Abstract
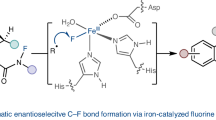
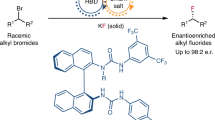
Despite increasing demand for chiral fluorinated organic molecules, enantioselective C–H fluorination remains among the most challenging and sought-after transformations in organic synthesis. Furthermore, utilizing nucleophilic sources of fluorine is especially desirable for 18F-radiolabelling. To date, methods for enantioselective nucleophilic fluorination of inert C(sp3)–H bonds remain unknown. Here we report our design and development of a palladium-based catalytic system bearing bifunctional monoprotected amino sulfonamide ligands which enabled highly regio- and enantioselective nucleophilic β-C(sp3)–H fluorination of synthetically important amides and lactams, commonly present in medicinal targets. The enantioenriched fluorinated products can be rapidly converted to corresponding chiral amines and ketones which are building blocks for a wide range of bioactive scaffolds. Mechanistic studies suggest that the C–F bond formation proceeds via outer-sphere reductive elimination with direct incorporation of fluoride, which was applied to late-stage 18F-radiolabelling of pharmaceutical derivatives using [18F]KF.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Crystallographic data for compound (S)-2b are available in the Supplementary Information files and from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre under deposition number CCDC 2211757. Copies of the data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/. Cartesian coordinates (Å) for the computed structures are provided in the xyz file. All other data are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Müller, K., Faeh, C. & Diederich, F. Fluorine in pharmaceuticals: looking beyond intuition. Science 317, 1881–1886 (2007).
Purser, S., Moore, P. R., Swallow, S. & Gouverneur, V. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 37, 320–330 (2008).
Gillis, E. P., Eastman, K. J., Hill, M. D., Donnelly, D. J. & Meanwell, N. A. Applications of fluorine in medicinal chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 58, 8315–8359 (2015).
Inoue, M., Sumii, Y. & Shibata, N. Contribution of organofluorine compounds to pharmaceuticals. ACS Omega 5, 10633–10640 (2020).
Wang, Q. et al. FDA approved fluorine-containing drugs in 2023. Chin. Chem. Lett. 35, 109780 (2024).
Britton, R. et al. Contemporary synthetic strategies in organofluorine chemistry. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 1, 47 (2021).
Caron, S. Where does the fluorine come from? A review on the challenges associated with the synthesis of organofluorine compounds. Org. Process Res. Dev. 24, 470–480 (2020).
Patel, C. et al. Fluorochemicals from fluorspar via a phosphate-enabled mechanochemical process that bypasses HF. Science 381, 302–306 (2023).
Khandelwal, M., Pemawat, G. & Kanwar Khangarot, R. Recent developments in nucleophilic fluorination with potassium fluoride (KF): a review. Asian J. Org. Chem. 11, e202200325 (2022).
Leibler, I. N. M., Gandhi, S. S., Tekle-Smith, M. A. & Doyle, A. G. Strategies for nucleophilic C(sp3)-(radio)fluorination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 9928–9950 (2023).
Ametamey, S. M., Honer, M. & Schubiger, P. A. Molecular imaging with PET. Chem. Rev. 108, 1501–1516 (2008).
Halder, R. & Ritter, T. 18F-Fluorination: challenge and opportunity for organic chemists. J. Org. Chem. 86, 13873–13884 (2021).
Wright, J. S., Sharninghausen, L. S., Lapsys, A., Sanford, M. S. & Scott, P. J. H. C–H labeling with [18F]fluoride: an emerging methodology in radiochemistry. ACS Cent. Sci. 10, 1674–1688 (2024).
Luu, T. G. & Kim, H.-K. Recent progress on radiofluorination using metals: strategies for generation of C–18F bonds. Org. Chem. Front. 10, 5746–5781 (2023).
Li, B., Xu, M., Feng, P. & Xu, S. Electrochemical construction of C–F bonds: recent advances and future perspectives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 27, e202400605 (2024).
Bui, T. T., Hong, W. P. & Kim, H. K. Recent advances in visible light-mediated mluorination. J. Fluor. Chem. 247, 109794 (2021).
Bui, T. T. & Kim, H. K. Recent advances in photo-mediated radiofluorination. Chem. Asian J. 16, 2155–2167 (2021).
Hollingworth, C. & Gouverneur, V. Transition metal catalysis and nucleophilic fluorination. Chem. Commun. 48, 2929–2942 (2012).
Campbell, M. G. & Ritter, T. Modern carbon–fluorine bond forming reactions for aryl fluoride synthesis. Chem. Rev. 115, 612–633 (2015).
Watson, D. A. et al. Formation of ArF from LPdAr(F): catalytic conversion of aryl triflates to aryl fluorides. Science 325, 1661–1664 (2009).
Pupo, G. et al. Asymmetric nucleophilic fluorination under hydrogen bonding phase-transfer catalysis. Science 360, 638–642 (2018).
Banik, S. M., Medley, J. W. & Jacobsen, E. N. Catalytic, asymmetric difluorination of alkenes to generate difluoromethylated stereocenters. Science 353, 51–54 (2016).
Molnár, I. G. & Gilmour, R. Catalytic difluorination of olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 5004–5007 (2016).
Wu, T., Yin, G. & Liu, G. Palladium-catalyzed intramolecular aminofluorination of unactivated alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 16354–16355 (2009).
Szpera, R., Moseley, D. F. J., Smith, L. B., Sterling, A. J. & Gouverneur, V. The fluorination of C–H bonds: developments and perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 14824–14848 (2019).
Chen, W. et al. Direct arene C–H fluorination with 18F− via organic photoredox catalysis. Science 364, 1170–1174 (2019).
Truong, T., Klimovica, K. & Daugulis, O. Copper-catalyzed, directing group-assisted fluorination of arene and heteroarene C–H bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 9342–9345 (2013).
Furuya, T. et al. Mechanism of C–F reductive elimination from palladium(IV) fluorides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 3793–3807 (2010).
McMurtrey, K. B., Racowski, J. M. & Sanford, M. S. Pd-catalyzed C–H fluorination with nucleophilic fluoride. Org. Lett. 14, 4094–4097 (2012).
Atkins, A. P., Dean, A. C. & Lennox, A. J. J. Benzylic C(sp3)–H fluorination. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 20, 1527–1547 (2024).
Braun, M. & Doyle, A. G. Palladium-catalyzed allylic C–H fluorination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 12990–12993 (2013).
Chatalova-Sazepin, C., Hemelaere, R., Paquin, J. F. & Sammis, G. M. Recent advances in radical fluorination. Synthesis 47, 2554–2569 (2015).
Liu, W. et al. Oxidative aliphatic C–H fluorination with fluoride ion catalyzed by a manganese porphyrin. Science 337, 1322–1325 (2012).
Liu, W. & Groves, J. T. Manganese-catalyzed oxidative benzylic C–H fluorination by fluoride ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 6024–6027 (2013).
Bafaluy, D., Georgieva, Z. & Muñiz, K. Iodine catalysis for C(sp3)–H fluorination with a nucleophilic fluorine source. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 14241–14245 (2020).
Leibler, I. N. M., Tekle-Smith, M. A. & Doyle, A. G. A general strategy for C(sp3)-H functionalization with nucleophiles using methyl radical as a hydrogen atom abstractor. Nat. Commun. 12, 6950 (2021).
Mal, S., Jurk, F., Hiesinger, K. & van Gemmeren, M. Pd-catalysed direct β-C(sp3)–H fluorination of aliphatic carboxylic acids. Nat. Synth. 3, 1292–1298 (2024).
Park, H., Verma, P., Hong, K. & Yu, J. Q. Controlling Pd(IV) reductive elimination pathways enables Pd(II)-catalysed enantioselective C(sp3)–H fluorination. Nat. Chem. 10, 755–762 (2018).
Zhu, R. Y. et al. Ligand-enabled stereoselective β-C(sp3)–H fluorination: synthesis of unnatural enantiopure anti-β-fluoro-α-amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 7067–7070 (2015).
Zhang, Q., Yin, X. S., Chen, K., Zhang, S. Q. & Shi, B. F. Stereoselective synthesis of chiral β-fluoro α-amino acids via Pd(II)-catalyzed fluorination of unactivated methylene C(sp3)–H bonds: scope and mechanistic studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 8219–8226 (2015).
Nagib, D. A. Catalytic desymmetrization by C–H functionalization as a solution to the chiral methyl problem. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 7354–7356 (2017).
Goodhue, C. T. & Schaeffer, J. R. Preparation of l (+)‐β‐hydroxyisobutyric acid by bacterial oxidation of isobutyric acid. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 13, 203–214 (1971).
Engle, K. M., Mei, T. S., Wang, X. & Yu, J. Q. Bystanding F+ oxidants enable selective reductive elimination from high-valent metal centers in catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 1478–1491 (2011).
Yuan, C., Wang, X. & Jiao, L. Ligand‐enabled palladium(II)‐catalyzed enantioselective β‐C(sp3)–H arylation of aliphatic tertiary amides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202300854 (2023).
Saint-Denis, T. G., Zhu, R.-Y., Chen, G., Wu, Q.-F. & Yu, J.-Q. Enantioselective C(sp3)‒H bond activation by chiral transition metal catalysts. Science 359, eaao4798 (2018).
Saint-Denis, T. G. et al. Mechanistic study of enantioselective Pd-catalyzed C(sp3)–H activation of thioethers involving two distinct stereomodels. ACS Catal. 11, 9738–9753 (2021).
Cheng, G. J. et al. A combined IM-MS/DFT study on [Pd(MPAA)]-catalyzed enantioselective C–H activation: relay of chirality through a rigid framework. Chem. Eur. J. 21, 11180–11188 (2015).
Thompson, S. et al. Synthesis of [18F]-γ-fluoro-α,β-unsaturated esters and ketones via vinylogous 18F-fluorination of α-diazoacetates with [18F]AgF. Synthesis 51, 4401–4407 (2019).
Donnelly, D. J. et al. Synthesis and biologic evaluation of a novel 18F-labeled adnectin as a PET radioligand for imaging PD-L1 expression. J. Nucl. Med. 59, 529–535 (2018).
Brandt, J. R., Lee, E., Boursalian, G. B. & Ritter, T. Mechanism of electrophilic fluorination with Pd(IV): fluoride capture and subsequent oxidative fluoride transfer. Chem. Sci. 5, 169–179 (2014).
Katcher, M. H., Norrby, P. O. & Doyle, A. G. Mechanistic investigations of palladium-catalyzed allylic fluorination. Organometallics 33, 2121–2133 (2014).
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge The Scripps Research Institute, the NIH (NIGMS, 2R01GM084019) and Bristol Myers Squibb for financial support. We thank D. Strassfeld and Y.-H. Li for proofreading and help with editing the manuscript. We thank T. Sheng and Y.-H. Li for help with spectral data analysis. We thank J. Lee, B. Sanchez, Q. N. Wong, J. Smith and J. Chen of the Scripps Research Automated Synthesis Facility for their assistance with SFC and LC-MS analysis and for help with compound purification. We thank M. Gembicky, J. Bailey and the University of California San Diego Crystallography Facility for X-ray crystallographic analysis and the Scripps Research High Performance Computing facility for computational resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.-Q.Y. conceived the concept. N.C. discovered and developed the enantioselective fluorination and L.-Y.L. discovered and developed the nucleophilic fluorination conditions. D.Q.P. designed MPASA ligands and prepared the corresponding library. D.J.D. performed radiochemistry studies. L.-Y.L. and N.C. developed the racemic fluorination substrate scope. N.C. developed the enantioselective fluorination substrate scope and product derivatization. Y.O. assisted with enantioselective fluorination scope development. N.C. performed mechanistic and computational studies. J.X.Q. and K.-S.Y. provided discussions and assistance in substrate screening. N.C. and J.-Q.Y. wrote the manuscript. J.-Q.Y. directed the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
N.C., D.Q.P., Y.O. and J.-Q.Y. are inventors on a patent application related to this work (USSN patent application 63/797,339) filed by The Scripps Research Institute. D.J.D., K.-S.Y. and J.X.Q. are employees of Bristol Myers Squibb. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Catalysis thanks Hee-Kwon Kim, Biplab Maji, Yun-Dong Wu and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Figs.1–34, Tables 1–31 and References.
Crystallographic Data 1
X-ray structure of 2b.
Computational Data 1
Cartesian coordinates of computed structures.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chekshin, N., Liu, LY., Phan, D.Q. et al. Enantioselective Pd-catalysed nucleophilic C(sp3)–H (radio)fluorination. Nat Catal 8, 678–687 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-025-01366-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-025-01366-x