Abstract
Objectives:
This review analyzed efficacy, tolerability and safety of oral antimuscarinic (AM) drugs in adults suffering from neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO).
Methods:
A comprehensive search of major literature bases was conducted to identify all references.
Results:
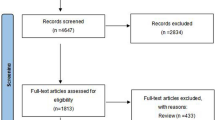
Thirty studies, thereof 16 randomized controlled trials (RCT), enrolling 1479 patients were identified and included in the review. Results were grouped in dose-finding, placebo- and active-controlled, flexible dose and combined high-dose AM drugs, and various studies. Key urodynamic outcome parameters, such as maximum detrusor pressure and maximum cystometric bladder capacity, demonstrated the efficacy of AM in NDO, following 2–3 weeks of treatment. Contrary to idiopathic detrusor overactivity (IDO), no placebo effects manifested. Other important parameters, such as impact on the upper urinary tract function and morphology, issues of continence, post-void residual urine, catheterisation, urinary tract infections and quality of life, were investigated to a limited extent only. Incidence rates of adverse events were comparable for NDO and IDO. Most of the studies, especially RCT, were undertaken with oxybutynin immediate release (IR), trospium chloride IR, propiverine IR and propiverine extended release. In NDO, these drugs are best investigated.
Conclusions:
AM drugs are effective in NDO, they normalize the intravesical pressure and increase cystometric bladder capacity. However, other important parameters are not adequately investigated so far and should be recognized in future studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Chapple C, Khullar V, Gabriel Z, Muston D, Bitoun CE, Weinstein D . The effects of antimuscarinic tretaments in overactive bladder: An update of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol 2008; 54: 543–562.
Novara G, Galfano A, Ficarra V, Artibani W . Anticholinergic drugs in patients with bladder outlet obstruction and lower urinary tract symptoms: a systematic review. Eur Urol 2006; 50: 675–683.
Kaplan SA, Roehrborn CG, Abrams P, Chapple CR, Bavendam T, Guan Z . Antimuscarinics for treatment of storage lower urinary tract symptoms in men: a systematic review. Int J Clin Pract 2011; 65: 487–507.
Stöhrer M, Blok B, Castro-Diaz D, Chartier-Kastler E, Del Popolo G, Kramer G et al. EAU guidelines on neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction. Eur Urol 2009; 56: 81–88.
Madhuvrata P, Hasafa Z, Singh M, Abdel-Fattah M . Anticholinergic drugs for adult neurogenic detrusor overactivity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol 2012; 62: 816–830.
Bycroft J, Leaker B, Wood S, Knight S, Shah G, Craggs M . The effect of darifenacin on neurogenic detrusor overactivity in patients with spinal cord injury. Annual meeting of the International Continence Society, Florence, Italy, 2003. Neurourol Urodyn 2003; 22: A190.
Kennelly MJ, Lemack GE, Foote JE, Trop CS . Efficacy and safety of oxybutynin transdermal system in spinal cord injury patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity and incontinence: an open-label, dose-titration study. Urology 2009; 74: 741–745.
Pannek J, Sommerfeld HJ, Bötel U, Senge T . Combined intravesical and oral oxybutynin chloride in adult patients with spinal cord injury. Urology 2000; 55: 358–362.
Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine Levels of evidence (May 2011). Produced by Bob Philips, Dave Sackett, Doug Badenoch, Sharon Straus, Brian Haynes, Martin Dawessince November 1998.
Mazur D, Göcking K, Wehnert J, Schubert G, Herfurth G, Alken RG . Clinical and urodynamic effects of oral propiverine therapy in neurogenic urinary incontinence: a multicentre dose-optimizing study. Urologe A 1994; 33: 447–452.
Van Kerrebroeck P, Amarenco G, Thüroff J, Madersbacher HG, Lock MT, Messelink EJ et al. Dose-ranging study of tolterodine in patients with detrusor hyperreflexia. Neurourol Urodyn 1998; 17: 499–512.
Stöhrer M, Bersch U, Göcking K, Schurch B, Kramer G . Dose finding study for treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia by trospium chloride. Presented at: Annual Meeting of the International Medical Society of Paraplegia. Iguassu, Brazil 1998.
Stöhrer M, Frohneberg D, Loechner-Ernst D, Sauter P, Mandaika B . Oxybutynin in the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia in patients with spinal cord injury: A multicentre randomised double-blind study. Presented at: Annual Meeting of the American Spinal Cord Injury Association. Orlando, USA 1990.
Stöhrer M, Madersbacher H, Richter R, Wehnert J, Dreikorn K . Efficacy and safety of propiverine in SCI-patients suffering from detrusor hyperreflexia—a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Spinal Cord 1999; 37: 196–200.
Stöhrer M, Bauer P, Giannetti BM et al. Effect of trospium chloride on urodynamic parameters in patients with detrusor hyperreflexia due to spinal cord injuries. A multicentre placebo-controlled double-blind trial. Urol Int 1991; 47: 138–143.
Ethans KD, Nance PW, Bard RJ, Casey AR, Schryvers OI . Efficacy and safety of tolterodine in people with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. J Spinal Cord Med 2004; 27: 214–218.
Amarenco G, Sutory M, Fagertun H, Wright M, Compion G, DeRidder D . Solifenacin is effective and well tolerated in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Preliminary results from the SONIC urodynamic study. Eur Urol, Suppl 2012; 11: e467.
Gajewski JB, Awad SA . Oxybutynin versus propantheline in patients with multiple sclerosis and detrusor hyperreflexia. J Urol 1986; 135: 966–968.
Madersbacher H, Stöhrer M, Richter R, Burgdörfer H, Hachen HJ, Mürtz G . Trospium chloride versus oxybuynin: a randomized, double-blind, multicentre trial in the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia. Brit J Urol 1995; 75: 452–456.
Stöhrer M, Mürtz G, Kramer G, Schnabel F, Arnold EP, Wyndaele JJ., Propiverine Study Group. Propiverine compared to oxybutynin in neurogenic detrusor overactivity—results of a randomized, double blind, multicenter clinical study. Eur Urol 2007; 51: 235–242.
Stöhrer M, Mürtz G, Kramer G, Warnack W, Primus G, Jinga V et al. Efficacy and tolerability of propiverine hydrochloride extended release compared to immediate release in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Spinal Cord 2013; 51: 209–213.
Bennett N, O’Leary M, Patel AS, Xavier M, Erickson JR, Chancellor MB . Can higher doses of oxybutynin improve efficacy in neurogenic bladder? J Urol 2004; 171: 749–751.
O‘Leary M, Erickson JR, Smith CP, McDermott C, Horton J, Chancellor MB . Effect of controlled-release oxybutynin on neurogenic bladder function in spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 2003; 26: 159–162.
Menarini M, Del Popolo G, Benedetto D, Haselmann J, Bödeker RH, Schwantes U et al. Trospium chloride in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: Is dose titration of benefit to the patients? Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2006; 44: 623–632.
Persu C, Gaevlete PA . Double dose of solifenacin for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Eur Urol, Suppl 2012; 11: e469.
Horstmann M, Schaefer T, Aguilar Y, Stenzl A, Sievert KD . Neurogenic bladder treatment by doubling the recommended antimuscarinic dosage. Neurourol Urodyn 2006; 25: 441–445.
Amend B, Hennenlotter J, Schaefer T, Horstmann M, Stenzl A, Sievert KD . Effective treatment of neurogenic detrusor dysfunction by combined high-dosed antimuscarinics without increased side-effects. Eur Urol 2008; 53: 1021–1028.
Cameron AP, Clemens JQ, Latini JM, McGuire EJ . Combination drug therapy improves compliance of the neurogenic bladder. J Urol 2009; 182: 1062–1067.
Madersbacher M, Stöhrer M, Richter R, Giannetti BM, Mürtz G . High-dose administration of trospium chloride in the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia. Urologe 1991; 30: 260–263.
Geirsson G, Schoefield D, Haughie S, Steihdotsdottir S, Hardardottir A, Glue P et al. Assessment of time to onset: the effect of single oral dose of tolterodine on neurogenic detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injury patients. Presented at: Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society 2006 (Abstract 309).
Yamanishi T, Mizuro T, Yoshida K, Uchiyama T, Sakakibara R . Efficacy of tolterodine ER for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity or low compliance bladder—assessment by urodynamic study. Presented at: Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society 2009 (Abstract 330).
Carl S, Laschke S . Darifenacin is also effective in neurogenic bladder dysfunction (multiple sclerosis). Urology 2006; 68 (Suppl): 250.
Spinelli M, Citari M, Zanollo L et al. Solifenacin in neurogenic overactive bladder. Eur Urol Suppl 2007; 6: 273.
van Rey F, Heesakkers J . Solifenacin in multiple sclerosis patients with overactive bladder: a prospective study. Adv Urol 2011; 2011: 834753.
Mazur D, Göcking K, Wehnert J, Dorschner W, Schubert G, HerFurth G et al. Verträglichkeit und Wirksamkeit einer Langzeittherapie mit Propiverinhydrochlorid bei neurogener Hatrninkontinenz. Eine multizentrische Studie. Kontinenz 1994; 2: 74–78.
Proietti S, Lepri E, Lepri L, Lolli C, Gubbiotti M, Giannantoni A . Efficacy and tolerability of fesoterodine fumarate in the treatment of overactive bladder symptoms in patients affected by multiple sclerosis: Long term follow up. Eur Urol, Suppl 2012; 11: e468.
Tan YK, Toh KL . Tolterodine improves the compliance and cystometric capacity of adult neurogenic bladders secondary to spinal cord injury. Presented at: Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society 2009 (Abstract 331).
Digesu GA, Khullar V, Cardozo L, Salvatore S . Overactive bladder symptoms: do we need urodynamics? Neurourol Urodyn 2003; 22: 105–108.
McGuire EJ, Woodside JR, Borden TA, Weiss RM . Prognostic value of urodynamic testing in myelodysplastic patients. J Urol 1981; 126: 205–209.
Kessler TM, Bachmann LM, Minder C, Löhrer D, Umbehr M, Schünemann HJ et al. Adverse event assessment of antimuscarinics for treating overactive bladder: A network meta-analytic apoproach. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16718.
Uchiyama T, Sakakibara R, Liu Z et al. The effects of anticholinergic drugs on cognitive impairment, mental dysfunction and motor dysfunction in patients with neurological disease. 35thAnnual Meeting of the ICS, 28 August-2 September 2005 Montreal, Canada. Conference Proceedings.
Wyndaele JJ, Gammie A, Bruschini H, De Wachter S, Fry CH, Jabr RI et al. Bladder compliance what does it represent: Can we measure it, and is it clinically relevant? Neurourol Urodyn 2011; 30: 714–722.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Guus Kramer and Saladin Alloussi for valuable contributions to the manuscript, and to Florian Schirm, Datamap Freiburg, Germany, for advise given with respect to statistical issues.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Helmut Madersbacher is a member of the advisory board of Allergan/Switzerland, Apogepha/Germany, Astellas/Austria, and a scientific advisor of Pohl-Boskamp/Germany. He received lecture honoraria from Allergan/Switzerland, Apogepha/Germany, Astellas/Austria, Dr Pfleger/Germany and Rottapharm-Madaus/Germany. Gerd Mürtz is a scientific advisor of Apogepha/Germany. Manfred Stöhrer received lecture honoraria from Allergan/Germany and Apogepha/Germany. He is a scientific advisor of Farco/Germany.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Spinal Cord website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madersbacher, H., Mürtz, G. & Stöhrer, M. Neurogenic detrusor overactivity in adults: a review on efficacy, tolerability and safety of oral antimuscarinics. Spinal Cord 51, 432–441 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2013.19
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2013.19
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Sex differences in urological management during spinal cord injury rehabilitation: results from a prospective multicenter longitudinal cohort study
Spinal Cord (2023)
-
Stem Cell Therapy in Spinal Cord Injury-Induced Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2023)
-
Non-pharmacological and drug treatment of autonomic dysfunction in multiple system atrophy: current status and future directions
Journal of Neurology (2023)
-
Efficacy, according to urodynamics, of OnabotulinumtoxinA compared with antimuscarinic drugs, for neurogenic detrusor overactivity: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Efficacy and safety of mirabegron for treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in adults with spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis: a systematic review
Spinal Cord (2022)