Abstract
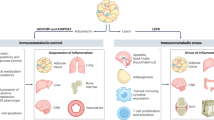
Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is a classical, pleiotropic pro-inflammatory cytokine. It is also the first ‘adipokine’ described to be produced from adipose tissue, regulated in obesity and proposed to contribute to obesity-associated metabolic disease. In this review, we provide an overview of TNF in the context of metabolic inflammation or metaflammation, its discovery as a metabolic messenger, its sites and mechanisms of action and some critical considerations for future research. Although we focus on TNF and the studies that elucidated its immunometabolic actions, we highlight a conceptual framework, generated by these studies, that is equally applicable to the complex network of pro-inflammatory signals, their biological activity and their integration with metabolic regulation, and to the field of immunometabolism more broadly.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathis, D. & Shoelson, S. E. Immunometabolism: an emerging frontier. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 81–83 (2011).
Padmanabha, D. & Baker, K. D. Drosophila gains traction as a repurposed tool to investigate metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 25, 518–527 (2014).
Mattila, J. & Hietakangas, V. Regulation of carbohydrate energy metabolism in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 207, 1231–1253 (2017).
Hotamisligil, G. S. Foundations of immunometabolism and implications for metabolic health and disease. Immunity 47, 406–420 (2017).
Agrawal, N. et al. The Drosophila TNF Eiger is an adipokine that acts on insulin-producing cells to mediate nutrient response. Cell Metab. 23, 675–684 (2016).
Fève, B. & Bastard, J. P. The role of interleukins in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 5, 305–311 (2009).
Tack, C. J., Stienstra, R., Joosten, L. A. & Netea, M. G. Inflammation links excess fat to insulin resistance: the role of the interleukin-1 family. Immunol. Rev. 249, 239–252 (2012).
Donath, M. Y. Targeting inflammation in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: time to start. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13, 465–476 (2014).
Hotamisligil, G. S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 542, 177–185 (2017).
Libert, C. Cytokine anniversary: TNF trailblazers five centuries apart. Nature 523, 158 (2015).
Tracey, K. J. & Cerami, A. Metabolic responses to cachectin/TNF. A brief review. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 587, 325–331 (1990).
Pennica, D. et al. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature 312, 724–729 (1984).
Beutler, B. et al. Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature 316, 552–554 (1985).
Ruddle, N. H. Lymphotoxin and TNF: how it all began—a tribute to the travelers. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 25, 83–89 (2014).
Hellman, B. Studies in obese-hyperglycemic mice. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 131, 541–558 (1965).
Hausberger, F. X. Pathological changes in adipose tissue of obese mice. Anat. Rec. 154, 651–660 (1966).
Pekala, P., Kawakami, M., Vine, W., Lane, M. D. & Cerami, A. Studies of insulin resistance in adipocytes induced by macrophage mediator. J. Exp. Med. 157, 1360–1365 (1983).
Mahoney, J. R. Jr et al. Lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW 264.7 cells produce a mediator that inhibits lipoprotein lipase in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Immunol. 134, 1673–1675 (1985).
Hotamisligil, G. S., Shargill, N. S. & Spiegelman, B. M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259, 87–91 (1993).
Bordon, Y. TNF short-circuits the insulin receptor. Nature Milestones: Diabetes, 12. https://www.nature.com/articles/d42859-021-00015-0 (2021).
Kern, P. A. et al. The expression of tumor necrosis factor in human adipose tissue. Regulation by obesity, weight loss, and relationship to lipoprotein lipase. J. Clin. Invest. 95, 2111–2119 (1995).
Saghizadeh, M., Ong, J. M., Garvey, W. T., Henry, R. R. & Kern, P. A. The expression of TNF alpha by human muscle. Relationship to insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 97, 1111–1116 (1996).
Hube, F. & Hauner, H. The role of TNF-alpha in human adipose tissue: prevention of weight gain at the expense of insulin resistance? Horm. Metab. Res. 31, 626–631 (1999).
Mohamed-Ali, V. et al. Production of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors by human subcutaneous adipose tissue in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. 277, E971–E975 (1999).
Lasselin, J. et al. Adipose inflammation in obesity: relationship with circulating levels of inflammatory markers and association with surgery-induced weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99, E53–E61 (2014).
Liu, C. et al. Adiponectin, TNF-α and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 86, 100–109 (2016).
Sookoian, S. C., González, C. & Pirola, C. J. Meta-analysis on the G-308A tumor necrosis factor alpha gene variant and phenotypes associated with the metabolic syndrome. Obes. Res. 13, 2122–2131 (2005).
Van der Poll, T. et al. Tumor necrosis factor mimics the metabolic response to acute infection in healthy humans. Am. J. Physiol. 261, E457–E465 (1991).
Plomgaard, P. et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces skeletal muscle insulin resistance in healthy human subjects via inhibition of Akt substrate 160 phosphorylation. Diabetes 54, 2939–2945 (2005).
Plomgaard, P., Fischer, C. P., Ibfelt, T., Pedersen, B. K. & van Hall, G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates human in vivo lipolysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 543–549 (2008).
Feingold, K. R. et al. Effect of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) on lipid metabolism in the diabetic rat. Evidence that inhibition of adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase activity is not required for TNF-induced hyperlipidemia. J. Clin. Invest. 83, 1116–1121 (1989).
Ling, P. R., Bistrian, B. R., Mendez, B. & Istfan, N. W. Effects of systemic infusions of endotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-1 on glucose metabolism in the rat: relationship to endogenous glucose production and peripheral tissue glucose uptake. Metabolism 43, 279–284 (1994).
Miles, P. D. et al. TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance in vivo and its prevention by troglitazone. Diabetes 46, 1678–1683 (1997).
Uysal, K. T., Wiesbrock, S. M., Marino, M. W. & Hotamisligil, G. S. Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-α function. Nature 389, 610–614 (1997).
Ventre, J. et al. Targeted disruption of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene: metabolic consequences in obese and nonobese mice. Diabetes 46, 1526–1531 (1997).
Uysal, K. T., Wiesbrock, S. M. & Hotamisligil, G. S. Functional analysis of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors in TNF-alpha-mediated insulin resistance in genetic obesity. Endocrinology 139, 4832–4838 (1998).
da Costa, R. M. et al. TNF-α induces vascular insulin resistance via positive modulation of PTEN and decreased Akt/eNOS/NO signaling in high fat diet-fed mice. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 15, 119 (2016).
Borst, S. E. & Bagby, G. J. Neutralization of tumor necrosis factor reverses age-induced impairment of insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscle of Sprague-Dawley rats. Metabolism 51, 1061–1064 (2002).
Liang, H. et al. Blockade of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type 1-mediated TNF-alpha signaling protected Wistar rats from diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Endocrinology 149, 2943–2951 (2008).
McKellar, G. E., McCarey, D. W., Sattar, N. & McInnes, I. B. Role for TNF in atherosclerosis? Lessons from autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 6, 410–417 (2009).
Salomon, B. L. Insights into the biology and therapeutic implications of TNF and regulatory T cells. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 17, 487–504 (2021).
Crespo, J. et al. Gene expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha and TNF-receptors, p55 and p75, in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Hepatology 34, 1158–1163 (2001).
Kugelmas, M., Hill, D. B., Vivian, B., Marsano, L. & McClain, C. J. Cytokines and NASH: a pilot study of the effects of lifestyle modification and vitamin E. Hepatology 38, 413–419 (2003).
Henao-Mejia, J. et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 482, 179–185 (2012).
Divella, R. et al. Synergism of adipocytokine profile and ADIPOQ/TNF-α polymorphisms in NAFLD-associated MetS predict colorectal liver metastases outgrowth. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 16, 519–530 (2019).
Park, E. J. et al. Dietary and genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell 140, 197–208 (2010).
Nakagawa, H. et al. ER stress cooperates with hypernutrition to trigger TNF-dependent spontaneous HCC development. Cancer Cell 26, 331–343 (2014).
Tomita, K. et al. Tumour necrosis factor alpha signalling through activation of Kupffer cells plays an essential role in liver fibrosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Gut 55, 415–424 (2006).
Bluemel, S., Wang, Y., Lee, S. & Schnabl, B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 1 deficiency in hepatocytes does not protect from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, but attenuates insulin resistance in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 26, 4933–4944 (2020).
Wandrer, F. et al. TNF-Receptor-1 inhibition reduces liver steatosis, hepatocellular injury and fibrosis in NAFLD mice. Cell Death Dis. 11, 212 (2020).
Verhoeven, F. et al. Safety of TNF inhibitors in rheumatic disease in case of NAFLD and cirrhosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 50, 544–548 (2020).
Tang, K. T., Dufour, J. F., Chen, P. H., Hernaez, R. & Hutfless, S. Antitumour necrosis factor-α agents and development of new-onset cirrhosis or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a retrospective cohort. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 7, e000349 (2020).
Ohta, H. et al. Disruption of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene diminishes the development of atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis 180, 11–17 (2005).
Avgerinou, G. et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor α treatment with adalimumab improves significantly endothelial function and decreases inflammatory process in patients with chronic psoriasis. Int. J. Cardiol. 151, 382–383 (2011).
Tam, L. S., Kitas, G. D. & González-Gay, M. A. Can suppression of inflammation by anti-TNF prevent progression of subclinical atherosclerosis in inflammatory arthritis? Rheumatology (Oxford) 53, 1108–1119 (2014).
Spinelli, F. R. et al. Decrease of asymmetric dimethyl arginine after anti-TNF therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Dev. Res. 75, S67–S69 (2014).
Francisco, V. et al. Adipokines: linking metabolic syndrome, the immune system, and arthritic diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 165, 196–206 (2019).
Everett, B. M. et al. Inhibition of Interleukin-1β and reduction in atherothrombotic cardiovascular events in the CANTOS trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 76, 1660–1670 (2020).
Nguyen, J. C., Killcross, A. S. & Jenkins, T. A. Obesity and cognitive decline: role of inflammation and vascular changes. Front. Neurosci. 8, 375 (2014).
Pugazhenthi, S., Qin, L. & Reddy, P. H. Common neurodegenerative pathways in obesity, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Basis Dis. 1037–1045, 2017 (1863).
Bomfim, T. R. et al. An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease–associated Aβ oligomers. J. Clin. Invest. 122, 1339–1353 (2012).
Ferreira, S. T., Clarke, J. R. & Bomfim, T. R. & De Felice, F. G. Inflammation, defective insulin signaling, and neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 10, S76–S83 (2014).
de la Monte, S. M. & Wands, J. R. Alzheimer’s disease is type 3 diabetes-evidence reviewed. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2, 1101–1113 (2008).
Aggarwal, B. B. et al. in Cytokines as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Inflammatory Skin Diseases (Ernst Schering Research Foundation Workshops, vol. 56) (eds. Numerof, R., Dinarello, C. A. & Asadullah, K.) 161–186 (Springer, 2006).
Sethi, G., Sung, B. & Aggarwal, B. B. TNF: a master switch for inflammation to cancer. Front. Biosci. 13, 5094–5107 (2008).
Lou, J., Lucas, R. & Grau, G. E. Pathogenesis of cerebral malaria: recent experimental data and possible applications for humans. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 14, 810–820 (2001).
Jacobs, M. et al. Tumor necrosis factor is critical to control tuberculosis infection. Microbes Infect. 9, 623–628 (2007).
Del Valle, D. M. et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 26, 1636–1643 (2020).
Robinson, P. C., Richards, D., Tanner, H. L. & Feldmann, M. Accumulating evidence suggests anti-TNF therapy needs to be given trial priority in COVID-19 treatment. Lancet Rheumatol 2, e653–e655 (2020).
Feldmann, M. et al. Trials of anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy for COVID-19 are urgently needed. Lancet 395, 1407–1409 (2020).
Mahase, E. Covid-19: anti-TNF drug adalimumab to be trialled for patients in the community. Br. Med. J. 371, m3847 (2020).
Sethi, J. K. & Hotamisligil, G. S. The role of TNF alpha in adipocyte metabolism. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 19–29 (1999).
Cawthorn, W. P. & Sethi, J. K. TNF-alpha and adipocyte biology. FEBS Lett. 582, 117–131 (2008).
Sethi, J. K. & Vidal-Puig, A. J. Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue function and plasticity orchestrate nutritional adaptation. J. Lipid Res. 48, 1253–1262 (2007).
Cawthorn, W. P., Heyd, F., Hegyi, K. & Sethi, J. K. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibits adipogenesis via a beta-catenin/TCF4(TCF7L2)-dependent pathway. Cell Death Differ. 14, 1361–1373 (2007).
Voloshyna, I. et al. Infliximab reverses suppression of cholesterol efflux proteins by TNF-α: a possible mechanism for modulation of atherogenesis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 312647 (2014).
Yanai, H. et al. The underlying mechanisms for development of hypertension in the metabolic syndrome. Nutr. J. 7, 10 (2008).
Fong, Y. et al. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J. Exp. Med. 170, 1627–1633 (1989).
Falvo, J. V., Tsytsykova, A. V. & Goldfeld, A. E. Transcriptional control of the TNF gene. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 11, 27–60 (2010).
Anderson, P. Post-transcriptional regulation of tumour necrosis factor alpha production. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 59, i3–i5 (2000).
Stamou, P. & Kontoyiannis, D. L. Posttranscriptional regulation of TNF mRNA: a paradigm of signal-dependent mRNA utilization and its relevance to pathology. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 11, 61–79 (2010).
Mazumder, B., Li, X. & Barik, S. Translation control: a multifaceted regulator of inflammatory response. J. Immunol. 184, 3311–3319 (2010).
Liu, J., Qian, C. & Cao, X. Post-translational modification control of innate immunity. Immunity 45, 15–30 (2016).
Xu, H., Sethi, J. K. & Hotamisligil, G. S. Transmembrane tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibits adipocyte differentiation by selectively activating TNF receptor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 26287–26295 (1999).
Xu, H., Uysal, K. T., Becherer, J. D., Arner, P. & Hotamisligil, G. S. Altered tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) processing in adipocytes and increased expression of transmembrane TNF-alpha in obesity. Diabetes 51, 1876–1883 (2002).
Black, R. A. et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature 385, 729–733 (1997).
Serino, M. et al. Mice heterozygous for tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme are protected from obesity-induced insulin resistance and diabetes. Diabetes 56, 2541–2546 (2007).
Medler, J. & Wajant, H. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-2 (TNFR2): an overview of an emerging drug target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 23, 295–307 (2019).
Tartaglia, L. A., Pennica, D. & Goeddel, D. V. Ligand passing: the 75-kDa tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor recruits TNF for signaling by the 55-kDa TNF receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 18542–18548 (1993).
Hotamisligil, G. S., Arner, P., Atkinson, R. L. & Spiegelman, B. M. Differential regulation of the p80 tumor necrosis factor receptor in human obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 46, 451–455 (1997).
Rönnemaa, T., Pulkki, K. & Kaprio, J. Serum soluble tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor 2 is elevated in obesity but is not related to insulin sensitivity: a study in identical twins discordant for obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 2728–2732 (2000).
Good, M. et al. TNF and TNF receptor expression and insulin sensitivity in human omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue—influence of BMI and adipose distribution. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 3, 26–33 (2006).
Kohno, T. et al. A second tumor necrosis factor receptor gene product can shed a naturally occurring tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 8331–8335 (1990).
Aderka, D., Engelmann, H., Maor, Y., Brakebusch, C. & Wallach, D. Stabilization of the bioactivity of tumor necrosis factor by its soluble receptors. J. Exp. Med. 175, 323–329 (1992).
Peraldi, P., Hotamisligil, G. S., Buurman, W. A., White, M. F. & Spiegelman, B. M. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibits insulin signaling through stimulation of the p55 TNF receptor and activation of sphingomyelinase. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 13018–13022 (1996).
Sethi, J. K. et al. Characterisation of receptor-specific TNFalpha functions in adipocyte cell lines lacking type 1 and 2 TNF receptors. FEBS Lett. 469, 77–82 (2000).
Martins, L. B. et al. Paradoxical role of tumor necrosis factor on metabolic dysfunction and adipose tissue expansion in mice. Nutrition 50, 1–7 (2018).
Sethi, J. K., Xu, H. Y. & Hotamisligil, G. S. Roles of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and receptor 2 in insulin receptor signaling. Diabetes 48, A219–A219 (1999).
Aquilano, K. et al. Adipocyte metabolism is improved by TNF receptor-targeting small RNAs identified from dried nuts. Commun. Biol. 2, 317 (2019).
Liu, L. S., Spelleken, M., Röhrig, K., Hauner, H. & Eckel, J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha acutely inhibits insulin signaling in human adipocytes: implication of the p80 tumor necrosis factor receptor. Diabetes 47, 515–522 (1998).
Wu, S., Dong, K., Wang, J. & Bi, Y. Tumor necrosis factor alpha improves glucose homeostasis in diabetic mice independent with tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and tumor necrosis factor receptor 2. Endocr. J. 65, 601–609 (2018).
Wajant, H. & Siegmund, D. TNFR1 and TNFR2 in the control of the life and death balance of macrophages. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 7, 91 (2019).
Karunakaran, D. et al. RIPK1 gene variants associate with obesity in humans and can be therapeutically silenced to reduce obesity in mice. Nat. Metab. 2, 1113–1125 (2020).
Sabio, G. & Davis, R. J. TNF and MAP kinase signalling pathways. Semin. Immunol. 26, 237–245 (2014).
Leiva, M., Matesanz, N., Pulgarín-Alfaro, M., Nikolic, I. & Sabio, G. Uncovering the role of p38 family members in adipose tissue physiology. Front. Endocrinol. 11, 572089 (2020).
Hirosumi, J. et al. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420, 333–336 (2002).
Tuncman, G. et al. Functional in vivo interactions between JNK1 and JNK2 isoforms in obesity and insulin resistance. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 10741–10746 (2006).
Waeber, G. et al. The gene MAPK8IP1, encoding islet-brain-1, is a candidate for type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 24, 291–295 (2000).
Weston, C. R. & Davis, R. J. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19, 142–149 (2007).
Hotamisligil, G. S. & Davis, R. J. Cell signaling and stress responses. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 8, a006072 (2016).
Hotamisligil, G. S. et al. IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-alpha- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Science 271, 665–670 (1996).
Kanety, H., Feinstein, R., Papa, M. Z., Hemi, R. & Karasik, A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Possible mechanism for suppression of insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 23780–23784 (1995).
Aguirre, V. et al. Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 1531–1537 (2002).
Copps, K. D. & White, M. F. Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2. Diabetologia 55, 2565–2582 (2012).
Gao, Z. et al. Serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by inhibitor kappa B kinase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 48115–48121 (2002).
Austin, R. L., Rune, A., Bouzakri, K., Zierath, J. R. & Krook, A. siRNA-mediated reduction of inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB kinase prevents tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in human skeletal muscle. Diabetes 57, 2066–2073 (2008).
Jiang, S. & Messina, J. L. Role of inhibitory κB kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase in the development of hepatic insulin resistance in critical illness diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 301, G454–G463 (2011).
Li, Y. et al. Protein kinase C Theta inhibits insulin signaling by phosphorylating IRS1 at Ser(1101). J. Biol. Chem. 279, 45304–45307 (2004).
Kim, J. K. et al. PKC-theta knockout mice are protected from fat-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 114, 823–827 (2004).
Nawaratne, R. et al. Regulation of insulin receptor substrate 1 pleckstrin homology domain by protein kinase C: role of serine 24 phosphorylation. Mol. Endocrinol. 20, 1838–1852 (2006).
De Fea, K. & Roth, R. A. Modulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 tyrosine phosphorylation and function by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 31400–31406 (1997).
Engelman, J. A., Berg, A. H., Lewis, R. Y., Lisanti, M. P. & Scherer, P. E. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated insulin resistance, but not dedifferentiation, is abrogated by MEK1/2 inhibitors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Endocrinol. 14, 1557–1569 (2000).
Bouzakri, K. & Zierath, J. R. MAP4K4 gene silencing in human skeletal muscle prevents tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 7783–7789 (2007).
Danai, L. V. et al. Inducible deletion of protein kinase Map4k4 in obese mice improves insulin sensitivity in liver and adipose tissues. Mol. Cell. Biol. 35, 2356–2365 (2015).
Chiang, S. H. et al. The protein kinase IKKepsilon regulates energy balance in obese mice. Cell 138, 961–975 (2009).
Patel, M. N. et al. Hematopoietic IKBKE limits the chronicity of inflammasome priming and metaflammation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 506–511 (2015).
Guney, E. et al. Aberrant Ca2+ homeostasis in adipocytes links inflammation to metabolic dysregulation in obesity. Preprint in bioRxiv at https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.28.360008 (2020).
Illario, M. et al. Calcium-calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) mediates insulin-stimulated proliferation and glucose uptake. Cell. Signal. 21, 786–792 (2009).
Shungin, D. et al. New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution. Nature 518, 187–196 (2015).
Mao, L., Fang, Y., Campbell, M. & Southerland, W. M. Population differentiation in allele frequencies of obesity-associated SNPs. BMC Genomics 18, 861 (2017).
Wiegmann, K., Schütze, S., Machleidt, T., Witte, D. & Krönke, M. Functional dichotomy of neutral and acidic sphingomyelinases in tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell 78, 1005–1015 (1994).
Aerts, J. M. et al. Pharmacological inhibition of glucosylceramide synthase enhances insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 56, 1341–1349 (2007).
Petersen, M. C. & Shulman, G. I. Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 98, 2133–2223 (2018).
Sethi, J. K. & Vidal-Puig, A. Wnt signalling and the control of cellular metabolism. Biochem. J. 427, 1–17 (2010).
Lagathu, C. et al. Dact1, a nutritionally regulated preadipocyte gene, controls adipogenesis by coordinating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling network. Diabetes 58, 609–619 (2009).
Lagathu, C. et al. Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 regulates adipose tissue expansion and is dysregulated in severe obesity. Int. J. Obes. 34, 1695–1705 (2010).
Isakson, P., Hammarstedt, A., Gustafson, B. & Smith, U. Impaired preadipocyte differentiation in human abdominal obesity: role of Wnt, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and inflammation. Diabetes 58, 1550–1557 (2009).
Gustafson, B. et al. Inflammation and impaired adipogenesis in hypertrophic obesity in man. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 297, E999–E1003 (2009).
Roubert, A. et al. The influence of tumor necrosis factor-α on the tumorigenic Wnt-signaling pathway in human mammary tissue from obese women. Oncotarget 8, 36127–36136 (2017).
Guo, C. et al. Genetic ablation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha attenuates the promoted colonic Wnt signaling in high fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 77, 108302 (2020).
Verjee, L. S. et al. Unraveling the signaling pathways promoting fibrosis in Dupuytren’s disease reveals TNF as a therapeutic target. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, E928–E937 (2013).
Ruan, H., Hacohen, N., Golub, T. R., Van Parijs, L. & Lodish, H. F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppresses adipocyte-specific genes and activates expression of preadipocyte genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: nuclear factor-kappaB activation by TNF-alpha is obligatory. Diabetes 51, 1319–1336 (2002).
Bhatnagar, S. et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α regulates distinct molecular pathways and gene networks in cultured skeletal muscle cells. PLoS One 5, e13262 (2010).
Cheshire, J. L. & Baldwin, A. S. Jr. Synergistic activation of NF-kappaB by tumor necrosis factor alpha and gamma interferon via enhanced I kappaB alpha degradation and de novo I kappaBbeta degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 6746–6754 (1997).
Wright, H. L., Thomas, H. B., Moots, R. J. & Edwards, S. W. RNA-seq reveals activation of both common and cytokine-specific pathways following neutrophil priming. PLoS One 8, e58598 (2013).
McGeough, M. D. et al. TNF regulates transcription of NLRP3 inflammasome components and inflammatory molecules in cryopyrinopathies. J. Clin. Invest. 127, 4488–4497 (2017).
Peraldi, P., Xu, M. & Spiegelman, B. M. Thiazolidinediones block tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced inhibition of insulin signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 1863–1869 (1997).
Cerami, A. TNF and EPO: major players in the innate immune response: their discovery. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, i55–i59 (2012).
Moreira, A. L. et al. Thalidomide exerts its inhibitory action on tumor necrosis factor alpha by enhancing mRNA degradation. J. Exp. Med. 177, 1675–1680 (1993).
Kruys, V., Marinx, O., Shaw, G., Deschamps, J. & Huez, G. Translational blockade imposed by cytokine-derived UA-rich sequences. Science 245, 852–855 (1989).
Belarbi, K. et al. TNF-α protein synthesis inhibitor restores neuronal function and reverses cognitive deficits induced by chronic neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflammation 9, 23 (2012).
Wong, E. et al. Harnessing the natural inhibitory domain to control TNFα converting enzyme (TACE) activity in vivo. Sci Rep. 6, 35598 (2016).
Cui, X. et al. Trivalent soluble TNF receptor, a potent TNF-α antagonist for the treatment collagen-induced arthritis. Sci Rep. 8, 7327 (2018).
Shepard, H. M., Phillips, G. L., D Thanos, C. & Feldmann, M. Developments in therapy with monoclonal antibodies and related proteins. Clin. Med. (Lond.) 17, 220–232 (2017).
Acknowledgements
J.K.S. is funded by the Welcome Trust (grant number 206453/Z/17/Z) and the UK National Institute for Health Research Southampton Biomedical Research Centre. G.S.H. is funded by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (grant numbers DK123458 and HL125753), the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation and Lab1636.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Metabolism thanks Mark Febbraio and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editors: George Caputa; Ashley Castellanos-Jankiewicz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sethi, J.K., Hotamisligil, G.S. Metabolic Messengers: tumour necrosis factor. Nat Metab 3, 1302–1312 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-021-00470-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-021-00470-z
This article is cited by
-
Bridging the tumor microenvironment: the pivotal role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor cachexia development
Molecular Cancer (2025)
-
Astaxanthin prevents postovulatory oocyte aging by targeting TNFR2 and inhibiting the TNF signaling pathway
BMC Biology (2025)
-
Incretin-based approaches for type 2 diabetes therapy: effects on circulating cytokines and adipocyte’s secretome
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2025)
-
Compositional analysis of coffee containing javamide I/II and investigation of health effects in rats fed a high fat diet
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
From fat to filter: the effect of adipose tissue-derived signals on kidney function
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2025)