Abstract
Sauropod dinosaurs were gigantic quadrupedal herbivores. They range from Early Jurassic to Late Cretaceous and have been found on all continents. The rich sauropod faunas in the Middle and Late Jurassic of China are mainly from southern or western China. Here, we describe a non-neosauropod eusauropod from the Middle Jurassic Xinhe Formation of Gansu Province, northwestern China, based on an associated partial skeleton that includes a nearly complete skull with mandible, the five anteriormost cervical vertebrae appressed with the skull and the posterior 29 articulated caudal vertebrae. It can be diagnosed as a new taxon Jinchuanloong niedu gen. et sp. nov. based on several cranial and postcranial autapomorphies. In Jinchuanloong, the posterior margin of the external naris lies in front of the posterior margin of the antorbital fenestra, similar to that in basal eusauropods, and the base of the maxillary ascending process presents a foramen, similar to that in neosauropods. The finding of Jinchuanloong adds diversity and helps elucidate the evolution of the sauropods in East Asia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Sauropod dinosaurs were gigantic quadrupedal herbivores, ranging from the Early Jurassic to Late Cretaceous, and have been found on all continents1,2. Due to the global warming event in the late Early Jurassic, eusauropods were the only surviving sauropod lineage subsequently1,3,4. In the Middle and Late Jurassic, the non-neosauropod eusauropod became dominant, represented by Shunosaurus, Omeisaurus, and ‘core Mamenchisaurus-like taxa’(CMTs)5,6. Shunosaurus comes from the Middle Jurassic Lower Shaximiao Formation, Sichuan Basin, China7,8. Omeisaurus has 8 species, which are from the Upper Jurassic, Sichuan Basin, China9,10,11,12,13,14,15. Gansu Province is one of the earliest and richest areas where dinosaurs have been found in China. However, most discoveries of Gansu’s Sauropodas dinosaurs are neosauropods from the Early Cretaceous, such as Gobititan shenzhouensis (Titanosauriformes)16, Huanghetitan liujiaxiaensis (Titanosauriformes)17, Daxiatitan binglingi (Titanosauriformes)18, Qiaowanlong kangxii (Brachiosauridae)19 and Yongjinglong datangi (Titanosauria)20. In 2017, Dr. Li Daqing and his team discovered a new vertebrate assemblage including dinosaurs, plesiosaur, and chelonian remains from the Middle Jurassic Xinhe Formation in Jinchang City, Gansu Province21. Most reports of Mamenchisauridae are from the Sichuan Basin and Dianzhong Basin (Middle-Upper Jurassic)22, China, represented by Mamenchisaurus (7 species)23,24,25,26,27,28,29, Chuanjiesaurus3,30, Xinjiangtitan31,32,33, Hudiesaurus34 and Klamelisaurus5. Besides, Wamweracaudia comes from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Tanzania, which represents a non-Asian representative of Mamenchisauridae6.
The complete skulls are rarely in non-neosauropod eusauropods due to their fragility, represented by Shunosaurus7,35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Nebulasaurus36, Mierasaurus37 and Turiasaurus38. Here, we describe a new eusauropod represented by a partial skeleton with a nearly complete skull. This is not only a rare non-neosauropod eusauropod in Gansu Province, but also the earliest sauropod found in Gansu Province.
Institutional abbreviations
JCMF Jinchang Museum Fossil
Results
Geological setting
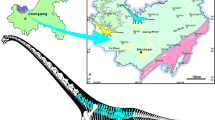
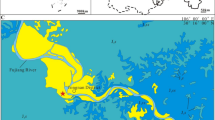
The study area is in the Jinchuan District of Jinchang City, Gansu Province (Fig. 1a,b. The stratigraphic regionalisation of this area is associated with the Chaoshui Basin within the North Qilian stratigraphic zone21. Jurassic sediments are primarily represented by the Early-Middle Jurassic Qingtujing Group and the Late Jurassic Shazaohe Formation21. A fault-induced truncation has removed the base of the Qingtujing Group, while the top of the Shazaohe Formation is unconformably overlain by Neogene deposits (Fig. 1c). The Qingtujing Group is subdivided into two lithostratigraphic units: the Longfengshan Formation and the Xinhe Formation. The Longfengshan Formation, exceeding 200 m in thickness, comprises grey conglomerate and pale-yellow sandstone interbedded with grey-black mudstone. The Xinhe Formation, approximately 120 m thick, has a lower section composed of medium to thick-bedded straw-yellow conglomerate, sandstone, and siltstone interbedded with greenish-yellow silty mudstone. Its upper section is characterised by interbedded bluish-grey shale and mudstone, with a tuffaceous interlayer that hosts a diverse lacustrine invertebrate assemblage, including bivalves and conchostracans. The dinosaur remains were discovered in the sandstone of the lower part of the Xinhe Formation (Fig. 1d). The megafossil plants, palynoflora from the lower part, as well as the lacustrine invertebrate assemblage from the upper part of the Xinhe Formation39,40,41, indicate that the dinosaur-bearing horizon is late Bathonian in age42,43,44.
Location and geological map of the fossil locality (from Gao et al. (2019)). (A,B) location of the fossiliferous locality in the Gansu Province. (C) Geological map of the involved strata of the studied fossil site (from State Buteau of Surveying and Mapping, GS (2016)2884). (D) Stratigraphic chart of the Jurassic at the Jinchuanloong niedu locality.
Systematic paleontology
Dinosauria Owen, 184245.
Saurischia Seeley, 188746.
Sauropodomorpha Huene, 193247.
Sauropoda Marsh, 187848.
Eusauropoda Upchurch, 199549.
Jinchuanloong niedu gen. et sp. nov.
Holotype
JCMF 0132 comprises an associated partial skeleton including a nearly complete skull with mandlble, the five anteriormost cervical vertebrae, and twenty-nine articulated middle and posterior caudal vertebrae, plus some fragmented caudal ribs and some haemal arches. The skull is appressed with the five anteriormost cervical vertebrae, about five meters from the twenty-nine articulated caudal vertebrae. Between the cervical vertebrae and the caudal vertebrae, the impressions of the pelvic girdle and sacral vertebrae are preserved. These bones belong to one individual.
The skull of Jinchuanloong is very well preserved and nearly complete. The left side of the skull has been deformed by a lateromedial compression. Most cranial sutures are readily visible in Jinchuanloong. Among the 34 cervical and caudal vertebrae, two series are articulated: cervical vertebrae 1–5 and a caudal series of 29; the two series were separated by a gap because the rest of the axial skeletons were missing. The anterior series are the five anteriormost cervical vertebrae appressed with the skull, comprising the atlas-axis complex and the poorly preserved cervical vertebrae3-5. The posterior 29 articulated vertebrae are preserved in situ, representing the middle and posterior caudal vertebrae. The first seven caudal vertebrae are represented by the neural spines, and the remaining articulated elements are well exposed on the right sides. Based on the original burial location, we conclude that Jinchuanloong was about 10 m long and maybe a subadult.
Etymology
The genus name ‘Jinchuan’ refers to the region where the specimens were found; ‘loong’ is Mandarin Chinese for ‘dragon’. ‘Nie’, the Mandarin Chinese for ‘nickel’; ‘du’, the Mandarin Chinese for ‘city’, reflecting that Jinchuan (Jinchang) is a city famous for its rich nickel resources.
Horizonandlocality
Jinchuan District, Jinchang City, Gansu Province, northwest of China; lower part of the Xinhe Formation (late Bathonian).
Diagnosis
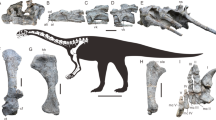
Jinchuanloong can be diagnosed by a suite of unique character combinations (autapomorphies are marked by *): (1) in lateral view, there is a small foramen at the base of the nasal process of the maxilla *. (2) The anterodorsal surface of the prefrontal bears a small round aperture near the bifurcation (Figs. 2 and 5) *. (3) In lateral view, the postorbital is very robust. The ratio of the anteroposterior length to the dorsoventral height of the posterior process of the postorbital of Jinchuanloong is 0.9 *. (4) The posteroventral process of the jugal contributes 22% of the ventral margin of the infratemporal fenestra; The dorsal process of the jugal contacts the lacrimal and has a small contribution to the antorbital fenestra (Fig. 2).
Skull of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132) in left lateral view. Abbreviations: a, aperture; an, angular; aof, antorbital fenestra; d, dentary; en, external naris; f, frontal; fo, foramen; inf, infratemporal fenestra;j, jugal; l, lacrimal; m, maxilla; n,nasal; o, orbit; p, parietal; pf, prefrontal; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pop, paraoccipital process; q, quadrate; qj, quadratojugal; sa, surangular; snf, subnarial foramen; sq, squamosal.
Description and comparisons
General
The skull of Jinchuanloongis approximately 310mm long and 125 mm tall (Table 1 and Fig. 2). In general, the skull of Jinchuanloong most closely resembles non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Mamenchisaurus youngi24, which lacks the V-shaped outline of early sauropodomorphs and the squared-off shape in diplodocoids in dorsal view. Although Jinchuanloong seems to have a broader snout in dorsal view than some coeval sauropods such as Shunosaurus7,35 and Mamenchisaurus youngi24, it could have been deformed (Fig. 3). The oval-shaped external naris is bounded by the premaxilla, maxilla and nasal. The position of the external naris is retracted to the level of the orbit, facing laterally (Fig. 5), similar to Yizhousaurus sunae50, Shunosaurus7,35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10 and Mamenchisaurus youngi24, different from Nigersaurus51 and Apatosaurus52, where the external nares are retracted to a position between the orbits, facing dorsolaterally. The ratio of the greatest diameter of the external naris to the greatest diameter of the orbit is 1.45. This ratio is 0.86 in Shunosaurus7, 1.09 in Mamenchisaurus youngi24, and 1.21 in Jobaria53. The subtriangular-shaped antorbital fenestra is bounded by the maxilla and lacrimal, which is bigger than that of Omeisaurus tianfuensis10. The subround orbit is bounded by the lacrimal, prefrontal, frontal, postorbital and jugal. The subtriangular shaped infratemporal fenestra is bounded by the jugal, postorbital, quadratojugal and squamosal. The anterior extension of the infratemporal fenestra reaches the midpoint of the orbit (Fig. 2), similar to the condition in Shunosaurus7,35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10 and Mamenchisaurus youngi24. The supratemporal fenestra is bounded by the parietal, postorbital and squamosal, and is oval-shaped, different to that in Bagualia54 where the supratemporal fenestra is about as anteroposteriorly long as lateromedially wide. Besides, the foramen magnum is elliptical and transversely oriented, different from toTazoudasaurus55, which is vertically oriented.
Skull of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132) in right lateral view. Abbreviations: an, angular; aof, antorbital fenestra; bo, basioccipital; bt, basal tubera; en, external naris; d, dentary; ept, ectopterygoid; f, frontal; fo, foramen; hy, hyoid; inf, infratemporal fenestra;j, jugal; l, lacrimal; m, maxilla; n, nasal; o, orbit; p, parietal; pf, prefrontal; pi, pit; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pop, paraoccipital process; q, quadrate; sa, surangular; so, supraoccipital; sq, squamosal; stf, supratemporal fenestra.
Skull roof bones
Premaxilla
The body of the premaxilla is subrectangular, anteroposteriorly short, similar to that in Shunosaurus7,35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, and Jobaria53, but different to Euhelopus56,57 in that the premaxilla is elongate with a boot-shaped snout. In lateral view, the anterior margin of the premaxilla is step-shaped (Fig. 2), similar to the condition in most Eusauropoda, such as Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Mamenchisaurus youngi24 and Jobaria53, but different from that of Bagualia54 without a marked step and most of the basal sauropodomorphs without a step, such as Yizhousaurus sunae50, Jingshanosaurus58 and Lishulong wangi59. The nasal process of the premaxilla is elongated, thin, and posterodorsally directed with an angle of about 60° from the horizontal plane, as that of Mamenchisaurus youngi24, which differs from the angle of 30°-40° of Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, and the angle of 40° of Abrosaurus9 and Bellusaurus60. The muzzle-like area anteroventral to the external nare is short as most basal eusauropods (i.e. Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Jobaria53 and Turiasaurus riodevensis38), rather than elongated as in Brachiosaurus61.
The nasal process is convex dorsally in lateral view (Fig. 2), similar to that of Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Jobaria53 and Euhelopus56,57. The distal end of the nasal process overlaps the anterior end of the premaxillary process of the nasal. In lateral view, the premaxilla and maxilla articulate by a straight contact that extends from the ventral skull margin to the level of the base of the dorsal process, but the premaxilla–maxilla sutural contact is sinuous in Abydosaurus62 and Nemegtosaurus63,64. The subnarial foramen is a small, suboval, and laterally facing opening, which is anterior to the dorsal part of the premaxilla–maxilla contact, as in some basal sauropods such as Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, and Patagosaurus65. The position of the subnarial foramen in Turiasaurus riodevensis is not shown due to bad preservation38.
Maxilla
The maxilla consists of a stoutly constructed main body and a thick, posterodorsally directed nasal process. The preantorbital fenestra on the maxilla is absent, similar to that in most sauropodomorphs, such as Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, and Mamenchisaurus youngi24, but it is present in Nemegtosaurus66, Rapetosaurus67. In lateral view, there is a small, dorsoventrally elongated foramen at the base of the nasal process of the maxilla (Fig. 2), which is deeper than other foramina along the lower half of the lateral surface of the maxilla other foramen. The foramen is absent in Shunosaurus7,35, Omeisaurus10,13, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Tuiasaurus38. In addition to this, there is a rostral maxillary foramen located in the anterodorsal portion of the main body of the maxilla, anteroventral to the ascending process of the maxilla. There are nine neurovascular foramen on the ventrolateral surface of the maxilla, with the posteriormost one being slightly larger than the anterior foramina, as in other sauropods.
In lateral view, the posterior extent of the nasal process ends anterior to the posterior end of the main body of the maxilla (Figs. 2 and 3). The distal end of the nasal process contacts the lacrimal and overlaps with a descending lateral process of the nasal. The nasal process of the maxilla of Omeisaurus tianfuensis10 is larger and robust than that of Jinchuanloong. The jugal process of the maxilla is overlapped by the broad anterior part of the jugal. The ventral margin of the jugal process of the maxilla is gently emarginated relative to the remainder of the ventral margin of the maxilla, in contrast to the condition of Shunosaurus35, where the ventral margin of the jugal process is strongly emarginated. The posteroventral corner of the body of the maxilla unites extensively with the anterior end of the quadratojugal, similar to that in Mamenchisaurus youngi24. The left maxilla contains 13 teeth and some dorsally-directed, oval nutrient foramina. In left lateral view, the antorbital fossa presents with a weakly developed anterior lamina margin and a well-developed sheet of bone from the ventral margin of the antorbital fossa, but the nasal fossa appeared to be underdeveloped. It is worth noting that the posteroventral margin of the main body of the maxilla suddenly contracted upward and arched as in Camarasaurus68, and there are no signs of fracture from the edge, which should be in a natural state. This suggests that the anterior lateroventral margin of the maxilla should be developed with a tooth plate. The dorsal surface of the maxilla is continuous with the lateral surface without a concavity in dorsal surface of the maxilla or any low ridge separating the dorsal surface and lateral surface of the main body of the maxilla, as in Turiasaurus38.
Nasal
The nasal is an anteroposteriorly long and transversely narrow bone with an anteromedial process, a posterolateral process and the main body (Figs. 3, 4, 5). The anteromedial process is strongly downturned and constricted as a long, rod-like bone to receive the ascending process of the premaxilla. The posterolateral process of the nasal is relatively short and tapers posteroventrally to contact the ascending process of the maxilla, while it extends more laterally than ventrally due to burial compression. In dorsal view, the main body is a convex quadrangular bone and is articulated with the frontal in a nearly transverse contact, while the sutural contacts between the nasals and frontal are crushed by burial compression. The posterolateral corner of the nasal is a triangular, tab-like process meeting the prefrontal laterally (Fig. 5). The anteromedial process of the nasal is narrow relative to the nasal process of the premaxilla and is covered by the latter. The anteromedial process of the nasal is slender as that in Bellusaurus60, but different from those of Shunosaurus7,35, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, and most basal sauropodomorphs50,58,69,70, which appear to be wide and short (Fig. 2).
Skull of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132) in anterior view. Abbreviations: aof, antorbital fenestra; en, external naris; f, frontal; j, jugal; l, lacrimal; m, maxilla; n,nasal; o, orbit; p, parietal; pf, prefrontal; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; qj,quadratojugal;sq, squamosal; stf, supratemporal fenestra.
Skull of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132) in dorsal view. Abbreviations: a, aperture; an, angular; aof, antorbital fenestra; bo, basioccipital; d, dentary; en, external naris; eo, exoccipital; ept, ectopterygoid; f, frontal; fo, foramen; j, jugal; l, lacrimal; m, maxilla; n, nasal; o, orbit; p, parietal; pf, prefrontal; pi, pit; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pop, paraoccipital process; qj, quadratojugal; sa, surangular; so, supraoccipital; sq, squamosal; stf, supratemporal fenestra.
Prefrontal
The prefrontal is relatively small, strap-like, and transversely convex as in some basal sauropodomorphs, such as Yizhousaurus50, Jinshanosaurus58, Massopondylus71 (Fig. 5), but very specifically, the anterior portion of the prefrontal is bifurcated into an anterior process and a lateral process in left lateral view, the former is blunt for receiving the frontal, and the lateral process is acute that maybe articulated with the laminal, though it has been dislocated from the lacrimal due to compression. It is located in the dorsal part of the preorbital foramen. The anterodorsal surface of the prefrontal bears a small round aperture near the bifurcation (Figs. 2 and 5). The anterior part of the prefrontal is displaced from its natural position, which curves anteroventrally to overlap the portion of the lacrimal and the ascending process of the maxilla, and contracts the frontal posteromedially (Fig. 3).
In dorsal view, the prefrontal joins the nasal medially and the frontal posteriorly (Fig. 5). The posterior end of the right prefrontal is square-shaped, although the right prefrontal is incomplete, its articulation surface with the frontal is pointed posteriorly. And the left frontal appears somewhat incomplete in its posterior portion. The condition may be due to fracture, though in contrast to the condition in Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24 and Bellusaurus60 that the posterior end of the prefrontal is subtriangular in outline.
Frontal
The frontals contact via a median suture and its anteroposterior length (22.8mm) is less than transverse width (29.5mm), similar to that in Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Jobaria53, and Bagualia54, but different to that of Shunosaurus, where its anteroposterior length is greater than transverse width7,35.In dorsal view, the frontal-nasal suture appears to transverse contact (Fig. 5). The lateral margin of the frontal curves very strongly posterolaterally as it forms the rounded, deep dorsal orbital rim, such as Bellusaurus60, different to the condition in Bagualia54, where the frontal has a short contribution to the orbit. The lateral margin of the frontal is horizontally to the medial margin in anterodorsal view. The frontal-parietal suture is nearly straight and extends slightly anterolaterally for its length. The suture skirts around the anteromedial margin of the supratemporal fenestra to contact the narrow flange of the parietal when it approaches the supratemporal fenestra, such as Bellusaurus60. The posterolateral border of the frontal contacts with the postorbital. There is an ovoid perforation located at the midline of the juncture of the frontal and parietal, also known as the frontoparietal foramen, pineal foramen. The position of the frontoparietal foramen is similar to that of Bellusaurus60, Spinophorosaurus72, Apatosaurus73 and dicraeosaurids74, but differs from the foramen surrounded by the frontals in Camarasaurus75, and from the fenestra bounded entirely by the paired parietals in Europasaurus76. Unlike the aforementioned sauropods, however, this foramen is larger, with a mediolateral width of 12.1mm and an anteroposterior length of 10.1mm. As in Bagualia54, the frontal does not contribute to the margin of the supratemporal fenestra, which may be a derived feature, but in contrast to that of Shunosaurus7,35, Spinophorosaurus72 and other basal Sauropodomorpha (e.g. Melanorosaurus69, Yizhousaurus sunae50, Jingshanosaurus58, Lishulong wangi59). This is a derived feature. Dorsally, the anterior edge of the frontal contacting the nasal and the prefrontal is almost equally wide as the widest in other sauropods (i.e. Mamenchisaurus youngi24 and Jobaria53, Bellusaurus60). The orbital margin of the frontal is completely smooth without any ornamentation. This condition is similar to that of Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Europasaurus76, Giraffatitan61, but different from the ornamented margin of Camarasaurus68 and Nemegtosaurus77.
Parietal
In dorsal view, the slender anterolateral process extends a short distance along the anterior wall of the supratemporal fenestra, unitingdistally with the postorbital, excluding the frontal from the supratemporal fenestra (Fig. 5). The distance between both fenestrae is shorter than the mediolateral width of the supratemporal fenestra (Fig. 5), similar to that Mamenchisaurus youngi24 and Jobaria53.The posterolateral process of the parietal contacts with the dorsal margin of the supraoccipital and squamosal on the occiput. The posterolateral process of the parietal forms the medial half of the posterior wall of the supratemporal fenestra, contacting the squamosal distally (Fig. 5). The parietal is not connected to the exoccipital-opisthotic complex directly, but the posterolateral edge of the parietal contacts the supraoccipital. This condition differs from Shunosaurus35 and Mamenchisaurus youngi24, in which the parietal connects to the exoccipital-opisthotic complex with a gently curved suture. The contact of the parietal with the supraoccipital is not flush as in Spinophorosaurus72. The dorsoventral height of the posterolateral part of the parietal is less than the greatest diameter of the foramen magnum (Fig. 6).
Skull of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132) in posterior view. Abbreviations: bo, basioccipital; bp, basipterygoid process; bt, basal tubera; co, columella; eo, exoccipital; fm, foramen magnum; p, parietal; po, postorbital; pop, paraoccipital process; q, quadrate; qj, quadratojugal; qpp, quadrate process of pterygoid; so,supraoccipital; sq, squamosal.
Lacrimal
The lacrimal is long, narrow, almost straight and rodlike in lateral view (Figs. 2 and 4). The right lacrimal is more complete than the left one. The ventral end of the lacrimal is fractured, but it can be seen that the ventral portion of the lacrimal is connected to the jugal and gradually tapering than its dorsal part (Fig. 2). The lacrimal extends from the lacrimal process of the jugal anterodorsally so that the dorsal portion of the lacrimal is inserted under the prefrontal. The orientation of the lacrimal is different from most sauropods, such as Shunosaurus7,35, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Jobaria53, Euhelopus56,57 and Camarasaurus78; this condition may be due to compressed distortion, since the skull was subjected to burial pressure from posterior to anterior. It is presumed that it should be almost vertical in its natural state. The lacrimal bounds a small subtriangular antorbital fenestra posteriorly. The posterodorsal portion of the maxilla concaves as a marked antorbital fossa (AOF) ventral to the antorbital fenestra (AOFE). Laterally, there appears to be no anterior process in the lacrimal.
Jugal
The jugal is not much reduced like some sauropods, such as Shunosaurus7,35, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Jobaria53, but is extended in three directions. The jugal is a crescentic bone composed of a convex, bladelike main body, a dorsal process, a posterior process and a posteroventral process. The middle portion of the main body is prominently convex, and the main body becomes gradually thin and smooth dorsally, posteriorly and ventrally. The dorsal process is the shortest of the three processes contacting the lacrimal. The posterior process of the jugal is an anteroposteriorly elongated bone, which tapers posteriorly and articulates with the postorbital. The posteroventral process of the jugal curves posteriorly to form the anterior and ventral margins of the infratemporal fenestra and bifurcates posteriorly to accommodate the anterior process of the quadratojugal. The ventral margin of the jugal contacts the lateral surface of the posterior portion of the maxilla, and it is completely excluded from the ventral margin of the skull by a contact between the maxilla and quadratojugal, as in Camarasaurus78.
The posteroventral process of the jugal together with the quadratojugal, forming the ventral margin of the infratemporal fenestra (Fig. 2), with the quadratojugal occupying 78% and the posteroventral process contributing only 22% of the ventral margin of the infratemporal fenestra, but the ratio is much lower than that of Camarasaurus, where the posteroventral process occupies 60% of the ventral margin of the infratemporal fenestra. The dorsal process of the jugal contacts the lacrimal and has a small contribution to the antorbital fenestra (Fig. 2). There is a small aperture penetrating the anteroventral horn of the jugal in left lateral view, and a similar one is located in the main body of the jugal, while not penetrate the jugal in right lateral view.
Postorbital
The postorbital is triradiate, similar to most sauropods, such as Shunosaurus7,35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10 and Mamenchisaurus youngi24. In lateral view, a short, triangular, distinct posterior process contacts the squamosal (Fig. 3). The ratio of the anteroposterior length to the dorsoventral height of the posterior process is 0.9. A thick, medially extended, anterior process contacts the anterolateral process of the parietal to form the anterior margin of the supratemporal fenestra (Fig. 5). The anterior and posterior processes are subequal in anteroposterior length. The ventral process of the postorbital is slender and longer than the anterior and posterior processes. The distal end of the ventral process contacts the postorbital process of the jugal, forming the posterior margin of the orbit, and the anterior margin of the infratemporal fenestra (Fig. 2). The anteroposterior and mediolateral widths of the ventral process are equal, similar to Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Qijianglong79, in contrast to Yizhousaurus50, Leyesaurus80, Anchisaurus81, Euhelopus56,57 and Turiasaurus38 that the mediolateral width wider than the anteroposterior length. The main body of the postorbital is concave relative to the anterior process such that the supratemporal fenestra is visible in lateral view, similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Bellusaurus60, Turiasaurus38, Mierasaurus37, Jobaria 53, Euhelopus56. The postorbital of Shunosaurus35 contains a lateral pit, but it is absent in Jinchuanloong.
Quadratojugal
The left quadratojugal is nearly complete and is L-shaped in lateral view. The dorsoventral height of the dorsal process is 32mm, and the anteroposterior length of the anterior process is 55mm, which means the dorsal process is much shorter than the anterior process, similar to Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Turiasaurus38 and Euhelopus56. The anterior process and the dorsal process form a nearly right angle and their union is robust (Fig. 2). The anterior margin of the dorsal process contacts the squamosal along its posterolateral surface, which forms an oblique suture (Fig. 2). The posteromedial part of the quadratojugal contact quadrate (Fig. 6). The anterior process is bowed downward at the midlength and curves slightly dorsally in its anterior half. The anterior end of the anterior process contacts the jugal and overlaps the posteroventral corner of the maxilla.
Quadrate
The quadrate forms the posterolateral margin of the skull and articulates with the squamosal dorsally and the mandible ventrally. In lateral view, the posterior surface of the quadrate is deeply concave (Fig. 3), similar to the condition in Mamenchisaurus youngi24 and Euhelopus56,57. In posterior view, the shaft of the quadrate is nearly straight. The distal end of the shaft expands laterally, contacting the quadratojugal. The quadrate fossa is a deep depression that orients posteriorly and extends from the proximal head to the distal end of the quadrate (Fig. 6), similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Bellusaurus60, Qijianglong79, Turiasaurus38, Mierasaurus37 and Euhelopus56.
Squamosal
In lateral view, the squamosal is S-shaped (Fig. 2). The descending process of the squamosal contacts the quadratojugal. The anterior surface of the descending shaft forms the posterodorsal margin of the infratemporal fenestra. The anterior process of the squamosal is transversely compressed and curved medially (Figs. 3 and 5). The ventral margin of the anterior process forms the dorsal corner of the infratemporal fenestra (Fig. 2). The anteromedial part of the anterior process of the squamosal forms the wall of the posterolateral corner of the supratemporal fenestra, uniting anteriorly with the postorbital and posteriorly with the parietal (Fig. 5). In lateral view, the anterior process extent restricted to postorbital region (Fig. 3), similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24 and Jobaria 53. In dorsal view, the posteromedial part of the dorsal head extends medially, contacting the parietal anteriorly and the paraoccipital process posteriorly. The posterior process and the postemporal fenestra of the squamosal are absent.
Braincase
Supraoccipital
The supraoccipital slopes anterodorsally, forming a 36 degree angle to the horizon. It is transversely wider than dorsoventrally high, similar to Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10 and Mierasaurus37. The dorsal margin of the supraoccipital contacts the ventral margins of the paired parietals. The lateral margin contacts the posteromedial portion of the dorsal head of the squamosal. The ventrolateral margins contact the exoccipital-opisthotic complex, and the ventral margin contributes to the entire dorsal margin of the foramen magnum. In dorsal and occipital views, the sutures between the supraoccipital, parietal, squamosal, and exoccipital are clear. The dorsoventral height of the supraoccipital is greater than the height of the foramen magnum, similar to Shunosaurus35, Qijianglong79, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Jobaria 53, Turiasaurus38 and Mierasaurus37. There is a midline nuchal crest that diminishes strongly in prominence ventrally, so that it barely reaches the dorsal margin of the foramen magnum as in other non-neosauropod eusauropods (Fig. 6), but the nuchal crest is more developed in Mamenchisaurus youngi24 and it reaches the dorsal margin of the foramen magnum as a prominent posterior projection in Lingwulong82.
Exoccipital-opisthotic complex
The distal end of the left paroccipital process is incomplete, and the right paroccipital process has been deformed (Fig. 6). The general morphology is similar to that observed in Mamenchisaurus youngi24. The exoccipital-opisthotic projects laterally as in other eusauropods83. The dorsal part of the medial margin of the exoccipital contacts the supraoccipital, and the ventral part contributes to the entire lateral margin of the foramen magnum, as in other sauropods38. The exoccipital extends laterally, forming the paroccipital process at the distal end, which contacts the squamosal dorsally.
Basioccipital
The occipital condyle is sub-crescent in posterior view and is wider transversely than high dorsoventrally. From the anteroventral margin of the condyle, the inferior surface of the basioccipital arches anterodorsally, then curves anteroventrally, forming relatively short basal tubera (Fig. 6). In ventral view, the occipital condyle and basal tubera are separated by a constricted neck. The basal tubera is restricted to the ventral half of itself, similar to Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Bellusaurus60 and Mierasaurus37, but the basal tubera extends into its dorsal half in Qijianglong79 and Jobaria 53. The posterior face of the basal tubera is slightly convex, as in Shunosaurus35 and Mamenchisaurus youngi24. In ventral view, the long axis of each basal tubera tip is subparallel to each other and extends transversely to the long axis of the basicranium (Fig. 7), as in other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Bellusaurus60.
Columella
The columella is nearly rod-shaped and its distal end contacts the dorsomedial portion of the quadrate process of the pterygoid (Figs. 6 and 7). In posterior view, it directs ventrolaterally and narrows gradually. In ventral view, it is thinner anteroposteriorly than in Shunosaurus35.
Palate
Pterygoid
The anterior process of the pterygoid is fractured together with the vomer and palatine (Fig. 7). In ventral view, the narrow end of the anterior process of the pterygoid reaches the vomer. The pterygoid bears a robust ectopterygoid process and a quadrate process. The ectopterygoid process is oriented anterolaterally and posterior to the palatine. The distal end of the ectopterygoid process reaches the posterior corner of the maxilla (Fig. 3), similar to Omeisaurus maoianus13, but different to the condition in Shunosaurus35, where the ectopterygoid contacts with the jugal. In ventral view, the quadrate process of the pterygoid contacts the anterior part of the quadrate. In posterior view, the quadrate process of pterygoid extends anteromedially along the anterior border of the medial surface of the quadrate shaft. There are distinct sutures between the quadrate process of the pterygoid and the shaft of the quadrate (Fig. 6). In lateral view, the basipterygoid processes direct anteroventrally. In posterior and ventral views, the basipterygoid processes diverge widely, similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Qijianglong79, Bellusaurus60, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10 and Turiasaurus38. The basipterygoid process is subtriangular in cross-section, and the distal end is not transversely expanded, similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Qijianglong79, Bellusaurus60, Mamenchisaurus youngi24 and Turiasaurus38.
Mandible
Dentary
The anterior portion of the left dentary and most portion of the right dentary are preserved, but the medial view of the dentary can not be seen (Fig. 8). There are 12 tooth alveoli on the left dentary. The midline symphysis of the dentary expanded dorsoventrally relative to the central part of the dentary, with a ratio of the height of the symphysis to the height of the dentary at midlength is about 1.4, similar to Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10 and Omeisaurus maoianus13. The anterior portion of the dentary extends ventromedially, and the anteroventral margin of the dentary is gently rounded in shape in lateral view (Figs. 3 and 5), similar to most non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Euhelopus56 and Jobaria 53, but the anteroventral margin of the dentary is chinned in shape in Mierasaurus37. In lateral view, the angle between the long axis of the anterior margin and the long axis of the main body of the dentary is greater than 90°, with the dorsal margin of the dentary extending further anteriorly than the ventral margin (Fig. 3), similar to that in Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Omeisaurus maoianus13 and Mamenchisaurus youngi24. There are some nutrient foramina on the ventrolateral surface of the dentary (Fig. 8), which are also present in Mamenchisaurus youngi24.
Surangular and angular
The left surangular and angular are nearly well preserved (Fig. 2). In lateral view, the angular is elongated, as in other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Mamenchisaurus youngi24 and Jobaria 53. The surangular narrows dorsoventrally at the distal end, contacting with angular. The maximum dorsoventral height of the surangular is greater than the maximum dorsoventral height of the angular, similar to Shunosaurus26.
Teeth
There are 17 tooth positions in each upper jaw: 4 in the premaxilla and 13 in the maxilla (Figs. 2, 3, 4), different from Shunosaurus has 4 to 5 premaxilla teeth and 20 maxilla teeth26, Mamenchisaurus youngi has 4 premaxilla teeth and 18 maxilla teeth21, and Omeisaurus tianfuensis has 4 premaxilla teeth and 11 maxilla teeth9. In general, the slenderness indices (i.e. apicobasal crown length/maximum mesiodistal width of crown) of the tooth crown are about 2.17. In labial view, the tooth crown narrows mesiodistally along its apical third. The tooth root constricts mesiodistally relative to the tooth crown.
In labial view, the shape of tooth crowns is ‘spoon ’-like (Figs. 4, 9), as in Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Turiasaurus38 and Mierasaurus37. The tooth crowns are concave in lingual surface and convex in labial surface (Fig. 9), similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods. The apicobasally oriented lingual ridge of tooth crowns and the longitudinal groove on the labial surface are present, similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods. The distinct mesial and distal carinae and denticles are absent, different to the condition in Bagualia54, Patagosaurus65, Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus maoianus13 and Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, where the tooth denticles are present. The cross-sectional shape at mid-crown is ‘D’-shaped (Fig. 7), similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Bellusaurus60, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Euhelopus56, Jobaria 53, Turiasaurus38 and Mierasaurus37, but it is cylindrical-shaped in some neosauropods, such as Nigersaurus51 and Apatosaurus52. The enamel surface is wrinkled in the regions closest to the base of the crown on the labial surface (Fig. 4). The maxillary teeth do not twist axially, similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Euhelopus56 and Jobaria 53. Tooth crowns are aligned anterolingually and overlap (Fig. 4), similar to other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Omeisaurus maoianus13, Euhelopus56, Jobaria 53, and Mierasaurus37. The tooth rows are restricted anterior to the orbit (Figs. 2 and 3), as in other non-neosauropod eusauropods, such as Shunosaurus35, Omeisaurus maoianus13, and Mamenchisaurus youngi24.
Axial skeleton
The first five cervical vertebrae, including the atlas-axis complex and twenty-nine articulated caudal vertebrae, are preserved in situ. The centra of the fourth to sixth caudal vertebrae were not fused by the pressure of surrounding matrix, combined with the presence of a large frontoparietal fenestra (i.e. pineal foramen) at the midline of the juncture of the frontal and parietal (see the skull), Jinchuanloong is inferred to be a possible juvenile individual. The measurements of the vertebrae can be found in Table 2.
Cervical vertebrae
Atlas-axis complex
The atlas is well preserved, including the atlantal intercentrum and the pair of neurapophyses. The intercentrum of the atlas is inclined anterodorsal-posteroventrally. In anterior view, the intercentrum is crescentic or U-shaped, the dorsal surface is a deep concavity for receiving the odontoid process of the axis, as in other sauropods, like Apatosaurus, Camarasaurus, Diplodocus, and Omeisaurus. While the intercentrum was transversely compressed diagenetically, resulting in the middle portion of the intercentrum being fissured. The intercentrum has a deep anterior cotyle for the reception of the occipital condyle, and a circular dorsal concavity into which the odontoid process protrudes. The intercentrum is subrectangular in lateral view as in Xinjiangtitan31, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, and Camarasaurus. It is worth noting that the intercentrum and paired neurapophyses are not fused, which also supports the possibility that Jinchuanloong is a juvenile. However, the anteroventral margin of the intercentrum is expanded anteriorly more prominently than those of Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Xinjiangtitan31 and Omeisaurus tianfuensis10.
The right and left neurapophyses of the atlas were not firmly fused to the intercentrum (Fig. 10). They are directed posterodorsally, and the distal portions are posterolaterally oriented. The bases of the neurapophyses gently flare laterally before expanding into short wings overlapping the prezygapophyses of the axis, while the anterior portions of the neurapophyses extend a few millimetres beyond the anterodorsal margin of the intercentrum.
Cervical vertebrae of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132). (A) five anteriormost cervical vertebrae of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132) in left lateral view; (B) four anteriormost cervical vertebrae of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132) in right lateral view; (C) four anteriormost cervical vertebrae of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132) in dorsal view. Abbreviations: aems, anterior epipophyseal muscle scar; ep, epipophysis; eprl, epipophyseal-prezygapophyseal lamina; podl, postzygodiapophyseal lamina; poz, postzygapophysis; prz, prezygapophysis; sdf, spinodiapophyseal fossa;spol, spinopostzygapophyseal lamina; sprl, spinoprezygapophyseal lamina. Scale bars: A-B, 10cm; C, 10 cm.
The axis is relatively complete in the preserved articulated cervical series. Laterally, the parapophyses are located at the anteroventral corner of the centrum, articulated with partial ribs. The rib extends posteriorly along the lateroventral margin of the centrum, ending (broken) at the level of the posterior articular surface of the centrum. The capitulum and the tuberculum of the rib are articulated with the parapophysis and the diapophysis, but not fused firmly. The right side of the centrum was poorly preserved; only the posterior one-third of the left lateral surface of the centrum was exposed, and the lateral concavity of the centrum could not be recognised. The anteroventral surface of the centrum is concave and bears a short longitudinal ventral keel (v.k) (Fig. 11) not unlike that of Xinjiangtitan31, which lacks the ventral keel concavity, not as an acute ventral keel of Shunosaurus7, Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, and differs from the low rounded ridge of Mamenchisaurus youngi24, and from those of Europasaurus, Euhelopus and Apatosaurus, where bear no ventral keel.
The four anteriormost cervicals of Jinchuanloongniedu (JCMF0132) in ventral view. (A) photo of the four anteriormost cervicals of Jinchuanloong niedu (JCMF0132) in ventral view; (B) close-up of the ventral keel of the axis. Abbreviations: rib, portion of rib of axis; v.k, ventral keel. Scale bars: A, 10 cm; B, not to scale.
The rod-like neural spine lies over the anterior half of the centrum. It is very low dorsoventrally and longer anteroposteriorly than it the wide transversely. In right lateral view, the postzygodiapophyseal lamina (PODL) directed posterodorsally is well developed, above which a simple and smooth-walled spinodiapophyseal fossa (SDF) is observed at the base of the neural spine, as that of Shunosaurus7, not as that of Qijianglong79, which has a rimmed fossa. The spinopostzygapophyseal laminae (SPOLs) extend from the posterior margin of the neural spine to the postzygapophyses, but no spinoprezygapophyseal laminae (SPRLs) are preserved.
Cervical vertebrae 3–5
These three cervical vertebrae are poorly preserved: in cervical 3, the neural spine was missing, and the middle portion of the centrum was damaged; only part of the neural arch and zygapophyses were preserved in the fourth cervical vertebra; the fifth cervical vertebra was severely damaged, with only part of the prezygapophyses preserved. The cervical neural arch and spine were not fused, suggesting that Jinchuanloong was a subadult. In lateral view of cervical 3, an epipophysis (ep) is present on the postzygapophysis, which is a blunt, small protuberance, projecting slightly beyond the postzygapophyseal facet, rather than the elongate finger-like projection as in Qijianglong79, Xinjiangtitan79. The parapophysis is preserved, articulating with the anterior end of the broken rib in cervical 3. The lateral surface of the postzygapophyseal ramus exhibits a low, rugose ridge, which does not take on a lamina that has been called an incipient epipophyseal-prezygapophyseal lamina (EPRL) in Xinjiangtitan31, Mamenchisaurus youngi24. The rugose ridge extends anterodorsally over the postzygodiapophyseal lamina (PODL). This condition is the case for cervical elements of Shunosaurus7, Omeisaurus10, Klamelisaurus5, Camarasaurus78, which has been called the anterior epipophyseal scar (AEMS) for the attachment scars for mm intercristales. In dorsal view, the fracture of the neural spine articulated with the neural arch is visible with a groove in the middle portion and the ridges on both sides in cervical 3. It can be seen from the fracture that the neural arch and the neural spine were not fused in life, so that the neural spine is not preserved during the burial compression. The base of the spinopostzygapophyseal lamina (SPOL) is preserved and extends from the neural arch fracture to the dorsomedial margin of the postzygapophysis. The rugose anterior epipophyseal scar (AEMS) presents on the dorsolateral surface of the postzygapophysis. The prezygapophysis of cervical 3 extends anterolaterally to be overlapped by the postzygapophysis of the axis, while the dorsal portion of the spinoprezygapophyseal lamina (SPRL). There is a shallow spinodiapophyseal fossa (SDF) at the base of the juncture of the neural arch and spine in dorsal or lateral view. In vetral view, the middle portion of the centrum is missing so that the exact anteroposterior length cannot be estimated. Differing from the axis, the anteroventral surface is slightly concave without a ventral keel. The ventral surface of cervical 4 is more fractured, while the centrum is missing in cervical 5. Whether the post-axis cervical has a ventral keel can not be known.
Caudal vertebrae
Twenty-nine articulated caudal vertebrae are preserved in situ (Fig. 12), of which only the neural spines were preserved in the first three caudal vertebrae. Unfortunately, the caudal vertebrae have not been excavated, are currently buried in situ, and the protective fences have been built around them, so only the right lateral surfaces of these caudal vertebrae can be seen. The centra of the fourth to sixth caudal vertebrae were not fused and separated from neural spines by the pressure of the surrounding matrix. The remaining elements are preserved, articulated with each other and provide some anatomical information from the middle-posterior caudal series of Jinchuanloong.
The neural spines of the first seven preserved caudal vertebrae are relatively anteroposteriorly narrower than the subsequent elements in right lateral view, and have posterodorsal inclination between 60° and 50°. The dorsal margin of the neural spines is slightly convex to straight horizontal. In right lateral view, the SPRL and SPOL run almost parallel to each other, with weakly developed transverse processes located over the neurocentral junction. Considering these features and location in the quarry, we identify these seven vertebrae as the middle caudal vertebrae. The lateral surface of the centrum is slightly concave, but it is difficult to identify the anterior and posterior surfaces due to weathering and articulated preservation, except in the seventh preserved caudal, where the anterior articular surface is disconnected from the previous caudal centra. Viewed from the fractured 7th caudal vertebra, the centrum is amphicoelous or nearly amphiplatyan. The middle-posterior caudal centra in Jinchuanloong are amphicoelous or nearly amphiplatyan, just as the condition of middle caudal vertebrae in Shunosaurus7, Chuanjiesaurus30, Mamenchisaurus youngi24. This condition is different from Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, Bellusaurus60, in which the caudal vertebrae are amphicoelous centra, and also different from the procoelous posterior caudal centra with intercalation of some amphicoelous-biconvex or amphicoelous-opisthocoelous biconvex centra in Rinconsaurus caudamirus, easily contrasted with the strongly procoelous caudals of Titanosauridae, and strongly opisthocoelous of Opisthocoelicaudia.
The subsequent caudal vertebrae are relatively simple, transverse processes dissipating succeedingly, having single lateral surfaces with markedly elongated anteroposteriorly perpendicular to the arched dorsally ventral surfaces, neural arches extended from the anterior to the middle portion of the centra, and neural spines that are posterodorsally inclined lamina with an angle that ranges from 40° to 15°. Posterior deflection of the neural spine is similar to several other Middle-Late Jurassic Chinese sauropods, such as Chuanjiesaurus30, Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Shunosaurus7, Omeisaurus10, Klamelisaurus5, but differently, the anterior and middle caudal centra bear longitudinal ridges on their lateral surfaces. The centra of the anterior and middle caudal vertebrae, compared with the middle caudal vertebrae, are lower dorsoventrally; however, their anteroposterior length is slightly shorter than that of the previous caudal vertebrae. Both the anterior and posterior articular chevron facets are preserved in articulation with the corresponding chevrons.
The last ten centra of the posterior caudal vertebrae have no longitudinal ridge on the lateral surface of the centre, and the ventral surface is not much contracted dorsally as to the previous centra and is almost flat.
Phylogenetic analysis
To assess the phylogenetic relationships of Jinchuanloong, we scored it in two modified versions of the datasets of Zhang et al. 32. The matrix 1 is based on Upchurch et al. 34 (update from Mannion and Upchurch (2019)Mannion et al. (2019)), which comprises 127 taxa scored for 551 characters. Matrix 2 is based on Upchurch et al. 34 (update from GEA of Moore and Upchurch (2020)), which comprises 106 taxa scored for 444 characters. The version of matrix1 incorporates a large number of eusauropods, which is better suited to evaluating the broader phylogenetic positions of Jinchuanloong within Eusauropoda. The version of matrix 2 incorporates a large number of non-neosauropod eusauropods (especially East Asian CMTs), which is more appropriate for testing their relationships with other East Asian Jurassic taxa. We use both matrices.
There are 123 characters of Jinchuanloong scored in Matrix 1, and 97 characters of Jinchuanloong scored in Matrix 2. Analysis of matrix 1 under equal weighting (EWP) produces 10,000 most parsimonious trees (MPTs) with lengths of 2705 steps. Applying extended implied weighting (EIW) to this dataset also results in 10,000 MPTs of 2705 steps, producing identical interrelationships to the EWP analysis. A strict consensus of these trees is shown in Fig. 13. This analysis recovered Jinchuanloong within non-neosauropod eusauropod, as a sister to (Turiasauria + Neosauropod). Jinchuanloong recovered within non-neosauropod eusauropod is supported by the following characters: 79 (0) preantorbital fenestra on the maxilla is absent; 108 (0) the shape of tooth crowns is spatulate or ‘spoon’-like (i.e. constricted at the base relative to midheight of the crown) in labial view and 118 (0) the anterior half of ventral surfaces of the postaxial cervical centra are flat or mildly convex mediolaterally. Bremer supports have values of 1 or 2 for most nodes. Analysis of matrix 2 under EWP produces 10,000 most parsimonious trees (MPTs) with lengths of 2065 steps. Applying EIW to this dataset also results in 2065 MPTs of 1000 steps. The strict consensus and the 50% majority rule consensus of EWP and EIW produce identical interrelationships, which are poorly resolved.
Discussion
In our EWP analyses using the data of Zhang et al. 32, Jinchuanloong is positioned as the diverged non-neosauropodan eusauropod. This position is supported by an unambiguous synapomorphy (the ventral midline keel is present on the postaxial cervical centra) in the main data matrix 1. The ventral midline keel is present on postaxial cervical centra and is widely observed in neosauropods such as Camarasaurus, Diplodocus, Alamosaurs, Daxiatitan, Euhelopus, Europasaurus, Giraffatitan, and Malawisaurus. Although it is observed in some basal Sauropodas, such as Spinophorosaurus and Bagualia, it is rarely observed in most non-neosauropodan eusauropods34,85. Jinchuanloong has a significant difference from other non-neosauropod eusauropods in the morphology of the skull. In Jinchuanloong, there is a foramen at the base of the maxillary ascending process, which is absent in most non-neosauropod eusauropods. The similar foramen is located on the ascending process of the maxilla, not the rostral maxillary foramen as in Aardonyx70 and Melanorosaurus69, which pierces the ascending process of the maxilla at the base, not the midheight as Bellusaurus60. The ratio of the anteroposterior length to the dorsoventral height of the posterior process is 0.9. This ratio is 0.83 in Shunosaurus35, 1.0 in Jobaria 53, 1.09 in Euhelopus56, 1.3 in Mamenchisaurus youngi24, 1.5 in Qijianglong79 and 1.5 in Omeisaurus tianfuensis10, which indicates the postorbital of Jinchuanloong is stronger than other non-neosauropod eusauropods except basal eusauropod Shunosaurus. The anterodorsal surface of the prefrontal bears a small round aperture near the bifurcation (Figs. 2 and 5), which is absent in other non-neosauropodan eusauropods. The posteroventral process of the jugal contributes 22% of the ventral margin of the infratemporal fenestra, as in Jobaria53, but the jugal contributes little to the ventral margin of the infratemporal fenestra in Mamenchisaurus youngi24, Euhelopus56,57. The dorsal process of the jugal contacts the lacrimal and has a small contribution to the antorbital fenestra, as in Shunosaurus35, which differs from those in Jobaria 53, Euhelopus56,57, Turiasaurus38, the jugal does not contribute to the edge of the antorbital fenestra because of the lacrimal positioned far anteriorly. It also differs from some basal Sauropodomorphas, such as Yizhousaurus sunae50, Jingshanosaurus58, and Melanorosaurus69, which also do not contribute to the antorbital fenestra.
The presence of a new non-neosauropodan eusauropod from China provides further evidence of the diversity and biogeography of the clade during the Middle Jurassic. Middle Jurassic sedimentary units from eight areas of East Asia bearing the eusauropod specimens including seven Chinese regions (Lower Shaximiao Formation and lower portion of Upper Shaximiao Formation from Sichuan and Chongqing, Chuanjie and Zhanghe Formations of Yunnan, Zhiluo Formation of Ningxia, Qigu and Shishugou Formations of Xinjiang, Hongqin Formation of Anhui, Xinhe Formation of Gansu) and Balabansai Formation of Kirghizia3,7,10,12,13,30,31,32,33,82,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93, and most of them are reported from the western of China93. Therefore, at least five different non-neosauropodan sauropod lineages exist in the Middle Jurassic of East Asia: the basal-most eusauropods (e.g. Shunosaurus; Protognathus), early-diverging non-neosauropodan mamenchisaurids such as most of Omeisaurus spp. and some of Omeisaurus-like taxa (Analong, Huangshanlong, Anhuilong, etc.), diverged non-neosauropodan mamenchisaurids (e.g. Chuanjiesaurus; Xinjiangtitan; Klamelisaurus; Omeisaurus maoi), diverged non-neosauropodan eusauropod (e.g. Jinchuanloong in this study), early diverging neosauropods such as Dashanpusaurus, Lingwulong, Yuzhoulong, Bashuosaurus. A recent study suggests that at least two different types of body plans and three morphological types of teeth could be distinguished in Dashanpu sauropods of China, and their morphological and body-size variations may explain the coexistence of these animals and high niche differentiation from the same area93. Moreover, the relatively high diversity of East Asian eusauropods in the Middle Jurassic, as aforementioned, especially most of these taxa concentrated in western China, may reflect an increasing shift to habitats and niche differentiation in this period. Moreover, the potential regional geographical barriers or changes94,95 between basins may enhance the differentiation of eusauropod genera such as the prosperous lineages in the Sichuan Basin during the Bajocian to Bathonian. The high diversification of the East Asian Middle Jurassic eusauropods further coordinates the high niche partitioning hypothesis during this era. In contrast to the isolated eusauropod reports in most other global regions, the high rates of morphology, diversification, and distribution of eusauropods in these areas may indicate East Asia as a potentially important origin region of some sauropod clades.
Conclusions
A partial skeleton collected from the Middle Jurassic Xinhe Formation of Gansu Province, northwestern China, represents a new taxon of non-neosauropod eusauropods, which we name Jinchuanloong niedu. Jinchuanloong enriches the diversity of the early diverging sauropods and provides additional information to help understand the evolutionary history of sauropods in northwest China.
Methods
Here we follow Upchurch et al.34 in treating C14, 20, 122, 130 and 413 as inactive in that version of the matrix. Multistate characters were ordered where appropriate, with 18 such characters in the matrix 1 (C11, 14, 15, 27, 40, 51, 104, 122, 147, 148, 195, 205, 259, 297, 426, 435, 472, and 510) and 16 in the matrix 2 (C11, 14, 15, 27, 40, 51, 104, 147, 148, 177, 195, 205, 259, 430, 432, and 438). Following previous iterations of these datasets, several unstable taxa were excluded a priori from analyses using both matrices (Astrophocaudia, Australodocus, Brontomerus, Fukuititan, Fusuisaurus, Liubangosaurus, Malarguesaurus, and Mongolosaurus), with Mamenchisaurus constructus and Xianshanosaurus also excluded from analyses using matrix 2.
Both matrices were analysed in a maximum parsimony framework, using equal weighting (EWP) and extended implied weighting (EIW) of characters. For the latter, we used a k-value of 12, following Moore et al.5 and Upchurch et al.34. In EWP and EIW analyses, we first applied the ‘Stabilize Consensus’ option in the ‘New Technology Search’ in TNT v. 1.596,97. Searches employed sectorial searches, drift, and tree fusing, with the consensus stabilized five times. The MPTs resulting from each of these runs were then used as the starting topologies for ‘Traditional Searches’, using Tree Bisection-Reconstruction. The most parsimonious trees (MPTs) resulting from the primary search were subjected to an additional round of tree bisection and reconnection (TBR) branch swapping to ensure a thorough sampling of MPTs, with the maximum number of trees in memory set to 10,000. However, there may be more than 10,000 MPTs, our experience suggests that including more trees will not change the consensus calculation. The data matrices are presented in Supplementary 1 and 2.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Upchurch, P., Barrett, P. M. & Dodson, P. Sauropoda. In The Dinosauria (2nd edition) (ed. Weishampel D. B. et al.) 259–322 (University of California Press, 2004).
Cerda, I. A. et al. The first record of a sauropod dinosaur from Antarctica. Naturwissenschaften 99, 83–87 (2012).
Ren, X., Sekiya, T., Wang, T., Yang, Z. & You, H. A revision of the referred specimen of Chuanjiesaurus anaensis Fang et al., 2000: A new early branching mamenchisaurid sauropod from the Middle Jurassic of China. Hist. Biol. 33, 1872–1887 (2021)
Pol, D., Ramezani, J., Gomez, K., Carballido, J. L., Carabajal, A. P. & Rauhut, O. W. M. et al. Extinction of herbivorous dinosaurs linked to Early Jurassic global warming event. Proc. R. Soc. Biol. Sci. 287 (2020)
Moore, A. J., Upchurch, P., Barrett, P. M., Clark, J. M. & Xing, X. Osteology of Klamelisaurus gobiensis (Dinosauria, Eusauropoda) and the evolutionary history of Middle-Late Jurassic Chinese sauropods. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 18, 1299–1393 (2020).
Mannion, P. D., Upchurch, P., Schwarz, D. & Wings, O. Taxonomic affinities of the putative titanosaurs from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Tanzania: phylogenetic and biogeographic implications for eusauropod dinosaur evolution. Zool. J. Linn. Soc.-Lond. 185, 784–909 (2019).
Zhang, Y. H. The Middle Jurassic Dinosaur Fauna from Dashanpu, Zigong, Sichuan, Volume 1: Sauropod Dinosaur (1) Shunosaurus 89 (Sichuan Scientific and Technological Publishing House, 1988).
Ma, Q. et al. New Shunosaurus (Dinosauria: Sauropoda) material from the middle Jurassic lower Shaximiao Formation of Yunyang, Chongqing, China. Hist. Biol. 34, 1085–1099 (2022).
Dong, Z. M., Zhou, S. W. & Zhang, Y. H. Dinosaurs from the Jurassic of Sichuan. Palaeontol. Sin. Ser. C 162, 1–136 (1983).
He, X. L., Li, K. & Cai, K. J. The Middle Jurassic dinosaur fauna from Dashanpu, Zigong, Sichuan, Vol 4. Sauropod dinosaurs (2). Omeisaurus tianfuensis 1–143 (Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, 1988).
Jiang, S., Li, F., Peng, G. Z. & Ye, Y. A new species of Omeisaurus from the Middle Jurassic of Zigong, Sichuan. Vertebrata Palasiatica. 49, 185–194 (2011) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tan, C. et al. A new species of Omeisaurus (Dinosauria: Sauropoda) from the Middle Jurassic of Yunyang, Chongqing, China. Hist. Biol. 33, 1817–1829 (2021).
Tang, F., Jin, X. S., Kang, X. M. & Zhang, G. J. Omeisaurus maoianus, a complete Sauropoda from Jinyan, Sichuan 128 (China Ocean Press, 2001).
Young, C. C. On a new Sauropoda, with notes on other fragmentary reptiles from Szechuan. Bull. Geol. Soc. China 19, 279–315 (1939).
Young, C. C. New sauropods from China. Vertebrata Palasiatica. 2, 1–28 (1958).
You, H. L., Tang, F. & Luo, Z. X. A New basal titanosaur (Dinosauria: Sauropoda) from the early cretaceous of China. Acta Geol. Sin. 424–429 (2003)
You, H. L., Li, D. Q., Zhou, L. Q. & Ji, Q. Huanghetitan liujiaxiaensis, a new sauropod dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous Hekou Group of Lanzhou Basin, Gansu Province, China. Geol. Rev. 5, 668–674 (2006).
You, H. L., LI, D. Q., Zhou, L. & Ji, Q. Daxiatitan Binglingi: a giant Sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of China. Gansu Geol. 17, 1–10 (2008)
You, H. L. & Li, D. Q. The first well-preserved Early Cretaceous brachiosaurid dinosaur in Asia. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 276, 4077–4082 (2009).
Li, L. G., Li, D. Q., You, H. L., Dodson, P. & Butler, R. J. A new titanosaurian sauropod from the Hekou Group (Lower Cretaceous) of the Lanzhou-Minhe Basin, Gansu Province, China. PLoS ONE 2014, e85979 (2014).
Gao, T., Li, D., Li, L. & Yang, J. The first record of freshwater plesiosaurian from the Middle Jurassic of Gansu, NW China, with its implications to the local palaeobiogeography. J. Palaeogeogr. 8, 360–367 (2019).
Zhang, X. Q. Study on Xinjiangtitan shanshanensis from the Late Jurassic of Shanshan, Xinjiang (China University of Geosciences Beijing, 2019).
He, X. L., Yang, S. H., Cai, K. J., Li, K. & Liu, Z. W. A new species of sauropod, Mamenchisaurus anyuensis sp. nov. Papers on geosciences contributed to the 30th International Geological Congress. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 1996:83–86.
Ouyang, H. & Ye, Y. The first mamenchisaurian skeleton with complete skull: Mamenchisaurus youngi 111 (Sichuan Science and Technology Pres, 2002).
Young, C. C. On a new sauropod from Yiping, Szechuan, China. Sci. Sin. 3, 491–505 (1954).
Young, C. C. & Zhao, X. J. Mamenchisaurus hochuanensis. Acad. Sin. 8, 10–30 (1972) (in Chinese).
Zhang, Y. H., Li, K. & Zeng, Q. H. A new species of sauropod from the Late Jurassic of the Sichuan Basin (Mamenchisaurus jingyanensis sp. Nov.). J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. 25, 61–68 (1998) (in Chinese with English summary).
Russell, D. A. & Zheng, Z. A large mamenchisaurid from the Junggar Basin, Xinjiang, People’s Republic of China. Can. J. Earth Sci. 30, 2082–2095 (1993).
Moore, A. J., Barrett, P. M., Upchurch, P., Liao, C. C., Ye, Y. & Hao, B. et al. Re-assessment of the Late Jurassic eusauropod Mamenchisaurus sinocanadorum Russell and Zheng, 1993, and the evolution of exceptionally long necks in mamenchisaurids. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 21 (2023)
Sekiya, T. Re-examination of Chuanjiesaurus anaensis (Dinosauria: Sauropoda) from the Middle Jurassic Chuanjie Formation, Lufeng County, Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Memoir of the Fukui Prefectural Dinosaur Museum 10, 1–54 (2011).
Zhang, X., Li, D., Xie, Y. & You, H. Redescription of the cervical vertebrae of the Mamenchisaurid Sauropod Xinjiangtitan shanshanesis Wu et al. 2013. Hist. Biol. 32, 803–822 (2018).
Zhang, X. Q., Li, N., Xie, Y., Li, D. Q. & You, H. L. Redescription of the dorsal vertebrae of the mamenchisaurid sauropod Xinjiangtitan shanshanesis Wu et al. 2013. Hist. Biol. 36, 49–75 (2024)
Wu, W. H., Zhou, C. F., Wings, O., Sekiya, T. & Dong, Z. M. A new gigantic sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic of Shanshan, Xinjiang. Glob. Geol. 32, 437–446 (2013).
Upchurch, P., Mannion, P. D., Xu, X. & Barrett, P. M. Re-assessment of the Late Jurassic eusauropod dinosaur Hudiesaurus sinojapanorum Dong, 1997, from the Turpan Basin, China, and the evolution of hyper-robust antebrachia in sauropods. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 41 (2021)
Chatterjee, S. & Zheng, Z. Cranial anatomy of Shunosaurus, a basal sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic of China. Zool. J. Linn. Soc.-Lond. 136, 145–169 (2002).
Xing, L. A new basal eusauropod from the Middle Jurassic of Yunnan, China, and faunal compositions and transitions of Asian sauropodomorph dinosaurs. Acta Palaeontol. Pol. (2013)
Royo-Torres, R., Upchurch, P., Kirkland, J. I., DeBlieux, D. D., Foster, J. R. & Cobos, A. et al. Descendants of the Jurassic turiasaurs from Iberia found refuge in the Early Cretaceous of western USA. Sci. Rep.-Uk. 7 (2017)
Royo-Torres, R. & Upchurch, P. The cranial anatomy of the sauropod Turiasaurus riodevensis and implications for its phylogenetic relationships. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 10, 553–583 (2012).
Deng, W., Ma, Y., Yang, T., Lang, K. & Li, Y. Study on source rock characteristics of middle-lower Jurassic in Chaoshui Basin, Gansu Province. Gansu Sci. Technol. 32, 12–16 (2016) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang, F., Wang, W., Lü, H. & Liu, C. Jurassic charophytes from the Qingtujing Group in the Chaoshui Basin, NW China. Acta Palaeontol. Sin. 42, 257–265 (2003) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu, S. B., Bai, Y. B. & Yang, Y. Y. The features of braided river deposits of Qingtujing formation, Changshan section in Chaoshui Basin. J. Xi’an Shiyou Univ Natl. Sci. Edn. 12, 8–11 (1997). in Chinese with English abstract
Du, B. Sporo-pollen assemblages from the middle Jurassic in the Wangjiashan Basin of Jingyuan, Gansu, and their stratigraphic and paleogeographic significance. Geol. Rev. 31, 131–141 (1985) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, B. et al. Middle Jurassic strata of Wangjiashan Basin, Jingyuan, Gansu. J. Stratigr. 6, 33–40 (1982) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, H. et al. Sedimentary environments and coal accumulation of the Baojishan-Honghui Basin, eastern Qilian Mountains. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 27, 622–631 (2009) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Owen, R. Report on British fossil reptiles. Rep. Br. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 11, 60–204 (1842).
Seeley, H. G. On the classification of the fossil animals commonly named Dinosauria. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 43, 165–171 (1888).
Huene, F. V. Die fossil Reptil-Ordnung Saurischia, ihre Entwicklung und Geschichte. Monographien zur Geologie und Palaeontologie. 1, 1–361 (1932).
Marsh, O. C. Principal characters of American Jurassic dinosaurs. Pt. I. Am. J. Sci. (Ser. 3) 16, 411–416 (1878)
Upchurch, P. The evolutionary history of sauropod dinosaurs. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 349, 365–390 (1995).
Zhang, Q., You, H., Wang, T. & Chatterjee, S. A new sauropodiform dinosaur with a ‘sauropodan’ skull from the Lower Jurassic Lufeng Formation of Yunnan Province, China. Sci. Rep.-Uk. 8 (2018)
Sereno, P. C. et al. Structural extremes in a Cretaceous dinosaur. PLoS ONE 2007, 1–13 (2007).
Berman, D. S. & McIntosh, J. S. Skull and relationships of the Upper Jurassic Sauropod Apatosaurus (Reptilia, Saurischia). Carnegie Museum Bull. 8, 1–35 (1978).
Sereno, P. C. et al. Cretaceous sauropods from the sahara and the uneven rate of skeletal evolution among dinosaurs. Science 286, 1342–1347 (1999).
Pol, D., Ramezani, J., Gomez, K., Jose, C., Paulina-Carabajal, A. & Rauhut, O. et al. Extinction of herbivorous dinosaurs linked to Early Jurassic global warming event. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 287, 20202310 (2020)
Allain, R. & Aquesbi, N. Anatomy and phylogenetic relationships of Tazoudasaurus naimi (Dinosauria, Sauropoda) from the late Early Jurassic of Morocco. Geodiversitas. 30, 345–424 (2008).
Poropat, S. F. & Kear, B. P. Photographic Atlas and three-dimensional reconstruction of the holotype skull of Euhelopus zdanskyi with description of additional cranial elements. PLoS ONE 8, e79932 (2013).
Mateer, N. J. & McIntosh, J. S. A new reconstruction of the skull of Euhelopus zdanskyi (Saurischia: Sauropoda). Bull. Geol. Inst. Univ. Uppsala 25–132 (1985)
Zhang, Q. N., Wang, T., Yang, Z. W. & You, H. L. Redescription of the Cranium of Jingshanosaurus xinwaensis (Dinosauria: Sauropodomorpha) from the Lower Jurassic Lufeng Formation of Yunnan Province, China. Anat. Rec. 303, 759–771 (2020).
Zhang, Q., Jia, L., Wang, T., Zhang, Y. & You, H. The largest sauropodomorph skull from the Lower Jurassic Lufeng Formation of China. PeerJ 12, e18629 (2024).
Moore, A. J., Mo, J., Clark, J. M. & Xu, X. Cranial anatomy of Bellusaurus sui (Dinosauria: Eusauropoda) from the Middle-Late Jurassic Shishugou Formation of northwest China and a review of sauropod cranial ontogeny. PeerJ 6, e4881 (2018).
Janensch, W. Die Schädel der Sauropoden Brachiosaurus, Barosaurus und Dicraeosaurus aus den Tendaguru-Schichten Deutsch-Ostafrikas. Palaeontographica 2, 147–298 (1935).
Chure, D. J., Britt, B. B., Whitlock, J. A. & Wilson, J. A. First complete sauropod dinosaur skull from the Cretaceous of the Americas and the evolution of sauropod dentition. Naturwissenschaften 97, 379–391 (2010).
Nowinski, A. Nemegtosaurus mongoliensis n. gen., n. sp. (Sauropoda) fromthe uppermost Cretaceous of Mongolia. Palaeontol. Pol. 25, 57–81 (1971)
Wilson, J. A redescription of the Mongolian sauropod Nemegtosaurus mongoliensis Nowinski (Dinosauria, Saurischia) and comments on Late Cretaceous sauropod diversity. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 24, 130 (2004).
Bonaparte, J. F. Les Dinosaures (Carnosaures, Allosauridés, Sauropodes, Cétiosauridés) du Jurassique moyen de Cerro Cóndor (Chubut, Argentine). Annales de Paléontologie. 72, 247–289 (1986).
Nowinski, A. Nemegtosaurus mongoliensis n. gen., n. sp., (Sauropoda) from the uppermost Cretaceous of Mongolia. Palaeontol. Pol. 25, 57–81 (1971)
Curry Rogers, K. & Forster, C. A. The last of the dinosaur titans: A new sauropod from Madagascar. Nature 412, 530–534 (2001)
Madsen, J. H., McIntosh, J. S. & Berman, D. S. Skull and atlas–axis complex of the Upper Jurassic sauropod Camarasaurus Cope (Reptilia: Saurischia). Bull. Carnegie Museum Natl. Hist. 31, 1–115 (1995).
Yates, A. M. The first complete skull of the Triassic dinosaur Melanorosaurus Haughton (Sauropodomorpha: Anchisauria). In Evolution and Palaeobiology of Early Sauropodomorph Dinosaurs (ed. Barrett P. M. et al.) 9–55 (Palaeontological Association, 2007).
Yates, A. M., Bonnan, M. F., Neveling, J., Chinsamy, A. & Blackbeard, M. G. A new transitional sauropodomorph dinosaur from the early jurassic of south africa and the evolution of sauropod feeding and quadrupedalism. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 277, 787–794 (2010).
Chapelle, K. E. J. & Choiniere, J. N. A revised cranial description of Massospondylus carinatus Owen (Dinosauria: Sauropodomorpha) based on computed tomographic scans and a review of cranial characters for basal Sauropodomorpha. PeerJ 6, e4224 (2018).
Knoll, F., Witmer, L. M., Ortega, F., Ridgely, R. C. & Schwarz-Wings, D. The braincase of the basal sauropod dinosaur Spinophorosaurus and 3D reconstructions of the cranial endocast and inner ear. PLoS ONE 7, e30060 (2012).
Balanoff, A. M., Bever, G. S. & Ikejiri, T. The braincase of Apatosaurus (Dinosauria: Sauropoda) based on computed tomography of a new specimen with comments on variation and evolution in sauropod neuroanatomy. Am. Mus. Novit. 3677, 1–32 (2010).
Salgado, L. & Calvo, J. O. Cranial osteology of Amargasurus cazaui Salgado & Bonaparte (Sauropoda, Dicraeosuridae) from the Neocomian of Patagonia. Ameghiniana 29, 337–346 (1992).
Woodruff, D. C. & Foster, J. R. The first specimen of Camarasaurus (Dinosauria: Sauropoda) from Montana: The northernmost occurrence of the genus. PLoS ONE 12, e177423 (2017).
Marpmann, J. S., Carballido, J. L., Sander, P. M. & Knötschke, N. Cranial anatomy of the Late Jurassic dwarf sauropod Europasaurus holgeri (Dinosauria, Camarasauromorpha): ontogenetic changes and size dimorphism. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 13, 221–263 (2015).
Wilson, J. A. Redescription of the mongolian sauropod Nemegtosaurus mongoliensis Nowinski (dinosauria: Saurischia) and comments on late cretaceous sauropod diversity. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 3, 283–318 (2005).
McIntosh, J. S., Miles, C. A., Cloward, K. C. & Parker, J. R. A new nearly complete skeleton of Camarasaurus. Bull. Gunma Museum Natl. Hist. 1, 1–87 (1996).
Xing, L. et al. A new sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of China and the diversity, distribution, and relationships of mamenchisaurids. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 35, 1–17 (2015).
Apaldetti, C., Martinez, R. N., Alcober, O. A. & Pol, D. A new basal sauropodomorph (Dinosauria: Saurischia) from Quebrada del Barro Formation (Marayes-El Carrizal Basin), northwestern Argentina. PLoS ONE 6, e26964 (2011).
Yates, A. M. A revision of the problematic sauropodomorph dinosaurs from Manchester, Connecticut and the status of Anchisaurus Marsh. Palaeontology 53, 739–752 (2010).
Xu, X. et al. A new Middle Jurassic diplodocoid suggests an earlier dispersal and diversification of sauropod dinosaurs. Nat. Commun. 9, 2700–2709 (2018).
Wilson, J. A. Sauropod dinosaur phylogeny: critique and cladistic analysis. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 136, 217–276 (2002).
Mannion, P. D., Upchurch, P., Jin, X. & Zheng, W. New information on the Cretaceous sauropod dinosaurs of Zhejiang Province, China: Impact on Laurasian titanosauriform phylogeny and biogeography. R. Soc. Open Sci. 6, 191057 (2019).
Gomez, K., Carballido, J. & Pol, D. The axial skeleton of Bagualia alba (Dinosauria: Eusauropoda) from the Early Jurassic of Patagonia. Palaeontol. Electron. (2021)
Ouyang, H. A new sauropod dinosaur from Dashanpu, Zigong County, Sichuan Province (Abrosaurus dongpoensis gen. et sp. nov.). Newsletter of Zigong Dinosaur Museum. 2, 10–14 (1989)
Fang, X. S., Zhao, X. J., Lu, L. W. & Cheng, Z. W. Discovery of Late Jurassic Mamenchisaurus in Yunnan, southwestern China. Geol. Bull. China 23, 1005–1011 (2004).
Lü, J. C. et al. New eusauropod dinosaur from Yuanmou of Yunnan Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 80, 1–10 (2006).
Lü, J. C., Li, T. G., Zhong, S. M., Ji, Q. & Li, S. X. A new mamenchisaurid dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic of Yuanmou, Yunan Province, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 82, 17–26 (2008).
Ren, X., Huang, J. & You, H. The second mamenchisaurid dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic of Eastern China. Hist. Biol. 32, 602–610 (2020).
Huang, J. D., You, H. L., Yang, J. T. & Ren, X. X. A new sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic of Huangshan, Anhui Province. Vertebrata Palasiatica. 52, 390–400 (2014).
Alifanov, V. R. & Averianov, A. O. Ferganasaurus verzilini. gen. et sp. Nov., a new neosauropod (Dinosaur, Saurischia, Sauropoda) from the Middle Jurassic of Fergana Valley, Kirghizia. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 23, 358–372 (2003).
Ren, X. et al. Re-examination of Dashanpusaurus dongi (Sauropoda, Macronaria) supports an early Middle Jurassic global distribution of neosauropod dinosaurs. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 610, 111318 (2023).
Li, Y. Q. et al. Sedimentary provenance constraints on the Jurassic to Cretaceous paleogeography of Sichuan Basin, SW China. Gondwana Res. 60, 15–33 (2018).
Huang, D. Y. Jurassic integrative stratigraphy and timescale of China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 62, 223–255 (2021).
Goloboff, P. A., Farris, J. S. & Nixon, K. C. TNT, a free program for phylogenetic analysis. Cladistics 24, 774–786 (2008).
Goloboff, P. A. & Catalano, S. A. TNT version 1.5, including a full implementation of phylogenetic morphometrics. Cladistics 32, 221–238 (2016).
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the Jinchang Museum and Jinchang Natural Resources Bureau for access to specimens in their care and for their hospitality. Gansu Zhendan Dinosaur Culture Communication Co. Ltd. for their field assistance and the preparation of the specimen. We also appreciate the thoughtful reviews provided by the anonymous reviewer, as well as the editor who contributed to enhancing an earlier version of this manuscript. This research was supported by the Scientific Innovative Fund of Gansu Agricultural University (Grant No. 066-056001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Li Ning, Zhang Xiaoqin wrote the main manuscript text and prepared all the figures, and measured the specimens. Ren Xinxin improved the manuscript text. Li Daqing and You Hailu oversaw the project. All authors reviewed the manuscript. Both Li Ning and Zhang Xiaoqin contributed equally to this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Zhang, X., Ren, X. et al. A new eusauropod (Dinosauria, Sauropodomorpha) from the Middle Jurassic of Gansu, China. Sci Rep 15, 17936 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-03210-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-03210-5