterials 229, 119584 (2020).
Guha Ray, P., Maity, D., Huang, J., Zulewski, H. & Fussenegger, M. A versatile bioelectronic interface programmed for hormone sensing. Nat. Commun. 14, 3151 (2023).
Vignesh, V. et al. Advancements in cortisol detection: from conventional methods to next-generation technologies for enhanced hormone monitoring. ACS Sens. 9, 1666–1681 (2024).
Bernacka‐Wojcik, I. et al. Implantable organic electronic ion pump enables ABA hormone delivery for control of stomata in an intact tobacco plant. Small 15, 1902189 (2019).
Ye, C. et al. A wearable aptamer nanobiosensor for non-invasive female hormone monitoring. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 330–337 (2024).
Rodriguez-Moncayo, R., Jimenez-Valdes, R. J., Gonzalez-Suarez, A. M. & Garcia-Cordero, J. L. Integrated microfluidic device for functional secretory immunophenotyping of immune cells. ACS Sens. 5, 353–361 (2020).
Dellacherie, M. O., Seo, B. R. & Mooney, D. J. Macroscale biomaterials strategies for local immunomodulation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 4, 379–397 (2019).
Xing, J. et al. Lentinan-modified carbon nanotubes as an antigen delivery system modulate immune response in vitro and in vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 19276–19283 (2016).
Mariani, F. et al. Advanced wound dressing for real-time pH monitoring. ACS Sens. 6, 2366–2377 (2021).
Kaveti, R. et al. Water-powered, electronics-free dressings that electrically stimulate wounds for rapid wound closure. Sci. Adv. 10, eado7538 (2024).
Khan, M. U. A. et al. Role of graphene oxide in bacterial cellulose–gelatin hydrogels for wound dressing applications. ACS Omega 8, 15909–15919 (2023).
Yang, Y., Du, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, H. & Guo, B. Structural and functional design of electrospun nanofibers for hemostasis and wound healing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 4, 1027–1057 (2022).
Sasaki, M. et al. Highly conductive stretchable and biocompatible electrode–hydrogel hybrids for advanced tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 3, 1919–1927 (2014).
Burnstine‐Townley, A., Eshel, Y. & Amdursky, N. Conductive scaffolds for cardiac and neuronal tissue engineering: governing factors and mechanisms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1901369 (2020).
Pinho, T. S., Cunha, C. B., Lanceros-Méndez, S. & Salgado, A. J. Electroactive smart materials for neural tissue regeneration. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 4, 6604–6618 (2021).
Yadid, M., Feiner, R. & Dvir, T. Gold nanoparticle-integrated scaffolds for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Nano Lett. 19, 2198–2206 (2019).
Eivazzadeh‐Keihan, R. et al. Metal‐based nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regener. Med. 14, 1687–1714 (2020).
Choi, H. et al. Adhesive bioelectronics for sutureless epicardial interfacing. Nat. Electron. 6, 779–789 (2023).
Lai, J. et al. Practical intelligent diagnostic algorithm for wearable 12-lead ECG via self-supervised learning on large-scale dataset. Nat. Commun. 14, 3741 (2023).
Kireev, D. et al. Fabrication, characterization and applications of graphene electronic tattoos. Nat. Protoc. 16, 2395–2417 (2021).
Sim, K. et al. An epicardial bioelectronic patch made from soft rubbery materials and capable of spatiotemporal mapping of electrophysiological activity. Nat. Electron. 3, 775–784 (2020).
Shim, J., Fleisch, E. & Barata, F. Circadian rhythm analysis using wearable-based accelerometry as a digital biomarker of aging and healthspan. npj Digit. Med. 7, 146 (2024).
Wang, B. et al. Wearable aptamer-field-effect transistor sensing system for noninvasive cortisol monitoring. Sci. Adv. 8, eabk0967 (2022).
Zhang, R. & Jia, Y. A disposable printed liquid gate graphene field effect transistor for a salivary cortisol test. ACS Sens. 6, 3024–3031 (2021).
Lee, G.-H. et al. Multifunctional materials for implantable and wearable photonic healthcare devices. Nat. Rev. Mater. 5, 149–165 (2020).
Kim, J. et al. Skin-interfaced wireless biosensors for perinatal and paediatric health. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 1, 631–647 (2023).
Chung, H. U. et al. Skin-interfaced biosensors for advanced wireless physiological monitoring in neonatal and pediatric intensive-care units. Nat. Med. 26, 418–429 (2020).
Liu, Z., Wan, X., Wang, Z. L. & Li, L. Electroactive biomaterials and systems for cell fate determination and tissue regeneration: design and applications. Adv. Mater. 33, 2007429 (2021).
Ang, M. C.-Y. et al. Nanosensor detection of synthetic auxins in planta using corona phase molecular recognition. ACS Sens. 6, 3032–3046 (2021).
Qu, C. C. et al. Flexible wearables for plants. Small 17, 2104482 (2021).
Boonyaves, K. et al. Near-infrared fluorescent carbon nanotube sensors for the plant hormone family gibberellins. Nano Lett. 23, 916–924 (2023).
Wang, W. et al. Imperceptible augmentation of living systems with organic bioelectronic fibres. Nat. Electron. 7, 586–597 (2024).
Ni, J. et al. Strong fatigue-resistant nanofibrous hydrogels inspired by lobster underbelly. Matter 4, 1919–1934 (2021).
Yang, R. et al. Assessment of visual function in blind mice and monkeys with subretinally implanted nanowire arrays as artificial photoreceptors. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 8, 1018–1039 (2024).
Glennon, E. et al. Locus coeruleus activity improves cochlear implant performance. Nature 613, 317–323 (2023).
Prévot, P.-H. et al. Behavioural responses to a photovoltaic subretinal prosthesis implanted in non-human primates. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 4, 172–180 (2020).
Yang, Y. et al. Preparation and use of wireless reprogrammable multilateral optogenetic devices for behavioral neuroscience. Nat. Protoc. 17, 1073–1096 (2022).
Jin, S. et al. Injectable tissue prosthesis for instantaneous closed-loop rehabilitation. Nature 623, 58–65 (2023).
Raspopovic, S., Valle, G. & Petrini, F. M. Sensory feedback for limb prostheses in amputees. Nat. Mater. 20, 925–939 (2021).
Liu, S., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y. & Zhu, R. A wearable motion capture device able to detect dynamic motion of human limbs. Nat. Commun. 11, 5615 (2020).
Kainz, A. et al. Distortion-free measurement of electric field strength with a MEMS sensor. Nat. Electron. 1, 68–73 (2018).
Tian, X. et al. Wireless body sensor networks based on metamaterial textiles. Nat. Electron. 2, 243–251 (2019).
Slade, P., Kochenderfer, M. J., Delp, S. L. & Collins, S. H. Sensing leg movement enhances wearable monitoring of energy expenditure. Nat. Commun. 12, 4312 (2021).
Selberg, J., Gomez, M. & Rolandi, M. The potential for convergence between synthetic biology and bioelectronics. Cell Syst. 7, 231–244 (2018).
He, R. et al. Flexible miniaturized sensor technologies for long-term physiological monitoring. npj Flex. Electron. 6, 20 (2022).
Mao, Y. et al. Genetically encoded biosensor engineering for application in directed evolution. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 33, 1257–1267 (2023).
Townshend, B., Xiang, J. S., Manzanarez, G., Hayden, E. J. & Smolke, C. D. A multiplexed, automated evolution pipeline enables scalable discovery and characterization of biosensors. Nat. Commun. 12, 1437 (2021).
Rivas, L. A. et al. A 200-antibody microarray biochip for environmental monitoring: searching for universal microbial biomarkers through immunoprofiling. Anal. Chem. 80, 7970–7979 (2008).
Pereira, E. et al. RFID technology for animal tracking: a survey. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 7, 609–620 (2023).
Rafiq, K. et al. WildWID: an open‐source active RFID system for wildlife research. Methods Ecol. Evol. 12, 1580–1587 (2021).
Kaberniuk, A. A., Baloban, M., Monakhov, M. V., Shcherbakova, D. M. & Verkhusha, V. V. Single-component near-infrared optogenetic systems for gene transcription regulation. Nat. Commun. 12, 3859 (2021).
Molesky, S. et al. Inverse design in nanophotonics. Nat. Photon. 12, 659–670 (2018).
Yu, N. & Capasso, F. Flat optics with designer metasurfaces. Nat. Mater. 13, 139–150 (2014).
Jakešová, M. et al. Coupling of photovoltaics with neurostimulation electrodes — optical to electrolytic transduction. J. Neural Eng. 21, 046003 (2024).
Hu, S. et al. Amorphous TiO2 coatings stabilize Si, GaAs, and GaP photoanodes for efficient water oxidation. Science 344, 1005–1009 (2014).
Yu, Y. et al. Enhanced photoelectrochemical efficiency and stability using a conformal TiO2 film on a black silicon photoanode. Nat. Energy 2, 17045 (2017).
Chen, F.-D. et al. Implantable silicon neural probes with nanophotonic phased arrays for single-lobe beam steering. Commun. Eng. 3, 182 (2024).
Balena, A. et al. Fabrication of nonplanar tapered fibers to integrate optical and electrical signals for neural interfaces in vivo. Nat. Protoc. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-024-01105-9 (2025).
Cardozo Pinto, D. F. & Lammel, S. Hot topic in optogenetics: new implications of in vivo tissue heating. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 1039–1041 (2019).
Kozai, T. D. Y. et al. Ultrasmall implantable composite microelectrodes with bioactive surfaces for chronic neural interfaces. Nat. Mater. 11, 1065–1073 (2012).
Nam, J. et al. Supramolecular peptide hydrogel-based soft neural interface augments brain signals through a three-dimensional electrical network. ACS Nano 14, 664–675 (2020).
Olejnik, A. et al. Tailoring diffusional fields in zwitterion/dopamine copolymer electropolymerized at carbon nanowalls for sensitive recognition of neurotransmitters. ACS Nano 16, 13183–13198 (2022).
Wu, Y., Chen, H. & Guo, L. Opportunities and dilemmas of in vitro nano neural electrodes. RSC Adv. 10, 187–200 (2020).
Liu, L. et al. Cell membrane coating integrity affects the internalization mechanism of biomimetic nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 12, 5726 (2021).
Mun, S. et al. Electro-active polymer based soft tactile interface for wearable devices. IEEE Trans. Haptics 11, 15–21 (2018).
Yoo, S. et al. Responsive materials and mechanisms as thermal safety systems for skin-interfaced electronic devices. Nat. Commun. 14, 1024 (2023).
Nie, S. et al. Soft, stretchable thermal protective substrates for wearable electronics. npj Flex. Electron. 6, 36 (2022).
Xie, Z., Liu, D., Gao, C., Dong, H. & Hu, W. High-mobility emissive organic semiconductors: an emerging class of multifunctional materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 9, 837–839 (2024).
Fratini, S., Nikolka, M., Salleo, A., Schweicher, G. & Sirringhaus, H. Charge transport in high-mobility conjugated polymers and molecular semiconductors. Nat. Mater. 19, 491–502 (2020).
Fang, H. et al. Capacitively coupled arrays of multiplexed flexible silicon transistors for long-term cardiac electrophysiology. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 1, 0038 (2017).
Phan, H.-P. et al. Long-lived, transferred crystalline silicon carbide nanomembranes for implantable flexible electronics. ACS Nano 13, 11572–11581 (2019).
Rana, D. & Matsuura, T. Surface modifications for antifouling membranes. Chem. Rev. 110, 2448–2471 (2010).
Picca, R. A. et al. Ultimately sensitive organic bioelectronic transistor sensors by materials and device structure design. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1904513 (2020).
Dweiri, Y. M., Eggers, T., McCallum, G. & Durand, D. M. Ultra-low noise miniaturized neural amplifier with hardware averaging. J. Neural Eng. 12, 046024 (2015).
Lee, J. et al. Neural recording and stimulation using wireless networks of microimplants. Nat. Electron. 4, 604–614 (2021).
Cui, F., Yue, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z. & Zhou, H. S. Advancing biosensors with machine learning. ACS Sens. 5, 3346–3364 (2020).
Wang, C. et al. Bioadhesive ultrasound for long-term continuous imaging of diverse organs. Science 377, 517–523 (2022).
Zhou, L., Guess, M., Kim, K. R. & Yeo, W.-H. Skin-interfacing wearable biosensors for smart health monitoring of infants and neonates. Commun. Mater. 5, 72 (2024).
Zhang, J. et al. Stretchable transparent electrode arrays for simultaneous electrical and optical interrogation of neural circuits in vivo. Nano Lett. 18, 2903–2911 (2018).
Miklavčič, D., Pavšelj, N. & Hart, F. H. Electric properties of tissues. Wiley Encycl. Biomed. Eng. 6, 3578–3589 (2006).
Marino, M., Cordero-Grande, L., Mantini, D. & Ferrazzi, G. Conductivity tensor imaging of the human brain using water mapping techniques. Front. Neurosci. 15, 694645 (2021).
Ramon, C., Garguilo, P., Fridgeirsson, E. A. & Haueisen, J. Changes in scalp potentials and spatial smoothing effects of inclusion of dura layer in human head models for EEG simulations. Front. Neuroeng. 7, 32 (2014).
Acknowledgements
B.T. acknowledges support from the US Army Research Office (W911NF-24-1-0053) and the National Institutes of Health (1R01EB036091-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.T. and P.L. conceived the manuscript. All authors contributed to the writing, discussion and reviewing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Materials thanks Guosong Hong, who co-reviewed with Han Cui; Mario Caironi, who co-reviewed with Adrica Kyndiah; and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Cheng, Z., Li, P. et al. Materials and device strategies to enhance spatiotemporal resolution in bioelectronics. Nat Rev Mater 10, 425–448 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-025-00798-y
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-025-00798-y
This article is cited by
-
Next-generation biosensing for in situ monitoring
Nature Sensors (2026)
-
Conforming strategies for bioelectronics on arbitrary surfaces
npj Biosensing (2025)