Abstract
The replacement of native forest by cattle pastures reduces functional diversity; however, little is known about whether the changes depend on regional variation. Dung beetles are one of the most diverse and functionally important taxa; through organic matter burial, dung beetles improve soil quality. We collected dung beetles in native forests and cattle ranching areas in subtropical forests with contrasting climatic conditions: the Atlantic Forest, the Humid Chaco, and the Dry Chaco. We measured 11 traits related to the ecology and the physiology of species. Irrespectively of the region, functional richness was higher in forests (native and with cattle) when compared to open pastures. Humid forests (Atlantic Forest and Humid Chaco) showed higher functional richness than Dry Chaco. Functional dispersion in humid forests was similar between native forest and livestock systems, however, functional dispersion in the Dry Chaco was higher in open pastures compared to native forest. According to our results, native forests and forests with cattle maintain functional diversity in all regions. However, in the case of open pastures, the response depends on the regional context; the replacement of native forest by open pastures strongly affected functional diversity in humid forests and showed less impact on dry forest.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Livestock is one of the main land uses worldwide, covering more than 25% of the global surface1,2. In the last decades, livestock was one of the principal causes of forest replacement in tropical and subtropical areas3,4. The replacement of native forests by cattle pastures strongly modifies biotic and abiotic conditions, resulting from the loss of tree cover and soil changes5. These changes modify the conditions of environmental filters which in turn affect the abundance, richness, and composition of biological communities and populations6. While livestock activities, mainly by grazing and trampling, in general, negatively affects native communities, the response of species to canopy loss is variable; native or exotic species adapted to open habitats are often positively affected while species requiring denser cover are negatively affected7.
Environmental filtering has been proposed as an assembly-forming mechanism at different scales8. Kraft et al.9 define environmental filtering sensu stricto, as environmental conditions and resources that prevent species with physiological or ecological requirements from establishing or persisting in a specific area. Environmental filters act on species traits, allowing the establishment and persistence of species with certain traits of specific conditions and excluding others9. Consequently, these ecological filters are generally structured hierarchically and select, or filter, a subset of species sharing functional traits from the regional pool, conforming local communities8,10,11. In the particular case of human disturbed-habitats, this mechanism has been proposed as the main driver in the formation of new species assemblages after disturbance12.
Climate acts as a regional filter that guides the distribution of species according to their tolerance to environmental conditions and resources requirements13. In particular, temperature and precipitations have a strong influence on both diversity and abundance patterns14. The role of climate determining functional patterns of diversity at the regional scale has been explored for several taxa, including plants15, insects16, and mammals17; among others. Previous studies in tropical and subtropical areas showed that the rainfall regime is usually the strongest predictor of regional functional diversity patterns at a regional scale18,19. In contrast, at a smaller scale, anthropogenic disturbance imposes local filters modifying the functional structure of local communities beyond changes in species richness20,21.
Dung beetles (Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae) are one of the most diverse taxa and a focal group in ecological studies22. Through organic matter burial, dung beetles have a central role in ecosystem functioning22,23. Considering the central functional role of these taxa, functional diversity provides a useful theoretical background to understand the effects of human land use on ecosystem processes mediated by species. Functional diversity can be comprehensively described using three functional indices. Functional richness (Fric) represents the volume of the functional space occupied by a community24,25. The functional evenness (Feve) measures the uniformity of the distribution of species abundances in the functional space24. Finally, the functional dispersion (Fdis) represents how far species are from the center of the functional space26. Several recent studies have evaluated the effect of livestock on the functional diversity of dung beetles using functional indices27,28,29,30. From these studies, two general patterns emerged. On one side, in humid subtropical and tropical forests with low or no seasonality, functional diversity is strongly and negatively affected by livestock. On the other side, in dry and xerophytic seasonal forests, livestock has lower, or even positive, effects on dung beetle functional diversity.
While previous studies focused on specific ecosystems, for the first time we simultaneously compared the functional response of dung beetles to livestock grazing, in forests with contrasting climatic conditions in the subtropic of Argentina. We also explored the role of local and regional factors influencing local and regional responses to this land uses.
Methods
Study area and experimental design
In this manuscript, we used primary data from a previous study31 and we measured a large database on morphometric and ecological traits for the species considered in this study. Sampling was performed between 2015 and 2017 in the spring season, the time of year with the highest activity of dung beetles in Neotropical forests32.
Three subtropical forest regions were sampled: the Atlantic Forest (AF), the Humid Chaco (HCh), and the Dry Chaco (DCh). According to Köppen's classification, the climate for the Atlantic Forest and Humid Chaco regions is Cfa (warm temperate, fully humid, and hot summers). In the Dry Chaco, the climate is Cwa (warm temperate with dry winter, and hot summer)33. The three regions present similar temperature ranges (20 °C for AF, 22 °C for HCh and 23 °C for DCh) and differ, mainly, in the total amount and seasonal pattern of precipitation: 1600–2000 mm with low seasonality in the Atlantic Forest, 750–1300 mm with medium seasonality in the Humid Chaco and 500–700 mm with high seasonality in the Dry Chaco33,34. In both Humid and Dry Chaco, precipitations are concentrated in spring–summer.
Within each region, we selected five replicates of three habitat types: open pastures with cattle, native forests with cattle, and native forests in protected areas without cattle (for a detailed description see Appendix S1 of Supporting Information). In the habitat type “forest with cattle”, farmers directly introduce cattle inside the forest, without any specific silvicultural management; animals opportunistically feed on native understory vegetation. The habitat type “open pastures” refers to deforested areas with implanted exotic pastures. Replicates within each sampling area were separated by at least 1000 m to reduce their dependence.
Dung beetles collection
For the dung beetle collection, 10 pitfall traps separated by 50 m were installed on each sampling site (three regions × 2 years × three habitats × five replicates × 10 traps = 900 traps). Traps were baited intercalated with human feces and rotting meat to attract coprophagous and necrophagous beetle species23,35. In each area, the sampling time was eight days, and the bait was renovated every 48 h. Species were determined through consultation with specialists and the use of taxonomic keys36. For more details on the collection of dung beetles see31.
Local and regional vegetation structure and environmental conditions
To describe vegetation structure at the local scale, we established three sub-plots of 5 × 15 m on each replicate of each habitat type and region (three plots × three regions × three habitats × five replicates = 135 plots). The three subplots within each replicate were averaged. In each subplot, four variables were estimated based on an abundance Braun-Blanquet's cover scale37 (0–100%) (1979): (1) bare soil, (2) herbaceous vegetation, (3) shrub vegetation, and (4) canopy cover. Automatic sensors (HOBO ProV2) were used to estimate temperature and humidity on each sampling site during field sampling. Automatic sensors recorded both variables every five minutes. From sensors data, the average maximum and minimum daily temperature were calculated. Additionally, the thermal amplitude was calculated by subtracting both minimum and maximum daily temperature. For more details on the local environmental characterization see31.
At the regional scale, three bioclimatic variables were selected and calculated for each sampling site: (a) mean annual temperature (BIO1), (b) mean day range (mean monthly temperature (maximum temperature − minimum temperature)) (BIO2), and (c) seasonality of precipitation (coefficient of variation) (BIO15). These variables were extracted from the WorldClim database38 and represent an average for the period 1970–2000 with a spatial resolution of 30 s (~ 1 km2)38.
Characterization of functional traits
Considering the sexual dimorphism of this taxon, three to 10 females of each species were selected for morphometric description. Individuals were independently selected in each region; in the case of species occurring in more than one region, individuals of each region were measured independently. In total, 448 females from 71 species were measured; 25 species and 131individuals in the Atlantic Forest, 213 individuals of 38 species for the Humid Chaco and for the Dry Chaco, 104 individuals of 23 species (see the data abailability for a complete list of traits). Each individual was photographed in dorsal, ventral, and lateral views (Fig. 1) using a LEICA EZ4 D magnifier and LASEZ software (Leica Application Suite) (version 3.3.0, https://www.leica-microsystems.com/).
Once the images were taken, imageJ software (version 1.49, https://imagej.nih.gov/ij) was used to estimate 10 morphological response traits related to the ecology and physiology of dung beetles: (1) body area, (2) biomass, (3) total length, (4) sphericity, (5) head area, (6) pronotum width, (7) anterior tibia length, (8) anterior tibia area, (9) anterior femur area and (10) tooth width (Fig. 1 and Appendix S2 Supporting Information). Sphericity was calculated using the formula: (S2/LI) 1/3, where L is the total length of the body, I is the width of the elytra, and S is the thickness of the body (Table 1). Biomass was measured using an analytical digital balance with a 0.0001 g precision. The ecological roles that are represented in the traits are shown in Table 1. Additionality, we included the relocation food pattern as a qualitative trait with three categories: telecoprid, paracoprid and endocoprid. This trait is associated with the capacity of manipulation and the amount of organic matter buried by dung beetles and was defined from previous studies39,40,41,42. In total, we used 11 traits.
Statistical analyses
First, a simple regression analysis was performed between each trait and the body area to explore the allometric relationships for species in each region. The allometric analysis was based on the conventional allometric equation Y = aXb, where Y is any morphological trait (dependent variable), X is the body area (independent variable), and a and b are the allometric coefficients43. For those traits that showed significant allometric relationships, residuals of the simple regression models were extracted to create new morphological traits independent of the body area. These corrected variables (regression residuals) were then used for single and multiple trait comparisons44.
Morphological traits in all regions, except the sphericity, were positively and strongly related to the body area (allometric dependence) (Appendix S6—Supporting Information). Therefore, for all morphological variables (except sphericity) the residuals of the allometric relationships were used as independent variables in statistical analysis.
Three indices were used to explore the amount of the functional space occupied by species and its distribution on each region and habitat type, using the ‘FD’ package45. Functional richness (Friq) considers all traits and their values within the functional space, without considering the relative abundance25. Functional evenness (Feve) measures the level of regularity of the functional assemblage; this index distributes abundances within the functional space25. Functional dispersion (Fdis) is the average distance of all species from the centroid of the functional space taking into account relative abundances26; Fdis describes the degree of heterogeneity of functional traits within an assemblage and increases with the number of ecological processes. To estimated functional indices, relocation food was considered a single variable with three levels: telecoprid, paracoprid and endocoprid. For the calculation of the indices, the species distance matrix based on each trait was constructed using the ldist.ktab and dist.ktab functions of the ‘ade4’ package. These functions are based on Gower's46 general distance measure and allow dealing with qualitative and quantitative traits47.
After functional indices estimation, generalized linear mixed models (GLMM) were performed to explore the effects of region and habitat types (explanatory variables) on functional diversity (Friq, Feve, and Fdis). To evaluate the assumption of spatial independence of observations, the Moran's index I48 (Moran, 1950) was calculated for the residuals of GLMM analysis as an overall measure of spatial autocorrelation; using SAM (version v4.0, https://ecoevol.ufg.br/sam/). Since no autocorrelation of the residuals was observed in any of the three models (Friq, Feve, and Fdis), geographical coordinates of sampling sites were not included in GLMM analysis (Appendix S3—Supporting Information).
To explore the role of local and regional environmental variables to explain patterns of functional diversity, three independent principal component analyses (PCAs) were first conducted to reduce the number of explanatory variables. Then, the first axis of each PCA was used as fixed factors in the GLMMs as explanatory variables. The first PCA was performed with local vegetation structure: canopy cover, shrub cover, herb cover, and bare soil cover. The second with local microclimatic conditions: thermal amplitude, average daily temperature and humidity, and average daily maximum temperature. And the last PCA with regional climatic variables: average annual temperature, average daytime temperature range, seasonality of precipitation. Normality and homocedasticity were evaluated through residuals vs. predicted and qqnorm plots. Finally, each model was compared with its respective null model to determine the significance of the factors analyzed. Collinearity between the first axis of each PCA (predictor variables of the models) was evaluated through the vif function of the ‘car’ package49.
To describe changes in the functional structure of dung beetles assemblages, the per-site weighted mean of each trait (CWM)50 was calculated with the functcomp function of the ‘FD’ package45. Two matrices were constructed, one with the abundance of individuals of each species per site (replicate), and the other with the functional traits of each species. Based on these matrices, a new matrix was generated with the values of the traits per site. From this new matrix, the variation explained by space (spatial coordinates) and environmental variables was estimated through variation partition analysis with the varpart function of the ‘vegan’ package51. To calculate the cwm, relocation food was considered three different variables (proportion of telecoprids, endocoprids, and paracoprids).
The partitioning of the variation showed that the spatial structure of the data had only a small influence on the variation in trait structure among habitat types and regions (7%) (see Appendix S4—Supporting Information); consequently, the spatial location of the sites was excluded as an explanatory variable in further analysis of the functional structure. An RDA analysis was then carried out to evaluate if the ordering of sites according to functional traits from CWMs was associated with environmental variables. This analysis was performed through an ANOVA based on permutations (9999 permutations restricted inside each region) with the ‘vegan’ package51. This analysis used a stepwise variable selection procedure to determine predictors with the highest proportion of explained variation in all models. Prior to the analysis, environmental variables were standardized and transformed with square root to reduce the influence of extreme outliers52. In case of multicollinearity among environmental variables (> 0.6), one of each pair was selected and the other was excluded from the analyses (Appendix S5—Supporting information). Finally, the effect of region, habitat types and the interaction between factors on groups formed was evaluated through a multivariate permutational analysis of variance (PERMANOVA), using the adonis function of the ‘vegan’ package51. Finally, to evaluate how traits vary by region and habitat type, generalized linear mixed models were performed for each trait. Only three traits fit the GLMM assumptions (normality of residuals and homogeneity of variances) the pronotum width, head area and femur area. All statistical analyses were performed in the R software (https://www.R-project.org/).
Results
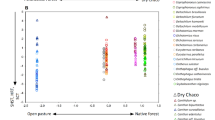
Based on the GLMM analysis, functional richness was higher in native forests and forest with cattle when compared to open pastures (Fig. 2, Table 2). For the regions, the Atlantic Forest and the Humid Chaco showed higher and similar functional richness compared with the Dry Chaco. The functional richness did not show a significant interaction between factors (region × habitat types). Functional evenness (Feve) was similar between regions and habitat types (Table 2) whereas functional dispersion (Fdis) in the Atlantic Forest and the Humid Chaco was similar between native forest and forest with cattle and open pasture. Finally, in the Dry Chaco, Fdis was higher in pastures compared to the native forest whereas forests with cattle represent an intermediate situation (Fig. 2, Table 2).
Dung beetle functional richness and dispersion among different regions and habitat types in subtropical forests of Argentina based on a GLMM analysis. AF: Atlantic Forest, HCH: Humid Chaco, DCH: Dry Chaco. Circles: native forest, triangles: forests with cattle, squares: open pastures. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). Brackets indicate differences in functional richness among regions.
The first axis of the three PCAs performed to reduce the number of explanatory variables (local vegetation structure, local microclimate conditions and regional climate) explained more than 50% of the variation in all cases (Appendix S7—Supporting Information). The GLMM analysis using this first axis of these PCA, showed that the functional richness was mainly explained by local vegetation structure (χ2 = 6.23, P < 0.012), while local microclimate conditions and regional climate had no effect (χ2 = 0.92 and 0.45, respectively, P > 0.1 in both cases). In the case of functional evenness none of the environmental variables explained observed patterns (Vegetation: χ2 = 0.09, P = 0.76; Microclimatic conditions: χ2 = 2.68, P = 0.10; Regional climate: χ2 = 1.22, P = 0.26) same as for Fdis (Vegetation: χ2 = 0.93, P = 0.33; Microclimatic conditions: χ2 = 1.61, P = 0.20; Regional climate: χ2 = 1.37, P = 0.24).
The first axis of the redundancy analysis (RDA) explained 52% of the changes in functional structure (composition and abundance) of dung beetles among regions and habitat types. In this axis, native forest and forests with cattle of the Atlantic Forest and the Humid Chaco formed a single group and separated from the Dry Chaco. The second axis explained 21% of the variation and separated the Atlantic Forest and Humid Chaco pastures from the rest of the sites (Fig. 3). PERMANOVA analysis validated these groups (F Model = 10.84, R2 = 0.52, g. l. = 8, P = 0.0001); according to the region (F = 19.03, R2 = 0.23, g.l. = 2, P = 0.0001), the habitat types (F = 4.52, R2 = 0.05, g.l. = 2, P = 0.0008) and the interaction of both factors (F = 9.90, R2 = 0.24, g.l. = 4, P = 0.0001).
Redundancy analysis based on functional traits of dung beetle assemblages in the native forest and two cattle systems in subtropical forests of Argentina. Black symbols: Atlantic Forest, dark grey symbols: Humid Chaco, light gray symbols: Dry Chaco. Circles: native forest, Triangles: forest with cattle, and Squares: open pasture.
Environmental variables explained 36.32% of changes in the functional structure of RDA formed groups (g.l. = 6, F = 7.88, P = 0.0004). The first axis was negatively associated with local mean temperature, canopy, and shrub cover and was positively associated with seasonality of rainfall, thermal amplitude, and shrub cover. The second axis was positively correlated with mean temperature and negatively with the other variables (Table 3). Native forest and forests with cattle in the Atlantic Forest and Humid Chaco were mainly characterized by a higher canopy and herb cover. In contrast, the Atlantic Forest open pastures were characterized mainly by higher local mean temperature. Finally, sites in the Dry Chaco were associated with higher seasonality of rainfall, thermal amplitude, and shrub cover (Fig. 3).
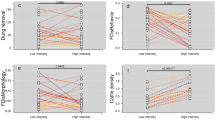
In relation to individual traits, native forest and forest with cattle of the Atlantic Forest and the Humid Chaco were characterized by species with larger head area, pronotum width, tibia, and anterior femur area, and by a higher frequency of endocoprid and paracoprid species (Fig. 3). In contrast, Dry Chaco and the pastures in the Humid Chaco were characterized by species with larger body area, total length, biomass, more spheric, and higher frequency of telecoprids (Fig. 3). Regarding the GLMMs of traits, it is observed that the pronotum width is greater for the Atlantic Forest, and does not differ among habitat types, in the Humid Chaco it is greater in native forests and forests with cattle and smaller in open pasture. In the Dry Chaco pronotum width is lower in native forests and higher in open pastures, being intermediate in forests with cattle. As for the head area in the Atlantic Forest, it is higher in pastures and lower in native forests and forests with cattle. In the Humid Chaco it does not differ among habitat types. In the Dry Chaco the head area is greater in open pastures and forests with cattle and smaller in native forests. As for the femur area in the Atlantic Forest and in the Humid Chaco, it is greater in native forests and forests with cattle and smaller in open pastures. In the Dry Chaco, the femur area is inverted, being smaller in native forests, larger in open pastures and intermediate in forests with cattle (Fig. 4, Table 4).
Pronotum width, head area and femur area of dung beetle among different regions and habitat types in subtropical forests of Argentina based on a GLMM analysis. AF: Atlantic Forest, HCH: Humid Chaco, DCH: Dry Chaco. Circles: native forest, triangles: forests with cattle, squares: open pastures. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
Discussion
While previous studies explored either local or regional functional responses of dung beetles to environmental gradients or human disturbances29,30,53,54,55; this is the first study that simultaneously explore both components through the comparison of similar land uses among different regions. Consistent with previous studies, the replacement of native forest by open pastures strongly reduced functional diversity in humid forest and showed low impact on dry forests27,29,56. In all regions, forests with cattle preserving native canopy also preserve the same functional diversity as native forest 28,57.
Seasonality and the total amount of precipitation were the major differences among regions in this study. Consistent with this pattern, Nichols et al.55, proposed that the functional response of dung beetles to anthropogenic disturbance depends on the regional context whereas da Silva and Cassenote53 proposed that climatic seasonality is the main determinant of functional dung beetles response. Environmental dissimilarity between native habitats and land uses has already been identified as one of the main predictors of changes in biological assemblages at both local and regional scales20,58. The extreme temperatures and simplified vegetation in the open pasture and the low tolerance of native humid forest dung beetles to these conditions may influence the loss of functional (and taxonomic) diversity in both the Atlantic Forest and the Humid Chaco59,60,61,62,63. In contrast to humid forests, in the Dry Chaco, native forests and pastures showed less contrast on environmental conditions and native dung beetles are probably more tolerant to extreme conditions. To sum up, differences in environmental similarity among regions and land uses, and the tolerance of native species to extreme conditions could explain the differences in the functional response of the assemblages between the humid forests (Humid Chaco and Atlantic Forest) and the Dry Chaco.
Similar to our results on forests with cattle, Cerullo et al.57 found that functional richness and dispersion (Fric and Fdis) of Borneo dung beetles in silvopastoral systems were similar to the ones observed in undisturbed forests. These systems, in contrast to open pastures, partially maintain microclimatic and soil conditions, which in turn, would favor the persistence of native species. In addition, other factors regulated by the canopy cover (such as light intensity and heat) may influence the observed patterns of functional diversity of dung beetles between open and closed habitats64,65. Several previous studies have shown the importance of vegetative cover to preserve dung beetle assemblages66,67,68.
The higher functional dispersion in pastures, compared to the native forest, of the dry Chaco suggests that anthropogenic disturbance generates a greater heterogeneity in the distribution of functional trait status; these results coincide with other studies conducted in xerophytic forests in Mexico28 as well as in the Cerrado in Brazil29. As in these previous studies, no evidence was found that cattle ranching reduces the functional richness of dung beetle communities in arid environments. One possible explanation is that the dry Chaco is a semi-arid region, inhabited by species that can use open areas lacking vegetation and can take advantage of the additional manure provided by livestock28,69. Fric and Feve's neutral response to cattle ranching in the dry Chaco could result from the balance between individuals and species loss and gains from adjacent habitats, which result in assemblages of similar functional trait space (Fric), or in the regularity of trait abundance distribution (Feve), regardless of species identity.
In turn, Davis et al.70 concluded that certain functional traits, such as the ability to roll balls, predominate in arid regions. Consistent with this pattern, rolling ball species (telecoprid) predominate in the Dry Chaco whereas in humid forests paracoprid and endocoprid predominate. The loss of canopy and the high thermal amplitude given in open pastures increase the drying rate of dung in open pastures and (particularly in open pastures of the Dry Chaco). Since dung beetles depend on the liquid component of dung for feeding, the water loss in dung paths reduces food quality and may explain the low abundance of endocoprid species in this habitat (dung beetles inhabiting inside dung paths). The absence of paracoprid species in pastures could be associated with the higher temperature and compaction as well as lower soil moisture in these habitats, leading to rapid drying of the manure and obstructing the handling and burying of the resource in the soil. On the other hand, telecoprid beetles have the ability to transfer the food to a more suitable place for burial and may therefore be able to persist in open habitats71.
Regarding the observed traits, for the most humid regions (Atlantic Forest and Humid Chaco), species with large femurs were typical forests (with and without cattle), which is probably associated with the ability of certain species to bury organic matter and the paracoprid's ability to tunnel. On the other hand, and contrary to what we expected and to previous studies72, the presence of large species with bodies, pronotum, heads and femurs larger in open pastures of the Dry Chaco can be associated to the thermoregulatory capacity of certain species, or the nocturnal or crepuscular activity which would enable them to make use of open habitats73,74. These morphological characteristics allow them a greater burial capacity in arid soils exposed to extreme temperatures and with little vegetation, which generates a decrease in water content in soils and consequently greater hardness75.
The opportunistic and extensive introduction of cattle inside the forest is an extended practice in humid and dry tropical and subtropical forests (namely forest with cattle in our study)56,76,77. Whereas this practice usually results in a degradation of habitat quality for animals78,79, functional dung beetle assemblages were not particularly affected by this livestock grazing. As we previously mentioned, the maintenance of canopy cover (particularly in humid forests) is the key management tool to maintain dung beetles diversity and their functional roles.
According to our results, as well as with a growing amount of recent evidence, the functional response of dung beetle assemblages to livestock grazing cannot be generalized for all biomes. Regional climate, the interaction between scales (local and regional), and the environmental similarity between native habitats and land uses are the major determinants of this response. In addition to taxonomic diversity, the preservation of functional diversity is of central importance to maintaining ecosystem functioning80,81. This is particularly important in livestock areas considering the central role of dung beetles in manure processing82. The results of this study provide a basis for future questions regarding the knowledge of how functional processes may be affected by changes in functional diversity in subtropical forests and how these changes may vary depending on the region and livestock grazing. In turn, these results contribute to the knowledge needed for decision-making in terms of biodiversity conservation in subtropical forests affected by land uses, in particular livestock grazing.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the Figshare repository. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.13313186.v4.
References
Herrero, M. et al. Livestock and the environment: What have we learned in the past decade?. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 40, 177–202 (2015).
Robinson, T. P. et al. Mapping the global distribution of livestock. PLoS ONE 9, e96084 (2014).
Firbank, L. G., Petit, S., Smart, S., Blain, A. & Fuller, R. J. Assessing the impacts of agricultural intensification on biodiversity: A British perspective. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 363, 777–787 (2007).
Laurance, W. F., Sayer, J. & Cassman, K. G. Agricultural expansion and its impacts on tropical nature. Trends Ecol. Evol. 29, 107–116 (2014).
Steinfeld, H., de Haan, C. & Blackburn, H. Livestock—Environment Interactions 88 (WRENmedia, 1997).
Eldridge, D. J., Poore, A. G. B., Ruiz-Colmenero, M., Letnic, M. & Soliveres, S. Ecosystem structure, function, and composition in rangelands are negatively affected by livestock grazing. Ecol. Appl. 26, 1273–1283 (2016).
Schieltz, J. M. & Rubenstein, D. I. Evidence based review: Positive versus negative effects of livestock grazing on wildlife. What do we really know?. Environ. Res. Lett. 11, 113003 (2016).
Cornwell, W. K. & Ackerly, D. D. Community assembly and shifts in plant trait distributions across an environmental gradient in coastal California. Ecol. Monogr. 79, 109–126 (2009).
Kraft, N. J. B. et al. Community assembly, coexistence and the environmental filtering metaphor. Funct. Ecol. 29, 592–599 (2015).
Keddy, P. A. Assembly and response rules: Two goals for predictive community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 3, 157–164 (1992).
Pärtel, M., Zobel, M., Zobel, K., van der Maarel, E. & Partel, M. The species pool and its relation to species richness: Evidence from Estonian plant communities. Oikos 75, 111–117 (1996).
Temperton, V., Hobbs, R. J., Nuttle, T. & Halle, S. Assembly Rules and Restoration Ecology. Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Practice (Island Press, 2004).
Leibold, M. A. Similarity and local co-existence of species in regional biotas. Evol. Ecol. 12, 95–110 (1998).
Hortal, J. et al. Ice age climate, evolutionary constraints and diversity patterns of European dung beetles: Ice age determines European scarab diversity. Ecol. Lett. 14, 741–748 (2011).
de Bello, F., Lepš, J. & Sebastià, M.-T. Variations in species and functional plant diversity along climatic and grazing gradients. Ecography 29, 801–810 (2006).
Reymond, A., Purcell, J., Cherix, D., Guisan, A. & Pellissier, L. Functional diversity decreases with temperature in high elevation ant fauna: Functional diversity in high elevation ant. Ecol. Entomol. 38, 364–373 (2013).
Safi, K. et al. Understanding global patterns of mammalian functional and phylogenetic diversity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 366, 2536–2544 (2011).
Mason-Romo, E. D., Farías, A. A. & Ceballos, G. Two decades of climate driving the dynamics of functional and taxonomic diversity of a tropical small mammal community in western Mexico. PLoS ONE 12, e0189104 (2017).
Wen, Z. et al. Functional diversity overrides community-weighted mean traits in linking land-use intensity to hydrological ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 682, 583–590 (2019).
Corbelli, J. M. et al. Integrating taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic beta diversities: Interactive effects with the biome and land use across taxa. PLoS ONE 10, e0126854 (2015).
Flynn, D. F. B. et al. Loss of functional diversity under land use intensification across multiple taxa. Ecol. Lett. 12, 22–33 (2009).
Spector, S. Scarabaeine dung beetles (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae): An invertebrate focal taxon for biodiversity research and conservation. Coleopt. Bull. 60, 71–83 (2006).
Gardner, T. A. et al. The cost-effectiveness of biodiversity surveys in tropical forests: Cost-effectiveness of biodiversity surveys. Ecol. Lett. 11, 139–150 (2008).
Mason, N. W. H., Mouillot, D., Lee, W. G. & Wilson, J. B. Functional richness, functional evenness and functional divergence: The primary components of functional diversity. Oikos 111, 112–118 (2005).
Villéger, S., Mason, N. W. H. & Mouillot, D. New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology 89, 2290–2301 (2008).
Laliberté, E. & Legendre, P. A distance-based framework for measuring functional diversity from multiple traits. Ecology 91, 299–305 (2010).
Audino, L. D., Louzada, J. & Comita, L. Dung beetles as indicators of tropical forest restoration success: Is it possible to recover species and functional diversity?. Biol. Cons. 169, 248–257 (2014).
Barragán, F., Moreno, C. E., Escobar, F., Halffter, G. & Navarrete, D. Negative impacts of human land use on dung beetle functional diversity. PLoS ONE 6, e17976 (2011).
Correa, C. M. A., Braga, R. F., Puker, A. & Korasaki, V. Patterns of taxonomic and functional diversity of dung beetles in a human-modified variegated landscape in Brazilian Cerrado. J. Insect Conserv. 23, 89–99 (2019).
Gómez-Cifuentes, A., Munevar, A., Gimenez, V. C., Gatti, M. G. & Zurita, G. A. Influence of land use on the taxonomic and functional diversity of dung beetles (Coleoptera: Scarabaeinae) in the southern Atlantic forest of Argentina. J. Insect Conserv. 21, 147–156 (2017).
Guerra Alonso, C. B., Zurita, G. A. & Bellocq, M. I. Dung beetles response to livestock management in three different regional contexts. Sci. Rep. 10, 3702 (2020).
de Siqueira Neves, F. et al. Successional and seasonal changes in a community of dung beetles (Coleoptera: Scarabaeinae) in a Brazilian tropical dry forest. Nat. Conserv. 08, 160–164 (2010).
Kottek, M., Grieser, J., Beck, C., Rudolf, B. & Rubel, F. World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 15, 259–263 (2006).
Brown, A. La situación ambiental Argentina 2005 (Fundación Vida Silvestre Argentina, 2006).
Larsen, T. H., Lopera, A. & Forsyth, A. Extreme trophic and habitat specialization by Peruvian dung beetles (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae). Coleopt. Bull. 60, 315–324 (2006).
Vaz-de-Mello, F. Z. A Multilingual Key to the Genera and Subgenera of the Subfamily Scarabaeinae of the New World (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) (Magnolia Press, 2011).
Braun-Blanquet, J. Fitosociología [Phytosociology]. Bases para el estudio de las comunidades vegetales [Basis for the study of plant communities] 820 (Editorial H. Blume, 1979).
Fick, S. E. & Hijmans, R. J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 37, 4302–4315 (2017).
Scholtz, C. H., Davis, A. L. V. & Kryger, U. Evolutionary Biology and Conservation of Dung Beetles (Pensoft, 2009).
Simmons, L. W. & Ridsdill-Smith, J. Reproductive competition and its impact on the evolution and ecology of dung beetles. In Ecology and Evolution of Dung Beetles (eds Simmons, L. W. & Ridsdill-Smith, T. J.) 1–20 (Wiley, 2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444342000.ch1.
Vaz-de-Mello, F. Scarabaeidae in Catálogo Taxonômico da Fauna do Brasil. Catálogo Taxonômico da Fauna do Brasil. http://fauna.jbrj.gov.br/fauna/faunadobrasil/128171 (2018).
Zunino, M. Food relocation behaviour: A multivalent strategy of Coleoptera. In Advances in Coleopterology (eds Zunino, M. et al.) 297–314 (AEC, 1991).
LaBarbera, M. Analyzing body size as a factor in ecology and evolution. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 20, 97–117 (1989).
Soto, C. S., Giombini, M. I., Giménez Gómez, V. C. & Zurita, G. A. Phenotypic differentiation in a resilient dung beetle species induced by forest conversion into cattle pastures. Evol. Ecol. 33, 385–402 (2019).
Laliberté, E., Legendre, P. & Shipley, B. Package ‘FD’. Measuring Functional Diversity (FD) from Multiple Traits, and Other Tools for Functional Ecology (2014).
Gower, J. C. A general coefficient of similarity and some of its properties. Biometrics 27, 857 (1971).
Pavoine, S., Vallet, J., Dufour, A.-B., Gachet, S. & Daniel, H. On the challenge of treating various types of variables: Application for improving the measurement of functional diversity. Oikos 118, 391–402 (2009).
Moran, P. A. P. Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika 37, 17–23 (1950).
Zuur, A. F., Ieno, E. N. & Elphick, C. S. A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems: Data exploration. Methods Ecol. Evol. 1, 3–14 (2010).
Lavorel, S. et al. Assessing functional diversity in the field—Methodology matters!. Funct. Ecol. 22, 134–147 (2008).
Oksanen, J. et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package (2017).
Clarke, K. R. & Green, R. H. Statistical design and analysis for a ‘biological effects’ study. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 46, 213–226 (1988).
da Silva, P. G. & Cassenote, S. Environmental drivers of species composition and functional diversity of dung beetles along the Atlantic Forest-Pampa transition zone. Austral. Ecol. 44, 786–799 (2019).
Giraldo, C., Escobar, F., Chará, J. D. & Calle, Z. The adoption of silvopastoral systems promotes the recovery of ecological processes regulated by dung beetles in the Colombian Andes: Ecological processes regulated by dung beetles. Insect Conserv. Divers. 4, 115–122 (2011).
Nichols, E. et al. Trait-dependent response of dung beetle populations to tropical forest conversion at local and regional scales. Ecology 94, 180–189 (2013).
Gómez-Cifuentes, A., Giménez Gómez, V. C., Moreno, C. E. & Zurita, G. A. Tree retention in cattle ranching systems partially preserves dung beetle diversity and functional groups in the semideciduous Atlantic forest: The role of microclimate and soil conditions. Basic Appl. Ecol. 34, 64–74 (2019).
Cerullo, G. R., Edwards, F. A., Mills, S. C. & Edwards, D. P. Tropical forest subjected to intensive post-logging silviculture maintains functionally diverse dung beetle communities. For. Ecol. Manage. 444, 318–326 (2019).
Filloy, J., Zurita, G. A., Corbelli, J. M. & Bellocq, M. I. On the similarity among bird communities: Testing the influence of distance and land use. Acta Oecol. 36, 333–338 (2010).
Chown, S. L., Sørensen, J. G. & Terblanche, J. S. Water loss in insects: An environmental change perspective. J. Insect Physiol. 57, 1070–1084 (2011).
Duncan, F. D. & Byrne, M. J. Discontinuous gas exchange in dung beetles: Patterns and ecological implications. Oecologia 122, 452–458 (2000).
Lobo, J. M., Lumaret, J.-P. & Jay-Robert, P. Sampling dung beetles in the French Mediterranean area: Effects of abiotic factors and farm practices. Pedobiología 42(3), 252–266 (1998).
Navarrete, D. & Halffter, G. Dung beetle (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae) diversity in continuous forest, forest fragments and cattle pastures in a landscape of Chiapas, Mexico: The effects of anthropogenic changes. Biodivers. Conserv. 17, 2869–2898 (2008).
Verdú, J. R., Arellano, L. & Numa, C. Thermoregulation in endothermic dung beetles (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae): Effect of body size and ecophysiological constraints in flight. J. Insect Physiol. 52, 854–860 (2006).
Davis, A. J., Huijbregts, H. & Krikken, J. The role of local and regional processes in shaping dung beetle communities in tropical forest plantations in Borneo. Glob. Ecol. 9, 281–292 (2000).
Tuff, K. T., Tuff, T. & Davies, K. F. A framework for integrating thermal biology into fragmentation research. Ecol. Lett. 19, 361–374 (2016).
Davis, A. L. V. Habitat fragmentation in southern Africa and distributional response patterns in five specialist or generalist dung beetle families (Coleoptera). Afr. J. Ecol. 32, 192–207 (1994).
Halffter, G. & Arellano, L. Response of dung beetle diversity to human-induced changes in a tropical landscape. Biotropica 34, 144–154 (2002).
Hill, C. Habitat specificity and food preferences of an assemblage of tropical Australian dung beetles. J. Trop. Ecol. 12, 449–460 (1996).
Supp, S. R. & Ernest, S. K. M. Species-level and community-level responses to disturbance: A cross-community analysis. Ecology 95, 1717–1723 (2014).
Davis, A. L. V., Scholtz, C. H. & Deschodt, C. Multi-scale determinants of dung beetle assemblage structure across abiotic gradients of the Kalahari-Nama Karoo ecotone, South Africa. J. Biogeogr. 35, 1465–1480 (2008).
Nervo, B., Tocco, C., Caprio, E., Palestrini, C. & Rolando, A. The effects of body mass on dung removal efficiency in dung beetles. PLoS ONE 9, e107699 (2014).
Bui, V. B., Ziegler, T. & Bonkowski, M. Morphological traits reflect dung beetle response to land use changes in tropical karst ecosystems of Vietnam. Ecol. Ind. 108, 105697 (2020).
Giménez Gómez, V. C., Verdú, J. R. & Zurita, G. A. Thermal niche helps to explain the ability of dung beetles to exploit disturbed habitats. Sci. Rep. 10, 13364 (2020).
Verdú, J. R., Alba-Tercedor, J. & Jiménez-Manrique, M. Evidence of different thermoregulatory mechanisms between two sympatric Scarabaeus species using infrared thermography and micro-computer tomography. PLoS ONE 7, e33914 (2012).
Gómez-Cifuentes, A., Vespa, N., Semmartín, M. & Zurita, G. Canopy cover is a key factor to preserve the ecological functions of dung beetles in the southern Atlantic Forest. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 154, 103652 (2020).
Fernández, P. D. et al. Understanding the distribution of cattle production systems in the South American Chaco. J. Land Use Sci. 15, 52–68 (2020).
Grau, H. R. & Aide, M. Globalization and land-use transitions in Latin America. Ecol. Soc. 13, 16 (2008).
Mastrangelo, M. E. & Gavin, M. C. Trade-offs between cattle production and bird conservation in an agricultural frontier of the Gran Chaco of Argentina. Conserv. Biol. 26, 1040–1051 (2012).
Macchi, L. et al. Thresholds in forest bird communities along woody vegetation gradients in the South American Dry Chaco. J. Appl. Ecol. 56, 629–639 (2019).
Díaz, S. & Cabido, M. Vive la différence: Plant functional diversity matters to ecosystem processes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 16, 646–655 (2001).
Slade, E. M., Mann, D. J., Villanueva, J. F. & Lewis, O. T. Experimental evidence for the effects of dung beetle functional group richness and composition on ecosystem function in a tropical forest. J. Anim. Ecol. 76, 1094–1104 (2007).
Ortega-Martínez, I. J., Moreno, C. E. & Escobar, F. A dirty job: manure removal by dung beetles in both a cattle ranch and laboratory setting. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 161, 70–78 (2016).
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Foletto F., Trejo J.M. and Guerra J.C. for their assistance in the fieldwork. We also thank Vaz-de-Mello F. for helping with dung beetle identification. The National Parks Administration provided the necessary permissions for dung beetle collection (NEA 424 Rnv1 and 9910-00150/14). Financial support was provided by the Unidad para el Cambio Rural program of Ministerio de Agroindustria UCAR-MINAGRI (BIO 23 and PIA 10105), the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica ANPCyT (PICT-PRH 2702 and PICT 2012-0898), and the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.M.I. conceived the idea; Z.G.A. and B.M.I. designed methodology; Z.G.A. revised the manuscript; Z.G.A. and G.A.C.B. collected the data; G.A.C.B. analyzed the data; G.A.C.B. led the writing of the manuscript. All authors contributed critically to the drafts and gave final approval for publication. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Guerra Alonso, C.B., Zurita, G.A. & Bellocq, M.I. Livestock grazing impact differently on the functional diversity of dung beetles depending on the regional context in subtropical forests. Sci Rep 12, 1636 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05616-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05616-x
This article is cited by
-
Physiological traits explain the response of dung beetles to land use at local and regional scales
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Silvopastoral systems in the Upper Atlantic Forest of Argentina: what type of farms adopt them and how?
Agroforestry Systems (2024)