Abstract
Study design:
A cross-sectional analysis.
Objective:
To examine whether intramedullary stress is related to the appearance of symptoms in cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM).
Setting:
Japan.
Methods:
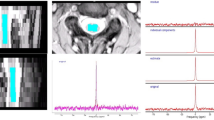
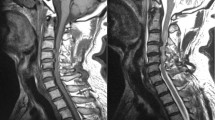
Thirty-three consecutive patients with CSM and 30 consecutive patients without CSM were enrolled. A total of 99 disc levels from C3 to C6 in 33 patients with CSM were divided into two groups: 33 disc levels with high signal intensity (HSI) on T2-weighted magnetic resonance image (HSI group) and 66 disc levels without HSI (Non-HSI group). Ninety disc levels from C3 to C6 in patients without CSM were set up in a control group. Intramedullary stress value at each level was analyzed using the finite element method. Stress was compared among the three groups. A cutoff value of stress to present HSI was investigated from receiver operator characteristics (ROC) curve.
Results:
In all the patients with CSM, the disc level with HSI presented the highest stress among the three disc levels evaluated. The stress was 3.16±0.86 kPa (mean±s.d.) in the HSI group, 1.81±0.72 kPa in the Non-HSI group and 1.01±0.37 kPa in the control group. The stress differed significantly among the three groups (P<0.0001). The qualified cutoff value derived from the ROC curve was 2.30 kPa (sensitivity 78.8%, specificity 91.9%). None of the disc levels in the control group exceeded 2.30 kPa.
Conclusion:
HSI was strongly associated with intramedullary stress. Threshold of intramedullary stress to present HSI that related closely to the symptoms of myelopathy was revealed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Teresi LM, Lufkin RB, Reicher MA, Moffit BJ, Vinuela FV, Wilson GM et al. Asymptomatic degenerative disk disease and spondylosis of the cervical spine: MR imaging. Radiology 1987; 164: 83–88.
Matsumoto M, Fujimura Y, Suzuki N, Nishi Y, Nakamura M, Yabe Y et al. MRI of cervical intervertebral discs in asymptomatic subjects. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1998; 80: 19–24.
Breig A, Turnbull I, Hassler O . Effects of mechanical stresses on the spinal cord in cervical spondylosis. A study on fresh cadaver material. J Neurosurg 1966; 25: 45–56.
Penning L, van der Zwaag P . Biomechanical aspects of spondylotic myelopathy. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1966; 5: 1090–1103.
Hinck VC, Sachdev NS . Developmental stenosis of the cervical spinal canal. Brain 1966; 89: 27–36.
Turnbull IM . Microvasculature of the human spinal cord. J Neurosurg 1971; 35: 141–147.
Bunge RP, Puckett WR, Becerra JL, Marcillo A, Quencer RM . Observations on the pathology of human spinal cord injury. A review and classification of 22 new cases with details from a case of chronic cord compression with extensive focal demyelination. Adv Neurol 1993; 59: 75–89.
Ozawa H, Wu ZJ, Tanaka Y, Kokubun S . Morphologic change and astrocyte response to unilateral spinal cord compression in rabbits. J Neurotrauma 2004; 21: 944–955.
Scifert J, Totoribe K, Goel V, Huntzinger J . Spinal cord mechanics during flexion and extension of the cervical spine: a finite element study. Pain Physician 2002; 5: 394–400.
Ichihara K, Taguchi T, Sakuramoto I, Kawano S, Kawai S . Mechanism of the spinal cord injury and the cervical spondylotic myelopathy: new approach based on the mechanical features of the spinal cord white and gray matter. J Neurosurg 2003; 99: 278–285.
Kato Y, Kanchiku T, Imajo Y, Kimura K, Ichihara K, Kawano S et al. Biomechanical study of the effect of degree of static compression of the spinal cord in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg Spine 2010; 12: 301–305.
Ozawa H, Sato T, Hyodo H, Ishii Y, Morozumi N, Koizumi Y et al. Clinical significance of intramedullary Gd-DTPA enhancement in cervical myelopathy. Spinal Cord 2010; 48: 415–422.
Ohshio I, Hatayama A, Kaneda K, Takahara M, Nagashima K . Correlation between histopathologic features and magnetic resonance images of spinal cord lesions. Spine 1993; 18: 1140–1149.
Ozawa H, Matsumoto T, Ohashi T, Sato M, Kokubun S . Comparison of spinal cord gray matter and white matter softness: measurement by pipette aspiration method. J Neurosurg 2001; 95: 221–224.
Mattei TA, Goulart CR, Milano JB, Dutra LP, Fasset DR . Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and surgical techniques. ISRN Neurol 2011; 2011: 463729.
Sparrey CJ, Manley GT, Keaveny TM . Effects of white, grey, and pia mater properties on tissue level stresses and strains in the compressed spinal cord. J Neurotrauma 2009; 26: 585–595.
Matsumoto M, Ishikawa M, Ishii K, Nishizawa T, Maruiwa H, Nakamura M et al. Usefulness of neurological examination for diagnosis of the affected level in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy: prospective comparative study with radiological evaluation. J Neurosurg Spine 2005; 2: 535–539.
Seichi A, Takeshita K, Kawaguchi H, Matsudaira K, Higashikawa A, Ogata N et al. Neurologic level diagnosis of cervical stenotic myelopathy. Spine 2006; 31: 1338–1343.
Suda K, Abumi K, Ito M, Shono Y, Kaneda K, Fujiya M . Local kyphosis reduces surgical outcomes of expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine 2003; 28: 1258–1262.
Machino M, Yukawa Y, Ito K, Nakashima H, Kato F . Dynamic changes in dural sac and spinal cord cross-sectional area in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy: cervical spine. Spine 2011; 36: 399–403.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, K., Ozawa, H., Sakamoto, N. et al. Influence of intramedullary stress on cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spinal Cord 51, 761–764 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2013.94
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2013.94
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Spinal Cord Stress After Anterior Cervical Diskectomy and Fusion: Results from a Patient-Specific Finite Element Model
Annals of Biomedical Engineering (2023)
-
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion may be more effective than anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015)