Abstract
Actinomycetes are a highly diverse group of microorganisms that have long been recognized as a valuable source of antibiotics and other bioactive metabolites. Recent advances in genome mining have revealed a wealth of previously unexplored silent secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters (smBGCs) in actinomycete genomes, underscoring their untapped bioactivity potential. Here, we present the genome sequences of 211 actinomycete strains isolated from various environmental sources, generated through high-throughput sequencing. The resulting genome assemblies exhibit high completeness and accuracy, offering high-quality data for downstream analyses and biological resource exploration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background & Summary
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has emerged as a critical global public health threat, exacerbated by the overuse and misuse of antibiotics, leading to the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This resistance results in treatment failures, rendering certain life-threatening infections untreatable. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), AMR is projected to become a leading cause of death worldwide by 2050, with an estimated 10 million deaths annually1,2,3. Antibiotic resistance poses a significant risk not only to individual health but also to global health and economic stability. Consequently, the discovery of novel antibiotics, especially those targeting multidrug-resistant bacteria, has become an urgent global priority.
Actinomycetes, a diverse group of microorganisms, have long been a cornerstone in the discovery of antibiotics4. These bacteria are distributed across various environments, including soil, wetlands, and marine ecosystems, where their broad distribution and environmental adaptability confer substantial genetic diversity5. This genetic diversity enables actinomycetes to thrive across different ecological niches, providing a valuable reservoir for discovering new antibiotics. Marine-derived actinomycetes, in particular, face unique ecological pressures—such as spatial competition, predation, and extreme environmental conditions—leading to the evolution of distinctive biochemical pathways and bioactive compounds not found in their terrestrial counterparts. These traits suggest that marine actinomycetes may hold untapped potential for antibiotic discovery6,7. Exploring actinomycetes from diverse habitats offers the opportunity to discover natural products with broad-spectrum antimicrobial, antifungal, and antiviral properties, with significant applications in clinical medicine, agriculture, and pest control4.
However, many potential antibiotic biosynthesis gene clusters in actinomycetes remain dormant under standard laboratory conditions. Recent research has uncovered numerous “silent gene clusters” in their genomes, which are not expressed during routine cultivation, limiting their discovery potential8,9. Streptomyces, the largest genus of actinomycetes, harbors 25 to 50 biosynthetic gene clusters per genome, but up to 90% of these clusters remain inactive under conventional laboratory conditions. Despite the vast biosynthesis potential encoded in actinomycete genomes, much of it remains untapped under natural growth conditions10,11,12. While substantial genomic resources from soil-derived actinomycetes have been accumulated13,14, the genomic data from actinomycetes originating from other environments remain limited, constraining the broader application of gene cluster activation strategies. Therefore, exploring the diversity of actinomycetes from various ecosystems is crucial for uncovering new biosynthetic pathways and advancing antibiotic discovery.
In this study, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of the high-quality genome sequences of 221 actinomycete strains collected from diverse sampling sites and environments, aiming to providing a valuable dataset for downstream analyses and biological resource exploration. The average sequencing depth of the 211 actinomycetes genomes was approximately 328X, with at least 95% completeness and less than 5% contamination level, indicating high-quality genome sequencing and assembly. Through genome alignment and classification, our study revealed that all 211 strains belong to the phylum Actinomycetota and the class Actinomycetes, encompassing four orders, eleven families, twenty genera, and seventy-six known species. The most abundant families identified were Streptomycetaceae (n = 134), Micromonosporaceae (n = 25), and Microbacteriaceae (n = 14). Additionally, 32 actinomycete strains could not be assigned to any defined species in the Genome Taxonomy Database (GTDB). These unclassified strains may possess genomic features and metabolic potentials distinct from known actinomycetes, and their uniqueness presents opportunities for further research. In conclusion, the diverse origins of the actinomycetes render this dataset highly representative, highlighting the extensive diversity and unexplored potential of these microorganisms. It offers a valuable resource for research in natural product discovery, environmental microbiology, and biotechnology, and facilitates the identification of novel secondary metabolites and a more comprehensive understanding of microbial bioactivity.
Methods
Sample collection, isolation, and culture of microbes
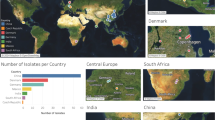
Samples were systematically collected over the course of 14 regularly scheduled sampling trips, spanning a period of 20 years from September 2001 to September 2021, across China and Vietnam. Sample collection encompassed a wide range of environmental sources, with the majority derived from mangrove sediment (77 samples), mountain soil (33 samples), and sponge homogenate (29 samples). Additional sources included seawater, sediment, rhizosphere soil, gut, and others (Fig. 1, Supplementary Table S1).
Map of Sample Collection Sites (a) and overview of the sample sources (b). (a) This map shows the geographic distribution of sample collection sites in southern China (including Guangxi, Guangdong, and Hainan) and Vietnam. The size of the red dots is proportional to the number of samples collected at each site (small dot: 10 samples; medium dot: 20 samples; large dot: 30 samples). A legend is provided in the upper right corner to explain the relationship between dot size and sample quantity. Provincial and national names are labeled in blue text, and a compass rose and scale bar (1000 km) are included for geographic reference. (b) The distribution of sample sources. The x-axis denotes the sources from which samples were isolated, while the y-axis indicates the total number of samples collected.
Soil, rhizosphere, and sea sand samples were systematically collected using a multi-point strategy, combining five random sampling points into a composite sample. Surface soil was collected from 0–10 cm depths with shovels and trowels, while rhizosphere soil was obtained by dislodging adhered soil from plant roots. Sea sand was collected from the surface layer. Seawater samples were collected after triple-rinsing bags in situ to ensure sterility. Marine organisms were processed by homogenizing tissues or isolating gut contents; approximately 1 g of tissue was homogenized in sterile seawater and serially diluted for analysis. All procedures adhered to aseptic techniques, with methods tailored to sample source. This approach ensures the integrity and representativeness of samples for subsequent microbiological isolation.
Actinomycete strains were isolated using the spread plate technique15 on 2216E agar (Hopebio, Qingdao, China) and Gauze’s agar (Hopebio, Qingdao, China). The 2216E agar was prepared with the following ingredients (g/L): peptone 5.0 g, yeast extract 1.0 g, ferric citrate 0.1 g, sodium chloride 19.45 g, magnesium chloride 5.98 g, sodium sulfate 3.24 g, calcium chloride 1.8 g, potassium chloride 0.55 g, sodium carbonate 0.16 g, potassium bromide 0.08 g, strontium chloride 0.034 g, boric acid 0.022 g, sodium silicate 0.004 g, sodium fluoride 0.0024 g, sodium nitrate 0.0016 g, and disodium hydrogen phosphate 0.008 g, with a pH value of 7.6 ± 0.2. The Gauze’s agar was composed of (g/L): potassium nitrate 1.0, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5, magnesium sulfate 0.5, ferrous sulfate 0.01, sodium chloride 0.5, soluble starch 20.0, and agar 15.0, with a pH value of 7.2–7.4. Plates were incubated at 28 °C for 7–14 days to allow colony formation. The selection of distinct colonies involved a careful visual examination of the colonies that had formed on the agar plates. Colonies differing in color, size, shape, elevation, surface characteristics, margin shape, and glossiness were all considered. These differences indicated potential genetic or phenotypic variations among the actinomycete strains. Using a sterile inoculating loop or needle, each visibly distinct colony was individually picked from the original agar plate and transferred to a fresh 2216E agar plate. Purified isolates were identified by 16S rDNA PCR analysis. For long-term storage, isolates were preserved in glycerol stocks at −80 °C.
Genomic DNA extraction and high-throughput sequencing
Isolates were cultured in 2216E broth at 28 °C for 36–48 hours. Cells in the mid-log phase (typically after 36–48 hours) were harvested by centrifugation at 4,000 rpm for 10 minutes. Genomic DNA was extracted using the TIANamp Bacteria DNA Kit (a spin column - based kit, Tiangen, China). Quality was assessed via spectrophotometer-measured A260/A280 (1.7–2.0) and A260/A230 (2.0–2.2) ratios, and integrity was checked by agarose gel electrophoresis. Sequencing libraries were prepared using the Illumina TruSeq DNA Sample Preparation Kit: genomic DNA was sonicated, followed by end-repair, A-tailing, and ligation of Illumina adapters, with magnetic bead purification and size selection. PCR amplification was performed using the KAPA HiFi HotStart DNA Polymerase with the Illumina TruSeq DNA Sample Preparation Kit, typically with 15 cycles, which is crucial for high GC content organisms. The PCR product was then purified and resuspended in Elution Buffer. Library concentration and size were detected using Qubit 4.0 and QSep400. Qualified libraries were sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq6000 platform: denatured with NaOH to single strands, diluted, hybridized to FlowCell adapters, amplified via bridge PCR on cBot, and then sequenced.
Genome assembly
Quality control of the raw sequencing data was conducted using Fastp (v0.12.0)16 with default parameters. Reads containing adapter sequences, those with more than five ambiguous bases (N), and low-quality reads (defined as reads where over 40% of bases have a quality score below 15) were excluded. The genomes of the cultivated isolates were assembled using Unicycler (v0.5.0)17 with the default parameters and only contigs ≥500 bp were retained. Unicycler functions as a SPAdes-optimiser when given short-read only sets. The completeness, contamination and strain heterogeneity of each genome were evaluated using the module ‘lineage_wf’ of CheckM (v1.2.1)18.
After quality control, a total of 460.49 Gbp of clean, high-quality data were retained for further analysis, with 97.67% of bases achieving a quality score of ≥ 20 and an average yield of 2.18 Gbp per sample (Supplementary Table S2). The full lengths of the 211 assembled genomes ranged from 2,462,157 to 14,777,510 bp, with an average length of 7,350,478 bp. The N50 values ranged from 58,110 to 2,055,415 bp, with an average length of 196,859 bp. The average sequencing depth across the 211 genomes was approximately 328X, with coverage ranging from 148X to 1485X. The first and third quartiles were 244X and 343X, respectively. The number of contigs per genomes ranged from 7 to 368, with an average of 109. All of the 211 genomes exhibited a completeness of at least 95% and a contamination level below 5%, meet the criteria of completeness and contamination defined in MISAG’s high-quality genomes (completeness >90% and contamination <5%)19 (Supplementary Table S1).
Taxonomic classification
Taxonomic classification of each genome was performed using the Genome Taxonomy Database Toolkit (GTDB-Tk v2.4.0)20 with reference to GTDB release r22021. The phylogenetic affiliation and diversity of the 211 actinomycete strains were determined using the “classify_wf” module in GTDB-TK, which identified 120 bacterial marker genes and constructed multiple sequence alignments based on them.
According to GTDB release r22021, all 211 genomes were classified within the phylum Actinomycetota and class Actinomycetes, encompassing 4 orders, 11 families, 20 genera, and 76 known species. Notably, 32 genomes (15.2%) could not be assigned to any defined species in GTDB, suggesting that these genomes represent novel taxa (Supplementary Table S1).
Genome annotation
Functional annotation of the 211 actinomycete genomes was performed using Prokka v1.14.622 with the default parameters. According to Prokka annotation, the number of CDS per genome ranged from 2,211 to 13,369, with an average of 6,541. The number of rRNA genes ranged from 1 to 6, with an average of 3, while the number of tRNA genes ranged from 43 to 101, with an average of 76 (Supplementary Table S1).
Data Records
The sequencing reads, assembled genomes (e.g., GCA_965341825.123, GCA_965341695.124, GCA_965342205.125) and corresponding sample metadata are available in the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) under Project accession number PRJEB8996626, detailed accession numbers for these genomes are provided in Supplementary Table S3. The data above have also been deposited in the CNGB Sequence Archive (CNSA)27 of the China National GeneBank Database (CNGBdb)28 under project accession number CNP000654329.
Technical Validation
To ensure the technical quality and reliability of the dataset, multiple validation steps were implemented. The extraction process for each sample source was designed to ensure sample integrity for culturable actinomycete isolation. Soil samples were collected from 0–10 cm depths using shovels and trowels, and rhizosphere soil was obtained by dislodging soil from plant roots. Sea sand samples were collected from the surface layer, and seawater samples were collected after triple-rinsing bags in situ. Marine organisms were processed by homogenizing tissues or isolating gut contents, with 1 g of tissue homogenized in sterile seawater and serially diluted. All procedures adhered to aseptic techniques, tailored to the specific sample type, to ensure the quality and reliability of the isolates. Genomic DNA quality was assessed via NanoDrop (A260/280 and A260/230 ratios), Qubit fluorometry, and agarose gel electrophoresis to confirm integrity and purity. DNA library quality was evaluated using Qubit 4.0 and QSep400 for insert size distribution. A total of 460.49 Gbp of high-quality data was generated (Supplementary Table S2). Raw reads underwent quality control using Fastp, with adapter trimming and filtering of low-complexity regions, followed by genome assembly using Unicycler. Assembly quality was validated using CheckM, yielding average completeness ≥95% and contamination <5% (Supplementary Table S1). The complete dataset, including assembly metrics and validation parameters is publicly available in the CNGB Sequence Archive to support reproducibility and community validation.
Code availability
The versions and parameters of all bioinformatics tools used in this study are detailed in the Methods section.
References
Mah, T.-F. Giving antibiotics an assist. Science 372, 1153–1153 (2021).
Tang, K.W.K., Millar, B.C. & Moore, J.E. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). British Journal of Biomedical Science 80 (2023).
Chiș, A. A. et al. Microbial Resistance to Antibiotics and Effective Antibiotherapy. Biomedicines 10, 1121 (2022).
De Simeis, D. & Serra, S. Actinomycetes: A Never-Ending Source of Bioactive Compounds—An Overview on Antibiotics Production. Antibiotics 10, 483 (2021).
Jose, P.A. & Jebakumar, S.R.D. Unexplored hypersaline habitats are sources of novel actinomycetes. Frontiers in Microbiology 5, (2014).
Stincone, P. & Brandelli, A. Marine bacteria as source of antimicrobial compounds. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology 40, 306–319 (2020).
Casertano, M., Menna, M. & Imperatore, C. The Ascidian-Derived Metabolites with Antimicrobial Properties. Antibiotics 9, 510 (2020).
Fayad, A. A. et al. From bugs to drugs: Combating antimicrobial resistance by discovering novel antibiotics. The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries 12, 3S (2018).
Liu, Z., Zhao, Y., Huang, C. & Luo, Y. Recent Advances in Silent Gene Cluster Activation in Streptomyces. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 9 (2021).
Walsh, C. T. & Fischbach, M. A. Natural Products Version 2.0: Connecting Genes to Molecules. Journal of the American Chemical Society 132, 2469–2493 (2010).
Rutledge, P. J. & Challis, G. L. Discovery of microbial natural products by activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters. Nature Reviews Microbiology 13, 509–523 (2015).
Beck, C. et al. Activation and Identification of a Griseusin Cluster in. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 26 (2021).
Sparholt, J. T. et al. A treasure trove of 1034 actinomycete genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 13 (2024).
Bentley, S. D. et al. Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417, 141–147 (2002).
Vijayalakshmi, S., Ramasamy, M. S., Murugesh, S. & Murugan, A. Isolation and screening of marine associated bacteria from Tamil Nadu, Southeast coast of India for potential antibacterial activity. Annals of Microbiology 58, 605–609 (2008).
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y. & Gu, J. fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, i884–i890 (2018).
Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Gorrie, C. L. & Holt, K. E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput Biol 13, e1005595 (2017).
Parks, D. H., Imelfort, M., Skennerton, C. T., Hugenholtz, P. & Tyson, G. W. CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res 25, 1043–1055 (2015).
Bowers, R. M. et al. Minimum information about a single amplified genome (MISAG) and a metagenome-assembled genome (MIMAG) of bacteria and archaea. Nature Biotechnology 35, 725–731 (2017).
Chaumeil, P.-A., Mussig, A. J., Hugenholtz, P. & Parks, D. H. GTDB-Tk v2: memory friendly classification with the genome taxonomy database. Bioinformatics 38, 5315–5316 (2022).
Parks, D. H. et al. A complete domain-to-species taxonomy for Bacteria and Archaea. Nature Biotechnology 38, 1079–1086 (2020).
Seemann, T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30, 2068–2069 (2014).
ENA https://identifiers.org/insdc.gca:GCA_965341825.1 (2025).
ENA https://identifiers.org/insdc.gca:GCA_965341695.1 (2025).
ENA https://identifiers.org/insdc.gca:GCA_965342205.1 (2025).
ENA Bioproject. https://identifiers.org/bioproject:PRJEB89966 (2025).
Guo, X. et al. CNSA: a data repository for archiving omics data. Database (Oxford) 2020 (2020).
Chen, F. Z. et al. CNGBdb: China National GeneBank DataBase. Yi Chuan 42, 799–809 (2020).
Liang, Z. et al. Whole-genome sequences of 211 actinomycete strains from diverse environments: A resource for biosynthetic potential exploration. CNGB https://db.cngb.org/search/project/CNP0006543 (2025).
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Project of Sanya Yazhou Bay Science and Technology City, Grant No: 【SKJC-2024-01-001, SKJC-2024-01-002】. This research was supported by Hainan Yazhou Bay Seed Lab.(JBGS B23YQ2003) and the High-performance Computing Platform of YaZhou Bay Science and Technology City Advanced Computing Center. We also acknowledge the China National GeneBank, BGI Research, Shenzhen 518120, China, for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.C. and Y.H. conceived and supervised the study. Y.L. wrote the manuscript. Y.L. and Z.L. designed the experiments. J.S., X.L., P.J., H.S. and F.C. conducted the experiments. Z.L. analyzed the data. Z.Y. and X.F. reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Liang, Z., Shi, J. et al. Genomes of 211 Actinomycete Strains from Diverse Environments. Sci Data 12, 1225 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-025-05567-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-025-05567-8