Abstract
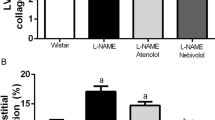
The aim of this double-blind, parallel group study was to compare the effects of nebivolol and atenolol on blood pressure (BP) and insulin sensitivity in hypertensive patients with type II, non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). After a 4-week run-in period on placebo, 30 patients (14 males and 16 females) aged 43 to 69 years, with stable NIDDM and mild to moderate hypertension (DBP ⩾95 and <116 mm hg) were randomised to receive either nebivolol 5 mg or atenolol 50 mg, both administered once daily for 6 months. at the end of the placebo and the active treatment periods, supine and standing bp was measured, 24-h urinary c-peptide, hba1c, plasma glucose and lipid levels were evaluated and an euglycaemic hyperinsulinaemic clamp was performed to evaluate insulin sensitivity: glucose infusion rate during the last 60 min of clamp and total glucose requirements were evaluated. Nebivolol 5 mg once daily was of an equivalent efficacy as atenolol 50 mg once daily at reducing supine and standing systolic and diastolic BP values. Neither β-blocker adversely affected carbohydrate metabolism in terms of insulin sensitivity, whole body glucose utilization, HbA1c and 24-h urinary C-peptide excretion. No significant changes in cholesterol (total, high density and low density lipoprotein) and triglycerides plasma levels were observed with both β-blockers. These findings indicate that, in hypertensive patients with NIDDM, ie, in subjects who have established insulin resistance, treatment with nebivolol and atenolol neither further deteriorated insulin sensitivity nor adversely affected the lipid profile.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fogari, R., Zoppi, A., Lazzari, P. et al. Comparative effects of nebivolol and atenolol on blood pressure and insulin sensitivity in hypertensive subjects with type II diabetes. J Hum Hypertens 11, 753–757 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000533
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000533
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic Properties of Highly Selective β-blockers With or Without Additional Vasodilator Properties: Focus on Bisoprolol and Nebivolol in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy (2022)
-
Differential Metabolic Effects of Beta-Blockers: an Updated Systematic Review of Nebivolol
Current Hypertension Reports (2017)
-
The Role of Beta-Blockers as First-Line Therapy in Hypertension
Current Atherosclerosis Reports (2011)
-
Adding nebivolol to ongoing antihypertensive therapy improves blood pressure and response rates in patients with uncontrolled stage I–II hypertension
Journal of Human Hypertension (2010)
-
The vasodilatory beta-blockers
Current Hypertension Reports (2007)