Abstract
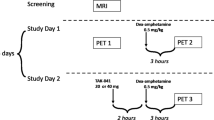
Acute phenylalanine/tyrosine depletion (APTD) has been proposed as a new method to decrease catecholamine neurotransmission safely, rapidly, and transiently. Validation studies in animals are encouraging, but direct evidence in human brain is lacking. In the present study, we tested the hypothesis that APTD would reduce stimulated dopamine (DA) release, as assessed by positron emission tomography (PET) and changes in [11C]raclopride binding potential (BP), a measure of DA D2/D3 receptor availability. Eight healthy men received two PET scans, both following d-amphetamine, 0.3 mg/kg, p.o., an oral dose known to decrease [11C]raclopride BP in ventral striatum. On the morning before each scan, subjects ingested, in counter-balanced order, an amino-acid mixture deficient in the catecholamine precursors, phenylalanine, and tyrosine, or a nutritionally balanced mixture. Brain parametric images were generated by calculating [11C]raclopride BP at each voxel. BP values were extracted from the t-map (threshold: t=4.2, equivalent to p<0.05, Bonferroni corrected) and a priori identified regions of interest from each individual's coregistered magnetic resonance images. Both receptor parametric mapping and region of interest analyses indicated that [11C]raclopride binding was significantly different on the two test days in the ventral striatum (peak t=6.31; x=−25, y=−8, and z=0.1). In the t-map defined cluster, [11C]raclopride BP values were 11.8±11.9% higher during the APTD session (p<0.05). The reduction in d-amphetamine-induced DA release exhibited a linear association with the reduction in plasma tyrosine levels (r=−0.82, p<0.05). Together, the results provide the first direct evidence that APTD decreases stimulated DA release in human brain. APTD may be a suitable new tool for human neuropsychopharmacology research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ames MM, Lerner P, Lovenberg W (1978). Tyrosine hydroxylase. Activation by protein phosphorylation and end product inhibition. J Biol Chem 253: 27–31.
Andreasen NC, Endicott J, Spitzer RL, Winokur G (1977). The family history method using diagnostic criteria: reliability and validity. Arch Gen Psychiatry 34: 1229–1235.
Angrist B, Corwin J, Bartlik B, Cooper T (1987). Early pharmacokinetics and clinical effects of oral d-amphetamine in normal subjects. Biol Psychiatry 22: 1357–1368.
Asghar SJ, Baker GB, Rauw GA, Silverstone PH (2002). A rapid method of determining amphetamine in plasma samples using pentafluorobenzenesulfonyl chloride and electron-capture gas chromatography. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 46: 111–115.
Aston JA, Gunn RN, Worsley KJ, Ma Y, Evans AC, Dagher A (2000). A statistical method for the analysis of positron emission tomography neuroreceptor ligand data. NeuroImage 12: 245–256.
Biggio G, Porceddu ML, Gessa GL (1976). Decrease of homovanillic, dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and cyclic-adneosine-3′,5′-monophosphate content in the rat caudate nucleus induced by the acute administration of an amino acid mixture lacking tyrosine and phenylalanine. J Neurochem 26: 1253–1255.
Brogden RN, Heel RC, Speight TM, Avery GS (1981). Methyl-p-tyrosine: a review of its pharmacology and clinical use. Drugs 21: 81–89.
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M (1978). Dependence of 5HT and catecholamine synthesis on concentrations of precursor amino acids in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 303: 157–164.
Casey K, Benkelfat C, Young SN, Weston F, Rivard M-E, Leyton M (2002). Catecholamine depletion reduces nicotine withdrawal related craving but not self-administration in nicotine dependent smokers. In: American College of Neuropsychopharmacology San Juan, Puerto Rico. 9–12 December.
Collins DL, Evans AC (1997). ANIMAL: validation and applications of non-linear registration-based segmentation. Int J Pattern Recognition Artif Int 11: 1271–1294.
Collins DL, Holmes CJ, Peters TM, Evans AC (1994a). Automated 3-D volume-based segmentation. Hum Brain Mapp 3: 190–208.
Collins DL, Neelin P, Peter TM, Evans AC (1994b). Automated 3D intersubject registration of MR volumetric data in standardized Talairach space. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18: 192–205.
Collins DL, Zijdenbos A, Kollokian V, Sled JG, Kabani NJ, Holmes CJ et al (1998). Design and construction of a realistic digital brain phantom. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17: 463–468.
Di Chiara G, Imperato A (1988). Drugs abused by humans preferentially increase synaptic dopamine concentrations in the mesolimbic system of freely moving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci 85: 5274–5278.
Drevets WC, Gautier C, Price JC, Kupfer DJ, Kinahan PE, Grace AA et al (2001). Amphetamine-induced dopamine release in human ventral striatum correlates with euphoria. Biol Psychiatry 49: 81–96.
Evans AC, Marrett S, Neelin P, Collins L, Worsley K, Dai W et al (1992). Anatomical mapping of functional activation in stereotactic coordinate space. NeuroImage 1: 43–53.
First MB, Spitzer RI, Gibbon M (1995). Axis I Disorders. New York State Psychiatric Institute: New York.
Fujita M, Verhoeff NP, Varrone A, Zoghbi SS, Baldwin RM, Jatlow PA et al (2000). Imaging extrastriatal dopamine D(2) receptor occupancy by endogenous dopamine in healthy humans. Eur J Pharmacol 387: 179–188.
Gunn RN, Lammertsma AA, Hume SP, Cunningham VJ (1997). Parametric imaging of ligand-receptor binding in PET using a simplified reference region model. NeuroImage 6: 279–287.
Haber SN, McFarland NR (1999). The concept of the ventral striatum in nonhuman primates. Ann NY Acad Sci 877: 33–48.
Harmer CJ, McTavish SFB, Clark L, Goodwin GM, Cowen PJ (2001). Tyrosine depletion attenuates dopamine function in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 154: 105–111.
Lammertsma AA, Hume SP (1996). Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. NeuroImage 4: 153–158.
Laruelle M, D'Souza CD, Baldwin RM, Abi-Dargham A, Kanes SJ, Fingado CL et al (1997a). Imaging D2 receptor occupancy by endogenous dopamine in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 17: 162–174.
Laruelle M, Iyer RN, al-Tikriti MS, Zea-Ponce Y, Malison R, Zoghbi SS et al (1997b). Microdialysis and SPECT measurements of amphetamine-induced dopamine release in nonhuman primates. Synapse 25: 1–14.
Leyton M, Boileau I, Benkelfat C, Diksic M, Baker G, Dagher A (2002). Amphetamine-induced increases in extracellular dopamine, drug wanting and novelty seeking: a PET/[11C]raclopride study in healthy men. Neuropsychopharmacology 27: 1027–1035.
Leyton M, Young SN, Blier P, Baker GB, Pihl RO, Benkelfat C (2000a). Acute tyrosine depletion and alcohol ingestion in healthy women. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res 24: 459–464.
Leyton M, Young SN, Pihl RO, Etezadi S, Lauze C, Blier P et al (2000b). Effects on mood of acute phenylalanine/tyrosine depletion in healthy women. Neuropsychopharmacology 22: 52–63.
Martinez D, Slifstein M, Broft A, Mawlawi O, Hwang D-R, Huang T et al (2003). Imaging human mesolimbic dopamine transmission with PET: II. Amphetamine-induced dopamine release in the functional subdivisions of the striatum. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23: 285–300.
Mawlawi O, Martinez D, Slifstein M, Broft A, Chatterjee R, Hwang DR et al (2001). Imaging human mesolimbic dopaminergic transmission with positron emission tomography; accuracy and precision of DA2 receptor measurements in ventral striatum. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21: 1034–1055.
McCann UD, Penetar DM, Belenky G (1990). Acute dystonic reaction in normal humans caused by catecholamine depletion. Clin Neuropharmacol 13: 565–568.
McTavish SF, Cowen PJ, Sharp T (1999a). Effect of a tyrosine-free amino acid mixture on regional brain catecholamine synthesis and release. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 141: 182–188.
McTavish SFB, McPherson MH, Harmer CJ, Clark L, Sharp T, Goodwin GM et al (2001). Antidopaminergic effects of dietary tyrosine depletion in healthy subjects and patients with manic illness. Br J Psychiatry 179: 356–360.
McTavish SFB, McPherson MH, Sharp T, Cowen PJ (1999b). Attenuation of some subjective effects of amphetamine following tyrosine depletion. J Psychopharmacol 13: 144–147.
Moja EA, Lucini V, Benedetti F, Lucca A (1996). Decrease in plasma phenylalanine and tyrosine after phenylalanine-tyrosine free amino acid solutions in man. Life Sci 58: 2389–2395.
Palmour RM, Ervin FR, Baker GB, Young SN (1998). Effects of acute tryptophan depletion and acute tyrosine/phenylalanine depletion on CSF amine metabolite levels and voluntary alcohol consumption in vervet monkeys. Psychopharmacology 136: 1–7.
Reilhac A, Sechet S, Boileau S, Gunn R, Evans AC, Dagher A (2003). Motion correction for PET ligand imaging. In: Human Brain Mapping Abstract New York. 18 June.
Rot MAH, Benkelfat C, Young SN, Baker GB, Leyton M (2003). Role of dopamine vs norepinephrine in effects of d-amphetamine: an acute phenylalanine/tyrosine depletion study in healthy men. In: Canadian College of Neuropsychopharmacology Montreal, Canada. 1–4 June.
Sechet S, Reilhac A, Gunn R, Evans AC, Dagher A (2002). Frame misalignment induced errors in PET studies: an investigation of strategies for correction. IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, Norfolk, VA 10–16 November 2002.
Sheehan BD, Tharyan P, McTavish SFB, Campling GM, Cowen PJ (1996). The use of dietary manipulation to deplete plasma tyrosine and phenylalanine in healthy subjects. J Psychopharmacol 10: 231–234.
Sled JG, Zijdenbos A, Evans AC (1998). A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17: 87–97.
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988). Co-Planar Stereotactic Atlas of the Human Brain. Thieme: Stuttgart.
Verhoeff NPLG, Kapur S, Hussey D, Lee M, Christensen B, Papatheodorou G et al (2001). A simple method to measure baseline occupancy of neostriatal dopamine D2 receptors by dopamine in vivo in healthy subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 25: 213–223.
Wu Q, Reith ME, Kuhar MJ, Carroll FL, Garris PA (2001). Preferential increases in nucleus accumbens dopamine after systemic cocaine administration are caused by unique characteristics of dopamine neurotransmission. J Neurosci 21: 6338–6347.
Worsley KJ, Marrett S, Neelin P, Vandal AC, Friston KJ, Evans AC (1996). A unified statistical approach for determining significant signals in images of cerebral activation. Hum Brain Mapp 4: 58–73.
Ylitalo P (1991). Effect of exercise on pharmacokinetics. Ann Med 23: 289–294.
Young SN, Leyton M (2002). The role of serotonin in human mood and social interaction: Insight from altered tryptophan levels. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71: 857–865.
Young SN, Smith SE, Pihl RO, Ervin FR (1985). Tryptophan depletion causes a rapid lowering of mood in normal males. Psychopharmacology 87: 173–177.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by two operating grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, MOP-36429 to ML, CB, and AD, and MOP-49480 to AD. ML, and CB who are recipients of salary awards from Fonds de la Recherche en Santé du Québec (FRSQ). We thank Rick Fukusawa, Dean Jolly, Mirjana Kovacevic, Francine Lenoff, Shadreck Mzengeza, Gary Sauchuk, Gail Rauw, and Francine Weston for excellent technical assistance, and Dr Robert Lisbona, Chief of Nuclear Medicine at the MNI, for valuable help during the PET scans.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A preliminary report based on this study was presented at the Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, San Juan, Puerto Rico, December 8–12, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leyton, M., Dagher, A., Boileau, I. et al. Decreasing Amphetamine-Induced Dopamine Release by Acute Phenylalanine/Tyrosine Depletion: A PET/[11C]Raclopride Study in Healthy Men. Neuropsychopharmacol 29, 427–432 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300328
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300328
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Clozapine but not lithium reverses aberrant tyrosine uptake in patients with bipolar disorder
Psychopharmacology (2023)
-
Acute depletion of dopamine precursors in the human brain: effects on functional connectivity and alcohol attentional bias
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)
-
Neuroscience of apathy and anhedonia: a transdiagnostic approach
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2018)
-
Dopamine and response selection: an Acute Phenylalanine/Tyrosine Depletion study
Psychopharmacology (2018)
-
Inflammation Effects on Motivation and Motor Activity: Role of Dopamine
Neuropsychopharmacology (2017)