Abstract
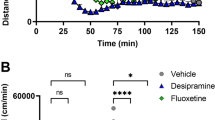
Coadministration of atypical antipsychotics and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) enhances the release of monoamines such as dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), and serotonin (5-HT) in the prefrontal cortex. To clarify the role of DA-D2/3 receptors in the combination effect, we examined the effects of coadministration of the selective DA-D2/3 antagonist sulpiride and the SSRI fluvoxamine on amine neurotransmitter release in rat prefrontal cortex. Sulpiride (10 mg/kg, i.p.) and fluvoxamine (10 mg/kg, i.p.) alone did not affect extracellular DA levels, while their coadministration caused a significant increase in DA levels. Sulpiride alone did not affect extracellular levels of 5-HT and NE in the prefrontal cortex, while fluvoxamine alone caused a marked increase in 5-HT levels and a slight increase in NE levels. Sulpiride did not affect the fluvoxamine-induced increases in extracellular levels of 5-HT and NE. The DA-D2/3 antagonist haloperidol (0.1 mg/kg) in combination with fluvoxamine also caused a selective increase in extracellular DA levels in the cortex. Coadministration of sulpiride and fluvoxamine did not affect extracellular DA levels in the striatum. Combination of systemic sulpiride and local fluvoxamine did not increase the DA levels, but that of systemic fluvoxamine with local sulpiride increased. The combination effect in increasing prefrontal DA levels was antagonized systemically, but not locally, by the 5-HT1A antagonist WAY100635 at a low dose. These findings suggest that the combination of prefrontal DA-D2/3 receptor blockade and 5-HT1A receptor activation in regions other than the cortex plays an important role in sulpiride and fluvoxamine-induced increase in prefrontal DA release.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ago Y, Koyama Y, Baba A, Matsuda T (2003). Regulation by 5-HT1A receptors of the in vivo release of 5-HT and DA in mouse frontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 45: 1050–1056.
Ago Y, Sakaue M, Baba A, Matsuda T (2002). Selective reduction by isolation rearing of 5-HT1A receptor-mediated dopamine release in vivo in the frontal cortex of mice. J Neurochem 83: 353–359.
Barbui C, Hotopf M (2001). Amitriptyline v. the rest: still the leading antidepressant after 40 years of randomized controlled trials. Br J Psychiatry 178: 129–144.
Bean AJ, During MJ, Roth RH (1990). Effects of dopamine autoreceptor stimulation on the release of colocalized transmitters: in vivo release of dopamine and neurotensin from rat prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Lett 108: 143–148.
Benkert O, Holsboer F (1984). Effect of sulpiride in endogenous depression. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 311: 43–48.
Bymaster FP, Calligaro DO, Falcone JF, Marsh RD, Moore NA, Tye NC et al (1996). Radioreceptor binding profile of the atypical antipsychotic olanzapine. Neuropsychopharmacology 14: 87–96.
Dawson LA, Nguyen HQ (1998). Effects of 5-HT1A receptor antagonists on fluoxetine-induced changes in extracellular serotonin concentrations in rat frontal cortex. Eur J Pharmacol 345: 41–46.
Ferrier IN (1999). Treatment of major depression: is improvement enough? J Clin Psychiatry 60 (Suppl 6): 10–14.
Gobert A, Rivet J-M, Audinot V, Cistarelli L, Spedding M, Vian J et al (1995). Functional correlates of dopamine D3 receptor activation in the rat in vivo and their modulation by the selective antagonist, (+)-S 14297: II. Both D2 and ‘silent’ D3 autoreceptors control synthesis and release in mesolimbic, mesocortical and nigrostriatal pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275: 899–913.
Gobert A, Rivet J-M, Cistarelli L, Melon C, Millan MJ (1999). Buspirone modulates basal and fluoxetine-stimulated dialysate levels of dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin in the frontal cortex of freely moving rats: activation of serotonin1A receptors and blockade of α2-adrenergic receptors underlie its actions. Neuroscience 93: 1251–1262.
Hajós-Korcsok É, McQuade R, Sharp T (1999). Influence of 5-HT1A receptors on central noradrenergic activity: microdialysis studies using (±)-MDL 73005EF and its enantiomers. Neuropharmacology 38: 299–306.
Hjorth S, Westlin D, Bengtsson HJ (1997). WAY100635-induced augmentation of the 5-HT-elevating action of citalopram: relative importance of the dose of the 5-HT1A (auto)receptor blocker versus that of the 5-HT reuptake inhibitor. Neuropharmacology 36: 461–465.
Ichikawa J, Ishii H, Bonaccorso S, Fowler WL, O'Laughlin IA, Meltzer HY (2001). 5-HT2A and D2 receptor blockade increases cortical DA release via 5-HT1A receptor activation: a possible mechanism of atypical antipsychotic-induced cortical dopamine release. J Neurochem 76: 1521–1531.
Ichikawa J, Meltzer HY (1999). R(+)-8-OH-DPAT, a serotonin1A receptor agonist, potentiated S(−)-sulpiride-induced dopamine release in rat medial prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens but not striatum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291: 1227–1232.
Imondi AR, Alam AS, Brennan JJ, Hagerman LM (1978). Metabolism of sulpiride in man and rhesus monkeys. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 232: 79–91.
Iyer RN, Bradberry CW (1996). Serotonin-mediated increase in prefrontal cortex dopamine release: pharmacological characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277: 40–47.
Koch S, Perry KW, Bymaster FP (2004). Brain region and dose effects of an olanzapine/fluoxetine combination on extracellular monoamine concentrations in the rat. Neuropharmacology 46: 232–242.
Koeltzow TE, Xu M, Cooper DC, Hu X-T, Tonegawa S, Wolf ME et al (1998). Alterations in dopamine release but not dopamine autoreceptor function in dopamine D3 receptor mutant mice. J Neurosci 18: 2231–2238.
Kuroki T, Meltzer HY, Ichikawa J (1999). Effect of antipsychotic drugs on extracellular dopamine levels in rat medial prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288: 774–781.
Liégeois J-P, Ichikawa J, Meltzer HY (2002). 5-HT2A receptor antagonism potentiates haloperidol-induced dopamine release in rat medial prefrontal cortex and inhibits that in the nucleus accumbens in a dose-dependent manner. Brain Res 947: 157–165.
Lucas G, De Deurwaerdère P, Caccia S, Spampinato U (2000). The effect of serotonergic agents on haloperidol-induced striatal dopamine release in vivo: opposite role of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor subtypes and significance of the haloperidol dose used. Neuropharmacology 39: 1053–1063.
Lucas G, Spampinato U (2000). Role of striatal serotonin2A and serotonin2C receptor subtypes in the control of in vivo dopamine outflow in the rat striatum. J Neurochem 74: 693–701.
Maier W, Benkert O (1994). Treatment of chronic depression with sulpiride: evidence of efficacy in placebo-controlled single case studies. Psychopharmacology 115: 495–501.
Meltzer HY, McGurk SR (1999). The effects of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine on cognitive function in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 25: 233–255.
Miller EK, Cohen JD (2001). An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24: 167–202.
Moghaddam B, Bunney BS (1990). Acute effects of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on the release of dopamine from prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and striatum of the rat: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem 54: 1755–1760.
Nelson JC (1999). A review of the efficacy of serotonergic and noradrenergic reuptake inhibitors for treatment of major depression. Biol Psychiatry 46: 1301–1308.
O'Connor M, Silver H (1998). Adding risperidone to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor improves chronic depression [letter]. J Clin Psychopharmacol 18: 89–91.
Ostroff RB, Nelson JC (1999). Risperidone augmentation of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in major depression. J Clin Psychiatry 60: 256–259.
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986). The Rat Brain in Sterotaxic Coordinates, 2nd edn Academic Press: San Diego.
Renard CE, Fiocco AJ, Clenet F, Hascoet M, Bourin M (2001). Is dopamine implicated in the antidepressant-like effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the mouse forced swimming test? Psychopharmacology 159: 42–50.
Romero L, Hervás I, Artigas F (1996). The 5-HT1A antagonist WAY-100635 selectively potentiates the presynaptic effects of serotonergic antidepressants in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 219: 123–126.
Sakaue M, Somboonthum P, Nishihara B, Koyama Y, Hashimoto H, Baba A et al (2000). Postsynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor activation increases in vivo dopamine release in rat prefrontal cortex. Br J Pharmacol 129: 1028–1034.
Schotte A, Janssen PF, Gommeren W, Luyten WH, Van Gompel P, Lesage AS et al (1996). Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding. Psychopharmacology 124: 57–73.
Serra G, Forgione A, D'Aquila PS, Collu M, Fratta W, Gessa GL (1990). Possible mechanism of antidepressant effect of L-sulpiride. Clin Neuropharmacol 13 (Suppl 1): S76–S83.
Shelton RC, Tollefson GD, Tohen M, Stahl S, Gannon KS, Jacobs TG et al (2001). A novel augmentation strategy for treating resistant major depression. Am J Psychiatry 158: 131–134.
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres M-P, Bouthenet M-L, Schwartz J-C (1990). Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature 347: 146–151.
Tanda G, Bassareo V, Di Chiara G (1996). Mianserin markedly and selectively increases extracellular dopamine in the prefrontal cortex as compared to the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Psychopharmacology 123: 127–130.
Tanda G, Carboni E, Frau R, Di Chiara G (1994). Increase of extracellular dopamine in the prefrontal cortex: a trait of drugs with antidepressant potential? Psychopharmacology 115: 285–288.
Vergoni AV, Forgione A, Bertolini A (1995). Chronic administration of l-sulpiride at non-neuroleptic doses reduces the duration of immobility in experimental models of ‘depression-like’ behavior. Psychopharmacology 121: 279–281.
Wolf ME, Roth RH (1987). Dopamine neurons projecting to the medial prefrontal cortex possess release-modulating autoreceptors. Neuropharmacology 26: 1053–1059.
Zhang W, Bymaster FP (1999). The in vivo effects of olanzapine and other antipsychotic agents on receptor occupancy and antagonism of dopamine D1, D2, D3, 5HT2A and muscarinic receptors. Psychopharmacology 141: 267–278.
Zhang W, Perry KW, Wong DT, Potts BD, Bao J, Tollefson GD et al (2000). Synergistic effects of olanzapine and other antipsychotic agents in combination with fluoxetine on norepinephrine and dopamine release in rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 23: 250–262.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan. We acknowledge the donation of WAY100635 (Mitsubishi Pharma Co., Yokohama), fluvoxamine (Solvay Seiyaku KK., Saitama), and sulpiride (Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Osaka).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ago, Y., Nakamura, S., Baba, A. et al. Sulpiride in Combination with Fluvoxamine Increases in vivo Dopamine Release Selectively in Rat Prefrontal Cortex. Neuropsychopharmacol 30, 43–51 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300567
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300567
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Risperidone and aripiprazole alleviate prenatal valproic acid-induced abnormalities in behaviors and dendritic spine density in mice
Psychopharmacology (2017)
-
Fluvoxamine enhances prefrontal dopaminergic neurotransmission in adrenalectomized/castrated mice via both 5-HT reuptake inhibition and σ1 receptor activation
Psychopharmacology (2011)
-
Profound Changes in Dopaminergic Neurotransmission in the Prefrontal Cortex in Response to Flattening of the Diurnal Glucocorticoid Rhythm: Implications for Bipolar Disorder
Neuropsychopharmacology (2009)
-
Augmentation effect of combination therapy of aripiprazole and antidepressants on forced swimming test in mice
Psychopharmacology (2009)
-
Effect of sertindole on extracellular dopamine, acetylcholine, and glutamate in the medial prefrontal cortex of conscious rats: a comparison with risperidone and exploration of mechanisms involved
Psychopharmacology (2009)