Abstract
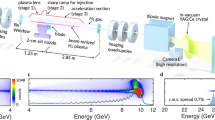
Laser wakefield acceleration can generate a femtosecond-scale broadband X-ray betatron radiation pulse from electrons accelerated by an intense laser pulse in a plasma. The micrometer-scale of the source makes wakefield betatron radiation well-suited for advanced imaging techniques, including diffraction and phase-contrast imaging. Recent progress in laser technology can expand these capabilities into the attosecond regime, where the practical applications would significantly benefit from the increased energy contained within the pulse. Here we use numerical simulations combined with batch Bayesian optimization to enhance the radiation produced by an attosecond betatron source. The method enables an efficient exploration of a multi-parameter space and identifies a regime in which a plasma density spike triggers the generation of a high-charge electron beam. This results in an improvement of more than one order of magnitude in the on-axis time-averaged power within the central time containing half of the radiated energy, compared to the reference case without the density spike.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
The FIKA code developed for this work is available on GitHub under the MIT License58.
References
McPherson, A. et al. Studies of multiphoton production of vacuum-ultraviolet radiation in the rare gases. J. Optical Soc. Am. B 4, 595–601 (1987).
Ferray, M. et al. Multiple-harmonic conversion of 1064 nm radiation in rare gases. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Optical Phys. 21, L31 (1988).
L’Huillier, A., Schafer, K. & Kulander, K. Higher-order harmonic generation in xenon at 1064 nm: the role of phase matching. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 2200 (1991).
Lewenstein, M., Balcou, P., Ivanov, M. Y., L’Huillier, A. & Corkum, P. B. Theory of high-harmonic generation by low-frequency laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 49, 2117 (1994).
Horný, V., Krus, M., Yan, W. & Fülöp, T. Attosecond betatron radiation pulse train. Sci. Rep. 10, 15074 (2020).
Ferri, J., Horný, V. & Fülöp, T. Generation of attosecond electron bunches and x-ray pulses from few-cycle femtosecond laser pulses. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 63, 045019 (2021).
Tajima, T. & Dawson, J. M. Laser electron accelerator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 43, 267 (1979).
Luttikhof, M., Khachatryan, A., Van Goor, F. & Boller, K.-J. Generating ultrarelativistic attosecond electron bunches with laser wakefield accelerators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 124801 (2010).
Tooley, M. et al. Towards attosecond high-energy electron bunches: controlling self-injection in laser-wakefield accelerators through plasma-density modulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 044801 (2017).
Zhao, Q. et al. Sub-femtosecond electron bunches in laser wakefield acceleration via injection suppression with a magnetic field. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 61, 085015 (2019).
Kim, J., Wang, T., Khudik, V. & Shvets, G. Subfemtosecond wakefield injector and accelerator based on an undulating plasma bubble controlled by a laser phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 164801 (2021).
Deng, A., Li, X., Luo, Z., Li, Y. & Zeng, J. Generation of attosecond micro bunched beam using ionization injection in laser wakefield acceleration. Opt. Express 31, 19958–19967 (2023).
Tomassini, P., Horny, V. & Doria, D. Attosecond pulses from ionization injection wakefield accelerators. Instruments 7, 34 (2023).
Sun, T., Zhao, Q., Wan, F., Salamin, Y. I. & Li, J.-X. Generation of ultrabrilliant polarized attosecond electron bunches via dual-wake injection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 045001 (2024).
Tomassini, P. et al. Ultra-high-brightness and tuneable attosecond-long electron beams with the laser wake field acceleration. Sci. Rep. 15, 40794 (2025).
Albert, F. & Thomas, A. G. Applications of laser wakefield accelerator-based light sources. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 58, 103001 (2016).
Nemeth, K. et al. Laser-driven coherent betatron oscillation in a laser-wakefield cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 095002 (2008).
Cipiccia, S. et al. Gamma-rays from harmonically resonant betatron oscillations in a plasma wake. Nat. Phys. 7, 867–871 (2011).
Kneip, S. et al. X-ray phase contrast imaging of biological specimens with femtosecond pulses of betatron radiation from a compact laser plasma wakefield accelerator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 093701 (2011).
Fourmaux, S., Hallin, E., Chaulagain, U., Weber, S. & Kieffer, J. Laser-based synchrotron X-ray radiation experimental scaling. Opt. Express 28, 3147–3158 (2020).
Cole, J. et al. Laser-wakefield accelerators as hard X-ray sources for 3D medical imaging of human bone. Sci. Rep. 5, 13244 (2015).
Hussein, A. E. et al. Laser-wakefield accelerators for high-resolution X-ray imaging of complex microstructures. Sci. Rep. 9, 3249 (2019).
Seres, E., Seres, J. & Spielmann, C. X-ray absorption spectroscopy in the keV range with laser-generated high harmonic radiation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 181919 (2006).
Yamada, S. et al. Broadband high-energy resolution hard X-ray spectroscopy using transition edge sensors at Spring-8. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 92, 013103 (2021).
Kiselev, S., Pukhov, A. & Kostyukov, I. X-ray generation in strongly nonlinear plasma waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 135004 (2004).
Rousse, A. et al. Production of a keV X-Ray beam from synchrotron radiation in relativistic laser-plasma interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 135005 (2004).
Corde, S. et al. Femtosecond X rays from laser-plasma accelerators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 1–48 (2013).
Huang, K. et al. Resonantly enhanced betatron hard x-rays from ionization injected electrons in a laser plasma accelerator. Sci. Rep. 6, 27633 (2016).
Mangles, S. P. et al. Laser-wakefield acceleration of monoenergetic electron beams in the first plasma-wave period. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 215001 (2006).
Chen, L. et al. Bright betatron X-ray radiation from a laser-driven-clustering gas target. Sci. Rep. 3, 1912 (2013).
Mangles, S. et al. Controlling the spectrum of x-rays generated in a laser-plasma accelerator by tailoring the laser wavefront. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl/article/95/18/181106/131664/Controlling-the-spectrum-of-x-rays-generated-in-a (2009).
Popp, A. et al. All-optical steering of laser-wakefield-accelerated electron beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 215001 (2010).
Wood, J. et al. Enhanced betatron radiation from a laser wakefield accelerator in a long focal length geometry. Gas 1, 2 (2017).
Yan, W. et al. Concurrence of monoenergetic electron beams and bright X-rays from an evolving laser-plasma bubble. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, 5825–5830 (2014).
Zhang, Z. et al. Enhanced x-rays from resonant betatron oscillations in laser wakefield with external wigglers. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 58, 105009 (2016).
Ho, Y.-C. et al. Induction of electron injection and betatron oscillation in a plasma-waveguide-based laser wakefield accelerator by modification of waveguide structure. Phys. Plasmas 20, 083104 (2013).
Wallin, E., Gonoskov, A. & Marklund, M. Radiation emission from braided electrons in interacting wakefields. Phys. Plasmas 24, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4997440 (2017).
Shaw, J. et al. Role of direct laser acceleration in energy gained by electrons in a laser wakefield accelerator with ionization injection. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 56, 084006 (2014).
Zhao, T. et al. High-flux femtosecond x-ray emission from controlled generation of annular electron beams in a laser wakefield accelerator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 094801 (2016).
Ferri, J. & Davoine, X. Enhancement of betatron X rays through asymmetric laser wakefield generated in transverse density gradients. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 21, 091302 (2018).
Ma, Y. et al. Angular streaking of betatron X-rays in a transverse density gradient laser-wakefield accelerator. Phys. Plasmas 25, https://pubs.aip.org/aip/pop/article/25/11/113105/263228/Angular-streaking-of-betatron-X-rays-in-a (2018).
Ta Phuoc, K. et al. Betatron radiation from density-tailored plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 15, https://pubs.aip.org/aip/pop/article/15/6/063102/923579/Betatron-radiation-from-density-tailored-plasmas (2008).
Guo, B. et al. Enhancement of laser-driven betatron x-rays by a density-depressed plasma structure. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 61, 035003 (2019).
Ferri, J. et al. High-brilliance betatron γ-ray source powered by laser-accelerated electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 254802 (2018).
Döpp, A. et al. Energy boost in laser wakefield accelerators using sharp density transitions. Phys. Plasmas 23, https://pubs.aip.org/aip/pop/article/23/5/056702/966617/Energy-boost-in-laser-wakefield-accelerators-using (2016).
Shalloo, R. et al. Automation and control of laser wakefield accelerators using Bayesian optimization. Nat. Commun. 11, 6355 (2020).
Jalas, S. et al. Bayesian optimization of a laser-plasma accelerator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 104801 (2021).
Jalas, S. et al. Tuning curves for a laser-plasma accelerator. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 26, 071302 (2023).
Irshad, F. et al. Pareto optimization and tuning of a laser wakefield accelerator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 085001 (2024).
Ferran Pousa, A. et al. Bayesian optimization of laser-plasma accelerators assisted by reduced physical models. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 26, 084601 (2023).
Irshad, F., Karsch, S. & Döpp, A. Multi-objective and multi-fidelity Bayesian optimization of laser-plasma acceleration. Phys. Rev. Res. 5, 013063 (2023).
Zhong, J. et al. Simulation of laser plasma wakefield acceleration with external injection based on Bayesian optimization. Plasma Sci. Technol. http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2058-6272/ad91e8 (2024).
Valenta, P., Esirkepov, T. Z., Ludwig, J. D., Wilks, S. C. & Bulanov, S. V. Bayesian optimization of electron energy from laser wakefield accelerator. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 28, 094601 (2025).
Ye, H. et al. Fast optimization for betatron radiation from laser wakefield acceleration based on Bayesian optimization. Results Phys. 43, 106116 (2022).
Bulanov, S., Naumova, N., Pegoraro, F. & Sakai, J. Particle injection into the wave acceleration phase due to nonlinear wake wave breaking. Phys. Rev. E 58, R5257 (1998).
Lu, W. et al. Generating multi-GeV electron bunches using single stage laser wakefield acceleration in a 3D nonlinear regime. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top. Accel. Beams 10, 061301 (2007).
Derouillat, J. et al. Smilei: A collaborative, open-source, multi-purpose particle-in-cell code for plasma simulation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 222, 351–373 (2018).
Maslarova, D. & Hansson, A. chalmersplasmatheory/fika: Version 1.0 https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15350881 (2025).
Lehe, R., Lifschitz, A., Thaury, C., Malka, V. & Davoine, X. Numerical growth of emittance in simulations of laser-wakefield acceleration. Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams 16, 021301 (2013).
Vay, J.-L., Geddes, C., Cormier-Michel, E. & Grote, D. Numerical methods for instability mitigation in the modeling of laser wakefield accelerators in a Lorentz-boosted frame. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 5908–5929 (2011).
Horný, V. et al. Temporal profile of betatron radiation from laser-driven electron accelerators. Phys. Plasmas 24, 063107 (2017).
Pausch, R. et al. Quantitatively consistent computation of coherent and incoherent radiation in particle-in-cell codes-a general form factor formalism for macro-particles. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 909, 419–422 (2018).
Močkus, J. On Bayesian methods for seeking the extremum. In Proc. Optimization Techniques IFIP Technical Conference Novosibirsk, July 1–7, 1974, Vol. 6, 400–404, https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/3-540-07165-2_55 (Springer, 1975).
Jones, D. R., Schonlau, M. & Welch, W. J. Efficient global optimization of expensive black-box functions. J. Glob. Optim. 13, 455–492 (1998).
Ginsbourger, D., Le Riche, R. & Carraro, L. Kriging is well-suited to parallelize optimization. In Computational Intelligence in Expensive Optimization Problems, 131–162, https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-10701-6_6 (Springer, 2010).
SecondMind Labs. Batch Bayesian optimization. https://secondmind-labs.github.io/trieste/4.2.2/notebooks/batch_optimization.html (2024).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Patrik Jansson and Ida Ekmark from Chalmers University of Technology, Miroslav Krus from the Institute of Plasma Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Sarah Newton from UKAEA and David Gregocki from CNR—Istituto Nazionale di Ottica for fruitful discussions. This project received funding from the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation (Grants Nos. KAW 2020.0111 and 2023.0249). The computations were enabled by resources provided by the National Academic Infrastructure for Supercomputing in Sweden (NAISS), partially funded by the Swedish Research Council through grant agreement No. 2022-06725, and by EuroHPC Joint Undertaking through access to Karolina at IT4Innovations (VŠB-TU), Czechia under project numberEHPC-REG-2025R01-007, together with Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic through the e-INFRA CZ (ID:90140). V.H. draws support from the European Union, the Romanian Government and the Health Program, within the project SMIS Code: 326475, and the Romanian Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitalization: Program Nucleu PN23210105.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Chalmers University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.M., J.F. and I.P. conceived the main idea with inputs from V.H. and M.L. D.M., A.H., and M.L. designed the numerical simulations. D.M. and A.H. conducted the numerical simulations and analyzed the results. D.M., T.F. and I.P. wrote the manuscript with inputs from V.H. and M.L.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Physics thanks Davorin Peceli and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Maslarova, D., Hansson, A., Luo, M. et al. Batch Bayesian optimization of attosecond betatron pulses from laser wakefield acceleration. Commun Phys (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-026-02542-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-026-02542-6