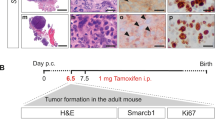
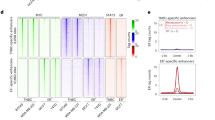
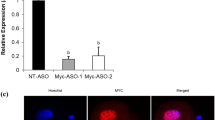
Abstract
The growth arrest and DNA damage inducible (gadd) genes are induced by various genotoxic and non-genotoxic stresses such as serum starvation, ultraviolet irradiation and treatment with alkylating agents. Their coordinate induction is a growth arrest signal which may play an important role in the response of cells to DNA damage. Conversely, c-myc is a strong proliferative signal, and overexpression of Myc is frequently observed in cancer cells. We have found that ectopic expression of v-myc in RAT-1 cells results in an attenuated induction of the three major gadd transcripts by methyl methanesulfonate (MMS), and almost completely blocks the response to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Myc acts in part by reducing the stress-responsiveness of the gadd45 promoter, as a c-myc expression vector strongly suppressed activation of gadd45-reporter constructs. This activity of Myc localizes to a recently described GC-rich binding site within the gadd45 promoter. These results indicate that a coordinate down-regulation of the gadd gene response is one mechanism by which Myc can circumvent growth arrest and contribute to the neoplastic phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amundson, S., Zhan, Q., Penn, L. et al. Myc suppresses induction of the growth arrest genes gadd34, gadd45, and gadd153 by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene 17, 2149–2154 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202136
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202136
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MYC: a multipurpose oncogene with prognostic and therapeutic implications in blood malignancies
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
Elucidation of a novel phenformin derivative on glucose-deprived stress responses in HT-29 cells
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2016)
-
Hes-1 SUMOylation by protein inhibitor of activated STAT1 enhances the suppressing effect of Hes-1 on GADD45α expression to increase cell survival
Journal of Biomedical Science (2014)
-
SIRT1 activation enhances HDAC inhibition-mediated upregulation of GADD45G by repressing the binding of NF-κB/STAT3 complex to its promoter in malignant lymphoid cells
Cell Death & Disease (2013)
-
Genome-wide mapping of Myc binding and gene regulation in serum-stimulated fibroblasts
Oncogene (2012)