Abstract
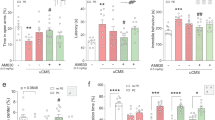
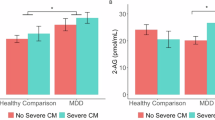
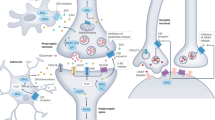
Deficits in cognitive functioning and flexibility are seen following both chronic stress and modulation of endogenous cannabinoid (eCB) signaling. Here, we investigated whether alterations in eCB signaling might contribute to the cognitive impairments induced by chronic stress. Chronic stress impaired reversal learning and induced perseveratory behavior in the Morris water maze without significant effect on task acquisition. These cognitive impairments were reversed by exogenous cannabinoid administration, suggesting deficient eCB signaling underlies these phenomena. In line with this hypothesis, chronic stress downregulated CB1 receptor expression and significantly reduced the content of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonylglycerol within the hippocampus. CB1 receptor density and 2-arachidonylglycerol content were unaffected in the limbic forebrain. These data suggest that stress-induced downregulation of hippocampal eCB signaling contributes to problems in behavioral flexibility and could play a role in the development of perseveratory and ruminatory behaviors in stress-related neuropsychiatric disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Alfarez DN, Joels M, Krugers HJ (2003). Chronic unpredictable stress impairs long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal CA1 area and dentate gyrus in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 17: 1928–1934.
Bagby RM, Rector NA, Segal ZW, Joffe RT, Levitt AJ, Kennedy SH et al (1999). Rumination and distraction in major depression: assessing responses to pharmacological treatment. J Affect Disord 55: 225–229.
Bartolomucci A, de Biurrun G, Czeh B, van Kampen M, Fuchs E (2002). Selective enhancement of spatial learning under chronic psychosocial stress. Eur J Neurosci 15: 1863–1866.
Breivogel CS, Childers SR, Deadwyler SA, Hampson RE, Vogt LJ, Sim-Selly LJ (1999). Chronic Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol treatment produces a time-dependent loss of cannabinoid receptors and cannabinoid receptor-activated G proteins in rat brain. J Neurochem 73: 2447–2459.
Brotto LA, Gorzalka BB, LaMarre AK (2001). Melatonin protects against the effects of chronic stress on sexual behavior in male rats. Neuroreport 12: 3465–3469.
Bubser M, Deutch AY (1999). Stress induces fos expression in neurons of the thalamic paraventricular nucleus that innervate limbic forebrain sites. Synapse 32: 13–22.
Carlson G, Wang Y, Alger BE (2002). Endocannabinoids facilitate the induction of LTP in the hippocampus. Nat Neurosci 5: 723–724.
Carr DB, Seasack SR (1996). Hippocampal afferents to the rat prefrontal cortex: synaptic targets and relation to dopamine terminals. J Comp Neurol 369: 1–15.
Chaperon F, Thiebot MH (1999). Behavioral effects of cannabinoid agents in animals. Crit Rev Neurobiol 13: 243–281.
de Quervain DG, Roozendaal B, McGaugh JL (1998). Stress and glucocorticoids impair retrieval of long term memory. Nature 394: 787–790.
Devane WA, Hanus L, Breuer A, Pertwee RG, Stevenson LA, Griffin G et al (1992). Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 258: 1946–1949.
Di S, Malcher-Lopes R, Halmos KC, Tasker JG (2003). Non-genomic glucocorticoid inhibition via endocannabinoid release in the hypothalamus: a fast feedback mechanism. J Neurosci 23: 4850–4857.
Di Marzo V, Goparaju SK, Wang L, Liu J, Batkai S, Jarai Z et al (2001). Leptin-regulated endocannabinoids are involved in maintaining food intake. Nature 410: 822–825.
Francis DD, Zaharia MD, Shanks N, Anisman H (1995). Stress-induced disturbances in Morris water maze performance: interstrain variability. Physiol Behav 58: 57–65.
Froger N, Palazzo E, Boni C, Hanoun N, Saurini F, Joubert C et al (2004). Neurochemical and behavioral alterations in glucocorticoid receptor-impaired transgenic mice after chronic mild stress. J Neurosci 24: 2787–2796.
Galea LA, McEwen BS, Tanapat P, Deak T, Spencer RL, Dhabhar FS (1997). Sex differences in dendritic atrophy of CA3 pyramidal neurons in response to chronic restraint stress. Neuroscience 81: 689–697.
Gamaro GD, Prediger ME, Lopes JB, Dalmaz C (2003). Interactions between estradiol replacement and chronic stress on feeding behavior and on serum leptin. Pharmacol Bioc Behav 76: 327–333.
Gold PW, Chrousos GP (2002). Organization of the stress system and its dysregulation in melancholic and atypical depression: high vs low CRH/NE states. Mol Psychiatry 7: 254–275.
Grippo AJ, Francis J, Beltz TG, Felder RB, Johnson A (2003). Elevated cytokines in the chronic mild stress animal model of depression. Soc Neurosci Abstr 927: 10.
Hampson RE, Deadwyler SA (1998). Role of cannabinoid receptors in memory storage. Neurobiol Dis 5: 474–482.
Hampson RE, Deadwyler SA (1999). Cannabinoids, hippocampal function and memory. Life Sci 65: 715–723.
Harrold JA, Elliott JC, King PJ, Widdowson PS, Williams G (2002). Down-regulation of cannabinoid-1 (CB-1) receptors in specific extrahypothalamic regions of rats with dietary obesity: a role for endogenous cannabinoids in driving appetite for palatable food? Brain Res 952: 232–238.
Heresco-Levy U, Kremer I, Javitt DC, Goichman R, Reshef A, Blanaru M et al (2002). Pilot-controlled trial of D-cycloserine for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 5: 301–307.
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR, Rice KC (1991). Characterization and localization of cannabinoid receptors in the rat brain: a quantitative in vitro autoradiographic study. J Neurosci 11: 563–583.
Hill MN, Gorzalka BB (2004). Enhancement of the anxiety-like response to the cannabinoid receptor agonist HU-210 following chronic stress. Eur J Pharmacol 24: 291–295.
Irving AJ, Coutts AA, Harvey J, Rae MJ, Mackie K, Bewick GS et al (2000). Functional expression of cell surface cannabinoid CB(1) receptors on presynaptic inhibitory terminals in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 98: 253–262.
Katona I, Sperlagh B, Sik A, Kafalvi A, Vizi ES, Mackie K et al (1999). Presynaptically located CB1 cannabinoid receptors regulate GABA release from axon terminals of specific hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci 19: 4544–4558.
King NS (2002). Perseveration of traumatic re-experiencing in PTSD; a cautionary note regarding exposure based psychological treatments for PTSD when head injury and dysexecutive impairment are also present. Brain Injury 16: 65–74.
Lichtman AH, Varvel SA, Martin BR (2002). Endocannabinoids in cognition and dependence. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 66: 269–285.
Lopez JF, Chalmers DT, Little KY, Watson SJ (1998). Regulation of serotonin1A, glucocorticoid, and mineralocorticoid receptor in rat and human hippocampus: implications for the neurobiology of depression. Biol Psychiatry 43: 547–573.
Luine V, Villegas M, Martinez C, McEwen BS (1994). Repeated stress causes reverible impairments of spatial memory performance. Brain Res 639: 167–170.
Mailleux P, Vanderhaeghen JJ (1993). Glucocorticoid regulation of cannabinoid receptor messenger mRNA levels in the rat caudate-putamen: an in-situ hybridization study. Neurosci Lett 156: 51–53.
Marsicano G, Wotjak CT, Azad SC, Bisogno T, Rammes G, Cascio MG et al (2002). The endogenous cannabinoid system controls extinction of aversive memories. Nature 418: 530–534.
Martin M, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Maldonado R, Valverde O (2002). Involvement of CB1 cannabinoid receptors in emotional behavior. Psychopharmacology 159: 379–387.
McEwen BS (2001). Plasticity of the hippocampus: adaptation to chronic stress and allostatic load. Ann NY Acad Sci 933: 265–277.
McEwen BS (2003). Mood disorders and allostatic load. Biol Psychiatry 54: 200–207.
McEwen BS, Magarinos AM (1997). Stress effects on morphology and function of the hippocampus. Ann NY Acad Sci 821: 271–284.
Miller EK (2000). The prefrontal cortex and cognitive control. Nat Rev Neurosci 1: 59–65.
Mizoguchi K, Yuzurihara M, Ishige A, Sasaki H, Chui D-H, Tabira T (2000). Chronic stress induces impairment of spatial working memory because of prefrontal dopaminergic dysfunction. J Neurosci 20: 1568–1574.
Ossowska G, Nowa G, Kata R, Klenk-Majewska B, Danilczuk Z, Zebrowski-Lupina I (2001). Brain monoamine receptors in a chronic unpredictable stress model in rats. J Neural Transm 108: 311–319.
Patel S, Cravatt BF, Hillard CJ (2004). Synergistic interactions between cannabinoids and environmental stress in the activation of the central amygdalae. Neuropsychopharmacology, doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300535.
Patel S, Rademacher DJ, Hillard CJ (2003). Differential regulation of the endocannabinoids anandamide and 2-arachidonylglycerol within the limbic forebrain by dopamine receptor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306: 880–888.
Pavlides C, Nivon LG, McEwen BS (2002). Effects of chronic stress on hippocampal long-term potentiation. Hippocampus 12: 245–257.
Pope Jr HG, Gruber AJ, Hudson JI, Huestis MA, Yurgelun-Todd D (2001). Neuropsychological performance in long-term cannabis users. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58: 909–915.
Romero J, Garcia L, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Cebeira M, Ramos JA (1995). Changes in rat brain cannabinoid binding sites after acute or chronic exposure to their endogenous agonist, anandamide, or to Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 51: 731–737.
Sim-Selley LJ, Martin BR (2002). Effect of chronic administration of R-(+)-[2,3-dihydro-5-methyl-3-[(morpholinyl)methyl]pyrrolo[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazinyl]-(1-naphthalenyl)methanone mesylate (WIN55212-2) or Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol on cannabinoid receptor adaptation in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303: 36–44.
Solowij N, Stephens RS, Roffman RA, Babor T, Kadden R, Miller M et al (2002). Cognitive functioning of long term heavy cannabis users seeking treatment. JAMA 287: 1123–1131.
Stella N, Schweitzer P, Piomelli D (1997). A second endogenous cannabinoid that modulates long-term potentiation. Nature 388: 773–778.
Sugiura T, Kondo S, Sukagawa A, Nakane S, Shinoda A, Itoh K et al (1995). 2-Arachidonylglycerol: a possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand in the brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 215: 89–97.
Terranova JP, Storme JJ, Lafon N, Perio A, Rinaldi-Carmona M, Le Fur G et al. (1996). Improvement of memory in rodents by the selective CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist, SR 141716. Psychopharmacology 126: 165–172.
Touyarot K, Venero C, Sandi C (2004). Spatial learning impairment induced by chronic stress is related to individual differences in novelty reactivity: search for neurobiological correlates. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29: 290–305.
Varvel SA, Lichtman AH (2002). Evaluation of CB1 receptor knockout mice in the Morris water maze. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301: 915–924.
Vasconcellos AP, Tabajara AS, Ferrari C, Rocha E, Dalmaz C (2003). Effect of chronic stress on spatial memory in rats is attenuated by lithium treatment. Physiol Behav 79: 143–149.
Vyas A, Mitra R, Shankaranarayana Rao BS, Chattarji S (2002). Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. J Neurosci 22: 6810–6818.
Weinberg J, Bezio S (1987). Alcohol-induced changes in pituitary–adrenal activity during pregnancy. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 11: 274–280.
Willner P (1997). Validity, reliability and utility of the chronic mild stress model of depression: a 10 year review and evaluation. Psychopharmacology 134: 319–329.
Wolf S, Matzinger P (2003). Relax—endogenous cannabinoids in enriched mice. 13th Annual Symposium on the Cannabinoids, p 89.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NIH Grant R01-DA016967 and an Independent Investigator Award from NARSAD to CJH; a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) grant to BBG; an NSERC postgraduate scholarship and a Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research (MSFHR) Research Training Award to MNH; an NIH-NRSA grant (F30 DA15575) to SP; an NIH-NRSA grant (F32 DA16510) to DJR. We like to thank Maric Tse, Indy Gill, Eda Karacabeyli and Wayne Yu for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, M., Patel, S., Carrier, E. et al. Downregulation of Endocannabinoid Signaling in the Hippocampus Following Chronic Unpredictable Stress. Neuropsychopharmacol 30, 508–515 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300601
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300601
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
How depression and antidepressant drugs affect endocannabinoid system?—review of clinical and preclinical studies
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2024)
-
Role of mesolimbic cannabinoid receptor 1 in stress-driven increases in cocaine self-administration in male rats
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
The antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of cannabinoids in chronic unpredictable stress: a preclinical systematic review and meta-analysis
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Chronic mild stress paradigm as a rat model of depression: facts, artifacts, and future perspectives
Psychopharmacology (2022)
-
The effects of FAAH inhibition on the neural basis of anxiety-related processing in healthy male subjects: a randomized clinical trial
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)