Abstract
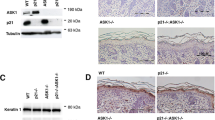
ped/pea-15 is a cytosolic protein performing a broad antiapoptotic function. We show that, upon DMBA/TPA-induced skin carcinogenesis, transgenic mice overexpressing ped/pea-15 (Tgped/pea-15) display early development of papillomas and a four-fold increase in papilloma number compared to the nontransgenic littermates (P<0.001). The malignant conversion frequency was 24% for the Tgped/pea-15 mice and only 5% in controls (P<0.01). The isolated application of TPA, but not that of DMBA, was sufficient to reversibly upregulate ped/pea-15 in both untransformed skin and cultured keratinocytes. ped/pea-15 protein levels were also increased in DMBA/TPA-induced papillomas of both Tgped/pea-15 and control mice. Isolated TPA applications induced Caspase-3 activation and apoptosis in nontransformed mouse epidermal tissues. The induction of both Caspase-3 and apoptosis by TPA were four-fold inhibited in the skin of the Tgped/pea-15 compared to the nontransgenic mice, accompanied by a similarly sized reduction in TPA-induced JNK and p38 stimulation and by constitutive induction of cytoplasmic ERK activity in the transgenics. ped/pea-15 expression was stably increased in cell lines from DMBA/TPA-induced skin papillomas and carcinomas, paralleled by protection from TPA apoptosis. In the A5 spindle carcinoma cell line, antisense inhibition of ped/pea-15 expression simultaneously rescued sensitivity to TPA-induced Caspase-3 function and apoptosis. The antisense also reduced A5 cell ability to grow in semisolid media by 65% (P<0.001) and increased by three-fold tumor latency time (P<0.01). Thus, the expression levels of ped/pea-15 control Caspase-3 function and epidermal cell apoptosis in vivo and determine susceptibility to skin tumor development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo H, Danziger N, Cordier J, Glowinski J and Chneiweiss H . (1993). J. Biol. Chem., 268, 5911–5920.
Baldi A, Santini D, Russo P, Catricala C, Amantea A, Picardo M, Tatangelo F, Botti G, Dragonetti E, Murace R, Tonini G, Natali PG, Baldi F and Paggi MG . (2004). Exp. Dermatol., 13, 93–97.
Balmain A and Harris CC . (2000). Carcinogenesis, 21, 371–377.
Burns FJ, Vanderlaan M, Snyder E and Albert RE . (1978). Carcinogenesis, Mechanisms of Tumour Promotion and Co-Carcinogenesis Slaga TJ and Boutwell RK (eds). Raven Press, Ltd: New York.
Calle EE and Kaaks R . (2004). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 4, 579–591.
Condorelli G, Trencia A, Vigliotta G, Perfetti A, Goglia U, Cassese A, Musti AM, Miele C, Santopietro S, Formisano P and Beguinot F . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 11013–11018.
Condorelli G, Vigliotta G, Iavarone C, Caruso M, Tocchetti CG, Andreozzi F, Cafieri A, Tecce MF, Formisano P, Beguinot L and Beguinot F . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 3858–3865.
Condorelli G, Vigliotta G, Cafieri A, Trencia A, Andalo P, Oriente F, Miele C, Caruso M, Formisano P and Beguinot F . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 4409–4415.
Debatin KM and Krammer PH . (2004). Oncogene, 23, 2950–2966.
Dong G, Loukinova E, Chen Z, Gangi L, Chanturita TI, Liu ET and Van Waes C . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 4797–4808.
Formstecher E, Ramos JW, Fauquet M, Calderwood DA, Hsieh JC, Canton B, Nguyen XT, Barnier JV, Camonis J, Ginsberg MH and Chneiweiss H . (2001). Dev. Cell., 2, 239–250.
Gaumont-Leclerc MF, Mukhopadhyay UK, Goumard S and Ferbeyre G . (2004). J. Biol. Chem., 279, 46802–46809.
Hao C, Beguinot F, Condorelli G, Trencia A, Van Meir EG, Yong VW, Parney IF, Roa WH and Petruk KC . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 1162–1170.
Harada H and Grant S . (2003). Rev. Clin. Exp. Hematol., 7, 117–138.
Kamata H, Honda S, Maeda S, Chang L, Hirata H and Karin M . (2005). Cell, 120, 649–661.
Kitsberg D, Formstecher E, Fauquet M, Kubes M, Cordier J, Canton B, Pan G, Rolli M, Glowinski J and Chneiweiss H . (1999). J. Neurosci., 19, 8244–8251.
Macpherson I and Montagnier L . (1964). Virology, 23, 291–294.
Portella G, Cumming SA, Liddell J, Cui W, Ireland H, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A . (1998). Cell Growth Differ., 9, 393–404.
Ramos JW, Hughes PE, Renshaw MW, Schwartz MA, Formstecher E, Chneiweiss H and Ginsberg MH . (2000). Mol. Biol. Cell, 11, 2863–2872.
Trencia A, Fiory F, Maitan MA, Vito P, Barbagallo AP, Perfetti A, Miele C, Ungaro P, Oriente F, Cilenti L, Zervos AS, Formisano P and Beguinot F . (2004). J. Biol. Chem., 279, 46566–46572.
Trencia A, Perfetti A, Cassese A, Vigliotta G, Miele C, Oriente F, Santopietro S, Giacco F, Condorelli G, Formisano P and Beguinot F . (2003). Mol. Biol. Cell, 23, 4511–4521.
Tsukamoto T, Yoo J, Hwang SI, Guzman RC, Hirokawa Y, Chou YC, Olatunde S, Huang T, Bera TK, Yang J and Nandi S . (2000). Cancer Lett., 149, 105–113.
Vaidayanathan H and Ramos WJ . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 32367–32372.
Vigliotta G, Miele C, Santopietro S, Portella G, Perfetti A, Maitan MA, Cassese A, Oriente F, Trencia A, Fiory F, Romano C, Tiveron C, Tatangelo L, Troncone G, Formisano P and Beguinot F . (2004). Mol. Cell. Biol., 24, 5005–5015.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr A Balmain for kindly providing C5N, P1 and A5 cells and Dr S Linardopoulos for critical reading of the manuscript. The technical help of Maria Russo, Salvatore Sequino and Dr Antonio Baiano is also acknowledged. This work was supported by the European Community's FP6 EUGENE2 (LSHM-CT-2004-512013), grants from the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) to FB and PF, and the Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca Scientifica (PRIN to FB, GiPo and PF and FIRB RBNE0155LB to FB). The financial support of Telethon – Italy is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Formisano, P., Perruolo, G., Libertini, S. et al. Raised expression of the antiapoptotic protein ped/pea-15 increases susceptibility to chemically induced skin tumor development. Oncogene 24, 7012–7021 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208871
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208871
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ZNF703 promotes tumor progression in ovarian cancer by interacting with HE4 and epigenetically regulating PEA15
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2020)
-
A pilot study comparing protein expression in different segments of the normal colon and rectum and in normal colon versus adenoma in patients with Lynch syndrome
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2013)
-
PEA-15 potentiates H-Ras-mediated epithelial cell transformation through phospholipase D
Oncogene (2012)
-
Expression of phosphoprotein enriched in astrocytes 15 kDa (PEA-15) in astrocytic tumors: a novel approach of correlating malignancy grade and prognosis
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2010)
-
Heterogeneous in vitro effects of doxorubicin on gene expression in primary human liposarcoma cultures
BMC Cancer (2008)