Abstract
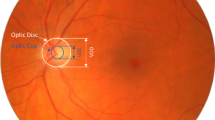
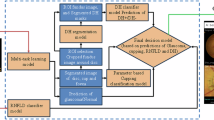
Glaucoma remains a critical cause of permanent global visual disability, and is produced by advancing destruction of the visual nerve head (ONH). Early detection is critical important in preventing vision loss. We propose a new fusion transformer pipeline, which integrates optic disc/cup and feature-based segmentation to aid in the effective screening of glaucoma, in this paper. The proposed approach integrates U-Net with an attention mechanism to cut the Optic Disc (OD) and Optic Cup (OC), enabling after processing spectral shape descriptors to evaluate Vertical Cup-to-Disc Ratio (CDR). Fundus image descriptors are extracted together with the Swin Transformer encoder to detect glaucoma at the image scale. They employ a probabilistic fusion method to merge structural biomarker (CDR) and deep learning features to finally obtain the final glaucoma classification. The framework was studied in detail on three popular publicly available datasets: LAG, ACRIMA, and DRISTHI-GS. According to the experimental results, SwinCup-DiscNet consistently outperforms the traditional CNN-based models and methods that are based only on segmentation, as it surpasses these approaches on all datasets. The framework proves to be robust, reliable, and clinically interpretable, using execution metrics like DSC IoU, accuracy measures, and F1-score, as well as Cup-to-Disc Ratio Mean Absolute Error (CDR MAE). Findings show that SwinCup-DiscNet is a highly effective clinical tool used in real-world clinical settings to detect glaucoma early.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- \(\:I\left(x,y\right)\) :
-
Original input fundus image at pixel coordinates \(\:\left(x,y\right)\)
- \(\:{I}_{p}\) :
-
Pre-processed image after resizing, normalization, enhancement, and denoising
- \(\:R\left(\cdot\:\right)\) :
-
The resizing operator is applied to the image
- \(\:N\left(\cdot\:\right)\) :
-
Normalization operator applied from the image
- \(\:CLAHE\left(\cdot\:\right)\) :
-
CLAHE for illumination correction
- \(\:{M}_{c}\) :
-
Segmented optic cup mask
- \(\:{M}_{d}\) :
-
Segmented optic disc mask
- \(\:{S}_{\theta\:}\left(\cdot\:\right)\) :
-
Cup segmentation function of Attention U-Net with parameters \(\:\theta\:\)
- \(\:{D}_{\theta\:}\left(\cdot\:\right)\) :
-
Disc segmentation function of Attention U-Net with parameters \(\:\theta\:\)
- \(\:\varPhi\:\left(\cdot\:\right)\) :
-
Post-processing operator for contour smoothing and ellipse fitting
- \(\:{E}_{c}\) :
-
Elliptical boundary within the optic cup
- \(\:{E}_{d}\) :
-
An elliptical boundary located optic disc
- \(\:{H}_{c}\) :
-
Vertical dimension optic cup
- \(\:{H}_{d}\) :
-
Vertical optic cup dimension
- vCDR:
-
Vertical Cup-to-Disc Ratio, defined as \(\:{H}_{c}/{H}_{d}\)
- OD:
-
Optic Disc
- OC:
-
Optic Cup
- \(\:{z}_{0}\) :
-
Initial tokenized representation of the pre-processed image
- \(\:{z}_{l}^{\prime\:}\) :
-
Intermediate representation at Swin Transformer stage \(\:l\) after window-based self-attention
- \(\:{z}_{l}\) :
-
Updated representation at stage \(\:l\) after feed-forward MLP
- LN(\(\:\cdot\:\)):
-
Layer Normalization operator
- SW-MSA(\(\:\cdot\:\)):
-
Swin Transformer Window-Multi-Head Self-Attention mechanism
- MLP(\(\:\cdot\:\)):
-
Multi-Layer-Perceptron Transformation
- \(\:{z}_{L}\) :
-
Final feature representation at the last Swin Transformer stage \(\:L\)
- GAP(\(\:\cdot\:\)):
-
Global Average Pooling operation
- \(\:{P}_{g}\) :
-
Probability of glaucoma predicted by the Swin Transformer branch
- \(\:W,b\) :
-
Learnable weight matrix and bias vector in the classification head
- \(\:\sigma\:\left(\cdot\:\right)\) :
-
Sigmoid activation function
- \(\:\varPsi\:\) :
-
Fused decision score combining Swin Transformer probability and vCDR
- \(\:\alpha\:\) :
-
Fusion weight factor balancing between \(\:{P}_{g}\) and vCDR
- \(\:\mu\:\) :
-
Mean vCDR value from the training set
- \(\:\sigma\:\) (in fusion):
-
Standard deviation of vCDR values in the training set
- \(\:\tau\:\) :
-
Threshold for binary decision (glaucoma vs. normal)
- \(\:\widehat{y}\) :
-
Final binary decision: \(\:1\) = Glaucoma, \(\:0\) = Normal
- \(\:N\) :
-
Number of test samples used for evaluation
- \(\:CD{R}_{i}\) :
-
Ground truth cup-to-disc ratio for sample \(\:i\)
- \(\:{\widehat{CDR}}_{i}\) :
-
Predicted cup-to-disc ratio for sample \(\:i\)
- \(\:MA{E}_{CDR}\) :
-
Mean Absolute Error in CDR estimation
- IoU:
-
Intersection over Union
- DSC:
-
Dice Score Coefficient
References
Lee, S. S. Y. & Mackey, D. A. Glaucoma–risk factors and current challenges in the diagnosis of a leading cause of visual impairment. Maturitas 163, 15–22 (2022).
Sun, Y. et al. Time trends, associations and prevalence of blindness and vision loss due to glaucoma: an analysis of observational data from the global burden of disease study 2017. BMJ open. 12 (1), e053805 (2022).
Jan, C. L. et al. Analysing diagnostic practices and referral pathways for glaucoma in Australian primary eye care. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 45 (5), 1211–1220 (2025).
Bazi, Y., Al Rahhal, M. M., Elgibreen, H. & Zuair, M. Vision transformers for segmentation of disc and cup in retinal fundus images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 91, 105915 (2024).
Tao, T. et al. Predicting diabetic retinopathy based on biomarkers: classification and regression tree models. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 222, 112091 (2025).
Ikram, A. & Imran, A. ResViT FusionNet model: an explainable AI-driven approach for automated grading of diabetic retinopathy in retinal images. Comput. Biol. Med. 186, 109656 (2025).
Khan, S. D., Basalamah, S. & Lbath, A. A novel deep learning framework for retinal disease detection leveraging contextual and local features cues from retinal images. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., 63(7).,1–18. (2025).
Guo, Y., Peng, Y., Sun, J., Li, D. & Zhang, B. DSLN: dual-tutor student learning network for multiracial glaucoma detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 34 (14), 11885–11910 (2022).
Tulsani, A., Kumar, P. & Pathan, S. Automated segmentation of optic disc and optic cup for glaucoma assessment using improved UNET + + architecture. Biocybernetics Biomedical Eng. 41 (2), 819–832 (2021).
Zhang, Y. et al. TAU: transferable attention U-Net for optic disc and cup segmentation. Knowl. Based Syst. 213, 106668 (2021).
Shen, Y. et al. Graph attention u-net for retinal layer surface detection and choroid neovascularization segmentation in Oct images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 42 (11), 3140–3154 (2023).
Xiong, H., Long, F., Alam, M. S. & Sang, J. Multi-GlaucNet: A multi-task model for optic disc segmentation, blood vessel segmentation and glaucoma detection. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 99, 106850 (2025).
Joshi, A. & Sharma, K. K. Graph deep network for optic disc and optic cup segmentation for glaucoma disease using retinal imaging. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 45 (3), 847–858 (2022).
Tabassum, M. et al. CDED-Net: joint segmentation of optic disc and optic cup for glaucoma screening. IEEE Access. 8, 102733–102747 (2020).
Elmoufidi, A., Skouta, A., Jai-Andaloussi, S. & Ouchetto, O. CNN with multiple inputs for automatic glaucoma assessment using fundus images. Int. J. Image Graphics. 23 (01), 2350012 (2023).
Közkurt, C. et al. Trish: an efficient activation function for CNN models and analysis of its effectiveness with optimizers in diagnosing glaucoma. J. Supercomputing. 80 (11), 15485–15516 (2024).
Sonti, K. & Dhuli, R. A new convolution neural network model KR-NET for retinal fundus glaucoma classification. Optik 283, 170861 (2023).
Velpula, V. K. & Sharma, L. D. Multi-stage glaucoma classification using pre-trained convolutional neural networks and voting-based classifier fusion. Front. Physiol. 14, 1175881 (2023).
Pattanaik, S., Behera, S., Majhi, S. K., Pradhan, R. & Dwibedy, P. An ensemble stacked bi-lstm with resnet50 method for glaucoma classification in Iot framework: an ensemble method for glaucoma classification Iot framework. J. Sci. Indust. Res. (JSIR). 84 (1), 24–35 (2025).
Sangeetha, J., Rekha, D. & Priyanka, M. A residual network integrated with multimodal fundus features for automatic glaucoma classification. Comput. Electr. Eng. 122, 109880 (2025).
Pathan, S., Kumar, P., Pai, R. M. & Bhandary, S. V. Automated segmentation and classifcation of retinal features for glaucoma diagnosis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 63, 102244 (2021).
Fang, L. & Qiao, H. Glaucoma multi-classification using the novel syndrome mechanism-based dual-channel network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 86, 105143 (2023).
Geetha, A. & Prakash, N. B. Classification of glaucoma in retinal images using EfficientnetB4 deep learning model. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng., 43(3). 1041-1055 (2022).
Meenakshi Devi, P., Gnanavel, S., Narayana, K. E. & Sangeethaa, S. N. Novel methods for diagnosing glaucoma: segmenting optic discs and cups using ensemble learning algorithms and Cdr ratio analysis. IETE J. Res. 70 (8), 6828–6847 (2024).
Bengani, S. & S, V. Automatic segmentation of optic disc in retinal fundus images using semi-supervised deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 80 (3), 3443–3468 (2021).
Naidana, K. S. & Barpanda, S. S. A unique discrete wavelet & deterministic Walk-Based glaucoma classification approach using Image-Specific enhanced retinal images. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 47(1). 699-720 (2023).
Li, L. et al. A large-scale database and a CNN model for attention-based glaucoma detection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 39 (2), 413–424 (2019).
Lin, M. et al. Automated diagnosing primary open-angle glaucoma from fundus image by simulating human’s grading with deep learning. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 14080 (2022).
Elangovan, P. & Nath, M. K. En-ConvNet: a novel approach for glaucoma detection from color fundus images using ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 32 (6), 2034–2048 (2022).
Mouhafid, M., Zhou, Y., Shan, C. & Xiao, Z. Towards efficient glaucoma screening with modular convolution-involution cascade architecture. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 11, e2844 (2025).
Elangovan, P. & Nath, M. K. Glaucoma assessment from color fundus images using convolutional neural network. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 31 (2), 955–971 (2021).
Barros, D. M. et al. Machine learning applied to retinal image processing for glaucoma detection: review and perspective. Biomed. Eng. Online. 19 (1), 20 (2020).
Virbukaitė, S., Bernatavičienė, J. & Imbrasienė, D. Glaucoma identification using convolutional neural networks ensemble for optic disc and cup segmentation. IEEE Access. 12, 82720–82729 (2024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Praveen P and Ranjith Kumar Gatla: supervision, validation, project administration, resources, writing, review & editing. Reem A. Almenweer: investigation, result interpretation, critical revision of the manuscript, writing, review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Chilukuri, R., Praveen, P., Gatla, R.K. et al. SwinCup-DiscNet: A fusion transformer framework for glaucoma diagnosis using optic disc and cup features. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39065-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39065-7