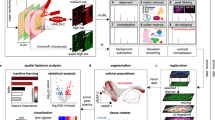
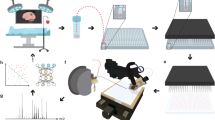
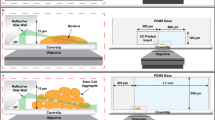
Abstract
Nanospray desorption electrospray ionization (nano-DESI) is a liquid extraction-based ambient ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) technique that enables quantitative molecular mapping of biological samples in their native state with high spatial resolution. To facilitate the wider adoption of nano-DESI MSI by the scientific community, we have developed a robust and user-friendly microfluidic probe (MFP). The probe has been used to achieve high spatial resolution of 8–10 µm and up to 10-fold improvement in the experimental throughput, enabling imaging of large tissue sections with cellular resolution. Here, we provide detailed instructions for designing, fabricating and operating MFPs. In addition, we describe a complete workflow for nano-DESI MSI, covering every step from probe assembly to data acquisition and analysis. Although the fabrication of MFPs requires expertise in microfluidics and can take a few days, the process can be outsourced to qualified companies for manufacturing. Once the MFP is fabricated, the entire imaging workflow can be completed in several hours, depending on the sample size. For example, a sample with an area of 1 cm² can be analyzed in <10 h at a spatial resolution of 10 µm. The exceptional performance and ease of use of these probes will make high-resolution nano-DESI MSI more accessible to the scientific community.
Key points
-
This protocol covers the fabrication of the microfluidic probe via photolithography and selective laser-assisted etching, its assembly, and the nano-DESI MSI experiments for imaging different types of tissue.
-
An alternative method is matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) that shows poor fragmentation of singly charged protein ions. DESI is an ambient ionization method that generates multiply charged protein ions, facilitating protein identification.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
The LabVIEW programs are available upon request. The MSIGen program can be accessed through GitHub at https://github.com/LabLaskin/MSIGen.
References
Buchberger, A. R., DeLaney, K., Johnson, J. & Li, L. Mass spectrometry imaging: a review of emerging advancements and future insights. Anal. Chem. 90, 240–265 (2018).
Norris, J. L. & Caprioli, R. M. Analysis of tissue specimens by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry in biological and clinical research. Chem. Rev. 113, 2309–2342 (2013).
Chughtai, K. & Heeren, R. M. A. Mass spectrometric imaging for biomedical tissue analysis. Chem. Rev. 110, 3237–3277 (2010).
Wu, C., Dill, A. L., Eberlin, L. S., Cooks, R. G. & Ifa, D. R. Mass spectrometry imaging under ambient conditions. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 32, 218–243 (2013).
Lanni, E. J., Rubakhin, S. S. & Sweedler, J. V. Mass spectrometry imaging and profiling of single cells. J. Proteom. 75, 5036–5051 (2012).
Boxer, S. G., Kraft, M. L. & Weber, P. K. Advances in imaging secondary ion mass spectrometry for biological samples. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 38, 53–74 (2009).
Römpp, A. & Spengler, B. Mass spectrometry imaging with high resolution in mass and space. Histochem. Cell Biol. 139, 759–783 (2013).
Prideaux, B. & Stoeckli, M. Mass spectrometry imaging for drug distribution studies. J. Proteom. 75, 4999–5013 (2012).
Watrous, J. D. & Dorrestein, P. C. Imaging mass spectrometry in microbiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 9, 683–694 (2011).
Vaysse, P. M., Heeren, R. M. A., Porta, T. & Balluff, B. Mass spectrometry imaging for clinical research—latest developments, applications, and current limitations. Analyst 142, 2690–2712 (2017).
Chung, H., Huang, P., Chen, C., Lee, C. & Hsu, C. Next‐generation pathology practices with mass spectrometry imaging. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 42, 2446–2465 (2023).
Holbrook, J. H., Kemper, G. E. & Hummon, A. B. Quantitative mass spectrometry imaging: therapeutics & biomolecules. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 60, 2137–2151 (2024).
de Rond, T., Danielewicz, M. & Northen, T. High throughput screening of enzyme activity with mass spectrometry imaging. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 31, 1–9 (2015).
Taira, S., Uematsu, K., Kaneko, D. & Katano, H. Mass spectrometry imaging: applications to food science. Anal. Sci. 30, 197–203 (2014).
Caprioli, R. M., Farmer, T. B. & Gile, J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 69, 4751–4760 (1997).
Wiseman, J. M., Ifa, D. R., Song, Q. & Cooks, R. G. Tissue imaging at atmospheric pressure using desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) mass spectrometry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 7188–7192 (2006).
Giesen, C. et al. Highly multiplexed imaging of tumor tissues with subcellular resolution by mass cytometry. Nat. Methods 11, 417–422 (2014).
Laskin, J., Heath, B. S., Roach, P. J., Cazares, L. & Semmes, O. J. Tissue imaging using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization sass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 84, 141–148 (2012).
Sampson, J. S., Hawkridge, A. M. & Muddiman, D. C. Generation and detection of multiply-charged peptides and proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (MALDESI) Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 17, 1712–1716 (2006).
Nemes, P. & Vertes, A. Laser ablation electrospray ionization for atmospheric pressure, in vivo, and imaging mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 79, 8098–8106 (2007).
Liu, Q., Guo, Z. & He, L. Mass spectrometry imaging of small molecules using desorption/ionization on silicon. Anal. Chem. 79, 3535–3541 (2007).
Roach, P. J., Laskin, J. & Laskin, A. Nanospray desorption electrospray ionization: an ambient method for liquid-extraction surface sampling in mass spectrometry. Analyst 135, 2233–2236 (2010).
Yang, M. et al. Nano-DESI mass spectrometry imaging of proteoforms in biological tissues with high spatial resolution. Anal. Chem. 95, 5214–5222 (2023).
Unsihuay, D. et al. High-resolution imaging and identification of biomolecules using Nano-DESI coupled to ion mobility spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1186, 339085 (2021).
Li, X. et al. High-throughput Nano-DESI mass spectrometry imaging of biological tissues using an integrated microfluidic probe. Anal. Chem. 94, 9690–9696 (2022).
Huffstutler, C. D. et al. Multiple selected ion monitoring mode for sensitive imaging of eicosanoids in tissues using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization (nano-DESI) mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 491, 117101 (2023).
Unsihuay, D. et al. Imaging and analysis of isomeric unsaturated lipids through online photochemical derivatization of carbon-carbon double bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 7559–7563 (2021).
Hale, O. J. & Cooper, H. J. Native mass spectrometry imaging of proteins and protein complexes by Nano-DESI. Anal. Chem. 93, 4619–4627 (2021).
Lillja, J. & Lanekoff, I. Quantitative determination of sn-positional phospholipid isomers in MSn using silver cationization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 414, 7473–7482 (2022).
Iqfath, M., Wali, S. N., Amer, S., Hernly, E. & Laskin, J. Nanospray desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging (nano-DESI MSI): a tutorial review. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 4, 475–487 (2024).
Yin, R., Burnum-Johnson, K. E., Sun, X., Dey, S. K. & Laskin, J. High spatial resolution imaging of biological tissues using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 14, 3445–3470 (2019).
Li, X. et al. An integrated microfluidic probe for mass spectrometry imaging of biological samples. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 22388–22391 (2020).
Li, X., Hu, H. & Laskin, J. High-resolution integrated microfluidic probe for mass spectrometry imaging of biological tissues. Anal. Chim. Acta 1279, 341830 (2023).
Jiang, L. X. et al. A monolithic microfluidic probe for ambient mass spectrometry imaging of biological tissues. Lab Chip 23, 4664–4673 (2023).
Weigand, M. R. et al. Lipid isobar and isomer imaging using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization combined with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 96, 2975–2982 (2024).
Duncan, K. D. & Lanekoff, I. Spatially defined surface sampling capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 91, 7819–7827 (2019).
Jiang, L.-X. et al. Nanospray desorption electrospray ionization (Nano-DESI) mass spectrometry imaging with high ion mobility resolution. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 34, 1798–1804 (2023).
Duncan, K. D. et al. Quantitative mass spectrometry imaging of prostaglandins as silver ion adducts with nanospray desorption electrospray ionization. Anal. Chem. 90, 7246–7252 (2018).
Weigand, M. R., Yang, M., Hu, H., Zensho, C. & Laskin, J. Enhancement of lipid signals with ammonium fluoride in negative mode Nano-DESI mass spectrometry imaging. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 478, 116859 (2022).
Mavroudakis, L. & Lanekoff, I. Identification and imaging of prostaglandin isomers utilizing MS3 product ions and silver cationization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 34, 2341–2349 (2023).
Soltwisch, J. et al. MALDI-2 on a trapped ion mobility quadrupole time-of-flight instrument for rapid mass spectrometry imaging and ion mobility separation of complex lipid profiles. Anal. Chem. 92, 8697–8703 (2020).
Kompauer, M., Heiles, S. & Spengler, B. Autofocusing MALDI mass spectrometry imaging of tissue sections and 3D chemical topography of nonflat surfaces. Nat. Methods 14, 1156–1158 (2017).
Kompauer, M., Heiles, S. & Spengler, B. Atmospheric pressure MALDI mass spectrometry imaging of tissues and cells at 1.4-μm lateral resolution. Nat. Methods 14, 90–96 (2016).
Niehaus, M., Soltwisch, J., Belov, M. E. & Dreisewerd, K. Transmission-mode MALDI-2 mass spectrometry imaging of cells and tissues at subcellular resolution. Nat. Methods 16, 925–931 (2019).
Prentice, B. M. Imaging with mass spectrometry: which ionization technique is best? J. Mass Spectrom. 59, e5016 (2024).
Ryan, D. J., Spraggins, J. M. & Caprioli, R. M. Protein identification strategies in MALDI imaging mass spectrometry: a brief review. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 48, 64–72 (2019).
Slijkhuis, N. et al. Identifying lipid traces of atherogenic mechanisms in human carotid plaque. Atherosclerosis 385, 117340 (2023).
Duncan, K. D. & Lanekoff, I. Oversampling to improve spatial resolution for liquid extraction mass spectrometry imaging. Anal. Chem. 90, 2451–2455 (2018).
Weigand, M. R. et al. Imaging of N-linked glycans in biological tissue sections using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization (nano-DESI) mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 34, 2481–2490 (2023).
Nguyen, S. N. et al. Towards high-resolution tissue imaging using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry coupled to shear force microscopy. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 29, 316–322 (2018).
Nguyen, S. N., Liyu, A. V., Chu, R. K., Anderton, C. R. & Laskin, J. Constant-distance mode nanospray desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging of biological samples with complex topography. Anal. Chem. 89, 1131–1137 (2017).
Lanekoff, I. et al. Automated platform for high-resolution tissue imaging using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 84, 8351–6 (2012).
Yang, M. et al. Proteoform‐selective imaging of tissues using mass spectrometry**. ngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202200721 (2022).
Hale, O. J., Hughes, J. W. & Cooper, H. J. Simultaneous spatial, conformational, and mass analysis of intact proteins and protein assemblies by nano-DESI travelling wave ion mobility mass spectrometry imaging. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 468, 116656 (2021).
Sisley, E. K., Hale, O. J., Styles, I. B. & Cooper, H. J. Native ambient mass spectrometry imaging of ligand-bound and metal-bound proteins in rat brain. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 2120–2128 (2022).
Unsihuay, D. et al. Imaging of triglycerides in tissues using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization (Nano-DESI) mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 448, 116269 (2020).
Nguyen, K., Carleton, G., Lum, J. J. & Duncan, K. D. Expanding spatial metabolomics coverage with lithium-doped nanospray desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging. Anal. Chem. 96, 18427–18436 (2024).
Mavroudakis, L., Duncan, K. D. & Lanekoff, I. Host–guest chemistry for simultaneous imaging of endogenous alkali metals and metabolites with mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 94, 2391–2398 (2022).
Gosline, S. J. C. et al. Proteome mapping of the human pancreatic islet microenvironment reveals endocrine–exocrine signaling sphere of influence. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 22, 100592 (2023).
Jiang, L., Hilger, R. T. & Laskin, J. Hardware and software solutions for implementing nanospray desorption electrospray ionization (nano‐DESI) sources on commercial mass spectrometers. J. Mass Spectrom. 59, e5065 (2024).
Hernly, E., Hu, H. & Laskin, J. MSIGen: an open-source Python package for processing and visualizing mass spectrometry imaging data. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 35, 2315–2323 (2024).
Jiang, L.-X., Yang, M., Wali, S. N. & Laskin, J. High-throughput mass spectrometry imaging of biological systems: current approaches and future directions. Trends Anal. Chem. 163, 117055 (2023).
Acknowledgements
L.-X.J., X.L. and J.L. acknowledge support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) awards RF1MH128866 (BICCN), R01MH136394 and UH3CA255132 (HuBMAP) along with support from the National Science Foundation (NSF-2108729 and 2333734). M.P. and D.B. acknowledge funding by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation; FOR 2177-251124697). We are grateful to J. Chen, C. Matthews and M. Campbell-Thompson (Department of Pathology, Immunology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Florida) and Y. Zhu and P. Piehowski (Pacific Northwest National Laboratory) for providing human pancreatic tissue sections. We thank M. Yang from Purdue University for sectioning mouse brain tissue and J. H. Park from the Birck Nanotechnology Center at Purdue University for helpful discussions and technical assistance with the development of the photomask.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L. and X.L. developed the iMFP procedure. J.L., D.B., L.-X.J. and M.P. developed the SLE-MFP procedure. X.L. and L.-X.J. performed imaging experiments and processed the data. J.L. and D.B. conceived the study and acquired funding. L.-X.J. and J.L. co-wrote the manuscript with assistance from X.L., D.B. and M.P.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Protocols thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Key references
Jiang, L. X. et al. Lab Chip 23, 4664–4673 (2023): https://doi.org/10.1039/D3LC00637A
Li, X. et al. Anal. Chim. Acta 1279, 341830 (2023): https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2023.341830
Li, X. et al. Anal. Chem. 94, 9690–9696 (2022): https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01093
Li, X. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 22388–22391 (2020): https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202006531
This protocol is an extension to: Nat. Protoc. 14, 3445–3470 (2019): https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0237-4
Supplementary information
Supplementary Table 1
3D CAD design file for the SLE-MFP.
Supplementary Table 2
3D CAD design file for the SLE-MFP holder.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, LX., Li, X., Polack, M. et al. High-spatial-resolution mass spectrometry imaging of biological tissues using a microfluidic probe. Nat Protoc 21, 18–36 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-025-01188-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-025-01188-y