Abstract
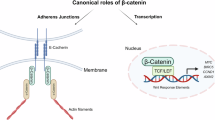
Wnt signaling follows canonical and non-canonical pathways to regulate a variety of processes during cellular homeostasis and development. The large T-antigen (T-Ag) of the human neurotropic JC virus, has been shown to modulate the Wnt-signaling pathway via interaction with β-catenin, one of the most important components of the canonical Wnt pathway. Here, we have identified an alternative non-canonical pathway that allows T-Ag to recruit Rac1 for stabilizing β-catenin by inhibiting its ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation. We demonstrate that inhibition of Rac1 by its dominant negative mutant, RacN17, abrogates T-Ag-mediated stabilization of β-catenin yet exhibits no impact on the transcriptional activity of β-catenin. Results from immunocytochemistry revealed that together with T-Ag, a pool of β-catenin appears at the cell surface, particularly at the membrane ruffles where active Rac1 is positioned. Interestingly, cooperativity between T-Ag and β-catenin leads to activation of Rac1, which in turn, stimulates its association with β-catenin. These observations unravel the interplay between β-catenin and Rac1 that is initiated by T-Ag and results in stabilization of β-catenin and its presence in cell membrane ruffles.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALLN:
-
acetyle-L-leucyl-L-norleucinal
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulfoxide
- GSK:
-
glycogen synthase kinase
- IB:
-
immunoblotting
- IP:
-
immunoprecipitation
- LiCl:
-
lithium chloride
- Rho:
-
Ras homology
- SRE:
-
serum response element
- T-Ag:
-
Large T-antigen of JC virus
- Ub:
-
ubiquitin
References
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A, Kemler R . (1997). Beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. EMBO J 16: 3797–3804.
Akiyama T, Kawasaki Y . (2006). Wnt signaling and the actin cytoskeleton. Oncogene 25: 7538–7544.
Bachar-Dahan L, Goltzmann J, Yaniv A, Gazit A . (2006). Engrailed-1 negatively regulates beta-catenin transcriptional activity by destabilizing beta-catenin via a glycogen synthase kinase-3beta-independent pathway. Mol Biol Cell 17: 2572–2580.
Bhattacharyya R, Wedegaertner PB . (2000). Galpha 13 requires palmitoylation for plasma membrane localization, rho-dependent signaling, and promotion of p115-rhogef membrane binding. J Biol Chem 275: 14992–14999.
Bienz M, Clevers H . (2000). Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell 103: 311–320.
Butel JS, Jarvis DL, Maxwell SA . (1989). SV40 T-antigen as a dual oncogene: structure and function of the plasma-membrane-associated population. Ann NY Acad Sci 567: 104–121.
Gan DD, Khalili K . (2004). Interaction between JCV large T-antigen and beta-catenin. Oncogene 23: 483–490.
Hwang SL, Lieu AS, Chang JH, Cheng TS, Cheng CY, Lee KS et al. (2005). Rac2 expression and mutation in human brain tumors. Acta Neurochirurgica 147: 551–554.
Khalili K, Gordon J, White MK . (2006). The polyomavirus, JCV and its involvement in human disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 577: 274–287.
Kikuchi A, Kishida S, Yamamoto H . (2006). Regulation of Wnt signaling by protein-protein interaction and post-translational modifications. Exp Mol Med 38: 1–10.
Malliri A, Collard JG . (2003). Role of Rho-family proteins in cell adhesion and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15: 583–589.
Mao J, Yuan H, Xie W, Simon MI, Wu D . (1998). Specific involvement of G proteins in regulation of serum response factor-mediated gene transcription by different receptors. J Biol Chem 273: 27118–27123.
Michaelson D, Silletti J, Murphy G, D'Eustachio P, Rush M, Philips MR . (2001). Differential localization of Rho GTPases in live cells: regulation by hypervariable Regions and RhoGDI binding. J Cell Biol 152: 111–126.
Nusse R . (2005). Wnt signaling in disease and in development. Cell Res 15: 28–32.
Senadheera D, Haataja L, Groffen J, Heisterkamp N . (2001). The small GTPase Rac interacts with ubiquitination complex proteins Cullin-1 and CDC23. Int J Mol Med 8: 127–133.
Shackelford J, Pagano JS . (2004). Tumor viruses and cell signaling pathways: deubiquitination versus ubiquitination. Mol Cell Biol 24: 5089–5093.
Shollar D, Del Valle L, Khalili K, Otte J, Gordon J . (2004). JCV T-antigen interacts with the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene product in a transgenic mouse model of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Oncogene 23: 5459–5467.
Welcker M, Clurman BE . (2005). The SV40 large T Antigen contains a decoy phosphodegron that mediates its interactions with Fbw7/hCdc4. J Biol Chem 280: 7654–7658.
White MK, Gordon J, Reiss K, DelValle L, Croul S, Giordano A et al. (2005). Human polyomaviruses and brain tumors. Brain Res Rev 50: 69–85.
Wildenberg GA, Dohn MR, Carnahan RH, Davis MA, Lobdell NA, Settleman J et al. (2006). p120-catenin and p190RhoGAP regulate cell-cell adhesion by coordinating antagonism between Rac and Rho. Cell 127: 1027–1039.
Acknowledgements
We thank past and present members of the Department of Neuroscience and the Center for Neurovirology for their support, and sharing of reagents and ideas. We also thank Dr Wedegaertner, Dr Grosscheld, Dr Sheikhattar, Dr Woodgett, Dr Tuszynski and Dr Marchese for providing the various plasmids and antibodies. We thank Dr Banerjee, Dr White and Dr Gordon for suggestions during manuscript preparation. This work was supported by NIH grants to KK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharyya, R., Noch, E. & Khalili, K. A novel role of Rac1 GTPase in JCV T-antigen-mediated β-catenin stabilization. Oncogene 26, 7628–7636 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210576
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210576
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Immune surveillance and response to JC virus infection and PML
Journal of NeuroVirology (2014)
-
Human polyomavirus JC reactivation and pathogenetic mechanisms of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and cancer in the era of monoclonal antibody therapies
Journal of NeuroVirology (2012)
-
JC virus in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer, an etiological agent or another component in a multistep process?
Virology Journal (2010)
-
Molecular association between β-catenin degradation complex and Rac guanine exchange factor DOCK4 is essential for Wnt/β-catenin signaling
Oncogene (2008)