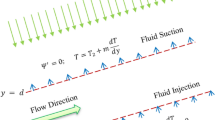
Abstract
Thermal transport in converging/diverging channels finds applications in various engineering fields, including heat exchangers, microfluidics, and biomedical devices, due to their ability to enhance heat transfer and control fluid flow. The use of nanoparticles cannot be circumvented because of their promising characteristics. These materials widely used in applied thermal engineering, to enhance or control thermal transport in machinery, transformer, chemical engineering. The flow in tank designed for oblique walls is common in practical situations and the dynamics of fluids are essential to maintain it for desired purposes. Therefore, the concept of traditional nanoliquid models is extended for advanced ternary fluids. To acquire the beneficial model results, the momentum slip, viscous dissipative phenomena and elastic walls conditions along with new innovative ternary nanoliquid characteristics are adopted for the model formulation. Then, the results with special emphasis on thermal, entropy optimization, shear drag and heat transport rate are obtained via RK scheme and a comprehensive physical description is provided. The ternary nanoliquid possesses remarkable thermal transport and dominant behaviour is inspected for entropy, shear drag and heat transfer rate at the elastic walls under \(Ec, Re, \alpha\) and \(\gamma\). These fluids are recommended for different application especially in applied thermal engineering.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Rashidi, M. M., Mahariq, I., Nazari, M. A., Accouche, O. & Bhatti, M. M. Comprehensive review on exergy analysis of shell and tube heat exchangers. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 147, 12301–12311 (2022).
Abbas, A. W., Eladeb, A. & Kolsi, L. Numerical analysis of thermal improvement in hydrogen-based host fluids under buoyancy force and EPNM effects: Study for vertical cylinder. ZAAM J. Appl. Math. Mech. https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.202200449 (2024).
Nidhish, K. M., Adnan, Sarfraz, G., Fwaz, M. Z. B. & Eldin, S. M. Dynamics of Corcione nanoliquid on a convectively radiated surface using Al2O3 nanoparticles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12448-y (2023).
Madhukesh, J. K. et al. Numerical simulation of AA7072-AA7075/water-based hybrid nanofluid flow over a curved stretching sheet with Newtonian heating: A non-Fourier heat flux model approach. J. Mol. Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116103 (2021).
Gowda, R. J. P., Kumar, R. N., Prasannakumara, B. C., Nagaraja, B. & Gireesha, B. J. Exploring magnetic dipole contribution on ferromagnetic nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet: An application of Stefan blowing. J. Mol. Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116215 (2021).
Aziz, S. et al. A revised double diffusion Cattaneo-Christov bioconvective model for unsteady Williamson nanofluid due to Riga surface with additional nonlinear thermal sources. ZAMM Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.202400225 (2024).
Sarfraz, G., Said, N. M., Bilal, M., Elhag, A. F. A. & Hassan, A. M. Significance of radiated ternary nanofluid for thermal transport in stagnation point flow using thermal slip and dissipation function. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2023.103631 (2023).
Ali, B. et al. Mixed convective flow of hybrid nanofluid over a heated stretching disk with zero-mass flux using the modified Buongiorno model. Alex. Eng. J. 72, 89–96 (2023).
Khadija, R., Mahmood, Z., Alqahtani, H. & Sayed, M. E. Various nanoparticle shapes and quadratic velocity impacts on entropy generation and MHD flow over a stretching sheet with joule heating. Alex. Eng. J. 71, 147–159 (2023).
Mishra, N. K., Ashraf, W., Mir, A. & Lioua, K. Thermal process computing in nanofluid using dissipation and squeezing constraints. ZAAM Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.202300195 (2024).
Nadeem, A., Mahmoud, H. A., Ali, A. & Eldin, S. M. Significance of Koo-Kleinstreuer-Li model for thermal enhancement in nanofluid under magnetic field and thermal radiation factors using LSM. Adv. Mech. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1177/16878132231206906 (2023).
Kumar, N. M., Rahman, K. U., Sayed, M. E. & Bani-Fwaz, M. Z. Investigation of blood flow characteristics saturated by graphene/CuO hybrid nanoparticles under quadratic radiation using VIM: study for expanding/contracting channel. Sci. Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35695-3 (2023).
Bilal, M. et al. Darcy-Forchheimer hybrid nano fluid flow with mixed convection past an inclined cylinder. Computers, Materials & Continua https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2020.012677 (2020).
Waqas, H. et al. Heat transfer analysis of hybrid nanofluid flow with thermal radiation through a stretching sheet: A comparative study. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2022.106303 (2022).
Kumar, R. N., Gamaoun, F., Abdulrahman, A., Chohan, J. S. & Gowda, R. J. P. Heat transfer analysis in three-dimensional unsteady magnetic fluid flow of water-based ternary hybrid nanofluid conveying three various shaped nanoparticles: A comparative study. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 25, 36 (2022).
Gul, T. et al. Viscous dissipated hybrid nanoliquid flow with Darcy-Forchheimer and forced convection over a moving thin needle. AIP Adv. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0022210 (2020).
Pattnaik, P. K., Mishra, S. R., Shamshuddin, M. D., Panda, S. & Baithalu, R. Significant statistical model of heat transfer rate in radiative Carreau tri-hybrid nanofluid with entropy analysis using response surface methodology used in solar aircraft. Renew. Energy https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2024.121521 (2024).
Dey, S., Ontela, S., Pattnaik, P. K. & Mishra, S. R. Particle shape analysis on thermally stratified 3D rotational Darcy-Forchheimer flow with hydromagnetic Williamson hybrid nanofluid containing Ag-MoS4. Colloid Polym. Sci. 303, 483–501 (2025).
Rauf, A., Hussain, F., Mushtaq, A., Shah, N. A. & Ali, M. R. MHD mixed convection flow for Maxwell Hybrid nanofluid with Soret, Dufour and Morphology effects. Arab. J. Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104965 (2023).
Dey, S., Ontela, S., Pattnaik, P. K. & Mishra, S. R. Blood-based tri-hybrid nanofluid flow through a porous channel with the impact of thermal radiation used in drug administration. Partial Differential Equations in Applied Mathematics https://doi.org/10.1016/j.padiff.2025.101137 (2025).
Panda, S. et al. Computation of Fe3O4-CoFe2O4 hybrid nanofluid flow in stretchable (Shrinkable) wedge with Variant magnetized force and heat generation. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2024.101839 (2024).
Ali, F., Kamal, M., Ahmed, M. F. & Zafar, S. S. Exact exploration of heat radiation and chemical reactive in the porosity flow of hybrid nanofluid using the Laplace transform. ZAMM Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.70050 (2025).
Rana, P., Shukla, N., Gupta, Y. & Pop, I. Analytical prediction of multiple solutions for MHD Jeffery–Hamel flow and heat transfer utilizing KKL nanofluid model. Phys. Lett. A 383(2–3), 176–185 (2019).
Dey, S., Ontela, S., Pattnaik, P. K. & Mishra, S. R. Convective heat transfer of tri-hybrid nanofluid through a curved expanding surface with the impact of velocity slip and exponential heat source. Colloid Polym. Sci. 302, 1573–1590 (2024).
Mishra, S. R. et al. Radiative heat transfer on the peristaltic flow of an electrically conducting nanofluid through wavy walls of a tapered channel. Results Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2023.106898 (2023).
Shah, N. A. et al. Dynamics of chemical reactive on magneto Hybrid Nanomaterial with heat radiation due to porous exponential plate: Laplace transform technique for the heat and mass. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2025.101295 (2025).
Rana, P., Shukla, N., Gupta, Y. & Pop, I. Homotopy analysis method for predicting multiple solutions in the channel flow with stability analysis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 66, 183–193 (2019).
Ahmed, M. F., Zaib, A., Ali, F., Khan, U. & Zafar, S. S. Thermal radiation of Walter-B magneto bioconvection nanofluid due to the stretching surface under convective condition and heat source/sink: A semi-analytical technique for the stagnation point. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2025.101291 (2025).
Rana, P., Shukla, N., Areekara, S. & Pop, I. Multiple solutions and temporal stability for ternary hybrid nanofluid flow between non-parallel plates with entropy generation analysis. ZAMM Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.202400124 (2024).
Rauf, A., Mushtaq, A., Shah, N. A. & Botmart, T. Heat transfer and hybrid ferrofluid flow over a nonlinearly stretchable rotating disk under the influence of an alternating magnetic field. Sci. Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21784-2 (2022).
Ashraf, W. Thermal efficiency in hybrid (Al2O3-CuO/H2O) and ternary hybrid nanofluids (Al2O3-CuO-Cu/H2O) by considering the novel effects of imposed magnetic field and convective heat condition. Waves Random Complex Media https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2022.2092233 (2022).
Adnan, & Ashraf, W. Heat transfer mechanism in ternary nanofluid between parallel plates channel using modified Hamilton-Crossers model and thermal radiation effects. Geoenergy Science and Engineering https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoen.2023.211732 (2023).
Zahan, I., Nasrin, R. & Khatun, S. Thermal performance of ternary-hybrid nanofluids through a convergent-divergent nozzle using distilled water - ethylene glycol mixtures. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2022.106254 (2022).
Faizan, M., Pati, S., Randive, P. R. & Baranyi, L. Numerical study of nanofluid flow and heat transfer through a non-uniformly heated converging duct. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2022.102545 (2022).
Boujelbene, M., Rehman, S., Alqahtani, S., Alshehery, S. & Sayed, M. E. Thermal transport and magnetohydrodynamics flow of generalized Newtonian nanofluid with inherent irreversibility between conduit with slip at the walls. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2023.2182364 (2023).
Waqas, A. Analysis of heat transfer performance for ternary nanofluid flow in radiated channel under different physical parameters using GFEM. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2023.104887 (2023).
Bég, O. A., Bég, T., Khan, W. A. & Uddin, M. J. Multiple slip effects on nanofluid dissipative flow in a converging/diverging channel: A numerical study. Heat Transfer https://doi.org/10.1002/htj.22341 (2021).
Laila, R. & Marwat, D. N. K. Nanofluid flow in a converging and diverging channel of rectangular and heated walls. Ain Shams Engineering Journal 12(4), 4023–4035 (2021).
Saifi, H., Sari, M. R., Kezzar, G. M., Sharifpur, M. & Sadeghzadeh, M. Heat transfer through converging-diverging channels using Adomian decomposition method. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics 14(20), 1373–1384 (2020).
Smida, K., Sohail, M. U., Tlili, I. & Javed, A. Numerical thermal study of ternary nanofluid influenced by thermal radiation towards convectively heated sinusoidal cylinder. Heliyon https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20057 (2023).
Vinutha, K. et al. Computational examination of heat and mass transfer induced by ternary nanofluid flow across convergent/divergent channels with pollutant concentration. Water https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162955 (2023).
Mishra, A., Pandey, A. K., Chamkha, A. J. & Kumar, M. Roles of nanoparticles and heat generation/absorption on MHD flow of Ag–H2O nanofluid via porous stretching/shrinking convergent/divergent channel. J. Egyptian Math. Soc. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42787-020-00079-3 (2020).
Waqas, A. Heat transfer in tetra-nanofluid between converging/diverging channel under the influence of thermal radiations by using Galerkin finite element method. Waves in Random and Complex Media https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2023.2171154 (2023).
Ashraf, W. Joule heating and heat generation/absorption effects on the heat transfer mechanism in ternary nanofluid containing different shape factors in stretchable converging/diverging Channel. Waves in Random and Complex Media https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2023.2198038 (2023).
Mishra, N. K., Khalid, A. M. A., Rahman, K. U., Eldin, S. M. & Fwaz, M. Z. B. Investigation of improved heat transport featuring in dissipative ternary nanofluid over a stretched wavy cylinder under thermal slip. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2023.103130 (2023).
AL-Zahrani, A. A. et al. Analytical study of (Ag–Graphene)/blood hybrid nanofluid influenced by (platelets-cylindrical)nanoparticles and Joule heating via VIM. ACS Omega 8(22), 19926–19938 (2023).
Abbas, W., Sayed, M. E. & Mutasem, Z. B. F. Numerical investigation of non-transient comparative heat transport mechanism in ternary nanofluid under various physical constraints. AIMS Mathematics 8(7), 15932–15949 (2023).
Nadeem, A. & Sayed, M. E. Heat transport mechanism in glycerin-titania nanofluid over a permeable slanted surface by considering nanoparticles aggregation and Cattaneo Christov thermal flux. Sci. Prog. https://doi.org/10.1177/00368504231180032 (2023).
Alharbi, K. A. M. & Galal, A. M. Novel magneto-radiative thermal featuring in SWCNT–MWCNT/C2H6O2–H2O under hydrogen bonding. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979224500176 (2023).
Adnan,. Heat transfer inspection in [(ZnO-MWCNTs)/water-EG(50:50)]hnf with thermal radiation ray and convective condition over a Riga surface. Waves in Random and Complex Media https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2022.2119300 (2022).
Adnan, Alharbi, K. A. M., Bani-Fwaz, M. Z., Eldin, S. M. & Yassen, M. F. Numerical heat performance of TiO2/Glycerin under nanoparticles aggregation and nonlinear radiative heat flux in dilating/squeezing channel. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2022.102568 (2023).
Abdulkhaliq, K. A. M., Adnan, & Akgul, A. Investigation of Williamson nanofluid in a convectively heated peristaltic channel and magnetic field via method of moments. AIP Adv. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0141498 (2023).
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Northern Border University, Rafha, KSA for funding this research work through the project number “NBU-FFR-2026-2942-01”.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Adnan and H.M, S.U.K: Conceptualization, Formulation, Formal analysis, writing original draft. M.J., Z.K., M.B., H.A., and Y.K.: Investigation, software, Execution of the results in Tables 1, 2, 3 and 4, Plotted the graphical results, language and editing, validation and discussion.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
There is no competing interest regarding this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Jebali, M., Adnan, Mukalazi, H. et al. Entropy and thermal dynamics motivated by ternary nanocomposites and geometric influence of oblique channel. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38880-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38880-2