Abstract
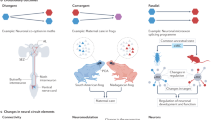
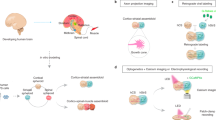
Understanding the relationship between genotype and neuronal circuit phenotype necessitates an integrated view of genetics, development, plasticity and learning. Challenging the prevailing notion that emphasizes learning and plasticity as primary drivers of circuit assembly, in this Perspective, we delineate a tripartite framework to clarify the respective roles that learning and plasticity might have in this process. In the first part of the framework, which we term System One, neural circuits are established purely through genetically driven algorithms, in which spike timing-dependent plasticity serves no instructive role. We propose that these circuits equip the animal with sufficient skill and knowledge to successfully engage the world. Next, System Two is governed by rare but critical ‘single-shot learning’ events, which occur in response to survival situations and prompt rapid synaptic reconfiguration. Such events serve as crucial updates to the existing hardwired knowledge base of an organism. Finally, System Three is characterized by a perpetual state of synaptic recalibration, involving continual plasticity for circuit stabilization and fine-tuning. By outlining the definitions and roles of these three core systems, our framework aims to resolve existing ambiguities related to and enrich our understanding of neural circuit formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zador, A. M. A critique of pure learning and what artificial neural networks can learn from animal brains. Nat. Commun. 10, 3770 (2019).
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y. & Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444 (2015).
Martini, F. J., Guillamón-Vivancos, T., Moreno-Juan, V., Valdeolmillos, M. & López-Bendito, G. Spontaneous activity in developing thalamic and cortical sensory networks. Neuron 109, 2519–2534 (2021).
Wu, M. W., Kourdougli, N. & Portera-Cailliau, C. Network state transitions during cortical development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 25, 535–552 (2024).
Kuwahara, H. & Gao, X. Stochastic effects as a force to increase the complexity of signaling networks. Sci. Rep. 3, 2297 (2013).
Confavreux, B., Agnes, E. J., Zenke, F., Sprekeler, H. & Vogels, T. P. Balancing complexity, performance and plausibility to meta learn plasticity rules in recurrent spiking networks. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.17.599260 (2024).
Váša, F. & Mišić, B. Null models in network neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 493–504 (2022).
Lendvai, B., Stern, E. A., Chen, B. & Svoboda, K. Experience-dependent plasticity of dendritic spines in the developing rat barrel cortex in vivo. Nature 404, 876–881 (2000).
DeBello, W. M. Micro-rewiring as a substrate for learning. Trends Neurosci. 31, 577–584 (2008).
Power, J. D. & Schlaggar, B. L. Neural plasticity across the lifespan. WIREs Dev. Biol., 6, e216 (2017).
Barabási, D. L., Schuhknecht, G. F. P. & Engert, F. Functional neuronal circuits emerge in the absence of developmental activity. Nat. Commun. 15, 364 (2024).
Warland, D. K., Huberman, A. D. & Chalupa, L. M. Dynamics of spontaneous activity in the fetal macaque retina during development of retinogeniculate pathways. J. Neurosci. 26, 5190–5197 (2006).
Ge, X. et al. Retinal waves prime visual motion detection by simulating future optic flow. Science 373, eabd0830 (2021).
Langen, M. et al. The developmental rules of neural superposition in Drosophila. Cell 162, 120–133 (2015).
Hiesinger, P. R. et al. Activity-independent prespecification of synaptic partners in the visual map of Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 16, 1835–1843 (2006).
Corver, A., Wilkerson, N., Miller, J. & Gordus, A. Distinct movement patterns generate stages of spider web building. Curr. Biol. 31, 4983–4997.e5 (2021).
Moss, S. Planet Earth II: A New World Revealed (Penguin Random House, 2016).
Honza, M., Vošlajerová, K. & Moskát, C. Eviction behaviour of the common cuckoo Cuculus canorus chicks. J. Avian Biol. 38, 385–389 (2007).
Maggini, I. & Bairlein, F. Innate sex differences in the timing of spring migration in a songbird. PLoS ONE 7, e31271 (2012).
Berthold, P. & Helbig, A. J. The genetics of bird migration: stimulus, timing, and direction. IBIS 134, 35–40 (2008).
Acworth, N. R. J. The healthy neonatal foal: routine examinations and preventative medicine. Equine Vet. Educ. 15, 207–211 (2003).
Fishell, G. & Kepecs, A. Interneuron types as attractors and controllers. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 43, 1–30 (2020).
Konstantinides, N. et al. A complete temporal transcription factor series in the fly visual system. Nature 604, 316–322 (2022).
Shabani, K. & Hassan, B. A. The brain on time: links between development and neurodegeneration. Development 150, dev200397 (2023).
Kurmangaliyev, Y. Z., Yoo, J., Valdes-Aleman, J., Sanfilippo, P. & Zipursky, S. L. Transcriptional programs of circuit assembly in the Drosophila visual system. Neuron 108, 1045–1057.e6 (2020).
Kerstjens, S., Michel, G. & Douglas, R. J. Constructive connectomics: how neuronal axons get from here to there using gene-expression maps derived from their family trees. PLoS Comput. Biol. 18, e1010382 (2022).
Agi, E. et al. Axonal self-sorting without target guidance in visual map formation. Science 383, 1084–1092 (2024).
Sanes, J. R. & Zipursky, S. L. Synaptic specificity, recognition molecules, and assembly of neural circuits. Cell 181, 1434–1435 (2020).
Flaherty, E. & Maniatis, T. The role of clustered protocadherins in neurodevelopment and neuropsychiatric diseases. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 65, 144–150 (2020).
Valdes-Aleman, J. et al. Comparative connectomics reveals how partner identity, location, and activity specify synaptic connectivity in Drosophila. Neuron 109, 105–122.e7 (2021).
Barabási, D. L. & Czégel, D. Constructing graphs from genetic encodings. Sci. Rep. 11, 13270 (2021).
Hiesinger, P. R. & Hassan, B. A. The evolution of variability and robustness in neural development. Trends Neurosci. 41, 577–586 (2018).
Hiesinger, P. R. The Self-Assembling Brain: How Neural Networks Grow Smarter (Princeton Univ. Press, 2021).
Farhoodi, R. & Kording, K. P. Sampling neuron morphologies. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/248385 (2018).
Xu, C. et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of teneurin signaling in synaptic partner matching. Cell 187, 5081–5101.e19 (2024).
Ferreira Castro, A. et al. Achieving functional neuronal dendrite structure through sequential stochastic growth and retraction. eLife 9, e60920 (2020).
McFarland, B. W. et al. Axon arrival times and physical occupancy establish visual projection neuron integration on developing dendrites in the Drosophila optic glomeruli. eLife 13, RP96223 (2024).
Barabási, D. L. & Barabási, A.-L. A genetic model of the connectome. Neuron 105, 435–445.e5 (2020).
Carrillo, R. A. et al. Control of synaptic connectivity by a network of Drosophila IgSF cell surface proteins. Cell 163, 1770–1782 (2015).
Munz, M. et al. Pyramidal neurons form active, transient, multilayered circuits perturbed by autism-associated mutations at the inception of neocortex. Cell 186, 1930–1949.e31 (2023).
Mòdol, L., Moissidis, M., Selten, M., Oozeer, F. & Marín, O. Somatostatin interneurons control the timing of developmental desynchronization in cortical networks. Neuron 112, 2015–2030.e5 (2024).
Antón-Bolaños, N. et al. Prenatal activity from thalamic neurons governs the emergence of functional cortical maps in mice. Science 364, 987–990 (2019).
Andreae, L. C. & Burrone, J. The role of spontaneous neurotransmission in synapse and circuit development. J. Neurosci. Res. 96, 354–359 (2018).
Sutton, M. A., Wall, N. R., Aakalu, G. N. & Schuman, E. M. Regulation of dendritic protein synthesis by miniature synaptic events. Science 304, 1979–1983 (2004).
Barabási, D. L. et al. Neuroscience needs network science. J. Neurosci. 43, 5989–5995 (2023).
Kovács, I. A., Barabási, D. L. & Barabási, A.-L. Uncovering the genetic blueprint of the nervous system. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 33570–33577 (2020).
Lior, G., Shalev, Y., Stanovsky, G. & Goldstein, A. Computation or weight adaptation? Rethinking the role of plasticity in learning. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.07.583890 (2024).
Kuutti, S., Fallah, S., Bowden, R. & Barber, P. Deep Learning for Autonomous Vehicle Control: Algorithms, State-of-the-Art, and Future Prospects (Morgan & Claypool, 2019).
Hürkey, S. et al. Gap junctions desynchronize a neural circuit to stabilize insect flight. Nature 618, 118–125 (2023).
Wehner, R. Desert Navigator: The Journey of an Ant (Harvard Univ. Press, 2020).
Ronacher, B. Path integration in a three-dimensional world: the case of desert ants. J. Comp. Physiol. A 206, 379–387 (2020).
Freas, C. A. & Schultheiss, P. How to navigate in different environments and situations: lessons from ants. Front. Psychol. 9, 841 (2018).
O’Shea, H. & Redmond, S. J. A review of the neurobiomechanical processes underlying secure gripping in object manipulation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 123, 286–300 (2021).
Ammari, R. et al. Hormone-mediated neural remodeling orchestrates parenting onset during pregnancy. Science 382, 76–81 (2023).
Wu, Z., Autry, A. E., Bergan, J. F., Watabe-Uchida, M. & Dulac, C. G. Galanin neurons in the medial preoptic area govern parental behaviour. Nature 509, 325–330 (2014).
Wu, M. V. & Tollkuhn, J. Estrogen receptor alpha is required in GABAergic, but not glutamatergic, neurons to masculinize behavior. Horm. Behav. 95, 3–12 (2017).
Lesar, A., Tahir, J., Wolk, J. & Gershow, M. Switch-like and persistent memory formation in individual. eLife 10, e70317 (2021).
Giurfa, M., Núñez, J., Chittka, L. & Menzel, R. Colour preferences of flower-naive honeybees. J. Comp. Physiol. A 177, 247–259 (1995).
Galvin, L., Mirza Agha, B., Saleh, M., Mohajerani, M. H. & Whishaw, I. Q. Learning to cricket hunt by the laboratory mouse (Mus musculus): skilled movements of the hands and mouth in cricket capture and consumption. Behav. Brain Res. 412, 113404 (2021).
Matsuzawa, T. Sweet-potato washing revisited: 50th anniversary of the Primates article. Primates 56, 285–287 (2015).
Bowman, C. R. & Zeithamova, D. Abstract memory representations in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus support concept generalization. J. Neurosci. 38, 2605–2614 (2018).
Tang, W., Shin, J. D. & Jadhav, S. P. Geometric transformation of cognitive maps for generalization across hippocampal-prefrontal circuits. Cell Rep. 42, 112246 (2023).
Jones, M. W. & McHugh, T. J. Updating hippocampal representations: CA2 joins the circuit. Trends Neurosci. 34, 526–535 (2011).
Flanagin, V. L. et al. Human exploration of enclosed spaces through echolocation. J. Neurosci. 37, 1614–1627 (2017).
Porter, J. et al. Mechanisms of scent-tracking in humans. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 27–29 (2007).
Bittner, K. C., Milstein, A. D., Grienberger, C., Romani, S. & Magee, J. C. Behavioral time scale synaptic plasticity underlies CA1 place fields. Science 357, 1033–1036 (2017).
Ahrens, M. B. et al. Brain-wide neuronal dynamics during motor adaptation in zebrafish. Nature 485, 471–477 (2012).
Bahl, A. & Engert, F. Neural circuits for evidence accumulation and decision making in larval zebrafish. Nat. Neurosci. 23, 94–102 (2020).
Arcaro, M., Schade, P. & Livingstone, M. Preserved cortical organization in the absence of early visual input. J. Vis. 18, 27–27 (2018).
Hubel, D. H. & Wiesel, T. N. The period of susceptibility to the physiological effects of unilateral eye closure in kittens. J. Physiol. 206, 419–436 (1970).
Sansom, S. N. & Livesey, F. J. Gradients in the brain: the control of the development of form and function in the cerebral cortex. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 1, a002519 (2009).
Ahmed, M. et al. Input density tunes Kenyon cell sensory responses in the Drosophila mushroom body. Curr. Biol. 33, 2742–2760.e12 (2023).
Sterling, P. & Laughlin, S. Principles of Neural Design (MIT Press, 2017).
Dean, P. et al. The cerebellar microcircuit as an adaptive filter: experimental and computational evidence. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 30–43 (2010).
Keller, G. B., Bonhoeffer, T. & Hübener, M. Sensorimotor mismatch signals in primary visual cortex of the behaving mouse. Neuron 74, 809–815 (2012).
Keller, G. B. & Hahnloser, R. H. Neural processing of auditory feedback during vocal practice in a songbird. Nature 457, 187–190 (2009).
Heindorf, M., Arber, S. & Keller, G. B. Mouse motor cortex coordinates the behavioral response to unpredicted sensory feedback. Neuron 99, 1040–1054.e5 (2018).
Moreno-Juan, V. et al. Prenatal thalamic waves regulate cortical area size prior to sensory processing. Nat. Commun. 8, 14172 (2017).
Guillamón-Vivancos, T. et al. Input-dependent segregation of visual and somatosensory circuits in the mouse superior colliculus. Science 377, 845–850 (2022).
Kirkby, L. A., Sack, G. S., Firl, A. & Feller, M. B. A role for correlated spontaneous activity in the assembly of neural circuits. Neuron 80, 1129–1144 (2013).
Matsumoto, N., Barson, D., Liang, L. & Crair, M. C. Hebbian instruction of axonal connectivity by endogenous correlated spontaneous activity. Science 385, eadh7814 (2024).
Wiesel, T. N. & Hubel, D. H. Single-cell responses in striate cortex of kittens deprived of vision in one eye. J. Neurophysiol. 26, 1003–1017 (1963).
Wiesel, T. N. & Hubel, D. H. Comparison of the effects of unilateral and bilateral eye closure on cortical unit responses in kittens. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 1029–1040 (1965).
Sharma, J., Angelucci, A. & Sur, M. Induction of visual orientation modules in auditory cortex. Nature 404, 841–847 (2000).
von Melchner, L., Pallas, S. L. & Sur, M. Visual behaviour mediated by retinal projections directed to the auditory pathway. Nature 404, 871–876 (2000).
Yu, C. R. et al. Spontaneous neural activity is required for the establishment and maintenance of the olfactory sensory map. Neuron 42, 553–566 (2004).
Shatz, C. J. & Stryker, M. P. Prenatal tetrodotoxin infusion blocks segregation of retinogeniculate afferents. Science 242, 87–89 (1988).
Chapman, B. & Stryker, M. P. Development of orientation selectivity in ferret visual cortex and effects of deprivation. J. Neurosci. 13, 5251–5262 (1993).
Roy, A. et al. Does experience provide a permissive or instructive influence on the development of direction selectivity in visual cortex? Neural Dev. 13, 16 (2018).
Zelazo, P. R., Zelazo, N. A. & Kolb, S. ‘Walking’ in the newborn. Science 176, 314–315 (1972).
Verhage, M. et al. Synaptic assembly of the brain in the absence of neurotransmitter secretion. Science 287, 864–869 (2000).
Silver, D. et al. A general reinforcement learning algorithm that masters chess, shogi, and Go through self-play. Science 362, 1140–1144 (2018).
Moravec, H. Mind Children: The Future of Robot and Human Intelligence (Harvard Univ. Press, 1988).
Richards, B. A. et al. A deep learning framework for neuroscience. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 1761–1770 (2019).
The new NeuroAI. Nat. Mach. Intell. 6, 245 (2024).
Silva, C. G., Peyre, E. & Nguyen, L. Cell migration promotes dynamic cellular interactions to control cerebral cortex morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 20, 318–329 (2019).
Knudsen, E. I. & Konishi, M. Mechanisms of sound localization in the barn owl (Tyto alba). J. Comp. Physiol. 133, 13–21 (1979).
Ito, M. The molecular organization of cerebellar long-term depression. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 896–902 (2002).
Knudsen, E. I. & Knudsen, P. F. Vision calibrates sound localization in developing barn owls. J. Neurosci. 9, 3306–3313 (1989).
Lackner, J. R. Influence of abnormal postural and sensory conditions on human sensorimotor localization. Environ. Biol. Med. 2, 137–177 (1976).
Hyde, P. S. & Knudsen, E. I. The optic tectum controls visually guided adaptive plasticity in the owl’s auditory space map. Nature 415, 73–76 (2002).
Linkenhoker, B. A. & Knudsen, E. I. Incremental training increases the plasticity of the auditory space map in adult barn owls. Nature 419, 293–296 (2002).
Gutfreund, Y., Zheng, W. & Knudsen, E. I. Gated visual input to the central auditory system. Science 297, 1556–1559 (2002).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank K. Miller and H. Baier for the fruitful discussions. This work was supported by New Science Microgrant to D.L.B. and by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Grant U19NS104653, NIH Grant 1R01NS124017, National Science Foundation Grant IIS-1912293, and Simons Foundation SCGB 542973 to F.E.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.L.B. and F.E. contributed to all aspects of the preparation of the manuscript. A.F.C. made a substantial contribution to the discussion of the content of the article and to the review and editing of the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Neuroscience thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barabási, D.L., Ferreira Castro, A. & Engert, F. Three systems of circuit formation: assembly, updating and tuning. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 26, 232–243 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-025-00910-9
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-025-00910-9