Abstract
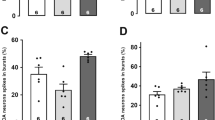
Antipsychotic drugs (APDs) have previously been shown to alter Fos expression in a regionally specific manner. Increases in Fos expression in the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) are common to all clinically effective APDs. In contrast, APD-induced Fos expression increases in the caudate-putamen (CPu) and prefrontal cortex (PFC) are associated with the extrapyramidal side effect liability of typical APDs or the effectiveness against negative symptoms of atypical APDs, respectively. Considerable evidence suggests that the neuropeptide neurotensin (NT) mediates some of the effects of APDs. To determine whether NT neurotransmission is also involved in APD-induced Fos expression in brain regions relevant for therapeutic efficacy, the NT receptor antagonist SR 142948A (10 or 100 μg/kg i.p.) was coadministered with APDs (haloperidol (2.0 mg/kg s.c.), olanzapine (5 mg/kg i.p.), or clozapine (20 mg/kg s.c.)). Fos expression was evaluated in the PFC, NAcc shell, dorsomedial, and dorsolateral CPu and the lateral septum. SR 142948A attenuated haloperidol-induced Fos expression in the CPu but, in contrast, increased olanzapine-induced Fos expression in this brain region. The effects of the NT receptor antagonist were paralleled by its effects on catalepsy in olanzapine—but not haloperidol—treated animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adams MR, Brandon EP, Chartoff EH, Idzerda RL, Dorsa DM, McKnight GS (1997). Loss of haloperidol induced gene expression and catalepsy in protein kinase A-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 12157–12161.
Binder EB, Kinkead B, Owens MJ, Kilts CD, Nemeroff CB (2001a). Enhanced neurotensin neurotransmission is involved in the clinically relevant behavioral effects of antipsychotic drugs: evidence from animal models of sensorimotor gating. J Neurosci 21: 601–608.
Binder EB, Kinkead B, Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB (2001b). The role of neurotensin in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and the mechanism of action of antipsychotic drugs. Biol Psychiat 50: 856–872.
Boudin H, Pélaprat D, Rostène W, Beaudet A (1996). Cellular distribution of neurotensin receptors in rat brain: immunohistochemical study using an antipeptide antibody against the cloned high affinity receptor. J Comp Neurol 373: 76–89.
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990). Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia. Human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiat 47: 181–188.
Cohen BM, Wan W (1996). The thalamus as a site of action of antipsychotic drugs. Am J Psychiat 153: 104–106.
Decker KP, Roy-Byrne PP, Merchant KM (1995). Effect of muscimol on haloperidol-induced alteration of neurotensin gene expression in the striatum and nucleus accumbens in the rat. Brain Res 691: 9–17.
Deutch AY (1994). Identification of the neural systems subserving the actions of clozapine: clues from immediate-early gene expression. J Clin Psychiat 55: 37–42.
Deutch AY, Lee MC, Iadarola MJ (1992). Regionally specific events of atypical antipsychotic drugs on striatal Fos expression: the nucleus accumbens shell as a locus of antipsychotic action. Mol Cell Neurosci 3: 332–341.
Deutch AY, Ongur D, Duman RS (1995). Antipsychotic drugs induce Fos protein in the thalamic paraventricular nucleus: a novel locus of antipsychotic drug action. Neuroscience 66: 337–346.
Dobner PR, Fadel J, Deitmeyer N, Carraway RE, Deutch AY (2001). Neurotensin-deficient mice show altered responses to antipsychotic drugs. PNAS 98: 8048–8053.
Ehlers II RA, Bonnor RM, Wang X, Hellmich MR, Evers BM (1998). Signal transduction mechanisms in neurotensin-mediated cellular regulation. Surgery 124: 239–246.
Ellenbroek BA (2000). The effect of olanzapine in animal models predictive of antipsychotic activity. In: Tran PV, Bymaster FP, Tye N, Herrera JM, Breier A, Tollefson GD (eds). Olanzapine (Zyprexa): A Novel Antipsychotic. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Healthcare: Philadelphia. pp 57–68.
Ellenbroek BA, Peeters BW, Honig WM, Cools AR (1987). The paw test: a behavioural paradigm for differentiating between classical and atypical neuroleptic drugs. Psychopharmacology 93: 343–348.
Fadel J, Dobner PR, Deutch AY (2001). The neurotensin antagonist SR 48692 attenuates haloperidol-induced striatal Fos expression in the rat. Neurosci Lett 303: 17–20.
Feifel D, Minor KL, Dulawa S, Swerdlow NR (1997). The effects of intra-accumbens neurotensin on sensorimotor gating. Brain Res 760: 80–84.
Fibiger HC (1994). Neuroanatomical targets of neuroleptic drugs as revealed by Fos immunochemistry. J Clin Psychiat 55: 33–36.
Goedert M, Pittaway K, Emson PC (1984). Neurotensin receptors in the rat striatum: lesion studies. Brain Res 299: 164–168.
Gully D, Canton M, Boigegrain R, Jeanjean F, Molimard JC, Poncelet M et al (1993). Biochemical and pharmacological profile of a potent and selective nonpeptide antagonist of the neurotensin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 65–69.
Gully D, Labeeuw B, Boigegrain R, Oury-Donat F, Bachy A, Poncelet M et al (1997). Biochemical and pharmacological activities of SR 142948A, a new potent neurotensin receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280: 802–812.
Huang W, Hanson GR (1997). Differential effect of haloperidol on release of neurotensin in extrapyramidal and limbic systems. Eur J Pharmacol 332: 15–21.
Kilts CD, Anderson CM, Bissette G, Ely TD, Nemeroff CB (1988). Differential effects of antipsychotic drugs on the neurotensin concentration of discrete rat brain nuclei. Biochem Pharmacol 37: 1547–1554.
Kinkead B, Binder EB, Nemeroff CB (1999). Does neurotensin mediate the effects of antipsychotic drugs? Biol Psychiat 46: 340–351.
Kinkead B, Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB (1997). The effects of subchronic antipsychotic drug administration on neurotensin concentrations in the rat brain. Soc Neurosci Abstr 23: 653.11.
Kinkead B, Shahid S, Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB (2000). Effects of acute and subchronic administration of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on the neurotensin system of the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Therap 295: 67–73.
Lambert PD, Ely TD, Gross RE, Kilts CD (1996). Neurotensin induces Fos and Zif268 expression in limbic nuclei of the rat brain. Neuroscience 75: 1141–1151.
Merchant KM, Dobie DJ, Dorsa DM (1992). Expression of the proneurotensin gene in the rat brain and its regulation by antipsychotic drugs. Ann NY Acad Sci 668: 54–69.
Merchant KM, Figur LM, Evans DL (1996). Induction of c-fos mRNA in rat medial prefrontal cortex by antipsychotic drugs: role of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. Cerebr Cortex 6: 561–570.
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic: San Diego.
Portier M, Combes T, Gully D, Maffrand JP, Casellas P (1998). Neurotensin type 1 receptor-mediated activation of krox24, c-fos and Elk-1: preventing effect of the neurotensin antagonists SR 48692 and SR 142948. FEBS Lett 432: 88–93.
Radke JM, MacLennan AJ, Beinfeld MC, Bissette G, Nemeroff CB, Vincent SR et al (1989). Effects of short- and long-term haloperidol administration and withdrawal on regional brain cholecystokinin and neurotensin concentrations in the rat. Brain Res 480: 178–183.
Radke JM, Owens MJ, Ritchie JC, Nemeroff CB (1998). Atypical antipsychotic drugs selectively increase neurotensin efflux in dopamine terminal regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 11462–11464.
Robertson GS, Fibiger HC (1992). Neuroleptics increase c-fos expression in the forebrain: contrasting effects of haloperidol and clozapine. Neuroscience 46: 315–328.
Robertson GS, Fibiger HC (1996). Effects of olanzapine on regional C-Fos expression in rat forebrain. Neuropsychopharmacology 14: 105–110.
Sebens JB, Koch T, Ter Horst GJ, Korf J (1995). Differential Fos-protein induction in rat forebrain regions after acute and long-term haloperidol and clozapine treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 273: 175–182.
Shibata K, Yamada K, Furukawa T (1987). Possible neuronal mechanisms involved in neurotensin-induced catalepsy in mice. Psychopharmacology 91: 288–292.
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1998). Using an animal model of deficient sensorimotor gating to study the pathophysiology and new treatments of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bull 24: 285–301.
Tyler B, Cusack B, Douglas C, Souder T, Richelson E (1998). Evidence for additional neurotensin receptor subtypes: neurotensin analogs that distinguish between neurotensin-mediated hypothermia and antinociception. Brain Res 792: 246–252.
Vincent JP, Mazella J, Kitabgi P (1999). Neurotensin and neurotensin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20: 302–309.
Wagstaff JD, Gibb JW, Hanson GR (1996). Dopamine D2-receptors regulate neurotensin release from nucleus accumbens and striatum as measured by in vivo microdialysis. Brain Res 721: 196–203.
Walker N, Lépée-Lorgeoux I, Fournier J, Betancur C, Rostene W, Ferrara P et al (1998). Tissue distribution and cellular localization of the levocabastine-sensitive neurotensin receptor mRNA in adult rat brain. Mol Brain Res 57: 193–200.
Ward RP, Dorsa DM (1999). Molecular and behavioral effects mediated by Gs-coupled adenosine A2a, but not serotonin 5-Ht4 or 5-Ht6 receptors following antipsychotic administration. Neuroscience 89: 927–938.
Acknowledgements
Supported by grants NIH MH-39415 and from the Eli Lilly Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binder, E., Kinkead, B., Owens, M. et al. Neurotensin Receptor Antagonist SR 142948A Alters Fos Expression and Extrapyramidal Side Effect Profile of Typical and Atypical Antipsychotic Drugs. Neuropsychopharmacol 29, 2200–2207 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300546
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300546
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of neurotensin gene knockout in mice on the behavioral effects of cocaine
Psychopharmacology (2012)
-
Regional Differences in the Action of Antipsychotic Drugs: Implications for Cognitive Effects in Schizophrenic Patients
Neurotoxicity Research (2010)
-
Endogenous Neurotensin in the Ventral Tegmental Area Contributes to Amphetamine Behavioral Sensitization
Neuropsychopharmacology (2005)