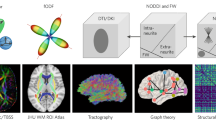
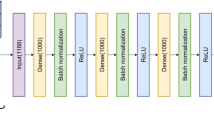
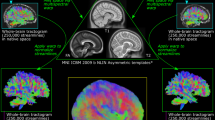
Abstract
Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) is a versatile imaging technique that has gained popularity thanks to its sensitive ability to measure displacement of water molecules within a living tissue on a micrometer scale. Although dMRI has been around since the early 1990s, its applications are constantly evolving, primarily regarding the inference of structural connectomics from nerve fiber trajectories. However, these applications require expertise in image processing and statistics, and it can be difficult for a newcomer to choose an appropriate pipeline to fit their research needs, not least because dMRI is such a flexible methodology that dozens of acquisition and analysis pipelines have been developed over the years. This introductory guide is designed for graduate students and researchers in the neuroscience community who are interested in integrating this new methodology regardless of their background in neuroimaging and computational tools. The guide provides a brief overview of the basic dMRI methodologies but focuses on its applications in neuroplasticity and connectomics. The guide starts with dMRI experimental designs and a complete step-by-step pipeline for structural connectomics. The following section covers the basics of dMRI, including parameters and clinical applications (apparent diffusion coefficient, mean diffusivity, fractional anisotropy and microscopic fractional anisotropy), as well as different approaches and models. The final section focuses on structural connectomics, covering subjects from fiber tracking (techniques, evaluation and limitations) to structural networks (constructing, analyzing and visualizing a network).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park, H. J. & Friston, K. Structural and functional brain networks: from connections to cognition. Science 342, 1238411 (2013).
Van Essen, D. C. et al. The WU-Minn human connectome project: an overview. Neuroimage 80, 62–79 (2013).
Jbabdi, S. & Johansen-Berg, H. Tractography: where do we go from here? Brain Connect. 1, 169–183 (2011).
Van Essen, D. C. & Glasser, M. F. The human connectome project: progress and prospects. Cerebrum 2016, cer-10-16 (2016).
Jones, D. K. Diffusion MRI: Theory, Methods, and Applications (Oxford University Press, 2012).
Dale, B. M., Brown, M. A. & Semelka, R. C. MRI: Basic Principles and Applications 5th edn. (Wiley-Blackwell, 2015).
Rubinov, M. & Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 52, 1059–1069 (2010).
Leemans, A., Jeurissen, B., Sijbers, J. & Jones, D. K. ExploreDTI: a graphical toolbox for processing, analyzing, and visualizing diffusion MR data. In 17th Annual Meeting of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 3537 (ISMRM, 2009).
Tournier, J. D. et al. Mrtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualization. Neuroimage 202, 116–137 (2019).
Theaud, G., Houde, J. C., Rheault, A. B. F., Morency, F. & Descoteaux, M. TractoFlow: a robust, efficient and reproducible diffusion MRI pipeline leveraging Nextflow & Singularity. Neuroimage 218, 116889 (2020).
Cieslak, M. et al. QSIPrep: an integrative platform for preprocessing and reconstructing diffusion MRI data. Nat. Methods 18, 775–778 (2021).
Cruces, R. R. et al. Micapipe: a pipeline for multimodal neuroimaging and connectome analysis. Neuroimage 263, 119612 (2022).
Assaf, Y. & Barazany, D. in Advances in Magnetic Resonance Technology and Applications Vol. 4 (eds. Cohi, Y. & Jezzard, P.) 157–173 (Academic Press, 2021).
Johansen-Berg, H. & Behrens, T. E. J. Diffusion MRI: From Quantitative Measurement to In vivo Neuroanatomy 2nd edn. (Elsevier, 2014).
Tavor, I., Hofstetter, S. & Assaf, Y. Micro-structural assessment of short term plasticity dynamics. Neuroimage 81, 1–7 (2013).
Assaf, Y. Imaging laminar structures in the gray matter with diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 197, 677–688 (2019).
Sotiropoulos, S. N. & Zalesky, A. Building connectomes using diffusion MRI: why, how and but. NMR Biomed. 32, e3752 (2019).
Rheault, F., Poulin, P., Valcourt Caron, A., St-Onge, E. & Descoteaux, M. Common misconceptions, hidden biases and modern challenges of dMRI tractography. J. Neural Eng. 17, 011001 (2020).
Yeh, C. H., Jones, D. K., Liang, X., Descoteaux, M. & Connelly, A. Mapping structural connectivity using diffusion MRI: challenges and opportunities. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 53, 1666–1682 (2021).
Helenius, J. et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in normal human brains in various age groups. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 23, 194–199 (2002).
Schlaug, G., Siewert, B., Benfield, A., Edelman, R. R. & Warach, S. Time course of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) abnormality in human stroke. Neurology 49, 113–119 (1997).
Kuroiwa, T. et al. Different apparent diffusion coefficient: water content correlations of gray and white matter during early ischemia. Stroke 29, 859–865 (1998).
van Everdingen, K. J., van der Grond, J., Kappelle, L. J., Ramos, L. M. P. & Mali, W. P. T. M. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in acute stroke. Stroke 29, 1783–1790 (1998).
Harkins, K. D., Galons, J. P., Secomb, T. W. & Trouard, T. P. Assessment of the effects of cellular tissue properties on ADC measurements by numerical simulation of water diffusion. Magn. Reson. Med. 62, 1414–1422 (2009).
Jose, J. M., Marques, P., Alves, V. & Nuno, S. A hitchhiker’s guide to diffusion tensor imaging. Front. Neurosci. 7, 1–14 (2013).
Sener, R. N. Diffusion MRI: apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values in the normal brain and a classification of brain disorders based on ADC values. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 25, 299–326 (2001).
Barrio-Arranz, G., de Luis-García, R., Tristán-Vega, A., Martín-Fernández, M. & Aja-Fernández, S. Impact of MR acquisition parameters on DTI scalar indexes: a tractography based approach. PloS ONE 10, e0137905 (2015).
Assaf, Y., Johansen-Berg, H. & Thiebaut de Schotten, M. The role of diffusion MRI in neuroscience. NMR Biomed. 32, e3762 (2019).
Blumenfeld-Katzir, T., Pasternak, O., Dagan, M. & Assaf, Y. Diffusion MRI of structural brain plasticity induced by a learning and memory task. PloS ONE 6, e20678 (2011).
Tavor, I., Botvinik-Nezer, R., Bernstein-Eliav, M., Tsarfaty, G. & Assaf, Y. Short-term plasticity following motor sequence learning revealed by diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 41, 442–452 (2020).
Assaf, Y. New dimensions for brain mapping. Science 362, 994–995 (2018).
Sagi, Y. et al. Learning in the fast lane: new insights into neuroplasticity. Neuron 73, 1195–1203 (2012).
Hofstetter, S., Tavor, I., Tzur-Moryosef, S. & Assaf, Y. Short-term learning induces white matter plasticity in the fornix. J. Neurosci. 33, 12844–12850 (2013).
Hofstetter, S., Friedmann, N. & Assaf, Y. Rapid language-related plasticity: microstructural changes in the cortex after a short session of new word learning. Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 1231–1241 (2017).
Henf, J., Grothe, M. J., Brueggen, K., Teipel, S. & Dyrba, M. Mean diffusivity in cortical gray matter in Alzheimer’s disease: The importance of partial volume correction. Neuroimage Clin. 17, 579–586 (2018).
Duncan, J. S. Imaging the brain’s highways-diffusion tensor imaging in epilepsy. Epilepsy Curr. 8, 85–89 (2008).
Szczepankiewicz, F. et al. Quantification of microscopic diffusion anisotropy disentangles effects of orientation dispersion from microstructure: applications in healthy volunteers and in brain tumors. Neuroimage 104, 241–252 (2015).
Kaden, E., Kelm, N. D., Carson, R. P., Does, M. D. & Alexander, D. C. Multi-compartment microscopic diffusion imaging. Neuroimage 139, 346–359 (2016).
Henriques, R. N., Jespersen, S. N. & Shemesh, N. Microscopic anisotropy misestimation in spherical-mean single diffusion encoding MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 81, 3245–3261 (2019).
Magdoom, K. N., Avram, A. V., Sarlls, J. E., Dario, G. & Basser, P. J. A novel framework for in-vivo diffusion tensor distribution MRI of the human brain. Neuroimage 271, 120003 (2023).
Stejskal, E. O. & Tanner, J. E. Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of time-dependent field gradient. J. Chem. Phys. 42, 288–292 (1965).
Assaf, Y., Mayk, A. & Cohen, Y. Displacement imaging of spinal cord using q-space diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 44, 713–722 (2000).
Cohen, Y. & Assaf, Y. High b-value q-space analyzed diffusion-weighted MRS and MRI in neuronal tissues—a technical review. NMR Biomed. 15, 516–542 (2002).
Jensen, H. J. & Helpern, J. A. MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed. 23, 698–710 (2010).
Steven, A. J., Zhuo, J. & Melhem, E. R. Diffusion kurtosis imaging: an emerging technique for evaluating the microstructural environment of the brain. Am. J. Roentgenol. 202, W26–W33 (2014).
Henriques, R. N. et al. Diffusional kurtosis imaging in the diffusion imaging in Python project. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 15, 675433 (2021).
Assaf, Y. & Basser, P. J. Composite hindered and restricted model of diffusion (CHARMED) MR imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage 27, 48–58 (2005).
Zhang, H., Schneider, T., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A. & Alexander, D. C. NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage 61, 1000–1016 (2012).
Scherrer, B. et al. Characterizing brain tissue by assessment of the distribution of anisotropic microstructural environments in diffusion-compartment imaging (DIAMOND). Magn. Reson. Med. 76, 963–977 (2016).
Assaf, Y., Blumenfeld-Katzir, T., Yovel, Y. & Basser, P. J. AxCaliber: a method for measuring axon diameter distribution from diffusion MRI. Mag. Reson. Med. 59, 1347–1354 (2008).
Barazany, D., Basser, P. J. & Assaf, Y. In vivo measurement of axon diameter distribution in the corpus callosum of rat brain. Brain 132, 1210–1220 (2009).
Assaf, Y. et al. The CONNECT project: combining macro- and micro-structure. Neuroimage 80, 273–282 (2013).
Daducci, A., Dal Palù, A., Lemkaddem, A. & Thiran, J. P. COMMIT: convex optimization modeling for microstructure informed tractography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34, 246–257 (2015).
Barakovic, M. et al. Bundle-specific axon diameter index as a new contrast to differentiate white matter tracts. Front. Neurosci. 15, 646034 (2021).
Drakesmith, M. et al. Estimating axon conduction velocity in vivo from microstructural MRI. Neuroimage 203, 116186 (2019).
Dyrby, T. B., Søgaard, L. V., Hall, M. G., Ptito, M. & Alexander, D. C. Contrast and stability of the axon diameter index from microstructure imaging with diffusion MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 70, 711–721 (2013).
Harkins, K. D., Beaulieu, C., Xu, J., Gore, J. C. & Does, M. D. A simple estimate of axon size with diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 227, 117619 (2021).
Daducci, A. et al. Accelerated Microstructure Imaging via Convex Optimization (AMICO) from diffusion MRI data. Neuroimage 15, 32–44 (2015).
Romascano, D. et al. ActiveAxADD: toward non-parametric and orientationally invariant axon diameter distribution mapping using PGSE. Magn. Reson. Med. 83, 2322–2330 (2020).
Veraart, J. et al. Noninvasive quantification of axon radii using diffusion MRI. eLife 9, e49855 (2020).
Horowitz, A. et al. In vivo correlation between axon diameter and conduction velocity in the human brain. Brain Struct. Funct. 220, 1777–1788 (2015).
Gast, H. et al. A method for in-vivo mapping of axonal diameter distributions in the human brain using diffusion-based axonal spectrum imaging (AxSI). Neuroinformatics 21, 469–482 (2023).
Sepehrband, F., Alexander, D. C., Kurniawan, N. D., Reutens, D. C. & Yang, Z. Towards higher sensitivity and stability of axon diameter estimation with diffusion-weighted MRI. NMR Biomed. 29, 293–308 (2016).
Heidemann, R. M., Anwander, A., Feiweier, T., Knösche, T. R. & Turner, R. k-space and q-space: combining ultra-high spatial and angular resolution in diffusion imaging using ZOOPPA at 7 T. Neuroimage 60, 967–978 (2012).
Tournier, J. D., Calamante, F. & Connelly, A. Determination of the appropriate b value and number of gradient directions for high-angular-resolution diffusion-weighted imaging. NMR Biomed. 26, 1775–1786 (2013).
Wakana, S., Jiang, H., Nagae-Poetscher, L. M., van Zijl, P. C. & Mori, S. Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy. Radiology 230, 77–87 (2004).
Fillard, P. et al. Quantitative evaluation of 10 tractography algorithms on a realistic diffusion MR phantom. Neuroimage 56, 220–234 (2011).
Zhan, L. et al. For the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Comparison of nine tractography algorithms for detecting abnormal structural brain networks in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 7, 48 (2015).
Poulin, P., Jörgens, D., Jodoin, P. M. & Descoteaux, M. Tractography and machine learning: Current state and open challenges. Magn. Reson. Imaging 64, 37–48 (2019).
Poulin, P. et al. TractoInferno—a large-scale, open-source, multi-site database for machine learning dMRI tractography. Sci. Data 9, 725 (2022).
Maier-Hein, K. H. et al. The challenge of mapping the human connectome based on diffusion tractography. Nat. Commun. 8, 1349 (2017).
Colon-Perez, L. M. et al. A majority rule approach for region-of-interest-guided streamline fiber tractography. Brain Imaging Behav. 10, 1137–1147 (2016).
David, S. et al. The superoanterior fasciculus (SAF): a novel white matter pathway in the human brain? Front. Neuroanat. 13, 24 (2019).
Sotiropoulos, S. N., Behrens, T. E. & Jbabdi, S. Ball and rackets: inferring fiber fanning from diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuroimage 60, 1412–1425 (2012).
Jeurissen, B., Tournier, J. D., Dhollander, T., Connelly, A. & Sijbers, J. Multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution for improved analysis of multi-shell diffusion MRI data. Neuroimage 103, 411–426 (2014).
St-Onge, E., Al-Sharif, N., Girard, G., Theaud, G. & Descoteaux, M. Cortical surfaces integration with tractography for structural connectivity analysis. Brain Connect. 11, 505–517 (2021).
Shastin, D. et al. Surface-based tracking for short association fibre tractography. Neuroimage 260, 119423 (2022).
Mu, J., Xu, Q., Tian, J. & Liu, J. The effect of feature image on sensitivity of the statistical analysis in the pipeline of a tractography atlas-based analysis. Sci. Rep. 7, 12669 (2017).
Hagmann, P. et al. Mapping human whole-brain structural networks with diffusion MRI. PLoS ONE 2, e597 (2007).
Côté, M. A., Boré, A., Girard, G., Houde, J. C. & Descoteaux, M. Tractometer: online evaluation system for tractography. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 15, 699–706 (2012).
Côté, M. A. et al. Tractometer: towards validation of tractography pipelines. Med. Image Anal. 17, 844–857 (2013).
Schilling, K. G. et al. Prevalence of white matter pathways coming into a single white matter voxel orientation: the bottleneck issue in tractography. Hum. Brain Mapp. 43, 1196–1213 (2022).
Shamir, I. & Assaf, Y. Expanding connectomics to the laminar level: a perspective. Netw. Neurosci. 7, 377–388 (2023).
Bastiani, M., Shah, N. J., Goebel, R. & Roebroeck, A. Human cortical connectome reconstruction from diffusion weighted MRI: The effect of tractography algorithm. Neuroimage 62, 1732–1749 (2012).
Jones, D. K., Knösche, T. R. & Turner, R. White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: The do’s and don’ts of diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 73, 239–254 (2013).
De Santis, S., Drakesmith, M., Bells, S., Assaf, Y. & Jones, D. K. Why diffusion tensor MRI does well only some of the time: variance and covariance of white matter tissue microstructure attributes in the living human brain. Neuroimage 89, 35–44 (2014).
Jeurissen, B., Descoteaux, M., Mori, S. & Leemans, A. Diffusion MRI fiber tractography of the brain. NMR Biomed. 32, e3785 (2019).
Brodmann, K. Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde (Johann Ambrosius, 1909).
Glasser, M. F. & Van Essen, D. C. Mapping human cortical areas in vivo based on myelin content as revealed by T1- and T2-weighted MRI. J. Neurosci. 31, 11597–11616 (2011).
Desikan, R. S. et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 31, 968–980 (2006).
Eickhoff, S. B., Heim, S., Zilles, K. & Amunts, K. Testing anatomically specified hypotheses in functional imaging using cytoarchitectonic maps. Neuroimage 32, 570–582 (2006).
Fornito, A., Zalesky, A. & Bullmore, E. Network scaling effects in graph analytic studies of human resting-state fMRI data. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 4, 22 (2010).
Fornito, A., Harrison, B. J., Zalesky, A. & Simons, J. S. Competitive and cooperative dynamics of large-scale brain functional networks supporting recollection. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 12788–12793 (2012).
Yeo, B. T. et al. The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J. Neurophysiol. 106, 1125–1165 (2011).
Power, J. D. et al. Functional network organization of the human brain. Neuron 72, 665–678 (2011).
van den Heuvel, M. P., Stam, C. J., Boersma, M. & Hulshoff Pol, H. E. Small-world and scale-free organization of voxel-based resting-state functional connectivity in the human brain. Neuroimage 43, 528–539 (2008).
Glasser, M. et al. A multi-modal parcellation of human cerebral cortex. Nature 536, 171–178 (2016).
Eickhoff, S. B., Yeo, B. T. T. & Genon, S. Imaging-based parcellations of the human brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 19, 672–686 (2018).
Craddock, R. C. et al. Imaging human connectomes at the macroscale. Nat. Methods 10, 524–539 (2013).
Smith, R. E., Tournier, J. D., Calamante, F. & Connelly, A. SIFT: spherical‐deconvolution informed filtering of tractograms. Neuroimage 67, 298–312 (2013).
Smith, R. E., Tournier, J. D., Calamante, F. & Connelly, A. The effects of SIFT on the reproducibility and biological accuracy of the structural connectome. Neuroimage 104, 253–265 (2015).
Pestilli, F., Yeatman, J. D., Rokem, A., Kay, K. N. & Wandell, B. A. Evaluation and statistical inference for human connectomes. Nat. Methods 11, 1058–1063 (2014).
van den Heuvel, M. P. & Sporns, O. Rich-club organization of the human connectome. J. Neurosci. 31, 15775–15786 (2011).
Wig, G. S. Segregated systems of human brain networks. Trends Cogn. Sci. 21, 981–996 (2017).
Bernhardt, B. C., Smallwood, J., Keilholz, S. & Margulies, D. S. Gradients in brain organization. Neuroimage 251, 1189872022 (2022).
Royer, J. et al. Cortical microstructural gradients capture memory network reorganization in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 146, 3923–3937 (2023).
Jones, D. K. The effect of gradient sampling schemes on measures derived from diffusion tensor MRI: a Monte Carlo study. Magn. Reson. Med. 51, 807–815 (2004).
Le Bihan, D. Diffusion/perfusion MR imaging of the brain: from structure to function. Radiology 177, 328–329 (1990).
Le Bihan, D., Urayama, S. I., Aso, T., Hanakawa, T. & Fukuyama, H. Direct and fast detection of neuronal activation in the human brain with diffusion MRI. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 8263–8268 (2006).
Le Bihan, D. The ‘wet mind’: water and functional neuroimaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 52, R57–R90 (2007).
Le Bihan, D. Diffusion, confusion and functional MRI. Neuroimage 62, 1131–1136 (2012).
Garyfallidis, E. et al. DIPY, a library for the analysis of diffusion MRI data. Front. Neuroinform. 8, 8 (2014).
Hagberg, A. A., Schult, D. A. & Swart, P. J. Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using NetworkX. In Proc. of the 7th Python in Science Conference (SciPy 2008) (eds. Varoquaux, G., Vaught, T. & Millman, J.) 11–15 (2008).
De Domenico, M., Porter, M. A. & Arenas, A. MuxViz: a tool for multilayer analysis and visualization of networks. J. Complex Netw. 3, 159–176 (2015).
Krzywinski, M. I. et al. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 19, 1639–1645 (2009).
Shamir, I. & Assaf, Y. An MRI-based, data-driven model of cortical laminar connectivity. Neuroinformatics 19, 205–218 (2021).
Shamir, I., Tomer, O., Krupnik, R. & Assaf, Y. Modelling the laminar connectome of the human brain. Brain Struct. Funct. 227, 2153–2165 (2022).
Callaghan, P. T. Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy (Oxford Univ. Press, 1993).
Le Bihan, D. Diffusion and Perfusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Applications to Functional MRI (Raven Press, 1995).
Pierpaoli, C. & Basser, P. J. Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn. Reson. Med. 36, 893–906 (1996).
Basser, P. J., Mattiello, J. & LeBihan, D. MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys. J. 66, 259–267 (1994).
Pierpaoli, C., Jezzard, P., Basser, P. J., Barnett, A. & Di Chiro, G. Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201, 637–648 (1996).
Basser, P. J. & Pierpaoli, C. A simplified method to measure the diffusion tensor from seven MR images. Magn. Reson. Med. 39, 928–934 (1998).
Tournier, J. D., Mori, S. & Leemans, A. Diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Magn. Reson. Med. 65, 1532–1556 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Note and Table 1.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shamir, I., Assaf, Y. Tutorial: a guide to diffusion MRI and structural connectomics. Nat Protoc 20, 317–335 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-024-01052-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-024-01052-5
This article is cited by
-
Multimodal brain network topology and enhanced computer-aided diagnosis in Parkinson’s Disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
npj Digital Medicine (2026)
-
The influence of psychosocial stress on functional connectivity and neuroendocrine markers in adolescents with depressive and comorbid anxiety disorders: a study protocol
BMC Psychiatry (2025)
-
Genetic and striatal structural connection linking behavioral inhibition/activation system to adolescent anxiety and depression
Translational Psychiatry (2025)
-
Enhanced structural brain connectivity analyses using high diffusion-weighting strengths
Brain Structure and Function (2025)
-
Extracellular vesicles from antler blastema progenitor cells reverse bone loss and mitigate aging-related phenotypes in mice and macaques
Nature Aging (2025)