Abstract
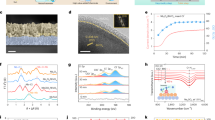
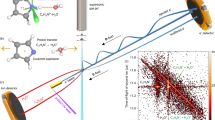
The mechanism of proton transfer (PT), and how it is affected by water structure, is a fundamental issue in numerous chemical and biological processes. Formulated more than 200 years ago, a possible model for PT in aqueous media was proposed by Grotthuss, which continues to be actively studied and debated. In this study, we exploit electron paramagnetic resonance to investigate PT in aqueous solutions. Our proposed method employs pH-sensitive stable nitroxyl radicals and makes use of photolysis of 2-nitrobenzaldehyde to generate protons in the sub-nanosecond timescale. This approach was used to study the impact of classical chaotropic compounds on PT as studied in various aqueous solutions, i.e. 8 M urea, 6 M guanidine hydrochloride (Gdn·HCl), and potassium chloride (KCl). Our findings confirm significant impacts on PT rates. For instance, in 6 M Gdn·HCl, PT occurred 40-fold slower than in water. The method’s sensitivity to water structure is demonstrated, highlighting its potential for monitoring the kinetics of PT in ice and in proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data used in this article is available in the following link: [https://weizmann.elsevierpure.com/en/datasets/9a1ffc70-729c-432a-9202-e7f051309c7b] (https:/weizmann.elsevierpure.com/en/datasets/9a1ffc70-729c-432a-9202-e7f051309c7b).
References
Bell, R. P. Proton in Chemistry (Chapman and Hall, 1973).
Eigen, M. Proton transfer, acid-base catalysis, and enzymatic hydrolysis. Part I: Elementary processes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 3, 1–19 (1964).
A. Müller, H. Ratajczak, W. Junge, E. Diemann (ed.s). Electron and proton transfer in chemistry and biology (Elsevier, 1992).
Warshel, A., Papazyan, A. & Kollman, P. A. On low-barrier hydrogen bonds and enzyme catalysis. Science 269, 102–106 (1995).
De-Grotthuss, C. J. T. Sur la decomposition de l’eau et des corps qu’elle tient en dissolution à l’aide de l’électricité galvanique [On the decomposition of water and of solutes by electrical currents]. Ann. Chim. LVIII, 54–74, (1806).
Hückel, E. Theorie der Beweglichkeit des Wasserstoff- und Hydroxylions in wasseriger Losung. Z. Elektrochem. Angew. Phys. Chem. 34, 546–566 (1928).
Bernal, J. D. & Fowler, R. H. A theory of water and ionic solution with particular reference to hydrogen and hydroxyl ions. J. Chem. Phys. 1, 515–548 (1933).
Eigen, M. & DeMaeyer, L. Self-dissociation and protonic charge transport in water and ice. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A247, 505–533 (1958).
Agmon, N. The Grotthuss mechanism. Chem. Phys. Lett. 244, 456–462 (1995).
George, M. V. & Scaiano, J. C. Photochemistry of o-nitrobenzaldehyde and related studies. J. Phys. Chem. 84, 492–495 (1980).
Edward, S. G., Karen, R. & Cort, A. Nitrobenzaldehyde as a chemical actinometer for solution and ice photochemistry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chemistry 209, 186–192 (2010).
Kohse, S., Neubauer, A., Pazidis, A., Lochbrunner, S. & Kragl, U. Photoswitching of Enzyme Activity by Laser-Induced pH Jump. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 9407–9411 (2013).
Khramtsov, V. V., Weiner, L. M., Grigoriev, I. A. & Volodarsky, L. B. Proton exchange in stable nitroxyl radicals. EPR study of the pH of aqueous solutions. Chem. Phys. Lett. 91, 69–72 (1982).
Keana, J. F. W., Acarregui, M. J. & Boyle, S. L. M. 2,2-Disubstituted-4,4-dimethylimidazolidinyl-3-oxy nitroxides: indicators of aqueous acidity through variation of an with pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104, 827–830 (1982).
V.V. Khramtsov, L. M. Weiner, Proton exchange in stable nitroxyl radicals: pH-sensitive spin probes. In Volodarsky L.B. (ed.). Imidazoline Nitroxides, pp.37–80 (CRS Press, 1988).
V.V. Khramtsov, L. B. Volodarsky. Use of imidazoline nitroxides in studies of chemical reactions. ESR measurements of the concentration and reactivity of protons, thiols, and nitric oxide. Biol. Magn. Res. 1998, 14, 109–180
Weiner, L. M. Stable nitroxyl radicals as pH, thiol and electron transfer probes. Appl. Magn. Res. 31, 357–373 (2007).
Barbon, A., Bortolus, M., Isse, A. A., Reznikov, V. A. & Weiner, L. Electron transfer in pH-sensitive nitroxide radicals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 665, 137–140 (2016).
Khramtsov, V. V. et al. Proton exchange in stable nitroxyl radicals of the imidazoline and imidazolidine series. J. Magn. Res. 61, 397–408 (1985).
Improta, R., Scalmani, G. & Barone, V. Quantum mechanical prediction of the magnetic titration curve of a nitroxide spin probe. Chem. Phys. Lett. 336, 349–356 (2001).
Improta, R. & Barone, V. Interplay of electronic, environmental, and vibrational effects in determining the hyperfine coupling constants of organic free radicals. Chem. Rev. 104, 1231–1254 (2004).
Leberman, R. & Soper, A. Effect of high salt concentrations on water structure. Nature 378, 364–366 (1995).
Hribar, B., Southall, N. T., Vlachy, V. & K. A.,. Dill How ions affect the structure of water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 12302–12311 (2002).
Marcus, Y. Effect of Ions on the structure of water: Structure making and breaking. Chem. Rev. 109, 1346–1370 (2012).
LoNostro, P. & Ninham, P. W. Hofmeister phenomena: An update on ion specificity in biology. Chem. Rev. 112, 2286–2322 (2012).
A.K Soper, E.W Castner, Jr. A. Luzar, Impact of urea on water structure: a clue to its properties as a denaturant? Biophys. Chem. 2003, 105, 649–666
Rezus, Y. L. A. & Bakker, H. J. Effect of urea on the structural dynamics of water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 103, 18417–18420 (2006).
Mason, P. E. et al. The Structure of aqueous guanidinium chloride solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 11462–11470 (2004).
Scott, J. N., Nucci, N. V. & Vanderkooi, J. M. Changes in water structure induced by the guanidinium cation and implications for protein denaturation. J. Phys. Chem. A. 112, 10939–10948 (2008).
Vanzi, F., Madan, B. & Sharp, K. Effect of the protein denaturants urea and guanidinium on water structure: A Structural and thermodynamic study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 10748–10750 (1998).
Ki Lim, W., Rösgen, J. & Englander, S. W. Urea, but not guanidinium, destabilizes proteins4 by forming hydrogen bonds to the peptide group. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106, 2595–2600 (2009).
Murata, K. & Tanaka, H. Liquid-liquid transition without macroscopic phase separation in a water-glycerol mixture. Nat. Mater. 11, 436–443 (2012).
Popov, I., Greenbaum, A., Sokolov, A. P. & Feldman, Y. The puzzling first-order phase transition in water-glycerol mixtures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 18063–18071 (2015).
V.F. Petrenko, R.W. Whitworth, Physics of Ice. (, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1999)
Lee, D. H. & Kang, H. Proton transport and related chemical processes of ice. J. Phys. Chem. B. 125, 8270–8281 (2021).
Kobayashi, C., Saito, S. & Ohmine, I. Mechanism of fast proton transfer in ice: Potential energy surface and reaction coordinate analyses. J. Chem. Phys. 113, 9090–9100 (2000).
Salna, B., Benabbas, A., Sage, J. T., van Thor, J. & Champion, P. M. Wide-dynamic-range kinetic investigations of deep proton tunnelling in proteins. Nat. Chem. 8, 874–880 (2016).
Li, X. Z., Walker, B. & Michaelides, A. Quantum Nature of the hydrogen bond. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108, 6369–6373 (2011).
Guo, J. et al. Nuclear Quantum effects of hydrogen bonds probed by tip-enhanced inelastic electron tunneling. Science 352, 321–325 (2016).
Wang, L., Fried, S. D., Boxer, S. G. & Markland, T. E. Quantum delocalization of protons in the hydrogen-bond network of an enzyme active site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, 18454–18459 (2014).
Krishtalik, L. I. The mechanism of the proton transfer: An outline. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1458, 6–279 (2000).
Freier, E., Wolf, S. & Gerwert, K. Proton transfer via a transient linear water-molecule chain in a membrane protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 108, 11435–11439 (2011).
Aqvist, J. & Warshel, A. Computer simulation of the initial proton transfer step in human carbonic anhydrase I. J. Mol. Biol. 224, 7–14 (1992).
Altenbach, C., Marti, T., Khorana, H. G. & Hubbell, W. L. Transmembrane protein structure: Spin labeling of bacteriorhodopsin mutants. Science 248, 1088–1092 (1990).
Steinhoff, H. J. et al. Resolved detection of structural changes during the photocycle of spin-labeled bacteriorhodopsin. Science 266, 105–107 (1994).
Eliash, T., Weiner, L., Ottolenghi, M. & Sheves, M. Specific binding sites for cations in bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys. J. 81, 1155–1162 (2001).
Khorana, H. G. et al. Amino acid sequence of bacteriorhodopsin Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 76, 5046–5050 (1979).
Gray, H. B. & Winkler, J. R. Electron tunneling through proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 36, 341–372 (2003).
Eliash, T. et al. Nitroxyl radicals for studying electron transfer. Angew. Chem Int. Ed. Engl. 52, 8689–8692 (2013).
Schmallegger, M. et al. Systematic quantification of electron transfer in a bare phospholipid membrane using nitroxide-labeled stearic acids: Distance dependence, kinetics And Activation Parameters. Langmuir 36, 10429–10437 (2020).
Hammes-Schiffer, S. & Stuchebrukhov, A. A. Theory of coupled electron and proton transfer. Chem. Rev. 110, 6939–6960 (2010).
Weinberg, D. R. et al. Proton-coupled electron transfer. Chem. Rev. 112, 4016–4093 (2012).
Tyburski, R., Liu, T., Glover, S. D. & Hammarström, L. Proton-coupled electron transfer guidelines, fair and square. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 560–576 (2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I.A.G., V.R., and I.K. did the synthesis, purification and characterization of used nitroxyl stable radicals. A.S. did the measurements and interpretation of PT at high field EPR spectrometer in ice. S.L. did molecular dynamic simulation. I.M. did determination of pK values of R2 in 6 M Gdn·HCl and 8 M urea. M.S. and T.E. did the spin labeling of mutants of bacteriorhodopsin and measurements PT in protein. N.F. did UV kinetics of photolysis of 2-NBA at different conditions. A.B. did time resolved experiments of R4 and R4 pK determination in Gdn·HCl solution. R.C. and L.W. did CW EPR investigation of kinetics of samples acidification at 2-NBA photolysis. A.B., M.S., R.C. and L.W. did the writing and editing of the manuscript. A.B. and L.W. conceptualization, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Barbon, A., Savitsky, A., Grigoriev, I. et al. Photoinduced proton transfer in differently structured water: an EPR approach to solving a classic problem. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38650-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38650-0