Abstract
JEV is one of the zoonotic pathogens that cause serious diseases in humans. JEV infection can cause abortion, mummified foetus and stillbirth in sows, orchitis and semen quality decline in boars, causing huge economic losses to pig industry. In order to investigate the epidemiology of JEV in pigs in Sichuan province, a rapid and efficient fluorescent Reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification (RT-RAA) detection method was established. Aborted fetuses and testicular swollen boar samples were detected by RT-RAA in pigs in the mountain areas around Sichuan Basin, and the detection rate of JEV was 6.49%. The positive samples were identified as JEV GI strain and GIIIstrain by sequencing analysis. We analyzed the whole gene sequence of a positive sample for the GI virus. The Envelope Protein (E protein) phylogenetic tree analysis was far related to the Chinese vaccine strain SA14-14-2, and was most closely related to the JEV GI strains SH17M-07 and SD0810 isolated from China. The results showed that we established an efficient, accurate and sensitive method for clinical detection of JEV, and JEV GI strains were prevalent in Sichuan area. It provides reference for the prevention and control of JEV in Sichuan.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Japanese Encephalitis virus (JEV) is a zoonotic virus of the genus flavivirus, damagecentral nervous system disease in both humans and animals. JEV is an endemic disease around the world, including Russia, China, Japan, India, Australia and Southeast Asia, with about 68,000 reported cases each year, and half of which occurred in China1. In human infections, most cases showed mild clinical symptoms, such as headache, fever and lethargy. However, severe neurological disorders, such as paralysis, memory deficits and seizures can occure sometimes, it can kill up to 40 percent of patients with severe illness2,3. Swine are the main host of JEV in livestock and poultry. Pigs infected with JEV usually suffer from reproductive disorders and4. Which brings great economic losses to pig industry. The JEV is mainly transmitted by mosquitoes. The climate in Sichaun is warm and humid, and large areas of rice cultivation nurture a large number of mosquitoes, forming a continuous viral cycle between mosquitoes and pigs, resulting in the widespread epidemic of JEV in Sichuan5. At present, there is no specific drug for the treatment of JEV infection, theprevention and control of JEV can only be carried out through vaccination6. Vaccinating pigs not only provides specific protection to pigs, but also breaks the cycle of transmission, thereby reducing the threat to human health. However, after the outbreak of African swine fever (ASF), the pig industry has rebounded, a large number of breeding sows and boars has been put into production, and the incidence of reproductive disorders has increased, which is of great significance for the formulation of JEV prevention and control strategies.
Many methods have been used in the epidemiological investigation of JEV. Including virus isolation, ELISA, RT-PCR, RT-QPCR, Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR), etc. Virus isolation is time-consuming and labor-intensive, taking more than a week to complete. In serological investigation using ELISA, it is difficult to analyze the results due to the cross-reaction between flaviviruses7. Serum Neutralization Test (SNT) is the reference method for serological detection of JEV, but there may be cross-reaction and it is necessary to detect other flaviviruses of the same genus as JEV to obtain correct results8. RT-PCR, RT-qPCR, ddPCR and other polymerase chain reaction based detection methods also need 2–3 h to complete9,10,11. We have establishes a real-time RT-RAA method with simple operation, strong specificity and high sensitivity. RT-RAA is an emerging nucleic acid detection method. Its principle is to add recombinase and single chain binding protein and other elements into the amplification system, so that the nucleic acid amplification can be rapidly amplified at 39 °C, and the results can be obtained within 10–30 min. We established the RT-RAA method for rapid detection of JEV, and used this method to conduct an epidemiological investigation of JEV in pig farms in Sichuan. The epidemiological data were analyzed in order to provide reference for the prevention and control of JEV in pig farms of Sichuan province in China.
Materials and methods
Establishment of RT-RAA detection method
Source of virus and sample
JEV/SC/2016-1 strain was provided by Sichuan Zoology Biotechnology Co., LTD12. Clinical samples were collected from 185 aborted fetuses and testicular with swelling in mountain areas around Sichuan Basin. The Sichuan provincial laboratory management committee (LicenceNo: SYXK (chuan) 2019–187) approval has been received. The “Guidelines for Experimental procedure” of the Ministry of Science and Technology (Beijing, China) were followed.
Primer design and synthesis
The sequence between E960-1100 in the reference sequence was analyzed, and the homology between the JEV strains was 79.8–100% (Supplementary Fig. 1). Choose to design primers between E960-E1100. A pair of RT-PCR primers, three RT-RAA forward primers, three RT-RAA reverse primers and one RT-RAA probe were designed according to the E protein sequence of JEV included in GenBank (Supplementary Table 1). The primers and probes were synthesized by Shanghai Sangong Bioengineering Technology Service Co., LTD.
RNA extraction
Cofitt®Total RNA Reagent (Cofitt Life Sciences, Kowloon, HK, China) was used to extract RNA from virus samples and clinical samples according to the kit instructions, and RNA was stored at − 80 °C.
Establishment of standard
Extract the RNA of JEV-SC-1, use PrimeScript™ RT Master Mix (Perfect Real Time) (Takara, Kusatsu, Shiga, Japan) to reverse transcribe the cDNA, and then use RT-PCR primers to amplify.. The product gel was recovered and ligated with pMD 19-T simple Vector and transformed into E.coli DH5α receptor cells. After culture, the plasmid was identified by PCR and sent to Shanghai Sangong Bioengineering Technology Service Co., LTD for sequencing. Bacteria with correct sequencing results were expanded and cultured, and plasmids were extracted using a plasmid extraction kit. The plasmids were linearized and digested with mMESSAGE mMACHINE™ T7 Transcription Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for in vitro transcription to obtain standard plasmid transcription13. This product is purified and aliquoted and stored at − 80 °C.
RT-RAA system and primer screening
Fluorescent RT-RAA use a fluorescent RT-RAA nucleic acid amplification kit (Jiangsu Qitian Gene Biotechnology, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China), and the RT-RAA reaction system refers to the kit instruction (Supplementary Table 2). Immediately after the system was configured, it was transferred to a fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument preheated at 39 °C. Denaturation temperature, annealing temperature and elongation temperature were all set at 39 °C, each cycle was 1 min, and 30 cycles were set. Nuclease—free water was used as negative control.
Three forward primers and three reverse primers were combined into 9 pairs of primers, 1–9 were F1/R1, F1/R2, F1/R3, F2/R1, F2/R2, F2/R3, F3/R1, F3/R2, and F3/R3 in sequence. The JEV cDNA was amplified by RT-PCR using the combination primers (Supplementary Table 3). The amplified bands were recycled by gel and then connected to pUCm-T Vector. It was transformed into E. coli DH5α for identification of expanded culture, and then sent to Shanghai Sangong Bioengineering Technology Service Co., LTD for sequencing to verify whether the sequencing results were JEV sequences. RT-RAA was performed on the primer combinations identified as positive by RT-PCR, and the primers were screened by fluorescence value and onset time.
Specificity and sensitivity tests of RT-RAA
The RNA extracted from JEV, swine fever virus (CSFV), blue ear virus (PRRSV), geta virus (GETV), epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) and infectious gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) were detected by the established RT-RAA fluorescence detection method to evaluate the specificity of the established method.
The recombinant plasmid transcript was diluted 10 times gradient by ddH2O, and the diluted plasmid transcript was detected by RT-RAA to evaluate the sensitivity of the established method.
Epidemiological investigation of JEV in Sichuan
Clinical sample testing
From September 2020 to September 2021, 185 samples of aborted fetuses and testicular swollen boars were collected from mountain area around Sichuan Basin, Sichuan Province. Fluorescent RT-RAA and Diagnostic Kit for JEV RNA (RT-PCR Fluorescence Probing) (Guangzhou VIPOTION) Biotechnology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China) were used to detect samples simultaneously. RT-qPCR system and reaction procedure refer to the kit instruction (Supplementary Table 4).
Whole gene sequencing of positive sample
The JEV whole gene primers were segmented according to the whole gene sequence of JEV registered in GenBank (Supplementary Table 5). The positive sample was amplified by PCR using the whole gene primers, and the amplification products were gel recovered and linked with pMD 19-T simple vector and transformed into E. coli DH5α sensitive cells. After culture, the plasmid was identified by PCR and sent to Shanghai Sangong Bioengineering Technology Service Co., LTD for sequencing.
Phylogenetic analysis
DNAMan software (DNASTAR Inc, Madison, WI, USA) was used to splice the sequence and then sequence analysis was performed (Supplementary Table 6). Based on best fit evolutionary model (TN93+G), the Maximum likelihood tree was constructed by using the Nearest-Neighbor-Interchange (NNI) and 1000 bootstraps.
Results
Establishment of RT-RAA method
Primer screening results
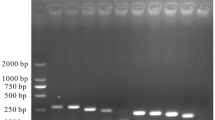
In the RT-PCR test of 9 pairs of primers, only combinations 4–9 could amplify JEV-specific bands (Fig. 1), which were identified as JEV sequences by recycled sequencing. The combination of primer 4–9 was used for RT-RAA test, and the combination of JEV-RAA-F2 and JEV-RAA-R2 caused the shortest peak time and the highest reaction fluorescence peak (Fig. 2). Therefore, JEV-RAA-F2 and JEV-RAA-R2 were selected as RT-RAA primers for the experiment.
Specificity and sensitivity of RT-RAA
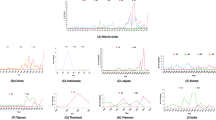
In the specificity test, only JEV RNA could generate fluorescence curves, and none of the other viral RNA generated a fluorescence curve (Fig. 3), indicating that the established RT-RAA had good specificity.
The sensitivity of RT-RAA was assessed using a recombinant plasmid transcript concentration of 5.5 × 104–5.5 × 10–1 copies/μL, and the lowest detection concentration of RT-RAA was 5.5 copies/μL (Fig. 4).
Epidemiological investigation of JEV in Sichuan
Clinical sample testing
Our results showed 11 samples were positive by RT-RAA and RT-qPCR detection. 1 sample was positive by RT-RAA detection butnegative by RT-qPCR detection. The positive coincidence rate of RT-RAA and RT-qPCR was 100%. The positive rate was 6.49% (Table 1). Among them, 11 positive samples were of GIstrain, and only one positive sample was of GIII strain.
Positive sample sequencing
Among the 12 positive samples, we obtained one JEV whole gene sequence and five JEV E gene sequences by sequencing analysis. The full gene sequence was named JEV-SC-2020-1, and the full length of the genome was 10,964 bp. The E gene sequences were named SCAB-202009, SCGZ-202002, SCLS-202002, SCLS-202005, SCPZH-202003. The gene sequences were uploaded to GenBank with accession numbers OK423757, ON416988, ON416989, ON416990, ON416991, ON416992.
Phylogenetic analysis
The phylogenetic tree analysis of E protein gene of JEV-SC-2020-1 showed that JEV-SC-2020-1 belonged to GI strain and was most closely related to SH17M-07 strain isolated from Shanghai in 2007 and SD0810 strain isolated from Shandong in 2009. It has a distant relationship with Chinese vaccine strain SA14-14-2 (Fig. 5).
The JEV E protein is a key region of the epitope, an important component that determines the virulence and antigenicity of JEV. The E proteingene homology between JEV-SC-2020-1 and the reference strain sequence was 98.4–76.6%, among which the homology with SD0810 was the hinghest, and the homology with Muar strain of GV strain was the lowest. The homology with Chinese vaccine strain SA14-14-2 was 87.3% (Supplementary Fig. 2). The E protein amino acid homology of JEV-SC-2020-1 with other reference sequences was 100%-91.6%, and the homology with GSBY0801, SD12, LN02-102, YN05155 and SD0810 was the highest. The homology of E protein with the Muar strain of GV strain was the lowest (Supplementary Fig. 3).
JEV-SC-2020-1 and the attenuated SA-14-14-2 strain share 14 amino acid mutations in the E protein, and share 8 amino acid mutations with the virulent vaccine strain Bejing-1 strain. In the key epitope region of E protein (E337-345, E377-382, E397-403)14, JEV-SC-2020-1 is completely consistent with SA-14-14-2, and Bejing-1 is only in E397 a mutation (Supplementary Fig. 4).
Discussion
RAA (Recomninase Aided Amplification) is a new thermostatic Amplification technology proposed in recent years. RAA has been widely used in pathogen detection due to its fast detection speed, strong specificity and high sensitivity15. In this study, we constructed a rapid detection RT-RAA method using JEV E protein sequnce to detection the virus. It can detect multiple genotypes of JEV, providing a wider range of JEV detection The RT-RAA detection method established in this study directly added reverse transcriptase into the reaction system, which is simpler and more convenient than the conventional PCR detection using cDNA to configure the PCR system after reverse transcription. The combination of recombinant enzyme, single chain binding protein and DNA polymerase in RAA system enables rapid amplification of nucleic acid at constant temperature, and the addition of fluorescent probe enables real-time monitoring of amplification reactions. For the JEV RT-RAA fluorescence detection method in this study, the amplification curve could be seen after reaction at 39 °C for 10 min, and the result could be judged after 30 min. However, the RT-LAMP and RT-qPCR take about 1 h for detection JEV, and the RT-PCR takes longer time than those two16,17. The detection limit for JEV plasmid transcripts was 5.5 copies/μL. It is similar to JEV RT-LAMP and TaqMan RT-qPCR9,16, slightly higher than SYBR Green I RT-qPCR, and 100 times higher than RT-PCR10. The fluorescence detection method of JEV RT-RAA established in this study is rapid, sensitive and specific, and can be used for clinical diagnosis.
JEV is one of the main arboviruses in my country and one of the main pathogens that cause reproductive failure in pigs. To investigate the prevalence of JEV in Sichuan, we performed JEV detection on 185 collected clinical samples using the established JEV RT-RAA. In the detection of 185 clinical samples, we detected 12 JEV positive cases, with a positive rate of 6.49%. JEV still accounts for a high proportion of abortion cases. The reason is the unique geographical location of mountain area around Sichuan Basin. Due to the lack of water, a large number of reservoirs have been built to store water, and these reservoirs are good shelters for mosquitoes18, which increase the risk of JEV transmission. In addition, under the influence of ASF epidemic, farmers paid less attention to JEV and the vaccination rate declined. Hence the prevalence of JEV increased in pigs19.
Among the 12 positive samples, there were 11 JEV GIstrains and 1 JEV GIII strain.strain The GIstrain was first identified in the 1980s, originated from Southeast Asia and then rapidly spread to the entire Asian continent20. After 2000, GIstrain replaced G III strain and become the pandemic strain in China, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam and Thailand21,22,23,24,25. After thatstrain, the number of clinical cases of JEV decreased, because the less virulent characteristic of the GI strain. However, study also proved that GIand GIII viruses have similar infection rates in asymptomatic infected patients, indicating that GIand GIII were equally virulent, and this conclusion was also verified in mice experiments26,27.
By analyzing the amino acid mutation sites of E protein of JEV-SC-2020-1 strain, it was found that JEV-SC-2020-1 was completely consistent with SA14-14-2 strain in the key epitope region of E protein, and had a mutation with Bejing-1. It is speculated that vaccines of SA14-14-2 and Bejing-1 strains can provide protection for JEV-SC-2020-1, but the protective efficacy of SA14-14-2 may be higher than that of Bejing-1. In previous studies, it has been believed that GIII strain vaccine can provide good immune protection effect against species genotype virus. However, recent studies have found that JEV vaccine inoculated with GIII strain has reduced neutralization efficacy against GIstrain JEV28. It has also been found that some individuals vaccinated with GIII JEV vaccine have a reduced ability to neutralize antibodies against different GIstrain strains29. This has raised concerns about whether differences in the presence of antigens between strains of different genotypes could affect the effectiveness of the vaccine. This has also accelerated the development of a new vaccine for JEV.
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its tables and figures. Additional data may be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Campbell, G. L. et al. Estimated global incidence of Japanese encephalitis: A systematic review. Bull World Health Organ. 89(10), 766–774. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.10.085233 (2011).
Monath, T. P. Japanese encephalitis vaccines: Current vaccines and future prospects. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 267, 105–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-59403-8_6 (2002).
Ghosh, D. & Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis-a pathological and clinical perspective. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 3(9), e437. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000437 (2009).
Li, Y. et al. Development of a convenient immunochromatographic strip for the diagnosis of infection with Japanese encephalitis virus in swine. J. Virol. Methods 168(1–2), 51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2010.04.015 (2010).
Yuan, L. et al. Tissue tropism and molecular characterization of a Japanese encephalitis virus strain isolated from pigs in southwest China. Virus Res. 215, 55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2016.02.001 (2016).
Huang, H. N. et al. Modulation of the immune-related gene responses to protect mice against Japanese encephalitis virus using the antimicrobial peptide, tilapia hepcidin 1–5. Biomaterials 32(28), 6804–6814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.05.053 (2011).
Maeki, T. et al. Analysis of cross-reactivity between flaviviruses with sera of patients with Japanese encephalitis showed the importance of neutralization tests for the diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis. J. Infect. Chemother. 25(10), 786–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2019.04.003 (2019).
Beck, C. et al. Improved reliability of serological tools for the diagnosis of West Nile fever in horses within Europe. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 11(9), e0005936. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0005936 (2017).
Shao, N. et al. TaqMan real-time RT-PCR assay for detecting and differentiating japanese encephalitis virus. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 31(3), 208–214. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2018.026 (2018).
Santhosh, S. R. et al. Development and evaluation of SYBR Green I-based one-step real-time RT-PCR assay for detection and quantitation of Japanese encephalitis virus. J. Virol. Methods 143(1), 73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2007.02.011 (2007).
Wu, X. et al. Development and application of a reverse transcriptase droplet digital PCR (RT-ddPCR) for sensitive and rapid detection of Japanese encephalitis virus. J. Virol. Methods 248, 166–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2017.06.015 (2017).
Zhou, Y., Zhuo, X., Ye, J. & Cai, Y. Complete genome sequence of a genotype III Japanese encephalitis virus, isolated from pigs in Sichuan, China. Genome Announc. 4(6), e01253-e1316. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01253-16 (2016).
Zhong, F., Zhong, Z. Y., Liang, S. & Li, X. J. Transfection of GFP mRNA in dendritic cells and analysis of some factors involved. Chin. J. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 22(6), 716–719 (2006).
Lobigs, M. et al. Host cell selection of Murray Valley encephalitis virus variants altered at an RGD sequence in the envelope protein and in mouse virulence. Virology 176(2), 587–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/0042-6822(90)90029-q (1990).
Wu, T. et al. A reverse-transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for the rapid detection of N gene of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2). Virology 549, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2020.07.006 (2020).
Zhang, L. et al. Detection and differentiation of Japanese encephalitis virus genotype I and genotype III by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with restriction fragment length polymorphism. Virus Genes 50(2), 231–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-014-1158-5 (2015).
Wang, X. et al. Rapid differential detection of genotype I and III Japanese encephalitis virus from clinical samples by a novel duplex TaqMan probe-based RT-qPCR assay. J. Virol. Methods 279, 113841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2020.113841 (2020).
Liu, M. D. et al. Monitoring and analysis of the mosouito vector of japanese b encephalitis in beijing olympic forest park. Acta Parasitologica et Medica Entomologica Sinica. 28(03), 153–158 (2021).
Kading, R. C., Abworo, E. O. & Hamer, G. L. Rift valley fever virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, and African swine fever virus: Three transboundary, vector-borne, veterinary biothreats with diverse surveillance, and response capacity needs. Front Vet. Sci. 13(6), 458. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2019.00458 (2019).
Gao, X. et al. Southernmost Asia is the source of Japanese encephalitis virus (genotype 1) diversity from which the viruses disperse and evolve throughout Asia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 7(9), e2459. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002459 (2013).
Nerome, R. et al. Molecular epidemiological analyses of Japanese encephalitis virus isolates from swine in Japan from 2002 to 2004. J. Gen. Virol. 88(Pt 10), 2762–2768. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.82941-0 (2007).
Yang, D. K. et al. Molecular characterization of full-length genome of Japanese encephalitis virus (KV1899) isolated from pigs in Korea. J. Vet. Sci. 5(3), 197–205 (2004).
Huang, J. H. et al. Molecular epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis virus, Taiwan. Emerg. Infect Dis. 16, 876–878. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1605.091055 (2010).
Yun, S. M. et al. Molecular epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis virus circulating in South Korea, 1983–2005. Virol. J. 7, 127. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-7-127 (2010).
Nga, P. T. et al. Shift in Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) genotype circulating in northern Vietnam: Implications for frequent introductions of JEV from Southeast Asia to East Asia. J. Gen. Virol. 85, 1625–1631. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.79797-0 (2004).
Fan, Y. C. et al. Virulence of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genotypes I and III, Taiwan. Emerg. Infect Dis. 23(11), 1883–1886. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2311.161443 (2017).
Beasley, D. W. et al. Protection against Japanese encephalitis virus strains representing four genotypes by passive transfer of sera raised against ChimeriVax-JE experimental vaccine. Vaccine 22, 3722–3726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.03.027 (2004).
Fan, Y. C. et al. Partially neutralizing potency against emerging genotype I virus among children received formalin-inactivated Japanese encephalitis virus vaccine. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 6(9), e1834. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001834 (2012).
Erra, E. O. et al. A single dose of vero cell-derived Japanese encephalitis (JE) vaccine (Ixiaro) effectively boosts immunity in travelers primed with mouse brain-derived JE vaccines. Clin. Infect. Dis. 55(6), 825–834. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cis542 (2012).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Zhiwen Xu for helpful discussions on topics related to this work. This work was partially funded by the Science and Technology Plan Project of Sichuan Province (Project No. 2020YFN0147). It is also supported by the Program Sichuan Veterinary Medicine and Drug Innovation Group of China Agricultural Research System (Project No. CARS-SVDIP).
Funding
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Plan Project of Sichuan Province (Project No. 2020YFN0147) and the Program Sichuan Veterinary Medicine and Drug Innovation Group of China Agricultural Research System (Project No. CARS-SVDIP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have made substantial contributions to design and acquisition of data. N.M.C., Z.Y.C. and L.F.Q. also contributed for analysis of data, drafting and revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, M., Zhou, Y., Li, F. et al. Epidemiological investigation of swine Japanese encephalitis virus based on RT-RAA detection method. Sci Rep 12, 9392 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13604-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13604-4