Volume 14
-
No. 12 December 2017
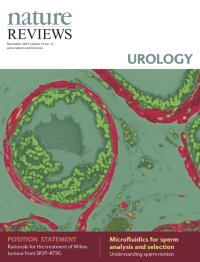
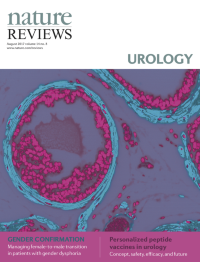
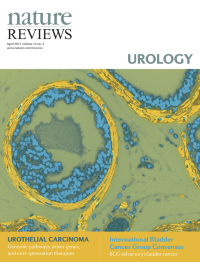
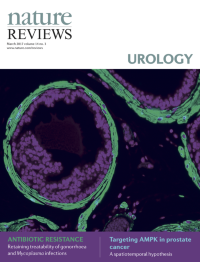
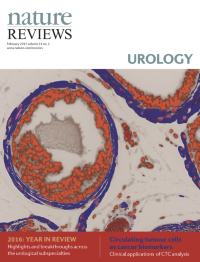
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 11 November 2017
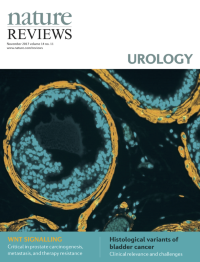
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 10 October 2017
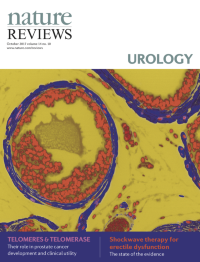
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 9 September 2017
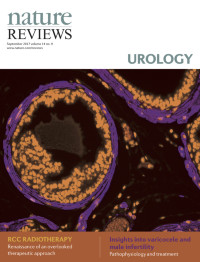
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 8 August 2017
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 7 July 2017
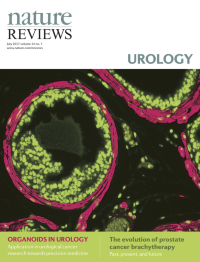
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 6 June 2017
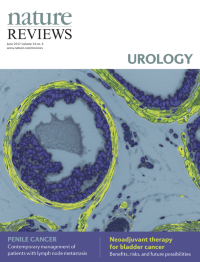
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 5 May 2017
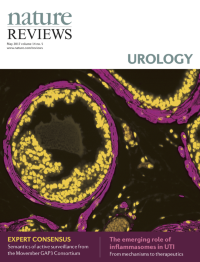
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 4 April 2017
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 3 March 2017
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 2 February 2017
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows a high-power fluorescence microscopy view of a FVB/N mouse prostate. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to stain nuclei and monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin to identify smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, tapering at each end with a centrally located nucleus. They encircle the basal epithelial, luminal epithelial, and neuroendocrine cells of each prostate gland. In prostate adenocarcinoma, breaks appear in the perimeter of circumferential smooth muscle cells; this discontinuity is a marker of invasion.
-
No. 1 January 2017
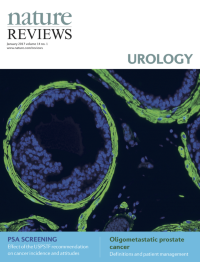
Cover image supplied by Sudeh Izadmehr, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA. The image shows stained prostate tissue, with smooth muscle cells surrounding luminal epithelial prostate cells. The image was taken using fluorescence microscopy of mouse prostate glands stained for á-smooth muscle actin and with DAPI staining of nuclei.