Abstract
Based on the perspective of green technology innovation, this paper takes listed companies in China’s manufacturing industry from 2012 to 2022 as the research sample, and adopts the Driscoll-Kraay standard error method to explore the relationship between intelligent manufacturing and the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. The results show that intelligent manufacturing can promote high-quality development of manufacturing industry Green technology innovation plays an mediating role in the above relationship. The above findings still hold after considering robustness tests and endogeneity treatments. Heterogeneity analysis indicates the application of intelligent manufacturing in state-owned enterprises, CEO separately enterprises and heavily polluting industries has a stronger role in promoting the development of manufacturing industry. This paper complements the existing research results on intelligent manufacturing and also establishes a realistic path for the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry.
Similar content being viewed by others
As an emerging economy, China has shown strong momentum in the manufacturing industry and has now become a manufacturing power with strong international influence. However, China’s manufacturing industry is still far behind the rest of the world in terms of awareness of ecological protection, resource utilization efficiency and sustainable innovation capacity, and is still weak in high-end manufacturing, which is difficult to achieve “manufacturing power”1. Therefore, China must promote the high-quality development of manufacturing2. Studies have shown that the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry requires manufacturing enterprises to have more sustainable innovation capability, more reasonable resource allocation, and greener production methods to promote China’s manufacturing industry from the traditional factor-driven to innovation-driven development mode3,4,5. Intelligent manufacturing is a new information technology-oriented manufacturing model, which is not only a strategic choice to cope with the new round of scientific and technological revolution, but also an important cornerstone of China’s progress towards a “manufacturing power”6,6,8. It can be said that the degree of development of intelligent manufacturing is directly related to the development level of China’s manufacturing industry. In the political context of accelerating the building of a strong socialist modernization country, it has become a research hotspot in China’s current academic community to explore how intelligent manufacturing can realize the transformation of polluting manufacturing to clean manufacturing mode9,10.
According to the literature now in publication, academics both domestically and internationally have given the subject of how to encourage the manufacturing industry’s high-quality development a great deal of attention. Their research has mostly focused on three perspectives: innovation drive 4,11,12, digital economy13,14,15 and environmental regulation16,17. Furthermore, some academics have talked about the connection between intelligent manufacturing and the manufacturing industry’s higher-quality development, most of this literature has used macro data for analysis18,19 or researched from mediating mechanisms, such as the mechanisms of cost stickiness20, labor mobility21, and organizational resilience22,23. However, there is a dearth of literature examining green technology innovations that break away from dependence on traditional production methods and help manufacturing firms realize both economic and ecological value. Therefore, this paper argues that the establishment of a research framework of “Intelligent Manufacturing–Green Technology Innovation–Quality Development of Manufacturing Industry” is of significance in promoting the construction of China’s “Manufacturing Power”.
In order to better guide the overall development of Chinese manufacturing, this article utilizes data from listed companies in China’s manufacturing industry from 2012 to 2022, and takes green technological innovation as a mediating variable to study the impact mechanism of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry. The possible contributions of this study are as follows: firstly, from the perspective of green technological innovation, we construct a research framework on intelligent manufacturing and high-quality development of manufacturing industry, and analyze the transmission mechanism between the above relationships. secondly, previous studies mainly use macro data to discuss the high-quality development of manufacturing industry19, while this paper focuses on the micro enterprises, and adopts the data of listed companies in the manufacturing industry to carry out a quantitative analysis. finally, it complements the relevant research of intelligent manufacturing and high-quality development of manufacturing industry, and expands the research boundary of the impact of green technology innovation on high-quality development of manufacturing industry.
Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
Intelligent manufacturing and high-quality development of manufacturing
The core characteristics of intelligent manufacturing can be summarized into three major aspects: adaptability, learning and predictability, which together build the cornerstone of its intelligent operation24. The first is adaptability, which gives intelligent manufacturing a certain degree of flexibility to adapt to various changes in the external environment without sacrificing the results of the established goals. This characteristic ensures the continuity and efficiency of the production process, and even in the face of sudden challenges, it can quickly adjust its strategy to maintain the optimal operating state. Secondly, learning is the key to the upgrading of intelligent manufacturing systems. Intelligent manufacturing system can significantly improve the autonomy of the system by continuously absorbing new knowledge and technology and automatically updating the internal knowledge base, which in turn promotes the self-optimization within the enterprise and provides strong support for the competitiveness of the enterprise. Finally, predictability is the embodiment of the forward-looking and preventive nature of the intelligent manufacturing system. It enables the system to gain insight in advance into potential change trends and the impact these changes may have on system operations. Based on this forward-looking insight, the intelligent manufacturing system can formulate response strategies in advance to effectively mitigate the impact of unfavorable factors and ensure the stability of production, which can also bring more strategic advantages for enterprises. Presently, investigations into intelligent manufacturing is mostly conducted from the following two perspectives by both domestic and international scholars: One is a study of the concept of intelligent manufacturing itself. Wright and Bourne25 first suggested that intelligent manufacturing could be accomplished by manipulating robots through information technology to perform manufacturing activities independently from human labor. In addition, some studies have concluded that intelligent manufacturing is a new manufacturing model oriented to the development of information technology, which can better realize the high-end manufacturing industry6. Another is to explore the application of intelligent manufacturing in various fields. For instance, optimizing production processes and improving enterprise production efficiency26,27, standardizing products and digitizing factories28, linking intelligent manufacturing with modern communication technology29, and the inherent logic of intelligent manufacturing and technological innovation30.
The high-quality development of the manufacturing industry is reflected in its technological innovation capacity, eco-friendliness and significant improvement in its position in the global value chain, the core of which lies in the realization of low-pollution, high-value-added product production, thereby simultaneously realizing economic, ecological and social value. For China, the primary task in promoting the high-quality development of the manufacturing sector is to utilize smart manufacturing to increase the total factor productivity of the manufacturing sector and realize its green and sustainable development31. Scholars primarily investigate the measuring standards and influencing variables of high-quality development in the manufacturing industry, based on the literature that is currently available. Regarding the measurement criteria, on the one hand, some studies have adopted the comprehensive evaluation system method32, on the other hand, some scholars believe that the evaluation system currently has no specific criteria and is highly subjective33. Therefore, they believe that the intermediate variable substitution method—total factor productivity of the manufacturing industry (TFP) — is more persuasive and uses TFP to gauge the manufacturing industry’s degree of high-quality development. In recent years, the research focus has been deepening, and many research perspectives have emerged, such as from service-oriented manufacturing34,35, supply chain36, intelligent transformation23, artificial intelligence18 and explore the influence factors of manufacturing high quality development. The above research provides a rich experience for understanding the motives and impact mechanisms of high-quality development in China’s manufacturing industry.
Current research indicates that enterprises need to optimize their production and operation processes through technological innovation to achieve economic and social value, therefore encouraging the manufacturing industry’s high-quality development37. However, with people’s increasing attention to social resource conservation and ecological environmental protection issues, green technology innovation has gradually become a crucial part of technological innovation38. Simultaneously, the blueprint for the development of China’s manufacturing industry is grounded in the historical context of the country’s entry into a new era of socialist with Chinese characteristics. This new era demands that the manufacturing industry not only consider its economic expansion but also prioritize its sustainable social and ecological development. In other words, high-quality development puts higher demands on production efficiency, innovation ability, green environmental protection concepts, and social benefits of manufacturing enterprises34. Accordingly, Chinese manufacturing enterprises need to constantly update and improve their technologies, and the concept of intelligent manufacturing is just in line with it. In summary, intelligent manufacturing is closely related to the development of China’s manufacturing.
The impact mechanism of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry
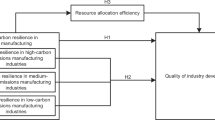
Based on the above analysis, this paper argues that intelligent manufacturing promotes the development of China’s manufacturing industry in a high-quality manner. The reasons are described below. Firstly, the application of intelligent manufacturing can notably promote the production efficiency of manufacturing enterprises. Intelligent manufacturing can not only achieve the dynamic integration of product design, production and sales within the enterprise, but also promote cooperation between enterprises based on the industrial Internet, so that technology can be shared and optimized outside the enterprise. This application can promote the production efficiency of significant manufacturing companies, strengthen cooperation, and improve the manufacturing industry39. Secondly, intelligent manufacturing can improve product quality in manufacturing firms. The emergence of artificial intelligence can be said to be a significant symbol of intelligent manufacturing. Suppose this technology is embedded in the production process. In that case, it can simplify production steps while accelerating the flow and sharing of information in the product production process, complete real-time control of product quality, improve product standardization and enterprise competitiveness, and help enhance the overall level of the manufacturing industry40. Finally, intelligent manufacturing can achieve green manufacturing. Intelligent manufacturing can obtain the quantity information of required materials more quickly, control the use of materials more precisely, can more sensibly assess how production affects the environment41. This indicates that the advancement of intelligent manufacturing can significantly foster the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry by preventing the waste of natural resources and increasing the effectiveness of resource utilization. Manufacturing enterprises can also achieve sustainable development of the environment by obtaining financial benefits41. Consequently, intelligent manufacturing can drive manufacturing companies to obtain economic, social, and ecological value and is an essential driving force for the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry. Following the analysis above, we propose the following hypothesis:
-
H1. Intelligent manufacturing can facilitate the high-quality development of Chinese manufacturing.
Mediating mechanisms for green technology innovation
“Green technology” is a term concept that used to describe a group of methods, devices, and supplies that have the potential to cut down on energy use, raw material use, and environmental damage42. With the advancement of technology and modifications in societal requirements, the connotation of green technology is also constantly evolving. It has transformed from the initial green governance technology to a technology that achieves a “win-win” situation for the national economy and ecological benefits38. “Green technological innovation” aims to achieve the dual goals of energy saving, emission reduction and resource efficient utilization through the innovation of products or production processes. This innovation not only reduces the environmental burden in the whole production cycle, such as reducing carbon emissions and pollutant emissions, but also promotes a leap in product quality, paving the way to green and sustainable development for enterprises. At present, the green technology innovation activities adopted by enterprises mainly cover three aspects: first, equipment improvement and renewal, enterprises can directly reduce energy consumption and waste generation through the introduction of more efficient and environmentally friendly production equipment. The second is technological innovation, which involves the optimization and innovation of the existing production process, and strives to maintain or enhance production efficiency while minimizing resource consumption and environmental pollution. For example, waste recycling not only reduces disposal costs, but also promotes the recycling of resources. Finally, green product innovation, that is, the concept of environmental protection is integrated at the beginning of the design of products, whether from the selection of raw materials, manufacturing process or final use, and strive to meet the market demand while minimizing the impact on the environment9,43.
In existing literature, domestic and foreign scholars have explored and analyzed green technology innovation from different perspectives. From the meaning of green technology innovation some studies have analyzed it from the perspective of product lifecycle and found that green technology innovation can reduce product lifecycle costs43. Others discovered that via process and product innovation, green technology innovation can accomplish sustainable economic, social, and ecological development, which is from the standpoint of sustainable development44. Recently, more and more scholars have expressed their views on the relationship between green technology innovation and companies. Hart45 believes that green technology innovation can improve enterprises’ innovation levels, thereby updating production technology and systems and enhancing enterprises’ core competitiveness. Furthermore, as an essential channel for green development, green technology innovation can help firms to utilize natural resources and reduce procurement and production costs more efficiently46. Therefore, scholars believe that the application of green technology innovation can make manufacturing enterprises gain more cost advantages and competitive advantages, conducive to the overall development of the manufacturing industry, and promote the development model of China’s manufacturing industry from pollution to clean transformation16,41. To sum up, previous researchers have conducted in-depth research on green technology innovation and achieved significant results, however, its significance in the connection between intelligent manufacturing and the high-quality development of Chinese manufacturing has not been adequately covered in earlier research. Hence, we will make efforts in this direction.
Not only can intelligent manufacturing help the manufacturing industry grow in a quality manner, but it may also motivate manufacturing companies to actively engage in green technology innovation projects. On the one hand, in addition to using intelligent manufacturing to enhance the added value of products, enterprises can also conveniently learn and apply green concepts and technologies, optimize the efficiency of resource allocation, and reduce the probability of environmental pollution. This is conducive to improving the green efficiency of manufacturing enterprises’ products and promoting the sustainable growth of enterprises. On the other hand, intelligent manufacturing accelerates the transmission of information within enterprises, which is conducive to the establishment of innovative knowledge co-creation networks among different enterprises47. This greatly improves the degree of green technology innovation of manufacturing enterprises and promotes the exchange of green innovation ideas among similar enterprises. Therefore, intelligent manufacturing provides a basis for manufacturing enterprises to carry out green technology innovation activities: the more in-depth the application of intelligent manufacturing by enterprises, the more they can maximize the green concept. It assists enterprises in obtaining economic and ecological benefits, encouraging the comprehensive progress of Chinese manufacturing31.
Green technology innovation broadens companies’ innovation boundaries and can bring them more output benefits. As a vital micro entity in the manufacturing industry, increasing company efficiency is advantageous to the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing. First of all, green technology innovation is an essential link for manufacturing firms to implement innovation-driven development strategies, which will profoundly impact their production performance48. Manufacturing enterprises can prevent environmental pollution from the source of production by adopting new generation green materials and process technologies through technological transformation, significantly reducing the probability of environmental governance. Improving green technology innovation also helps companies recycle and reproduce old products, creating additional economic benefits for companies to a certain extent. Then, green technology innovation can boost businesses’ competitiveness49. Green technology innovation can greatly enhance the competitive advantage of enterprises, accelerate the realization of green manufacturing, and promote the transformation of traditional polluting manufacturing enterprises into new intelligent clean manufacturing enterprises. Eventually, green technology innovation can simultaneously improve environmental protection and progressiveness of products50. Some equipment and technologies with high green costs, energy consumption, and pollution can be optimized in green technology innovation and application. While product resource consumption is reduced, product quality and technological content can be improved, which undoubtedly promotes the progress of an industry. Thus, raising the bar for innovation in green technology will accelerate the progress of the Chinese manufacturing industry in developing high-quality technology. Following the analysis above, we propose the following hypothesis:
-
H2. Green technology innovation has a mediating role between intelligent manufacturing and high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry.
Research and data methodology
Sample and data
Due to the third revision of the National Economic Industry Classification in 2011, to ensure the reliability of the study, this paper focuses on all listed companies in China’s manufacturing industry from 2012 to 2022 and the screening principles for initial sample are as follows: (1) considering the completeness of data and accuracy of research results, only samples with no missing data for at least 5 consecutive years will be retained; (2) excluding firms with negative operating income or total assets; (3) excluding ST, *ST and PT type enterprises; (4) excluding firms with IPOs in from 2012 to 2022; (5) to mitigate the impact of outliers, the main variables are winsorized at the 1% and 99% levels. The final number of observations obtained was 22,362, the share of companies in heavily polluting industries was about 23.5%. The raw data for this study are derived from annual reports of Chinese listed companies and the China Stock Market and Accounting Research (CSMAR). In addition, the green technology innovation data are from the CNRDS database, and other related data are acquired from the WIND database.
Definition of variables
Explained variable: High-quality development of Chinese manufacturing industry (TFP)
The intermediate variable substitution approach and the comprehensive evaluation system are the two techniques used in current research to gauge the high-quality development in manufacturing. There is currently no scientifically based, unified assessment index system that will significantly reduce the scientificity of the conclusion, despite the fact that the comprehensive evaluation system may assess the manufacturing development status from a variety of perspectives. Moreover, the measurement of most indicators has specific difficulties and is rarely used in research 33. Therefore, we believe that using the intermediate variable substitution method, Total Factor Productivity (TFP), is a more comprehensive measurement method for the high quality development level of Chinese manufacturing industry51.
In existing studies, TFP is mainly measured by the method of OP52, GMM53, LP54 with ACF55, of which the most widely used is OP and LP method. Accordingly, this paper adopts the LP approach to calculate the TFP of the manufacturing industry56 to measure the level of high-quality development of the Chinese manufacturing. Additionally, a robustness test was performed using the OP approach.
Core explanatory variable: Intelligent Manufacturing (IM)
The concept of “intelligent manufacturing” is abstract and complex to measure directly with indicators. Drawing on Zhao57’s study, our index of intelligent manufacturing level is based on the frequency of keywords connected to “intelligent manufacturing” that appear frequently in the annual reports of manufacturing industry listed businesses. Meanwhile, according to government documents, industry reports, International Federation of Robotics Organization (IFR) definitions and cases, and Webb’s definition of “intelligent machine”, the keywords shown in Table 1 were selected. Table 1 explains the close connection between the meanings of each keyword and intelligent manufacturing.
Mediating variable: Green Technology Innovation (GTI)
There are two primary methods that emerge from the body of research on quantifying green technology innovation: the first is to use the R&D investment to energy consumption ratio to gauge the degree of innovation in green technology. Wang and Chen49; the second measure is reflected by the natural logarithm of the number of green invention patents and green utility model patent applications in the sample, which is based on the International Green Patent Classification (IPC) developed by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in 2010 58. This article selects the second method to gauge manufacturing firms’ use of green technology innovation based on data availability.
Control variables
In empirical analysis, we take into account the following variables (as shown in Table 2), making reference to earlier research13,14:
Model design
Building upon the above theoretical analysis and research hypothesis, this paper adopts fixed effects model to construct a linear regression model with firm effect and year effect, aiming to assess the influence of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of manufacturing industry:
In order to further test the influence of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of manufacturing industry through green technology innovation, this paper draws on the stepwise regression method of Wen et al.59 to test the mediating effect, and the model is set up as follows:
Where TFPi, t is the explanatory variable, indicating the level of high-quality development of the manufacturing industry in year t of enterprise i, the larger the value, the higher the level of high-quality development of the manufacturing industry; IMi, t is the explanatory variable, indicating the level of intelligent manufacturing in year t of enterprise i, the larger the value, the higher the level of intelligent manufacturing; GTIi, t stands for green technology innovation, the larger the value, the stronger the green technology innovation capability; CNi, t is the control variable; εi, t is the random error term. Model (1) is the regression model of the independent variable IMi, t on TFPi, t, model (2) is the regression analysis of IMi, t on the mediating variable green technology innovation, and model (3) is the mediating effect model of GTIi, t. Specifically: the first step, whether β1 in model (1) is significant; the second step; whether β1 in model (2) is significant; and the third step, whether β1 and β2 in model (3) are significant; if β2 is not significant, the mediating effect does not hold, and if it is significant, there is a mediating effect.
Empirical results
Descriptive analysis
The variables’ descriptive statistics are displayed on Table 3. Firstly, the minimum value of TFP is 3.543, the maximum value is 11.61, the median is 8.129, and the standard deviation is 0.975, which indicates that the level of high-quality development of manufacturing firms in this sample is uneven. Secondly, the minimum value of IM is 0, indicating that there are firms that have not yet applied intelligent manufacturing, and the maximum value of 2.86, with a 0.216 standard deviation, shows that manufacturing firms are equally varied in terms of intelligent manufacturing. Thirdly, the minimum value of GTI is 0, and the maximum value is 6.848 with a 0.216 standard deviation, once more highlighting some disparities in the sample firms’ levels of innovation in green technology.
Table 4 shows the correlation coefficients of the main variables. As shown in Table 4, the correlation coefficient between intelligent manufacturing and high-quality development of the manufacturing industry is 0.066, intelligent manufacturing and green technology innovation is 0.254, and green technology innovation and high-quality development of the manufacturing industry is 0.276. The above coefficients are positive and have passed the 1% significance level test, demonstrating a significant positive correlation between the above relationships.
Regression analysis
Table 5 shows benchmark and mediating regression results for IM and high-quality manufacturing development. The outcome of not accounting for the explanatory variable is Model (1), while Model (2) shows a significant positive correlation between IM and high-quality development of the manufacturing industry (Beta = 0.0861, p < 0.01), indicating that when IM increases by 1%, the degree of high-quality development of Chinese manufacturing industry will increase by 8.61%. Consequently, H1 is empirically supported.
From model (3), it can be seen that IM has a significant positive effect on GTI (Beta = 0. 0861, p < 0.01), suggesting that a 1% increase in IM will enhance the level of GTI by 15.4%. Then, the results of Model (4) show there is a significant positive correlation between GTI and high-quality development of the manufacturing industry (Beta = 0. 0114, p < 0.05) when the level of GTI increases by 1%, the level of high-quality development of Chinese manufacturing industry will be increased by 1.14% accordingly. Finally, the test findings for GTI’s mediating influence on the relationship between IM and the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing are shown in Model (5). The regression coefficient of GTI (Beta = 0.0094, p < 0.1) reaches a positive and significant level, showing that GTI plays a mediating role. Therefore, H2 is valid. After manufacturing enterprises improve the level of GTI, they can reduce enterprise losses, improve unit output, utilize ecological resources more rationally, and promote the improvement of the level of high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry.
Robustness rest
Endogeneity issues
There may exist a bidirectional causality between intelligent manufacturing and the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing. This paper employs the 2sls instrumental variable (IV) method, as the instrumental variable in the same year in order to resolve the endogeneity problem. Table 6 illustrates that the F-value of the first stage is 130.94, which exceeds 10, indicating the absence of a weak instrumental variable problem. Furthermore, the regression results of the second stage reveal that the regression coefficient of intelligent manufacturing is significantly positive at the 1% level. Given this, the conclusion that intelligent manufacturing catalyses the high-quality advancement of China’s manufacturing industry is not overturned due to the endogeneity problem, further supporting Hypothesis 1.
Substitution of dependent variable
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of regression results, we adopt the method of replacing the explanatory variables for the robustness test—TFP is re-measured using the OP approach. The results are shown in Table 7 for Models (2) through (5), and H1 and H2 still hold.
Heterogeneity analysis
Micro-level heterogeneity analysis
Nature of ownership
Under China’s unique economic system, the state exercises ownership or control over the capital of state-owned enterprises (SOE), giving them unique resource endowments, corporate goals and management structures27,60, which implies that SOE and non-SOE may differ in planning and decision-making for applying intelligent manufacturing. Considering this, regression analysis is performed in this paper after the sample is split into SOE and non-SOE groups.
Table 8 shows that in SOE, the regression coefficient of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry is positive, and the test of significance reaches the level of 5%. The results for the group of non-state-owned enterprises show that the promotion effect of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry only passes the statistical significance test of 10%. This paper argues that SOEs have a natural advantage in policy, funding and resources and a higher focus on cutting-edge technologies, while non-SOEs lack the motivation and incentive to utilize intelligent manufacturing due to higher market competition pressure and limited financial support. As a result, state-owned enterprises in the manufacturing industry of China are more likely to accept and promote intelligent manufacturing than non-SOE.
CEO concurrently
The effect on corporate governance and development produced by a chairman who is also the general manager differs from that produced by a separate chairman and general manager61,62. Given this, this paper divides the sample firms into two groups based on whether the CEOs are concurrently employed or not, in order to test the differences in the promotion of high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry by intelligent manufacturing under different circumstances.
Table 9 illustrates the influence of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of Chinese manufacturing is positively associated with the concurrent appointment of a CEO, although it does not achieve statistical significance. However, when the CEO is divided into different positions, the advancement of intelligent manufacturing can effectively enhance the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry (the coefficient is 0.1247, which achieves statistical significance at the 1% level). This paper argues that the division of responsibilities through CEO split will be more conducive to clarifying work content and avoiding possible omissions in part-time job duties. Additionally, the split will lead to a more professional approach in decision-making development, improving work efficiency, reducing unnecessary communication and coordination costs, and ensuring scientific and rational decision-making processes. Therefore, compared to concurrently serving as a CEO, the optimization effect of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry will be more substantial during CEO division.
Macro-level heterogeneity analysis
The environmental problems caused by manufacturing companies mainly originate from heavily polluting industries, while these industries are the focus of environmental control63. Intelligent manufacturing produces the “manufacturing green” effect, which is vital for realising pollution prevention and emission reduction, but whether it only has a significant effect on the heavy pollution industry is yet to be verified. Based on this, businesses classified as heavy-polluting (HPI) and non-heavy-polluting (non-HPI) are included in the sample according to whether they are heavy-polluting or not. Table 10 presents the test results about the difference in the role of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry.
In the group of heavily polluted industries, the impact of intelligent manufacturing on the enhancement of high-quality development in China’s manufacturing industry is significant (Beta = 0.4774, p < 0.01). However, for non-heavily polluted industries, the regression coefficients for the implementation of intelligent manufacturing did not achieve statistical significance. This suggests that the emission potential of heavy polluting industries is high and the role of intelligent manufacturing in protecting the ecosystem is more pronounced in such industries, while the environmental impact of non-heavy polluting industries is less pronounced in comparison. Consequently, intelligent manufacturing has a stronger effect on promoting China’s manufacturing industry’s high-quality development when applied to heavily polluting industries.
Discussion and conclusion
Discussion
This paper takes the listed Chinese manufacturing companies as a research sample, and empirically examines the mechanism of the impact of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of manufacturing industry, and the mediating role of green technology innovation in the above relationship. Based on previous studies, this study focuses on examining the following areas.
First of all, this paper recognizes the importance of green technology innovation, which is an important supplement to the traditional research framework. Previous scholars have mostly focused on cost stickiness, organizational toughness and other perspectives to explore the impact of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. In fact, green technology innovation plays a key role in the transmission between the two, which can more effectively achieve the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry under the impetus of intelligent manufacturing. Secondly, unlike previous studies that mainly use macro data to examine the manufacturing industry, this paper shifts the focus of research to individual enterprises at the micro level. By using the data of listed companies in the manufacturing industry, we can analyze how intelligent manufacturing specifically works within the enterprise, which in turn has a far-reaching impact on the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. This not only enriches the existing research, but also provides managers with a more specific basis for decision-making. Finally, in the heterogeneity analysis, this study introduces the variable of whether the CEO is part-time or not. This is because it may affect the strategic decisions and resource allocation of the firms, which may have different impacts on the implementation effect of intelligent manufacturing and the level of green technology innovation. This consideration contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of the differentiated impacts of intelligent manufacturing among different enterprises, and also complements and improves the existing research system.
Conclusion
Based on the data of listed companies in China’s manufacturing industry from 2012 to 2022, this paper analyzes the relationship between intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of manufacturing industry and the mediating role of green technology innovation in the two. The results of the study show that intelligent manufacturing and manufacturing high quality are significantly positively correlated, that is, intelligent manufacturing can accelerate the process of manufacturing high quality development. Green technology innovation has an mediating effect in the above relationship, and the development of intelligent manufacturing can improve the level of green technology innovation of the manufacturing enterprises, which can in turn promote the high quality of the manufacturing industry. Heterogeneity analysis show that, in the state-owned enterprises, CEO separately enterprises and heavy pollution industries, the promotion effect of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of manufacturing industry is stronger.
This paper has some limitations. Firstly, no group analysis was conducted on listed manufacturing companies, and the application of intelligent manufacturing may have varying impacts on different types of companies in the manufacturing industry. Secondly, many factors impact the high-quality development of manufacturing industry, which cannot be controlled one by one in empirical analysis. Finally, the sample has certain restrictions and the data used in this article only covers listed businesses in China’s manufacturing industry from 2012 to 2022.In future research, we will conduct group discussions based on manufacturing enterprise sectors to analyze the development paths of different types and sizes of manufacturing enterprises under the wave of intelligent manufacturing. For example, focusing on the technical level, the group discusses how digital technology provides technical support for intelligent manufacturing and promotes the change of enterprise production mode, thus injecting new impetus into the high-quality development of manufacturing industry.
Managerial implication
According to the research findings, this paper proposes three managerial implications: Firstly, promote the application of intelligent manufacturing, complete the innovation of production technology and equipment, and accelerate the transformation or elimination of low-end and medium-end manufacturing industries. Therefore, the government should introduce relevant policies to promote the application of intelligent manufacturing, and improve the R&D funds of enterprises, so as to provide better manufacturing capabilities for the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. Secondly, make green technology innovation the driving force behind the manufacturing industry’s transition and upgrading. The government should encourage enterprises to use intelligent manufacturing to improve the level of green technological innovation, thereby realizing the greening of products and injecting new momentum into intelligent manufacturing to promote the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. Thirdly, China’s labor-intensive enterprises account for a relatively high proportion of the manufacturing industry, the government should focus on and give policy support to encourage them to actively introduce intelligent manufacturing, enhance enterprise competitiveness, and drive the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry.
Practical implications
The findings of this paper also have strong practical implications. First, intelligent manufacturing can provide enterprises with a solid technical guarantee and enhance their dynamism. Through the introduction of intelligent production lines, big data analysis and other cutting-edge technologies, enterprises can achieve a qualitative leap in production efficiency and product quality, which wins a broader development space for enterprises and promotes their sustainable development. Second, intelligent manufacturing is an important path to promote the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. Enterprises by vigorously promoting intelligent manufacturing, can reduce the rate of product defects and pollution rate, while improving the level of green technology innovation in the manufacturing industry, to achieve the “greening of manufacturing”, which is conducive to accelerating China’s pace of building a “manufacturing power”. Third, as the world’s largest emerging economy, China has a relatively mature manufacturing system, but it has neglected to improve the quality of its manufacturing industry when it has been developing rapidly, which has caused serious environmental problems, and this is also the current situation of most developing countries. Therefore, this study not only guides the future development direction of China’s manufacturing industry, but also has reference value for the construction of manufacturing industry in other developing countries in the world.
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Fan, X., Wang, Y. & Lu, X. Digital transformation drives sustainable innovation capability improvement in manufacturing enterprises: based on FsQCA and NCA approaches. Sustainability. 15 (1), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010542 (2022).
Miao, Z. & Zhao, G. Configurational paths to the green transformation of Chinese manufacturing enterprises: a TOE framework based on the fsQCA and NCA approaches. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 19181. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-46454-9 (2023).
Yuan, B., Ren, S. & Chen, X. Can environmental regulation promote the coordinated development of economy and environment in China’s manufacturing industry?–A panel data analysis of 28 sub-sectors. J. Clean. Prod. 149 (4), 11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.065 (2017).
Zhu, X., Dong, Y. & Xu, Q. Factor-driven or innovation-driven? The role of digital technology in the cleanliness of industrial structure. J. Clean. Prod. 452 (5), 142136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142136 (2024).
Zhaocheng, X. Will CEO-TMT overseas experience differences reduce innovation investment? Evidence from Chinese manufacturing listed companies. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 15(1), 771–800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-023-01103-4 (2024).
Davis, J., Edgar, T., Porter, J., Bernaden, J. & Sarli, M. Smart manufacturing, manufacturing intelligence and demand-dynamic performance. Comput. Chem. Eng. 47 (12), 145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2012.06.037 (2012).
Li, L. China’s manufacturing locus in 2025: with a comparison of made-in-China 2025 and industry 4.0. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 135 (10), 66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.05.028 (2018).
Meng, F., Xu, Y. & Zhao, G. Environmental regulations, green innovation and intelligent upgrading of manufacturing enterprises: evidence from China. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 14485. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71423-x (2020).
Gao, J., Feng, Q., Guan, T. & Zhang, W. Unlocking paths for transforming green technological innovation in manufacturing industries. J. Innov. Knowl. 8 (3), 100394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2023.100394 (2023).
Wei, X., Jiang, F., Chen, Y. & Hua, W. Towards green development: the role of intelligent manufacturing in promoting corporate environmental performance. Energy Econ. 131 (2), 107375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2024.107375 (2024).
Jibir, A. & Abdu, M. Human capital and propensity to protect intellectual properties as innovation output: the case of Nigerian manufacturing and service firms. J. Knowl. Econ. 12 (2), 595–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-020-00657-x (2021).
Kim, W. & Kim, M. Reference quality-based competitive market structure for innovation driven markets. Int. J. Res. Mark. 32 (3), 284–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijresmar.2014.10.003 (2015).
Deng, H., Bai, G., Shen, Z. & Xia, L. Digital economy and its spatial effect on green productivity gains in manufacturing: evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 378 (12), 134539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134539 (2022).
Hao, X., Wang, X., Wu, H. & Hao, Y. Path to sustainable development: does digital economy matter in manufacturing green total factor productivity? Sustain. Dev. 31 (1), 360–378. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2397 (2023).
Wang, S., Liang, Y., Li, W. & Cai, X. Big data enabled intelligent immune system for energy efficient manufacturing management. J. Clean. Prod. 195 (9), 507–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.203 (2018).
Du, K., Cheng, Y. & Yao, X. Environmental regulation, green technology innovation, and industrial structure upgrading: the road to the green transformation of Chinese cities. Energy Econ. 98 (6), 105247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105247 (2021).
Rubashkina, Y., Galeotti, M. & Verdolini, E. Environmental regulation and competitiveness: empirical evidence on the Porter hypothesis from European manufacturing sectors. Energy Policy. 83 (8), 288–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.02.014 (2015).
Yang, T., Yi, X., Lu, S., Johansson, K. H. & Chai, T. Intelligent manufacturing for the process industry driven by industrial artificial intelligence. Engineering. 7 (9), 1224–1230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2021.04.023 (2021).
Yang, H., Li, L. & Liu, Y. The effect of manufacturing intelligence on green innovation performance in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 178 (5), 121569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121569 (2022).
Rounaghi, M. M., Jarrar, H. & Dana, L. P. Implementation of strategic cost management in manufacturing companies: overcoming costs stickiness and increasing corporate sustainability. Future Bus. J. 7 (31), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-021-00079-4 (2021).
Liu, Y. & Zhang, X. Does labor mobility follow the inter-regional transfer of labor-intensive manufacturing? The spatial choices of China’s migrant workers. Habitat Int. 124 (6), 102559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2022.102559 (2022).
Aleksić, A., Stefanović, M., Arsovski, S. & Tadić, D. An assessment of organizational resilience potential in SMEs of the process industry, a fuzzy approach. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 26 (6), 1238–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2013.06.004 (2013).
Ding, X., Shi, L., Shi, M. & Liu, Y. Influencing factors of enterprise intelligent manufacturing based on the three stages of intelligent manufacturing ecosystems. J. Inform. Technol. Res. (JITR). 15(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.4018/JITR.299925 (2022).
Wang, B. et al. Smart manufacturing and intelligent manufacturing. Comp. Rev. Eng. 7(6), 738–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.07.017 (2021).
Wright, P. K. & Bourne, D. A. Manufacturing intelligence (Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc, 1988).
Devedzic, V. & Radovic, D. A framework for building intelligent manufacturing systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Part. C (Applic. Rev.) 29(1), 422–439. https://doi.org/10.1109/5326.777077 (1999).
Meziane, F., Vadera, S., Kobbacy, K. & Proudlove, N. Intelligent systems in manufacturing: current developments and future prospects. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 11(4), 218–238. https://doi.org/10.1108/09576060010326221 (2000).
Cheng, G. J., Liu, L. T., Qiang, X. J. & Liu, Y. Industry 4.0 development and application of intelligent manufacturing. (2016 international conference on information system and artificial intelligence (ISAI), 2016).
Shi, Y., Han, Q., Shen, W. & Zhang, H. Potential applications of 5G communication technologies in collaborative intelligent manufacturing. Iet Collaborative Intell. Manuf. 1 (4), 109–116. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cim.2019.0007 (2019).
Li, F., Liu, W. & Bi, K. Exploring and visualizing spatial-temporal evolution of patent collaboration networks: a case of China’s intelligent manufacturing equipment industry. Technol. Soc. 64 (2), 101483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101483 (2021).
Wang, H. & Li, B. Environmental regulations, capacity utilization, and high-quality development of manufacturing: an analysis based on Chinese provincial panel data. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 19566. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98787-y (2021).
Xu, X. & Han, P. Digital economy and high-quality development of manufacturing industry. (Business Intelligence and Information Technology: Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Intelligence and Information Technology BIIT 2021, 2022).
Chen, H. M., Kuo, T. C. & Chen, J. L. Impacts on the ESG and financial performances of companies in the manufacturing industry based on the climate change related risks. J. Clean. Prod. 380 (12), 134951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134951 (2022).
Baines, T., Lightfoot, H. & Smart, P. Servitization within manufacturing: exploring the provision of advanced services and their impact on vertical integration. J. Manuf. Technol. Manage. 22(7), 947–954. https://doi.org/10.1108/17410381111160988 (2011).
Yang, L. & Kumarasinghe, P. A behavioral model of service-derived manufacturing in e-commerce companies from the innovation chain perspective: a case study from China. Heliyon, 9(12). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23080 (2023).
Moh’d Anwer, A. S. Enabling manufacturing firms’ supply chain performance in the Middle East region through boosting the quality of multi-directional relationship, and supply chain risk dilution: A moderated-mediation model. Heliyon. 9 (11). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22059 (2023).
Lin, K. J., Lu, X., Zhang, J. & Zheng, Y. State-owned enterprises in China: a review of 40 years of research and practice. China J. Acc. Res. 13 (1), 31–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjar.2019.12.001 (2020).
Peng, B., Zheng, C., Wei, G. & Elahi, E. The cultivation mechanism of green technology innovation in manufacturing industry: from the perspective of ecological niche. J. Clean. Prod. 252, 119711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119711 (2020).
Zhou, J. et al. Toward new-generation intelligent manufacturing. Engineering. 4 (1), 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2018.01.002 (2018).
Ghobakhloo, M. Determinants of information and digital technology implementation for smart manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Res. 58 (8), 2384–2405. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1630775 (2020).
Shen, Y. & Zhang, X. Intelligent manufacturing, green technological innovation and environmental pollution. J. Innov. Knowl. 8 (3), 100384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2023.100384 (2023).
Braun, E. & Wield, D. Regulation as a means for the social control of technology. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 6 (3), 259–272. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537329408524171 (1994).
Li, J., Dong, K. & Dong, X. Green energy as a new determinant of green growth in China: the role of green technological innovation. Energy Econ. 114, 106260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106260 (2022).
Jiakui, C., Abbas, J., Najam, H., Liu, J. & Abbas, J. Green technological innovation, green finance, and financial development and their role in green total factor productivity: empirical insights from China. J. Clean. Prod. 382, 135131 (2023).
Hart, S. A natural-resource-based view of the firm. Acad. Manage. Rev. 20 (4), 986–1014. https://doi.org/10.2307/258963 (1995).
Sun, L., Miao, C. & Yang, L. Ecological-economic efficiency evaluation of green technology innovation in strategic emerging industries based on entropy weighted TOPSIS method. Ecol. Ind. 73, 554–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.10.018 (2017).
Subramaniam, M. & Youndt, M. A. The influence of intellectual capital on the types of innovative capabilities. Acad. Manag. J. 48 (3), 450–463. https://doi.org/10.5465/AMJ.2005.17407911 (2005).
Wang, L., Long, Y. & Li, C. Research on the impact mechanism of heterogeneous environmental regulation on enterprise green technology innovation. J. Environ. Manage. 322, 116127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116127 (2022).
Wang, F. & Chen, F. Board governance, environmental regulation and green technology innovation: Empirical test based on listed companies in China’s heavy polluting industry. Stud. Sci. Sci. 36(2), 361–369 (2018).
Liu, Y., Zhao, X. & Kong, F. The dynamic impact of digital economy on the green development of traditional manufacturing industry: evidence from China. Econ. Anal. Policy 80(1), 143–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2023.08.005 (2023).
Ruihui, Z., Xinmei, Y. & Yu, H. Cleaner production and total factor productivity of polluting enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 423(10), 138827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138827 (2023).
Olley, G. S. & Pakes, A. The dynamics of productivity in the telecommunications equipment industry. (1992).
Blundell, R. & Bond, S. GMM estimation with persistent panel data: an application to production functions. Econom. Rev. 19 (3), 321–340. https://doi.org/10.1080/07474930008800475 (2000).
Levinsohn, J. & Petrin, A. Estimating production functions using inputs to control for unobservables. Rev. Econ. Stud. 70 (2), 317–341. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-937X.00246 (2003).
Ackerberg, D. A., Caves, K. & Frazer, G. Identification properties of recent production function estimators. Econometrica. 83(6), 2411–2451. https://doi.org/10.3982/ECTA13408 (2015).
Lu, X. & Lian, Y. Estimation of total factor productivity of industrial enterprises in China: 1999–2007. China Econ. Q. 11(2), 541–558 (2012).
Zhao, S. Enterprise performance under the influence of intelligent manufacturing: Empirical evidence based on text analysis of annual reports of Chinese listed companies. J. Industrial Technol. Econ. 42(7), 95–101 (2023).
Wurlod, J. D. & Noailly, J. The impact of green innovation on energy intensity: an empirical analysis for 14 industrial sectors in OECD countries. Energy Econ. 71, 47–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.12.012 (2018).
Wen, Z., Chang, L., Hau, K. T. & Liu, H. Testing and application of the mediating effects. Acta Physiol. Sinica. 36 (05), 614–620 (2004).
Zhaocheng, X. & Jingchuan, H. Effects of CEO overseas experience on corporate social responsibility: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing listed companies. Sustainability, 13(10): 5335. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105335 (2021).
Finkelstein, S. & D’aveni, R. A. CEO duality as a double-edged sword: how boards of directors balance entrenchment avoidance and unity of command. Acad. Manag. J. 37 (5), 1079–1108. https://doi.org/10.2307/256667 (1994).
Zhaocheng, X. & Jingchuan, H. CEO overseas experience, dynamic capabilities and corporate digital transformation: An imprinting theory perspective. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 11(1), 743. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03227-7 (2024).
Zhang, Y., Song, Y. & Zou, H. Transformation of pollution control and green development: evidence from China’s chemical industry. J. Environ. Manage. 275, 111246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111246 (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.X. conceived the idea of the paper, carried out the empirical studies, participated in writing and provided constructive suggestions to improve the research and the financial support; R.P. participated in writing and revising the manuscript, and wrote the original draft, and revised the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Pan, R. Effects of intelligent manufacturing on the high-quality development of manufacturing industry: The mediating role of green technology innovation. Sci Rep 14, 26145 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-77584-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-77584-3
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nonlinear relationship between innovation input and intelligent manufacturing from an absorptive capacity perspective
Scientific Reports (2026)
-
Dual dimension assessment and green driven model for high quality industrial development level in Yangtze River Delta
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Predictive model on employee stock ownership impacting corporate performance
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Digital, intelligent, and all-round optical manufacturing method-magnetorheological finishing (wheel type): a review
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology (2025)