Abstract
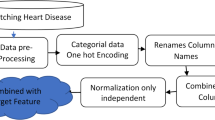
In real-time health monitoring systems, Wireless Body Area Networks (WBAN) are widely recognized for collecting various disease parameters using sensors. The collected data can be used for the early prediction of diseases. To address the growing need for accurate and efficient heart disease prediction, we introduce a novel hybrid approach that combines K-Means clustering with advanced regression techniques to analyze various factors in heart health monitoring. This integrated method utilizes the strengths of unsupervised and supervised learning to enhance predictive accuracy across both training and testing datasets. Our analysis focuses on 12 critical feature parameters, systematically clustered using K-Means to uncover inherent patterns and relationships. These parameters are then rigorously evaluated through multiple regression models to determine their predictive significance. By employing K-Means to assess parameter relevance within defined ranges, the proposed framework ensures robust feature selection and improved model interpretability. To validate its effectiveness, we benchmark our approach against widely used machine learning models, including Decision Tree Regression, K-Nearest Neighbor, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Kernel SVM, and others. The results demonstrate that our method not only outperforms traditional techniques but also offers a scalable and reliable solution for real-world healthcare applications. The prediction accuracy and false-prediction performance parameters were analyzed to compare the proposed method with existing heart disease prediction models. Earlier approaches reported accuracies up to 85%, with limited improvement in recall, specificity, and F1 score. In contrast, the newly proposed hybrid model–integrating Random Forest regression with K-Means clustering–achieved a significantly higher accuracy of 91%, along with improved recall (0.8864), specificity (0.9583), F1 score (0.8977), and ROC–AUC (0.9155). These quantitative performance gains, obtained without increasing model complexity, clearly demonstrate the superiority and robustness of the proposed approach over traditional prediction methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used in this study are publicly available and can be accessed through the below-given link/platform. University of California Irvine’s Machine Learning Repository at https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Heart+Disease.
References
Ciotti, M. et al. The covid-19 pandemic. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 57(6), 365–388 (2020).
Indrakumari, R., Poongodi, T. & Jena, S. R. Heart disease prediction using exploratory data analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 173, 130–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.06.017 (2020).
Ayub, K. & AlShawa, R. Revolutionizing healthcare with iomt and wban: A comprehensive analysis. In: 2025 6th International Conference on Bio-engineering for Smart Technologies (BioSMART), 1–4 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1109/biosmart66413.2025.11046147.
Tolani, M., Bajpai, A., Sunny, Singh, R.K., Wuttisittikulkij, L. & Kovintavewat, P. Energy efficient hybrid medium access control protocol for wireless sensor network. In: 2021 36th International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers and Communications (ITC-CSCC), 1–4. IEEE, ??? (2021).
Tolani, M., Sunny & Singh, R. K. Energy efficient adaptive bit-map-assisted medium access control protocol. Wireless Personal Communication 108(3), 1595–1610 (2019).
Boulis, A. Castalia: A Simulator for Wireless Sensor Networks and Body Area Networks. (2011). User’s manual version 3.2, NICTA.
Mohan, S., Thirumalai, C. & Srivastava, G. Effective heart disease prediction using hybrid machine learning techniques. IEEE Access 7, 81542–81554. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923707 (2019).
Rodriguez, M. Z. et al. Clustering algorithms: A comparative approach. PLoS One 14(1), 0210236. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210236 (2019).
Damarla, R. Heart Disease Prediction. Available: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/rishidamarla/heart-disease-prediction (2020).
Yuan, X., Chen, J., Zhang, K., Wu, Y. & Yang, T. A stable ai-based binary and multiple class heart disease prediction model for iomt. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 18(3), 2032–2040. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2021.3098306 (2022).
Fitriyani, N. L., Syafrudin, M., Alfian, G. & Rhee, J. Hdpm: An effective heart disease prediction model for a clinical decision support system. IEEE Access 8, 133034–133050. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010511 (2020).
Ordonez, C. Association rule discovery with the train and test approach for heart disease prediction. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 10(2), 334–343. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2006.864475 (2006).
Pan, Y., Fu, M., Cheng, B., Tao, X. & Guo, J. Enhanced deep learning assisted convolutional neural network for heart disease prediction on the internet of medical things platform. IEEE Access 8, 189503–189512. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3026214 (2020).
Rohan, D., Reddy, G. P., Kumar, Y. V. P., Prakash, K. P. & Reddy, C. P. An extensive experimental analysis for heart disease prediction using artificial intelligence techniques. Sci. Rep. 15, 6132. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-90530-1 (2025).
Indrakumari, R., Poongodi, T. & Jena, S. R. Heart disease prediction using exploratory data analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 173, 130–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.06.017 (2020).
Prakash, C.S., MadhuBala, M. & Rudra, A. Data science framework - heart disease predictions, variant models and visualizations. In: 2020 International Conference on Computer Science, Engineering and Applications (ICCSEA), 1–4. IEEE, ??? (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCSEA49143.2020.9132920.
Kavitha, M., Gnaneswar, G., Dinesh, R., Sai, Y.R. & Suraj, R.S. Heart disease prediction using hybrid machine learning model. In: 2021 6th International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), 1329–1333. IEEE, ??? (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICT50816.2021.9358597.
Lakshmanarao, A., Srisaila, A. & Kiran, T.S.R. Heart disease prediction using feature selection and ensemble learning techniques. In: 2021 Third International Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks (ICICV), 994–998. IEEE, ??? (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICV50876.2021.9388482.
Alim, M.A., Habib, S., Farooq, Y. & Rafay, A. Robust heart disease prediction: A novel approach based on significant feature and ensemble learning. In: 3rd International Conference on Computing Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET) (2020).
Ismaeel, S., Miri, A. & Chourishi, D. Using the extreme learning machine technique for heart disease. In: IEEE Canada International Humanitarian Technology Conference (IHTC) (2020).
Ahmed, R., Mahmud, S.M.H., Hossin, M.A., Jahan, H. & Noori, S.R.H. A cloud based four-tier architecture for early detection of heart disease with machine learning algorithms. In: 4th International Conference on Computer and Communications (2018).
Kapila, R. & Saleti, S. Federated learning-based disease prediction: A fusion approach with feature selection and extraction. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 100, 106961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2024.106961 (2025).
Khan, M. A. et al. Optimal feature selection for heart disease prediction using modified artificial bee colony (m-abc) and k-nearest neighbors (knn). Sci. Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-78021-1 (2024).
Gavhane, A., Kokkula, G., Pandya, P.I. & Devadkar, K. Prediction of heart disease using machine learning. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Electronics Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA 2018).
Atallah, R. & Al-Mousa, A. Heart disease detection using machine learning majority voting ensemble method. In: 2nd International Conference on New Trends in Computing Sciences (ICTCS) (2019).
Rajdhan, A., Agarwal, A. & Ghuli, P. Heart disease prediction using machine learning. International Journal Of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) 9(4), (2020).
Wijayaa, G.B.S. & Astuti, L.G. Analysis of the effect of hidden layer units on coronary heart prediction using the radial basis functions algorithm. JELIKU 9(2), (2020).
Mienye, I. D., Sun, Y. & Wang, Z. Improved sparse autoencoder based artificial neural network approach for prediction of heart disease. Inf. Med. Unlocked https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100307 (2020).
Balodi, A., Anand, R. S., Dewal, M. L. & Rawat, A. Severity analysis of mitral regurgitation using discrete wavelet transform. IETE J. Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2020.1814880 (2020).
Balodi, A., Anand, R. S., Dewal, M. L. & Rawat, A. Computer-aided classification of the mitral regurgitation using multiresolution local binary pattern. Neural Comput. Appl. 32(7), 2205–2215 (2020b).
Bajpai, A. & Balodi, A. Role of 6g networks: Use cases and research directions. In: IEEE Bangalore Humanitarian Technology Conference (B-HTC), 1–5 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/B-HTC50970.2020.9298017.
Repository, U.M.L. Heart Disease. Available: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Heart+Disease (2020).
Devi, A. & Raj, T.N. Plmpfs: Predictive learning with polynomial features and smotetomek balancing based heart disease prediction. In: 2025 6th International Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks (ICICV), 453–459 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1109/icicv64824.2025.11085773.
Vibha, M. B., Sneha, S. R., Kiran, U., & Kirana, Y. Exploratory data analysis of heart disease prediction using machine learning techniques-rs algorithm. In: 2024 Second International Conference on Intelligent Cyber Physical Systems and Internet of Things (ICoICI), Coimbatore, India, 209–216 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICoICI62503.2024.10696414.
Lakshmi, A. & Devi, R. Heart disease prediction using enhanced whale optimization algorithm based feature selection with machine learning techniques. In: 2023 12th International Conference on System Modeling & Advancement in Research Trends (SMART), Moradabad, India, 644–648 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/SMART59791.2023.10428617.
Allgaier, J. & Pryss, R. Cross-validation visualized: A narrative guide to advanced methods. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 6(2), 1378–1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/make6020065 (2024).
Smith, J. & Doe, J. Impact of high cholesterol on cardiovascular health. JAMA Cardiol. 7(4), 456–464. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2022.0912 (2022).
Doe, J. & Smith, J. St depression and its prognostic significance in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 75(10), 1234–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2022.01.045 (2022).
Zeid, S. et al. Heart rate variability: Reference values and role for clinical profile and mortality in individuals with heart failure. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 113, 1317–1330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-023-02248-7 (2024).
Acknowledgements
This data comes from the University of California Irvine’s Machine Learning Repository at https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Heart+Disease9,32
Funding
Open access funding provided by Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal. This research is not funded by any agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Manoj Tolani, Yazeed AlZahrani contributed to the conceptualization, methodology, coding, and writing of the original draft. Gaurav Suman, Arun Balodi is responsible for validation, formal analysis, and investigation. Ambar Bajpai, Pankaj Kumar handled the writing review and editing, as well as visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Tolani, M., AlZahrani, Y., Suman, G. et al. Clustering-cum-regression based model and performance analysis for early prediction of heart disease. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40626-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40626-z