Abstract
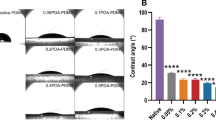
PDMS/NdFeB composites are promising materials for soft magnetic actuators, but NdFeB particles corrode in body fluids and release toxic metal ions, limiting their biomedical use. We developed ~ 100 µm spin-coated PDMS-chitosan (PDMS-CHIT) and PDMS-polycaprolactone (PDMS-PCL) coatings that solve this problem. Over 24 weeks of immersion, these coatings reduced neodymium and iron release by more than 95%, keeping ion concentrations well below cytotoxicity thresholds. Importantly, the PDMS-PCL coating fully preserved magnetorheological actuation (ΔG’ ≈ 61 kPa under 0.5 T, comparable to uncoated composite), while PDMS-CHIT provided superior ion barrier at the cost of reduced actuation force. Biological validation confirmed cytocompatibility with fibroblasts, hemocompatibility with erythrocytes, and strong suppression of bacterial biofilm formation. These results establish a validated materials platform for biocompatible soft magnetic actuators.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Kim, Y. & Zhao, X. Magnetic soft materials and robots. Chem. Rev. 122, 5317–5364 (2022).
Johnston, I. D., McCluskey, D. K., Tan, C. K. L. & Tracey, M. C. Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J. Micromechanics Microengineering. 24, 035017 (2014).
Liu, Z., He, J. & Ramanujan, R. V. Significant progress of grain boundary diffusion process for cost-effective rare Earth permanent magnets: A review. Mater. Des. 209, 110004 (2021).
Zhou, C. et al. Ferromagnetic soft catheter robots for minimally invasive Bioprinting. Nat. Commun. 12, 5072 (2021).
Zhang, M. et al. A magnetically actuated microcatheter with soft rotatable tip for enhanced endovascular access and treatment efficiency. Sci. Adv. (2025).
Sun, Y. et al. Magnetically driven capsules with multimodal response and multifunctionality for biomedical applications. Nat. Commun. 15, 1839 (2024).
Hu, Q. et al. A magnetic soft robotic system for intelligent bladder volume control. Npj Flex. Electron. 9, 33 (2025).
Powojska, A., Niewęgłowska, J., Suska, S., Cavadas, A. & Mystkowska, J. Chemical stability assessment of soft magnetic composites for biomedical applications. Engineering of Biomaterials, 164, 2–8 (2022). https://doi.org/10.34821/ENG.BIOMAT.164.2022.2-8
Donohue, V. E., McDonald, F. & Evans, R. Vitro cytotoxicity testing of neodymium-iron‐boron magnets. J. Appl. Biomater. 6, 69–74 (1995).
Powojska, A., Mystkowski, A., Gundabattini, E. & Mystkowska, J. Spin-Coating fabrication method of PDMS/NdFeB composites using Chitosan/PCL coating. Materials 17, 1973 (2024).
Yap, T. F. et al. Understanding silicone elastomer curing and adhesion for stronger soft devices. Sci. Adv. (2025).
Mao, Y., Pechenizkiy, I., Stieglitz, T. & Doll, T. Numerical evaluation on residual thermal Stress-Induced delamination at PDMS–Metal interface of neural prostheses. Micromachines 12, 669 (2021).
Piao, Z., Xu, B., Wang, H. & Pu, C. Effects of thickness and elastic modulus on stress condition of fatigue-resistant coating under rolling contact. J. Cent. South. Univ. Technol. 17, 899–905 (2010).
Tsikriteas, Z. M., Roscow, J. I., Bowen, C. R. & Khanbareh, H. Flexible ferroelectric wearable devices for medical applications. iScience 24, 101987 (2021).
Lim, K. et al. Material and structural considerations for high-performance electrodes for wearable skin devices. Commun. Mater. 5, 49 (2024).
Khubiev, O. M. et al. Chitosan-Based antibacterial films for biomedical and food applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 10738 (2023).
Dehghanghadikolaei, A. & Fotovvati, B. Coating techniques for functional enhancement of metal implants for bone replacement: A review. Materials 12, 1795 (2019).
Goldmann, W. H. Biosensitive and antibacterial coatings on metallic material for medical applications. Cell. Biol. Int. 45, 1624–1632 (2021).
Ntrivala, M. A. et al. Polycaprolactone (PCL): the biodegradable polyester shaping the future of materials – a review on synthesis, properties, biodegradation, applications and future perspectives. Eur. Polym. J. 234, 114033 (2025).
Nasaj, M. et al. Factors influencing the antimicrobial mechanism of Chitosan action and its derivatives: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 277, 134321 (2024).
Popescu, A. M. et al. Corrosion behavior of NdFeB magnets in different aqueous solutions. J. Braz Chem. Soc. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20230089 (2024).
Bosworth, L. A. & Downes, S. Physicochemical characterisation of degrading Polycaprolactone scaffolds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 95, 2269–2276 (2010).
Ivanova, D. G. & Yaneva, Z. L. Antioxidant properties and Redox-Modulating activity of Chitosan and its derivatives: biomaterials with application in cancer therapy. BioResearch Open. Access. 9, 64–72 (2020).
Koenig, M. F. & Huang, S. J. Evaluation of crosslinked poly(caprolactone) as a biodegradable, hydrophobic coating. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 45, 139–144 (1994).
Verma, C. & Quraishi, M. A. Chelation capability of Chitosan and Chitosan derivatives: recent developments in sustainable corrosion Inhibition and metal decontamination applications. Curr. Res. Green. Sustain. Chem. 4, 100184 (2021).
Ahmed, F. M., Edgley, D. S. & Harris, I. R. Effect of Niobium addition on the Nd Fe B alloy and magnet. J. Alloys Compd. 209, 363–368 (1994).
Terpiłowska, S., Siwicka-Gieroba, D. & Siwicki, A. K. Cell viability in normal fibroblasts and liver cancer cells after treatment with iron (III), nickel (II), and their mixture. J. Vet. Res. 62, 535–542 (2018).
Boczkowska, A. & Awietj, S. Microstructure and properties of magnetorheological elastomers. in Advanced Elastomers - Technology, Properties and Applications (ed. Boczkowska, A.) (InTech, 2012). https://doi.org/10.5772/50430
Hyun, K., Kim, S. H., Ahn, K. H. & Lee, S. J. Large amplitude oscillatory shear as a way to classify the complex fluids. J. Non-Newton Fluid Mech. 107, 51–65 (2002).
Payne, A. R. The dynamic properties of carbon black-loaded natural rubber vulcanizates. Part I. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 6, 57–63 (1962).
Chazeau, L., Brown, J. D., Yanyo, L. C. & Sternstein, S. S. Modulus recovery kinetics and other insights into the Payne effect for filled elastomers. Polym. Compos. 21, 202–222 (2000).
Bokobza, L. Elastomer nanocomposites: Effect of filler–matrix and filler–filler interactions. Polymers 15, 2900 (2023).
Janmey, P. A., Fletcher, D. A. & Reinhart-King, C. A. Stiffness sensing by cells. Physiol. Rev. 100, 695–724 (2020).
Grau, L., Fleissner, P., Kobe, S. & Burkhardt, C. Processability and separability of commercial Anti-Corrosion coatings produced by in situ Hydrogen-Processing of magnetic scrap (HPMS) recycling of NdFeB. Materials 17, 2487 (2024).
Volynskii, A. L., Bazhenov, S. & Lebedeva, O. V. & Bakeev, N. F. Mechanical buckling instability of thin coatings deposited on soft polymer substrates.
Lu, N., Wang, X., Suo, Z. & Vlassak, J. Metal films on polymer substrates stretched beyond 50%. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 221909 (2007).
Huang, T. & Bobyr, M. A. Review of delamination damage of composite materials. J. Compos. Sci. 7, 468 (2023).
Mystkowska, J. et al. The effect of physiological incubation on the properties of elastic magnetic composites for soft biomedical sensors. Sensors 21, 7122 (2021).
Funding
This research was financed by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (Poland) under the Regional Excellence Initiative 2024–2027, grant title “Actively controlled elastic magnetic band for lymphatic drainage”, grant no MRID/WM/5/2024 (project manager: Assoc. Prof. Joanna Mystkowska), and by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (Poland) through the project “A system for rheological measurements and observation of biological samples in a magnetic field,” contract no. 7135/IA/SP/2020 (project manager: Prof. Robert Bucki).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: J.M., D.Ł., A.Cz., R.B., A.M.; methodology and investigation: J.M., D.Ł., A.Cz., E.P., P.D.; writing—original draft preparation: J.M., D.Ł., A.Cz.; writing—review and editing: J.M., D.Ł., A.Cz., E.P., P.D., R.B., D.P., J.A., A.M.; visualization, D.Ł., P.D., E.P.; supervision, project administration and funding acquisition: J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Mystkowska, J., Łysik, D., Czerniakiewicz, A. et al. Chitosan and polycaprolactone blended PDMS coatings improve biocompatibility of magnetic elastomers. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40085-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40085-6