Abstract
This research paper discusses a wind turbine system and its integration in remote locations using a hybrid power optimization approach and a hybrid storage system. Wind turbine systems’ optimization controllers operate MPPT strategies efficiently, optimizing the system’s overall performance. The proposed approach is HTb(P&O/FLC), which combines the P&O and FLC methods. This innovative hybrid MPPT strategy takes advantage of the two methods. It maximizes the wind power thus minimizing stress on the storage system. For storage, batteries are important in isolated renewable energy systems due the interminent renewable sources. Unfortunately, they have some drawbacks as lower energy density, and limited charge-discharge. Besides, supercapacitors (SCs) have advantages as quick charging and discharging and long cycle life and some drawbacks as lower energy density and specific voltage requirements. This paper proposes a hybrid storage system combining batteries and SCs. To manage the two storage technologies, an effective algorithm isproposed focusing on managing their storage systems. The findings indicate that the proposed strategy effectively maintains the state of charge (SOC) of both the batteries and SCs in the intended limits. Simulation under MATLAB and Real-time with RT-LAB were carried out to validate the proposed control approach for the wind turbine system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Wind energy systems are important in the transition towards a clean energy economy.Research into wind turbine systems has therefore attracted great interest, focusing on aspects such as design, control, optimization, storage and performance analysis1,2,3,4,5. These studies provide valuable insights into integrating wind turbine systems with various energy storage technologies. The most commonly used wind turbine systems are those with battery and flywheel storage. Other systems with diesel generators, fuel cells, supercapacitors (SCs) and hydraulic power have also been widely adopted. Recently, hybrid storage systems have gained prominence in wind power systems6. By associating various storage technologies, these systems aim to optimize the energy storage and its utilization, thereby boosting wind turbine systems’ overall efficiency and reliability. The latter can be wind turbine systems with hydroelectric and batteries, with batteries and flywheels, batteries and fuel cells, batteries and diesel generators, and batteries and supercapacitors.
The main areas of research in wind turbine systems encompass several key domains. Principally, modeling and simulation1,2,3,4,5 act as fundamental components, with researchers concentrating to validate models under simulations of wind turbines (WTBs), and also wind power systems. These models allow the analysis of the performance, behaviorand dynamics. Economic studies7,8,9,10,11 have been conducted, employing methodologies such as life cycle assessment (LCA), levelized cost of energy (LCOE),.Moreover, optimzing control strategies is another important area12,13,14, in view of enhancing their performance, stability and reliability. Lately, the focus has moved to developp power management control approaches (PMC)15,16,17 in order to maximize the operation of wind power systems. Further research has led to advancements in energy storage and their integration into WTBs18,19,20,21,22. Also, significant attention has been directed toward improving the design of WTBs23,24,25,26,27,28 to optimize their performance (Fig. 1).
The primary challenge associated with wind energy sources lies in their irregular nature, hence need to use MPPT algorithms to maximize output power29,30. Various methods are used31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46, they all want more power but they function differently. The Perturb and Observation (P&O) method26,27,28,31,32,33,34,35 is the commonly uapplied in wind turbines, along with other techniques, including Optimal Torque Control (OTC)26, Tip Speed Ratio (TSR) and Power Signal Feedback (PSF). Advanced techniques, including Fuzzy Logic Controller (FLC) and Adaptive Fuzzy Logic Control (AFLC), Genetic Algorithm (GA), Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS), and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) controllers, are also frequently employed36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45.
The second challenge is on storage in WTBs. The extra energy produced by wind turbines during times of low demand or high wind production is stored in energy storage systems (ESSs) made up of batteries, flywheels, or other storage technologies. This stored energy can be utilized during high power demand or when wind conditions are unfavorable for sufficient electricity generation. By storing the surplus energy and releasing it when needed, the energy storage systems help balance supply and demand, enhance grid stability, and maximize the utilization of wind energy sources46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53.Batteries are the most used, they provide a reliable solution for energy storage, allowing for efficient storage and discharge of electricity54. Additionally, batteries offer a wide range of sizes, making them suitable for various applications in renewable energy systems (RESs), electric vehicles, and grid-scale storage projects. Conversely, supercapacitors have benefits including rapid charging and discharging rates. They can rapidly store and release energy, making them ideal for high-power bursts or frequent cycling applications. Nevertheless, SCs have drawbacks such a low energy density, a high price, and a short lifespan55. Despite these limitations, advancements in SCs technology enable to continue improving their performances and expand their potential applications, particularly in conjunction with batteries for hybrid energy storage solutions. Off-grid wind turbine systems that integrate two or more storage technologies provide a more flexible and dependable energy storage option. Using different storage technologies allows for reducing individual technological limits while optimizing the overall benefits of energy storage56. It provides various benefits for off-grid WTB deployments, including flexibility, reliability, efficiency, and economy57. The successful and efficient operation of wind turbine systems with multiple energy storage devices depends on an optimal and effective control strategy. Numerous research publications have addressed the challenges and opportunities associated with the power management in these systems. This power management involves controlling and optimizing power flow among various storage components to maintain a constant supply to the load58. By strategically allocating and managing energy storage resources, operators can mitigate the variability in wind power generation, improve grid stability, and maximize the output power wind turbine.
In recent years, integrating ESSs with advanced MPPT methods has garnered increasing attention due to the rising demand for efficient renewable energy systems59. Hybrid energy storage systems (HESS), typically combining batteries and supercapacitors, have been widely studied for their ability to balance energy and power density while ensuring stable operation in renewable energy applications, particularly in wind and solar systems19,60. The integration of HESS is essential for smoothing power fluctuations and enhancing the reliability of renewable energy systems. Researchers have explored various configurations and control strategies, with a strong focus on combining batteries and supercapacitors in wind and photovoltaic systems60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68. Power management strategies for HESS can be categorized into two broad types: classical approaches and intelligent control methods60,69. Classical control techniques rely on deterministic rules and well-established algorithms, making them widely used due to their simplicity and proven reliability in various applications (e.g., Droop Control70, Filter-Based Control60,71, Sliding Mode Control72, PID Control73,.). A detailed comparison of these classical approaches highlights their respective advantages and limitations has been presented in60. On the other hand, intelligent control strategies incorporate advanced algorithms, machine learning, and adaptive techniques to handle complex, nonlinear systems effectively74,75. These methods are particularly useful in uncertain and dynamic environments, employing techniques like FLC73, Model Predictive Control (MPC)10,11,76, Neural Networks (NN)77,78, and Genetic Algorithms (GA)79. In general, classical control approaches are favored in applications requiring simplicity, reliability, and ease of implementation, whereas intelligent control methods provide greater flexibility, adaptability, and enhanced performance in complex scenarios. The choice of strategy depends on the specific application (e.g., microgrids, electric vehicles, renewable energy systems), system complexity, and performance goals like efficiency and response time. Advanced approaches like predictive control, adaptive methods, and AI-driven techniques are at the forefront of improving efficiency, optimizing power distribution, and reducing energy losses80.
Recent studies81,82,83,84 have proposed adaptive energy management strategies for HESS in photovoltaic systems, emphasizing the dynamic allocation of power between batteries and supercapacitors based on load demands and renewable power fluctuations. Additionally, research has highlighted the importance of State of Charge (SOC) balancing and degradation management for extending battery lifespan in HESS85. In wind energy applications, recent efforts86,87,88 have focused on developing efficient energy management strategies, considering various parameters to optimize system performance, stability, and efficiency. MPPT techniques have also evolved with more sophisticated algorithms that adapt to rapidly changing conditions. While traditional methods like Hill Climbing Search (HCS) and Tip Speed Ratio (TSR) remain in use, they often face limitations in dynamic environments49. Advanced approaches, such as ANN-based MPPT algorithms89,90, have demonstrated superior convergence speed and accuracy. Hybrid MPPT strategies, combining techniques like fuzzy logic and particle swarm optimization (PSO)91, as well as adaptive sliding mode control (SMC) and extremum seeking control (ESC)92, have been proposed to address the nonlinear characteristics of wind turbines and maximize energy capture under varying conditions93.
A Power Management Control (PMC) system is presented in this work to regulate the operation of the WTB and the various storage systems. The PMC was implemented in a region with substantial wind speed potential, accommodating different wind profile scenarios. Weather conditions and geographic considerations were meticulously accounted for, resulting in consistently high system performance across various profiles. A comparative study of existing systems that use batteries as the only storage component and the proposed wind turbine system with hybrid storage (batteries/supercapacitors) shows that the suggested approach significantly decreases battery stress. This reduction enhances the system’s overall performance, presenting a notable advantage over conventional setups. The simulation results indicate the usefulness of the proposed PMC and also show its ability to maximize power generation in wind energy systems. Combining several storage systems with a power management control system enhances the system’s dependable and effectiveness even more.
The main contributions of this work include:
-
The integration complexity by coordinating the operation of a WTB with a hybrid storage and hybrid MPPT method, which involves integrating multiple components and algorithms,
-
The optimization by achieving optimal power management control requires algorithms and strategies to balance the energy supply and demand, considering the dynamic nature of wind energy and varying grid conditions,
-
The validation and testing of the effectiveness of the proposed optimal control system by simulation and real-time experimentation to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results.
Proposed system
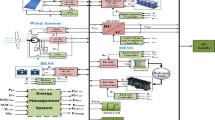
It is made up of three separate parts (Fig. 2). First, there is a permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG) and a wind turbine.
The proposed technique, which is known as HTb(P&O/FLC), maximizes WTB power. The second part is a hybrid storage system (batteries/SCs). The third part, the Power Management Controller (PMC) system, collects data from the optimal wind power, the batteries’ and solar cells’ state of charge (SOC), and the load power.
Modeling of the different components
Wind turbine modeling
The different equations for the mechanical power and torque and their optimal values are respectively given inthe following Eqs10,11,94:
where:
The mechanical equation is given as10,11:
The voltages in (d, q) reference framearedefined by10,11:
The electromagnetic torque is expressed as9,10:
The wind turbine used is 900 W and installed in our laboratory (Fig. 3). The different parameters are listed in Table 1.
Measurement acquisition equipment was used in the lab to measure wind speeds during four distinct profiles are obtained (very high, high, medium and low wind speeds). It is essentially composed of sensors in order to transfer the different signals to a data processing interface and then to a PC where they will be displayed using ACQUIsol software in real-time (Fig. 4).
So simulations have been made under data profile of wind speeds measured (Fig. 5.)during four days (96 h).
The wind speedsvariations for each profile are represented in Fig. 6.
And the obtained wind power for each profile are represented in Fig. 7.
Proposed hybrid storage modeling
The multi-storage studied in this work is the combination of batteries and supercapacitors.
Battery modeling
In our work, we employed the following model in Fig. 8, utilizing various voltage and charge state Eqs22,31,32.
In this work, we assume that the batteries are new and do not take into account the degradation of the system; therefore, we do not consider the state of health (SOH) of the batteries. This simplification allows us to focus on the performance and efficiency of the hybrid storage system without the complexities introduced by aging and capacity loss.
Model of the supercapacacitors
The model utilized in this study is the appropriate electric circuit with two RC branches (Fig. 9).
The different equations are33:
Using different storage technologies allows for reducing individual technological limits while optimizing the overall benefits of energy storage34,35,36,37,38. An optimal control is presented to regulate the operation of the wind turbine and the various storage components. The proposed control of the hybrid storage is shown in Fig. 10, where the SOCs of the batteries and SCs are calculated utilizing their respective reference powers, which are obtained following the supervision of the system (Fig. 11).
Determining the reference power value for a battery and supercapacitor in a hybrid energy storage system involves considering the dynamic power demands of the system, the power management control strategy, and the characteristics of each storage component95,96. We have:
We apply a low-pass filter to get the battery’s reference power and a complementary high-pass filter for the supercapacitor. We first calculate the battery power reference (PBattref):
where: FLPF is the transfer function of the low-pass filter.
Then, we deduce the supercapacitor power reference (Pscref):
We apply a control strategy to manage the power flow between the battery and supercapacitor based on their reference values. The strategy take account of the limits of state of charge of battery (SOCBatt−min=30% et SOCBatt−max=90%), and the limits of state of charge of supercapacitors (SOCsc−min=30% et SOCsc−max=90%).
Optimization of wind turbine
Efficiently extracting the maximum power from varying wind speeds is a primary objective of wind turbine control (Fig. 12). Using changes in duty cycle, voltage, and electro-magnetic torque, the rotational speed variation is related to determining the optimal power point.
Calculation of optimal duty cycle
We performed a theoretical analysis of the system under consideration to determine the expression for the optimum duty cycle. Figure 13 shows a representation of the researched system.
Ignoring the different losses and assuming the system is perfect (unit efficiency), the electrical power generated equals that of the one received by the battery32.
The equivalent diagram of one phase of the generator is given in Fig. 14.
The electrical power delivered by the generator is:
Finally, by combining Eq. (14) and Eq. (15),it is obtained:
To obtain maximum power:
For more simplifications, Eq. (16) can be written as:
with:
It is obtained:
After resolution, the optimal turbine duty cycle is:
where: RLoad is the load resistance, ω the angular rotational speed, Rs is the resistance of each phase, and Ls is the self-inductance of each phase.
Based on the optimal duty cycle (Eq. 21), the MPPT algorithm was developed. Figure 15 shows the block diagram of this strategy.
The optimal duty cycle is altered by variations in rotational speed, and this leads to a recalculation of the voltage applied to the generator, which regulates the electromagnetic torque. It is then compared with the wind turbine to provide a new optimum speed. In this way, the cycle is repeated continuously searching for the optimum power point.
Proposed hybrid MPPT
Two MPPT methods (P&O and FLC) were merged in our work. A method that joins the two procedures is obtained. The purpose of this optimization method is to improve performances. We can select different optimal values for each MPPT algorithm in the first phase. The optimal rotational speed and electromagnetic torque values are returned in the second stage. The most optimal turbine power is obtained at the third stage. Figure 16 presents the optimized power calculation that has been suggested.
Proposed PMC of wind turbine system with HESS
Effective power control in WTB systems ensures their efficiency and reliability. It improvespower production, enhance the system’s stability, and optimize available resources33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44. The flowchart of the proposed PMC is displayed in Fig. 17.
Eleven different modes are used by the system under study to operate (Table 2). These modes cover a range of scenarios. When energy storage components are operating at maximum load capacity, this is referred to as the full-load scenario. The regular, balanced energy flow inside the system was indicated by the conventional charge/discharge scenario, in contrast. On the contrary, the transient scenario refers to the system’s capacity to efficiently handle abrupt or transient variations in energy dynamics.
Simulation results
The proposed system is compared to five other configurations in Table 3 to highlight its superior performance.
case 1
This configuration involves a wind turbine system with a Perturb and Observe (P&O) MPPT controller and battery storage.
case 2
The system is equipped with supercapacitors (SCs) as the storage solution, while the MPPT controller remains the same as in Case 1.
case 2
In this case, a wind turbine is paired with supercapacitors for storage and utilizes a hybrid MPPT controller.
case 4
This configuration combines both batteries and supercapacitors for hybrid storage, coupled with a hybrid MPPT controller.
case 5
Here, the system also uses hybrid storage (batteries/SCs) but operates with a simple MPPT controller instead of a hybrid one.
case 6
This is similar to Case 1, with battery storage, but employs a hybrid MPPT approach instead of a single MPPT controller.
This comparison across different configurations clearly illustrates the advantages offered by the proposed system in Case 4, which integrates hybrid storage and a hybrid MPPT for enhanced performance and efficiency.
The battery, supercapacitor, load, and wind turbine powers are all shown simultaneously for each scenario in Fig. 18.
Wind power profiles vary with changing weather conditions. It is observed that a negative curve for the batteries and SCs indicates power recovery, whereas a positive curve signifies power supply to the load. In a wind energy system with supercapacitors as the storage solution, supercapacitors typically cannot continuously compensate for the wind turbine to power a load over long periods. Instead, they are designed to provide quick compensation for short durations It is noticed in case 2 (Fig. 18(b)), that Supercapacitors respond quickly for rapid compensation needs when there are sudden fluctuations in wind power However, they cannot sustain power delivery for hours like a battery as in case 1 (Fig. 18(a)). However, in the four cases, it is not readily apparent that case 4 is superior to the others despite its maximum wind power output of 969.1 W.
Figure 19 shows the expected load power and the calculated load power generated by all the power sources through the proposed PMC strategy. The curves of the two power profiles are largely superimposed, indicating that the calculated power closely matches the expected load power. However, there are certain moments where slight overshoots occur, revealing a surplus in the calculated power compared to the expected power. These overshoots may indicate brief instances where the PMC strategy generates more power than required, which could be due to transient conditions or conservative estimations within the control algorithm.
The accuracy and precision of a Power Management Control (PMC) strategy can be assessed by examining the difference (GP) between the expected load power (based on user demands) and the calculated load power (determined by the PMC strategy through variable condtitions measurements, management of hybrid storage using hybrid MPPT and proposed control strategy calculations). The smaller this difference, the more effective and accurate the PMC strategy is. In an ideal scenario, the gained load power (GP)—which represents the discrepancy between the expected and calculated power—should be minimal.
This indicates that the PMC can meet the load demands with minimal deviation, deliver the correct amount of power, even as conditions or demands fluctuate, and adapt dynamically to real-time changes in load requirements or available energy resources. The more effectively the PMC can minimize the gained load power, the better it can optimize energy resources and ensure that the power system remains responsive and reliable under varying conditions. The surplus power was determined and is illustrated in Fig. 20. It is observable that, occasionally, the calculated power surpasses the expected load power. Despite the PMC being properly designed and effectively utilized, a small power surplus was still noted, amounting to 544 W, and 8.255 W for cases 1, and 4, respectively. The notably low value in case 4 indicates that the proposed combination of hybrid storage and a hybrid MPPT was effectively managed across the different power sources. As a result, the load was more efficiently supplied in case 4 compared to the other scenarios. Of course, in cases 2 and 3, the GP is important because supercapacitors are not capable of continuously meeting power demands.
These cases are not interesting in a wind energy system, so for consistent and prolonged power delivery, supercapacitors whichare used for quick, short-term interventions, need to be combined with other storage solutions like batteries (as in case 1, 4, 5 and 6). By keeping the batteries at a higher SOC, the system reduces the depth of discharge and frequency of cycling, which are key factors in extending battery life. In other words, the batteries experience less stress, which leads to better preservation of their health over time. A comparison in terms of SOC evolution was conducted to demonstrate the efficacy of the suggested system design and to highlight the positive impact on the battery state of charge, which is crucial for the lifespan and overall performance of the energy storage components. The analysis covered just the cases where there is a battery storage (cases 1, 4, 5 and 6) as shown in Fig. 21.
For each wind speed profile analyzed, the State of Charge (SOC) of the batteries is consistently higher in case 4 compared to the other cases. This higher SOC level indicates that the configuration and control strategy employed in case 4 are more effective at optimizing energy utilization. As a result, both the performance and longevity of the energy storage components are significantly improved. This higher SOC is an indicator that the energy management strategy is efficiently balancing the load demands with the available energy resources. Case 4 manages the energy flows more effectively by distributing power generation and storage between the batteries and supercapacitors in a way that minimizes unnecessary charging and discharging cycles. This also reduces dammage on the storage components and ensures that energy is conserved and made available when it is most needed. The results clearly show that case 4 offers a noticeable improvement, even though this improvement is not overwhelmingly large. The specific load considered in this study does not exceed 1 kW/day, which is relatively modest in the context of the system being studied. Given this smaller scale, the advantages of the optimized energy management strategy are evident, but they are naturally constrained by the size of the system. However, the potential impact of case 4’s strategy could be much more significant if applied to a larger system. On a larger scale, where energy demands are greater and more storage capacity is involved, the benefits of a well-optimized control strategy, like the one used in case 4, would likely become even more pronounced. This suggests that the proposed configuration could deliver even greater efficiency, enhanced reliability, and extended lifespan of the storage components in larger wind energy systems. SOC variations are being analyzed under different cases. The wind speed is varied in discrete steps. Figure 22: illustrates how the SOC changes in each case when the wind speed changes in steps. It visually depicts the relationship between wind speed and the battery’s SOC during these steps. Table 4. contains specific SOC values for each case under the stepwise wind speed profile. It quantifies the SOC percentages for the different cases being compared. It is noticed that Case 4 has the superior SOC values, ranging between 74.24% and 81.61%. This indicates that, in this case, the system is more efficient in maintaining a higher battery charge, confirming earlier conclusions about its effectiveness.
The efficiency of a hybrid energy storage system that combines batteries and supercapacitors depends on the efficiencies of each component (battery, supercapacitor) and the power electronics (PE) that manage the energy flow between them, which assumed ideal in simlations. The overall storage efficiency can be estimated as the product of the individual component efficiencies:
where: hbatt, hSC are the battery and SC efficiency, Pbatt−discharge,tdischarge are battery power and time during discharge, Pbatt−charge,tcharge, are battery power, and time during charging, CSC is Capacitance of the supercapacitor, VSC−charge,VSC−discharge are charge and discharge voltages of the superca pacitor.
The efficiency of a hybrid system depends on how effectively it manages power distribution between the battery and the supercapacitor. Supercapacitors handle short, high-power bursts, while batteries provide long-term energy supply. System design plays a crucial role, as the ability to balance power demands between the two components significantly impacts overall efficiency. Additionally, proper State of Charge (SOC) management maximizes the efficiency of both the battery and supercapacitor by minimizing losses. Efficient power management strategies further optimize energy sharing between the components, enhancing system performance. Adding supercapacitors (SCs) to a hybrid energy storage system can decrease overall storage efficiency. This is primarily due to the extra energy required to manage the SC’s charge and discharge cycles, which may surpass the benefits of using SCs for handling high-power bursts. While SCs help reduce the stress on batteries by taking on the rapid power demands, thereby minimizing the strain on the battery by managing rapid power demands, they can introduce slight inefficiencies, leading to lower total storage efficiency compared to systems that utilize only batteries. Since, in our work, some configurations use both supercapacitors (SC) and batteries, while others use only batteries, we calculated the storage efficiencies for each scenario (as shown in Fig. 23). In the findings, Case 6 demonstrated the highest storage efficiency, achieved by maximizing power through the hybrid MPPT method, which minimized battery stress while not utilizing the supercapacitor. Case 1, which used a simple MPPT without supercapacitors, followed in efficiency. Cases 4 and 5, while showing slightly lower efficiency, offered superior SOC values—ranging from 84.10 to 86.55% in Case 4 and 84.81–86.2% in Case 5.
The introduction of supercapacitors slightly reduced hybrid system efficiency but ensured effective power management and battery health preservation. Case 4, despite not achieving the highest efficiency, excels in maintaining higher SOC levels, ranging between 74.24% and 81.61%, demonstrating its effectiveness in sustaining battery charge. Higher SOC values reduce the depth of discharge, extending battery lifespan and ensuring energy availability. Supercapacitors handle short power bursts, relieving stress on the battery, minimizing frequent charge-discharge cycles, and reducing wear, thus enhancing the battery’s longevity and ensuring stable energy supply.
OPAL-RT validation
A number of experimental tests were carried out on a real-time simulator (RT Lab) to evaluate the suggested control approaches in order to validate the simulation results that were achieved using MATLAB/Simulink. The system parameters were the same as in the numerical simulation conducted with MATLAB/Simulink. Figure 24 shows the established real-time simulation bench. It is comprised of an OP8660 data collection interface, an HIL controller, a digital oscilloscope, a real-time digital simulator (OP5700), and a host PC.
To confirm the numerical simulation results accuracy, a series of experimental tests were conducted on a real-time simulator (RT-LAB). These tests were designed to assess the performance of the proposed coordinated power management strategy under conditions closely resembling real-world operations. The system settings remained consistent with those used in the MATLAB/Simulink numerical simulation, ensuring that both environments provided a fair comparison of the results. This alignment in settings helps just to reinforce the credibility and reliability of the proposed strategy. Figures 25, 26 and 27 present the results obtained from simulations conducted using Matlab/Simulink, comparing the performance of the hybrid energy storage system across different scenarios. Figure 25 illustrates the fluctuations in wind power profiles, which vary based on changing weather conditions. These fluctuations are a common feature in wind energy systems due to the intermittent nature of wind. In this figure, when the batteries are supplying power to the load, the power output is depicted with a negative curve, indicating that the batteries are discharging energy. Conversely, when the supercapacitors (SCs) are involved, the power output is represented by a positive curve, signifying that the SCs are in a charging mode, as they regenerate power. This positive curve reflects the process of storing excess energy in the supercapacitors.
Figure 26 provides insights into the power generation and consumption dynamics of the storage system under different cases. It shows how the power from the wind turbine is managed and distributed between the batteries and supercapacitors. Each case represents a different set of conditions or configurations for the hybrid storage system.
Calculated \(\:{\text{P}}_{\text{L}\text{o}\text{a}\text{d}-\text{c}\text{a}\text{l}}\) and developed load power \(\:{\text{P}}_{\text{L}\text{o}\text{a}\text{d}\:}\)in case 4 (real-time simulation).
Figure 27 focuses on the performance comparison of the four cases, particularly highlighting the advantages of case 4. While all cases display variations in power profiles due to fluctuating wind conditions and load demands. Case 4. stands out because it shows a more balanced and efficient distribution of power between the batteries and supercapacitors. The results suggest that case 4 achieves better management of the energy storage system, minimizing inefficiencies and optimizing power delivery.
Gained power in case 4 (Real time simulation).
The figures collectively show how the hybrid storage system responds to varying wind conditions and load demands. The negative and positive curves in Fig. 24 highlight the complementary roles of batteries and supercapacitors in managing energy flow.
Conclusion
This research study discusses the integration of a multi-energy storage system consisting of batteries and supercapacitors with a wind turbine system in remote locations, using a hybrid power optimization approach. We have made a substantial contribution to the field of renewable energy systems with our work on a Power Management Controller (PMC) and a multi-storage system integrated into a wind turbine system. Our work was optimized and validated through simulation using MATLAB/Simulink. The results demonstrate how well the suggested PMC managed meteorological factors, resulting in excellent system performance over a range of profiles in a Mediterranean region. The effectiveness of the proposed system in terms of State of Charge, voltage battery, and current battery fluctuations is shown by comparing the SOC evolution of the analyzed system with three other situations. The development of hybrid MPPT and additional storage technology has decreased the stress on batteries.
The integration of supercapacitors in the hybrid storage system slightly decreased overall efficiency, but significantly enhanced power management and battery health. While Case 4 did not deliver the highest efficiency, it performed exceptionally well in maintaining higher SOC levels, showcasing its ability to sustain battery charge effectively. A detailed analysis of the battery’s State of Health (SOH) could further reveal the system’s long-term sustainability. Looking ahead, incorporating intelligent PMC control technologies can optimize energy use and extend the lifespan of system components.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Alternate current
- AFLC:
-
Adaptive Fuzzy Logic Control
- ANFIS:
-
Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System
- ANN:
-
Artificial Neural Network
- DC:
-
Direct current
- ESSs:
-
Energy Storage Systems
- FLC:
-
Fuzzy logic controller
- FLPF:
-
Transfer function of the low-pass filter
- HCS:
-
Hill climbing seach
- HTb:
-
Hybrid turbine MPPT
- HESS:
-
Hybrid energy storage systems
- GA:
-
Genetic Algorithm
- GP:
-
Gained power (W)
- LCA:
-
Life Cycle Assesment
- LCOE:
-
Levelized Cost Of Energy
- MPPT:
-
Maximum power point tracking
- OTC:
-
Optimal Torque Control
- PMC:
-
Power management control
- P&O:
-
Perturb & Observe
- PSF:
-
Power Signal Feedback
- PMSG:
-
Permanent synchronous generator
- RESs:
-
Renewable Energy Systems
- RT-LAB:
-
Real Time Laboratory
- SCs:
-
Supercapacotors
- SOC:
-
State of Charge (%)
- SOCBatt :
-
Battery State of Charge (%)
- SOCBattmax :
-
Maximum battery State of Charge (%)
- SOCsc :
-
SC State of Charge (%)
- SOCscmax :
-
Maximum SC State of Charge (%)
- SOCBattmin :
-
Minimum battery State of Charge (%)
- SOCscmin :
-
Minimum SC State of Charge (%)
- TSR:
-
Tip Speed Ratio
- WTBs:
-
Wind turbines
- Eo :
-
Open circuit voltage (V)
- Veff :
-
Efficace voltage (V)
- CBatt :
-
Capacity battery (A.h)
- Cp :
-
Power coefficient
- Cp-opt :
-
Optimal power coefficient
- C1 :
-
Main capacity (Ah)
- C2 :
-
Secondary capacity (Ah)
- DTb :
-
Turbine duty cyle
- f:
-
Friction coefficient (N.m.s rad-1)
- IBatt :
-
Battery current (A)
- Isd, Isq :
-
(d, q) stator currents (A)
- Idref :
-
Direct reference current (A)
- Idc :
-
Direct bus current (A)
- Isc :
-
Supercapacitor current (A)
- i1 :
-
Main current capacitor(A)
- i2 :
-
Secondary Current (A)
- J:
-
Total inertia (kg/m²)
- k:
-
Battery coefficient
- Kφ :
-
Flux coefficient
- Ls :
-
Inductance (H)
- Ld, Lq :
-
(d, q) inductances (H)
- Nsc-s :
-
Serial SC number
- Nsc-p :
-
Parallel SC number
- P:
-
Pair pole number
- PBatt :
-
Battery power (W)
- Pelec :
-
Electrical power (W)
- PLoad :
-
Load power (W)
- PLoad-calc :
-
Calculated load power (W)
- PN :
-
Rated power (W)
- Psc :
-
SC power (W)
- PTb :
-
Turbine power (W)
- PTb-opt :
-
Oprimized Turbine power (W)
- Pwind :
-
Wind power (W)
- Pwind−optimal :
-
Optimized wind power (W)
- Q:
-
Elementary battery charge, (C)
- RBatt :
-
Internal battery resistance (Ω)
- Rdc :
-
DC resistance (Ω)
- Req :
-
Equivalent resistance (Ω)
- RTb :
-
Turbine radius (m)
- Rs :
-
Stator windings resistance
- RLoad :
-
Load resistance (Ω)
- R1 :
-
Main resistance (Ω)
- R2 :
-
Secondary resistance (Ω)
- Tem :
-
Electromagnetic torque (N.m)
- TT :
-
Turbine torque (N.m)
- TTb-opt :
-
Optimal Turbine torque (N.m)
- VBatt :
-
Battery voltage (V)
- Usc :
-
Supercacitor voltage (V)
- Vdc :
-
DC bus voltage (V)
- Vsd, Vsq :
-
(d-q)Stator voltages (V)
- Vwind :
-
Wind speeds (m/s)
- V1 :
-
Main voltage (V)
- V2 :
-
Secondary voltage (V)
- ΔP:
-
Excess power (W)
- Φf :
-
PermanenMagnetic flux (Wb)
- Φeff :
-
Efficace flux (Wb)
- λ:
-
Tip speed ratio
- λopt :
-
Optimal tip speed ratio
- ρ:
-
Air density (kg/m3)
- ω:
-
Electrical angular speed (rad/s)
- ωTb :
-
Wind turbine velocity (rad/s)
References
Kushwaha, P. K. & Bhattacharjee, C. An extensive review of the configurations, modeling, Storage Technologies, Design parameters, sizing methodologies, Energy Management, System Control, and Sensitivity Analysis Aspects of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 51(20), 2603–2642. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325008.2023.2210556 (2023).
Mayilsamy, G. et al. A Review of State Estimation Techniques for Grid-Connected PMSG-Based Wind Turbine Systems.Energies. 16 (2), art. no. 634, pp.1–27.doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020634 (2023).
Rekioua, D. et al. Optimization and intelligent power management control for an autonomous hybrid wind turbine photovoltaic diesel generator with batteries. Sci. Rep. 13, 21830. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-49067-4 (2023).
Zhao, H., Wu, Q., Hu, S., Xu, H. & Rasmussen, C. N. Review of energy storage system for wind power integration support. Appl. Energy 137, pp. 545–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.04.103(2015).
Meryeme Azaroual, D. T. et al. Optimal solution of peer-to-peer and peer-to-Grid Trading Strategy sharing between Prosumers with Grid-connected Photovoltaic/Wind Turbine/Battery Storage systems. Int. J. Energy Res., (2023).
Cakiroglu, C. et al. Data-driven interpretable ensemble learning methods for the prediction of wind turbine power incorporating SHAP analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 237, 121464 (2024).
Rekioua, D. & Idjdarene, R. T. TounziA.,an approach for the modeling of an autonomous induction generator taking into account the saturation effect. Int. J. Emerg. Electr. Power Syst. 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1109/EPE.2007.4417591 (2005).
Srikanth Goud, B. et al. PV/WT Integrated System Using Grey Wolf Optimization Technique for Power Quality Improvement. Front. Energy Res. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2022.957971 (2022).
Idjdarene, K., Rekioua, D., Rekioua, T. & Tounzi, A. Wind energy conversion system associated to a flywheel energy storage system. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 69(1), 67–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-011-9629-2 (2011).
Aissou, R., Rekioua, T., Rekioua, D. & Tounzi, A. Application of nonlinear predictive control for charging the battery using wind energy with permanent magnet synchronous generator. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41(45), 20964–20973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.05.249 (2016).
Aissou, R., Rekioua, T., Rekioua, D. & Tounzi, A. Robust nonlinear predictive control of permanent magnet synchronous generator turbine using Dspace hardware. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41(45), 21047–21056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.06.109 (2016).
Rajagopalan, A. et al. Multi-objective energy management in a renewable and EV-integrated microgrid using an iterative map-based self-adaptive crystal structure algorithm. Sci. Rep. 14, 15652. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-66644-3 (2024).
Celik, A. N. Optimization and techno-economic analysis of autonomous photovoltaic-wind hybrid energy systems in comparison to single photovoltaic and wind system. Energy. Conv. Manag. 43, 2453–2468. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0196-8904(01)00198-4 (2002).
Li, R. et al. Techno-economic analysis of a wind-photovoltaic-electrolysis-battery hybrid energy system for power and hydrogen generation. Energy. Conv. Manag. 281, art116854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2023.116854 (2023).
Amoussou, I. et al. Enhancing residential energy access with optimized stand-alone hybrid solar-diesel-battery systems in Buea. Cameroon Sci. Rep. 14, 15543. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-66582-0 (2024).
Rekioua, T. & Rekioua, D. Direct torque control strategy of permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Bologna PowerTech - Conference Proceedings, 2, art. no. 1304660, pp. 861–866. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/PTC.2003.1304660 (2003).
Khosravi, N. et al. A novel control approach to improve the stability of hybrid AC/DC microgrids. Appl. Energy 344, 121261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121261 (2023).
García, P. T. J. P. & Jurado, F. Optimal energy management system for stand-alone wind turbine/photovoltaic/hydrogen/battery hybrid system with supervisory control based on fuzzy logic. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 38(33), 14146–11415. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHYDENE.2013.08.106 (2013).
Rekioua, D. Energy Storage Systems for photovoltaic and wind systems: a review. Energies 16(9), 3893. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16093893 (2023).
Lopez-Flores, D. R. (ed Duran-Gomez, J. L.) Control and energy management system techniques in renewable sources: a brief review. Int. Power Electron. Congress-CIEP 2018–October art. 8573320 139–145 https://doi.org/10.1109/CIEP.2018.8573320 (2018). (2018).
Punyavathi, R. et al. Sustainable power management in light electric vehicles with hybrid energy storage and machine learning control. Sci. Rep. 14, 5661. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-55988-5 (2024).
Mohammedi, A., Rekioua, D., Rekioua, T. & Bacha, S. Valve regulated lead acid battery behavior in a renewable energy system under an ideal Mediterranean climate. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41(45), 20928–20938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.05.087 (2016).
Serpi, A., Porru, M. & Damiano, A. An optimal power and energy management by hybrid energy storage systems in microgrids. Energies 10(11), art1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/EN10111909 (2017).
Syed, A. & Din Mufti (ed, M.) Coordinated control of wind farm and supercapacitor energy storage system for dynamic performance reinforcement of multi-area power systems. Int. J. Power Electron. 17 3 261–279 https://doi.org/10.1504/ijpelec.2023.129981 (2023).
Barra, P., de Carvalho, W., Menezes, T., Fernandes, R. & Coury, D. A review on wind power smoothing using high-power energy storage systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 137, 110455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110455 (2021).
Zhao, H., Wu, Q., Hu, S., Xu, H. & RasmussenC.N. Review of energy storage system for wind power integration support. Appl. Energy 137, 545–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.04.103 (2015).
Olabi, A. G. et al. Wind energy contribution to the Sustainable Development Goals: Case Study on London array. Sustainability 15, 4641. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054641 (2023).
Korpaas, M., Holen, A. T. & Hildrum, R. Operation and sizing of energy storage for wind power plants in a market system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 25(8), 599–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-0615(03)00016-4 (2003).
Zhu, C. et al. Optimization, validation and analyses of a hybrid PV-battery-diesel power system using enhanced electromagnetic field optimization algorithm and ε-constraint. Energy Rep. 11, 5335–5349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2024.04.043 (2024).
Liu, Z. et al. A review of common-mode voltage suppression methods in wind power generation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 203, 114773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2024.114773 (2024).
Kazmi, A., Goto, H., Guo, H-J. & IchinokuraO Sept. Review and critical analysis of the research papers published till date on maximum power point tracking in wind energy conversion system. 2010 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition. 12–16 Atlanta, GA, USA. 4076–4082.doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-0615(03)00016-4 (2010).
Abdullah, M. A. et al. A review of maximum power point tracking algorithms for wind energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 16(5), 3220–3227doi. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.02.016 (2012).
Kumar, M. B. H., Saravanan, B. & Sanjeevikumar, P. Blaabjerg F.Review on control techniques and methodologies for maximum power extraction from wind energy systems. IET Renewable Power Generation, 12 (14), art. no. Y, 1609–1622. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.02.016 (2018).
Heydari, M. & Smedley, K. Comparison of maximum power point tracking methods for medium to high power wind energy systems, 20th Conference on Electrical Power Distribution Networks Conference (EPDC), Zahedan, Iran, pp. 184–189.doi: (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/EPDC.2015.7330493 (2015).
Tanaka, T. & Toumiya, T. Pergamon output control by hill-climbing method for a small scale wind power generating system. Renew. Energy 12(4), 387–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-1481(97)00055-4 (1997).
Mishra, S. et al. Comprehensive review on maximum power point tracking techniques: wind energy. Communication Control Intelligent Systems. Mathura, India, pp.464–46.doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CCINTELS.2015.7437961 (2015).
Muhammad Raza, K. S., Goto, H., Guo, H. J. & Ichinokura, O. A novel speed-sensorless adaptive hill climbing algorithm for fast and efficient maximum power point tracking of wind energy conversion systems. 2008 IEEE International Conference on Sustainable Energy Technologies, Singapore, pp. 628–633.doi: (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2010.2044732
Karabacak, M. A new perturb and observe based higher order sliding mode MPPT control of wind turbines eliminating the rotor inertial effect. Renew. Energy 133, 807–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.10.079 (2019).
Yurdusev, M. A., Ata, R. & Çetin, N. S. Assessment of optimum tip speed ratio in wind turbines using artificial neural networks. Energy 31(12), 1817–1825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2005.09.007 (2006).
Balasundar, C., Sudharshanan, S. & Elakkiyavendan, R. Design of an optimal tip speed ratio control MPPT algorithm for standalone WECS. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 3(V), 443–450 (2015).
Nasiri, M., Milimonfared, J. & Fathi, S. H. Modeling, analysis and comparison of TSR and OTC methods for MPPT and power smoothing in permanent magnet synchronous generator-based wind turbines. Energy Convers. Manage. 86, 892–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.06.055 (2014).
Abdel-Raheem, Y. Maximum power point tracking of a wind power system based on five phase PMSG using optimum torque control. 17th International Middle-East Power System conference (MEPCON’15). Mansoura University, Egypt, December 15–17. (2015).
Simoes, M. G., Bose, B. K. & Spiegel, R. J. Fuzzy logic based intelligent control of a variable speed cage machine wind generation system. IEEETrans Power Electron. 12(1), 87–95. https://doi.org/10.1109/63.554173 (1997).
Amine, H. M. & Abdelaziz, H. Najib E.Wind turbine maximum power point tracking using FLC tuned with GA. Energy Procedia 62, 364–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.12.398 (2014).
Pucci, M., Cirrincione, M. & Neural MPPT control of wind generators with induction machines without speed sensors’. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58(1), 37–47. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2010.2043043 (2011).
Tiwari, R., Kumar, K., Neelakandan, R. B., Padmanaban, S. & Wheeler, P. W. Neural network based maximum power point tracking control with quadratic boost converter for PMSG—wind energy conversion system. Electron. (Switzerland). 7 (2), art20. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7020020 (2018).
Kumar, A. & Rathore, A. Modelling and testing of wind energy fed hybrid battery-supercapacitor energy storage operating in pulsed charging mode. Wind Eng. 48(2), 228–242. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309524X231203689 (2024).
Kakouche, K. et al. Model Predictive Direct Torque Control and Fuzzy Logic Energy Management for Multi Power Source Electric Vehicles Sensors, 22 (15), art. no. 5669. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155669 (2022).
Belaid, S., Rekioua, D., Oubelaid, A., Ziane, D. & Rekioua, T. A power management control and optimization of a wind turbine with battery storage system. J. Energy Storage 45, 103613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2021.103613 (2022).
Rekioua, D. et al. Optimized Power Management Approach for Photovoltaic Systems with Hybrid Battery-Supercapacitor Storage. Sustainability.15, 14066. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914066 (2023).
Sahri, Y. et al. Performance improvement of Hybrid System based DFIG-Wind/PV/Batteries connected to DC and AC grid by applying Intelligent Control. Energy Rep. 9, 2027–2043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2023.01.021 (2023).
Djouadi, H., Ouari, K., Belkhier, Y., Lehouche, H. & Bajaj, M. Improved Robust Model Predictive Control for PMSM using Backstepping Control and Incorporating Integral Action with experimental validation. Results Eng. 102416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102416 (2024).
Amel Kasri, K. et al. Real-time and hardware in the loop validation of electric vehicle performance: robust nonlinear predictive speed and currents control based on space vector modulation for PMSM, results in Engineering, 22, 102223, ISSN 2590 – 1230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102223 (2024).
Ma, K., Yang, J. & Liu, P. Relaying-assisted communications for demand response in Smart Grid: cost modeling, game strategies, and algorithms. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 38 (1), 48–60. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2019.2951972 (2020).
Ju, Y., Liu, W., Zhang, Z. & Zhang, R. Distributed three-Phase Power Flow for AC/DC Hybrid Networked microgrids considering Converter limiting constraints. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 13(3), 1691–1708. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2022.3140212 (2022).
Pandya, S. B. et al. Multi-objective snow ablation optimization algorithm: an Elementary Vision for Security-constrained Optimal Power Flow Problem incorporating wind Energy Source with FACTS devices. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 17(1), 33 (2024).
Saeed, M. A. et al. Forecasting wind power based on an improved Al-Biruni Earth radius metaheuristic optimization algorithm. Front. Energy Res. 11, 1220085 (2023).
Meng, Q., Jin, X., Luo, F., Wang, Z. & Hussain, S. Distributionally Robust Scheduling for Benefit Allocation in Regional Integrated Energy System with multiple stakeholders. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean. Energy 1–12. https://doi.org/10.35833/MPCE.2023.000661 (2024).
Dunna, V. K. et al. Super-twisting MPPT control for grid-connected PV/battery system using higher order sliding mode observer. Sci. Rep. 14(1), 16597 (2024).
Abo-Khalil, A. G., Sobhy, A., Abdelkareem, M. A. & Olabi, A. G. Advancements and challenges in hybrid energy storage systems:Components, control strategies, and future directions.International Journal of Thermofluids, 20, art. no. 100477, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijft.2023.100477 (2023).
Roy, P., Liao, Y. & He, J. Economic Dispatch for Grid-connected wind power with battery-supercapacitor Hybrid Energy Storage System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 59(1), 1118–1128. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2022.3203663 (2023).
Rashid, G., Lone, S. A. & Mufti, M. U. din. Dynamic performance improvement of an isolated wind-diesel system with intelligently controlled supercapacitor energy storage system. Wind Engineering 48(2):217–227. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0309524X231203952 (2024).
Pourmousavi, S. A., Nehrir, M. H., Colson, C. M. & Wang, C. Real-time energy management of a stand-alone hybrid wind-microturbine energy system using particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 1 (3), 193–201. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2010.2061881 (2010).
Mokrani, Z., Rekioua, D., Mebarki, N., Rekioua, T. & Bacha, S. Energy management of battery-PEM fuel cells hybrid energy storage system for electric vehicle. Proc. 2016 Int. Renew. Sustainable Energy Conf. IRSEC 2016 7984073, 985–990. https://doi.org/10.1109/IRSEC.2016.7984073 (2017).
Elmorshe, M. F., Elkadeem, M. R., Kotb, K. M., Taha, I. B. M. & Mazzeo, D. Optimal design and energy management of an isolated fully renewable energy system integrating batteries and supercapacitors. Energy Convers. Manage. 245, art114584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2021.114584 (2021).
Azuara-Grande, L. S., Arnaltes, S., Alonso-Martinez, J. & Rodriguez-Amenedo, J. L. Comparison of two Energy Management System strategies for real-time operation of isolated hybrid microgrids. Energies 14, 6770. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206770 (2021).
Hamed, S. B. et al. Robust Optimization and Power Management of a Triple Junction Photovoltaic Electric Vehicle with Battery Storage sensors 22, no. 16: 6123. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22166123 (2022).
Robyns, B., Davigny, A. & Saudemont, C. Methodologies for supervision of hybrid energy sources based on storage systems – a survey. Math. Comput. Simul. 91, 52–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2012.06.014 (2013).
Li, P., Hu, J., Qiu, L., Zhao, Y. & Ghosh, B. K. A distributed economic dispatch strategy for power–water networks. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 9(1), 356–366. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCNS.2021.3104103 (2022).
Teng, J. H., Luan, S. W., Lee, D. J. & Huang, Y. Q. Optimal charging/discharging scheduling of battery storage systems for distribution systems interconnected with sizeable PV generation systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 28(2), 1425–1433. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2012.2230276 (2013).
Sayed, K., Abo-Khalil, A. G. & Alghamdi, S. A. Optimum Resilient Operation and Control DC Microgrid Based Electric Vehicles Charging Station Powered by Renewable Energy Sources. Energies 12, 4240. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224240 (2019).
Mishra, S., Pullaguram, D., AcharyBuragappu, S. & Ramasubramanian, D. Single-phase synchronverter for a grid-connected roof top photovoltaic system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 10, 1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rpg.2015.0224 (2016).
Wang, S. et al. Design and advanced control strategies of a hybrid energy storage system for the grid integration of wind power generations, IET renew. Power Gener 9, 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rpg.2013.0340 (2015).
Meng, Q., Hussain, S., Luo, F., Wang, Z. & Jin, X. An online reinforcement learning-based Energy Management Strategy for microgrids with Centralized Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2024.3430264 (2024).
Shirkhani, M. et al. A review on microgrid decentralized energy/voltage control structures and methods. Energy Rep. 10, 368–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2023.06.022 (2023).
Govindan, K., Jafarian, A. & Azbari, M. E. Choi,Optimal bi-objective redundancy allocation for systems reliability and risk management. IEEE Trans. Cybern 46, 1735–1748. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2014.2382666 (2016).
Ramu, S. K., Vairavasundaram, I., Palaniyappan, B. & Bragadeshwaran, A. AljafariB.,Enhanced energy management of DC microgrid: Artificial neural networks-driven hybrid energy storage system with integration of bidirectional DC-DC converter, Journal of Energy Storage, 88, art. no. 111562.doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2024.111562 (2024).
Barbosa, A. M., Rotella Junior, P., Rocha, L. C. S., Barbosa, A. D. S. & Bolis, I. Optimization methods of distributed hybrid power systems with battery storage system: a systematic review. J. Energy Storage 97, 112909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2024.112909 (2024).
Aktas, A., Onar, O. C., Asa, E., Ozpineci, B. & Tolbert, L. M. Genetic algorithm-based optimal sizing of Hybrid Battery/Ultracapacitor Energy Storage System for Wave Energy Harvesting Applications, in IEEE Access, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3414433 (2024).
Mazouzi, A., Hadroug, N., Alayed, W., Hafaifa, A. & Iratni, A. KouzouA.,Comprehensive optimization of fuzzy logic-based energy management system for fuel-cell hybrid electric vehicle using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 81, 889–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.07.237 (2024).
Liu, Y. et al. An Adaptive Energy Management Strategy of Stationary Hybrid Energy Storage System. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrification 8(2), 2261–2272. https://doi.org/10.1109/TTE.2022.3150149 (2022).
Wasim, M. S. et al. An efficient energy management scheme using rule-based swarm intelligence approach to support pulsed load via solar-powered battery-ultracapacitor hybrid energy system. Sci. Rep. 14, 3962 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-53248-0(2024).
MaB., G. X. LiP., Adaptive energy management strategy based on a model predictive control with real-time tuning weight for hybrid energy storage system, Energy,Volume 283,129128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.129128 (2023).
Emrani, A., Achour, Y., Sanjari, M. J. & Berrada, A. Adaptive energy management strategy for optimal integration of wind/PV system with hybrid gravity/battery energy storage using forecast models. J. Energy Storage Volume 96, 112613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2024.112613 (2024).
Hussein, H. M., Aghmadi, A., Abdelrahman, M. S., Rafin, S. M. S. H. & Mohammed, O. A review of battery state of charge estimation and management systems: models and future prospective, batteries, 10.3390/batteries10030089, 10, 3, (89), doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/wene.507 (2024).
Kord, H., Zamani, A. A. & Barakati, S. M. Active hybrid energy storage management in a wind-dominated standalone system with robust fractional-order controller optimized by gases brownian motion optimization algorithm. J. Energy Storage 66, 107492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2023.107492 (2023).
Rekioua, D. et al. Coordinated power management strategy for reliable hybridization of multi-source systems using hybrid MPPT algorithms. Sci. Rep. 14, 10267. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60116-4 (2024).
Adeyinka, A. M. et al. Advancements in hybrid energy storage systems for enhancing renewable energy-to-grid integration. Sustainable Energy res. 11, 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40807-024-00120-4 (2024).
Toumi, I., Boulmaiz, A., Meghni, B. & Hachana, O. Robust variable step P&O algorithm based MPPT for PMSG wind generation system using estimated wind speed compensation technique. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 60, 103420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2023.103420 (2023).
Ravi, S., Premkumar, M. & Abualigah, L. Comparative analysis of recent metaheuristic algorithms for maximum power point tracking of solar photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions. Int. J. Appl. Power Eng. 12(2), 196–217 (2023).
Bouchakour, A. et al. MPPT algorithm based on metaheuristic techniques (PSO & GA) dedicated to improve wind energy water pumping system performance. Sci. Rep. 14, 17891. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-68584-4(2024).
Torchani, B., Azar, A. T., Ahmed, S., Mahlous, A. R. & Kasim Ibraheem, I. Sliding mode control based on maximum power point tracking for dynamics of wind turbine system. Front. Energy Res. 12, 1434695. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2024.1434695 (2024).
Premkumar, M. et al. Optimal operation and control of hybrid power systems with stochastic renewables and FACTS devices: an intelligent multi-objective optimization approach. Alexandria Eng. J. 93, 90–113 (2024).
Anagreh, Y. & Al-Quraan, A. The behavior of terminal voltage and frequency of wind-driven single-phase induction generators under variations in Excitation Capacitances for different operating conditions. Energies 17 (15), 3604 (2024).
Pandya, S. B. et al. Multi-objective RIME algorithm-based techno economicd analysis for security constraints load dispatch and power flow including uncertainties model of hybrid power systems. Energy Rep. 11, 4423–4451 (2024).
Fadheel, B. A. et al. A Hybrid Sparrow Search Optimized Fractional Virtual Inertia Control for Frequency Regulation of Multi-Microgrid System (IEEE Access, 2024).
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to Taif University, Saudi Arabia, for supporting this work through the project number (TU-DSPP-2024-14).
Funding
This research was funded by Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia, Project No. (TU-DSPP-2024-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D. Rekioua, N. Mezzai, Z. Mokrani, A. Oubelaid, K. Kakouche: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Investigation, Writing- Original draft preparation. P.O Logerais, Muhannad Alshareef: Data curation, Validation, Supervision, Resources, Writing - Review & Editing. Mohit Bajaj, Milkias Berhanu Tuka, Sherif S. M. Ghoneim: Project administration, Supervision, Resources, Writing - Review & Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Rekioua, D., Mezzai, N., Mokrani, Z. et al. Effective optimal control of a wind turbine system with hybrid energy storage and hybrid MPPT approach. Sci Rep 14, 30013 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-78847-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-78847-9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A smart single stage solar battery driven desalination system with hybrid MPPT and optimal control for brackish water treatment
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
A high-speed MPPT based horse herd optimization algorithm with dynamic linear active disturbance rejection control for PV battery charging system
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
A novel adaptive FOCV algorithm with robust IMRAC control for sustainable and high-efficiency MPPT in standalone PV systems: experimental validation and performance assessment
Scientific Reports (2024)