Abstract
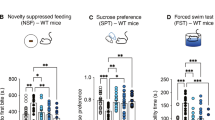
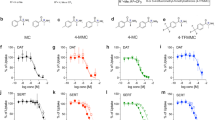
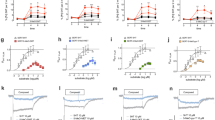
The addition of low doses of atypical antipsychotic drugs, which saturate 5-HT2A receptors, enhances the therapeutic effect of selective serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in patients with major depression as well as treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. The purpose of the present studies was to test the effects of combined treatment with a low dose of a highly selective 5-HT2A receptor antagonist (M100907; formerly MDL 100,907) and low doses of a SSRI using a behavioral screen in rodents (the differential-reinforcement-of low rate 72-s schedule of reinforcement; DRL 72-s) which previously has been shown to be sensitive both to 5-HT2 antagonists and SSRIs. M100907 has a ∼100-fold or greater selectivity at 5-HT2A receptors vs other 5-HT receptor subtypes, and would not be expected to appreciably occupy non-5-HT2A receptors at doses below 100 μg/kg. M100907 increased the reinforcement rate, decreased the response rate, and shifted the inter-response time distributions to the right in a pattern characteristic of antidepressant drugs. In addition, a positive synergistic interaction occurred when testing low doses of the 5-HT2A receptor antagonist (6.25–12.5 μg/kg) with clinically relevant doses of the SSRI fluoxetine (2.5–5 mg/kg), which both exerted minimal antidepressant-like effects by themselves. In vivo microdialysis study revealed that a low dose of M100907 (12.5 μg/kg) did not elevate extracellular 5-HT levels in the prefrontal cortex over those observed with fluoxetine alone (5 mg/kg). These results will be discussed in the context that the combined blockade of 5-HT2A receptors and serotonin transporters (SERT) may result in greater efficacy in treating neuropsychiatric syndromes than blocking either site alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adell A, Artigas F (1998). A microdialysis study of the in vivo release of 5-HT in the median raphe nucleus of the rat. Br J Pharmacol 125: 1361–1367.
Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ (1997). Serotonin induces excitatory postsynaptic potentials in apical dendrites of neocortical pyramidal cells. Neuropharmacology 36: 589–599.
Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ (1999). Serotonin, via 5-HT2A receptors, increases EPSCs in layer V pyramidal cells of prefrontal cortex by an asynchronous mode of glutamate release. Brain Res 825: 161–171.
Amargos-Bosch M, Bortolozzi A, Puig MV, Serrats J, Adell A, Celada P et al (2004). Co-expression and in vivo interaction of serotonin1a and serotonin2a receptors in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 14: 281–299.
Araneda R, Andrade R (1991). 5-Hydroxytryptamine2 and 5-Hydroxytryptamine1A receptors mediate opposing responses on membrane excitability in rat association cortex. Neuroscience 40: 399–412.
Ashby CR, Edwards E, Wang RY (1994). Electrophysiological evidence for a functional interaction between 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors in the rat medial prefrontal cortex: an iontophoretic study. Synapse 17: 173–181.
Borsini F (1995). Role of the serotonergic system in the forced swimming test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 19: 377–395.
Bymaster FP, Calligaro DO, Falcone JF, Marsh RD, Moore NA, Tye NC et al (1996). Radioceptor binding profile of the atypical antipsychotic olazepine. Neuropsychopharmacology 14: 87–96.
Cousins MS, Seiden LS (2000). The serotonin-1A receptor antagonist WAY-100635 modifies fluoxetine's antidepressant-like profile on the differential reinforcement of low rates 72-s schedule in rats. Psychopharmacology 148: 438–442.
Delgado PL, Charney DS, Price LH, Aghajanian GK, Landis H, Heninger GR (1990). Serotonin function and the mechanism of antidepressant action. Reversal of antidepressant-induced remission by rapid depletion of plasma tryptophan. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47: 411–418.
Delgado PL, Miller HL, Salomon RM, Licinio J, Krystal JH, Moreno FA et al (1999). Tryptophan-depletion challenge in depressed patients treated with desipramine or fluoxetine: implications for the role of serotonin in the mechanism of antidepressant action. Biol Psychiatry 46: 212–220.
Hervas I, Artigas F (1998). Effect of fluoxetine on extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in rat brain. Role of autoreceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 358: 9–18.
Hirose S, Ashby CRJ (2002). An open pilot study combining risperidone and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor as initial antidepressant therapy. J Clin Psychiatry 63: 733–736.
Jakab RL, Goldman-Rakic PS (1998). 5-HT2A serotonin receptors in the primate cerebral cortex: possible site of action of hallucinogens in pyramidal cell apical dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 735–740.
Jakab RL, Goldman-Rakic PS (2000). Segregation of serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT3 receptors in inhibitory circuits of the primate cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol 417: 337–348.
Kapur S, Zipursky RB, Remington G (1999). Clinical and theoretical implications of 5-HT2 and D2 receptor occupancy of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156: 286–293.
Kehne JH, Baron BM, Carr AA, Chaney SF, Elands J, Feldman DJ et al (1996). Preclinical characterization of the potential of the putative atypical antipsychotic MDL 100,907 as a potent 5-HT2A antagonist with a favorable CNS safety profile. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277: 968–981.
Lakoski JM, Aghajanian GK (1985). Effects of ketanserin on neuronal responses to serotonin in the prefrontal cortex, lateral geniculate and dorsal raphe nucleus. Neuropharmacology 24: 265–273.
Luttinger D, Freedman M, Hamel L, Ward SJ, Perrone M (1985). The effects of serotonin antagonists in a behavioral despair procedure in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 107: 53–58.
Marcoli M, Maura G, Munari C, Ruelle A, Raiteri M (1999). Pharmacological diversity between native human 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors sited on different neurons and involved in different functions. Br J Pharmacol 126: 607–612.
Marek GJ (2000). A novel approach to the identification of psychiatric drugs: serotonin–glutamate interactions in the prefrontal cortex. CNS Drug Rev 6: 205–217.
Marek GJ, Carpenter LL, McDougle CJ, Price LH (2003). Synergistic action of 5-HT2A antagonists and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 28: 402–412.
Marek GJ, Li AA, Seiden LS (1989). Selective 5-hydroxytryptamine2 antagonists have antidepressant-like effects on differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate 72-second schedule. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250: 52–59.
Marek GJ, McDougle CJ, Price LH, Seiden LS (1992). A comparison of trazodone and fluoxetine: implications for a serotonergic mechanism of antidepressant action. Psychopharmacology 109: 2–11.
Marek GJ, Seiden LS (1988). Effects of selective 5-hydroxytryptamine-2 and nonselective 5-hydroxytryptamine antagonists on the differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate 72-second schedule. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244: 650–658.
Marek GJ, Seiden LS (1994). Antidepressant drug screens and the serotonin system. In: Palomo T, Archer T (eds). Strategies for Studying Brain Disorders: Depressive, Anxiety and Drug Abuse Disorders. Vol 1. Farrand Press: London. pp 23–40.
Marek GJ, Wright RA, Gewirtz JC, Schoepp DD (2001). A major role for thalamocortical afferents in serotonergic hallucinogen receptor function in neocortex. Neuroscience 105: 113–126.
Martin JR, Bos M, Jenck F, Moreau J, Mutel V, Sleight AJ et al (1998). 5-HT2C receptor agonists: pharmacological characteristics and therapeutic potential. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286: 913–924.
Maura G, Marcoli M, Tortarolo M, Andrioli GC, Raiteri M (1998). Glutamate release in human cerebral cortex and its modulation by 5-hydroxytryptamine acting at h 5HT1D receptors. Br J Pharmacol 123: 45–50.
Miner LAH, Backstrom JR, Sanders-Bush E, Sesack SR (2003). Ultrastructural localization of serotonin2A receptors in the middle layers of the rat prelimbic prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience 116: 107–117.
Murphy GMJ, Kremer C, Rodriques HE, Schatzberg AF (2003). Pharmacogenetics of antidepressant medication intolerance. Am J Psychiatry 160: 1830–1835.
O'Connor M, Silver H (1998). Adding risperidone to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor improves chronic depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol 18: 89–90.
O'Donnell JM, Marek GJ, Seiden LS (2005). Antidepressant effects assessed using behavior maintained under a differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate (DRL) operant schedule. Neurosci Biobehav Rev (in press).
O'Donnell JM, Seiden LS (1982). Effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors on performance during differential reinforcement of low response rate. Psychopharmacology 78: 214–218.
Ostroff RB, Nelson JC (1999). Risperidone augmentation of SSRIs in major depression. J Clin Psychiatry 60: 256–259.
Pandey GN, Dwivedi Y, Rizavi HS, Ren X, Pandey SC, Pesold C et al (2002). Higher expression of 5-HT2A receptors in the postmortem brains of teenage suicide victims. Am J Psychiatry 159: 419–429.
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986). The Rat Brain in Stereotoxic Coordinates. Academic Press: Orlando, FL.
Pericic D (2003). Swim stress inhibits 5-HT2A receptor-mediated head twitch behavior in mice. Psychopharmacology 167: 373–379.
Peroutka SJ, Snyder SH (1980). Long-term antidepressant treatment decreases spiroperidol-labeled serotonin receptor binding. Science 210: 88–90.
Puig MV, Celada P, Diaz-Mataix L, Artigas F (2003). In vivo modulation of the activity of pyramidal neurons in the rat medial prefrontal cortex by 5-HT2A receptors. Relationship to thalamocortical afferents. Cereb Cortex 13: 870–882.
Puller IA, Carney SL, Colvin EM, Lucaites VL, Nelson DL, Wedley S (2000). LY367265, an inhibitor of the 5-hydroxytryptamine transporter and 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor antagonist: a comparison with the antidepressant, nefazodone. Eur J Pharmacol 407: 39–46.
Redrobe JP, Bourin M (1997). Partial role of 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors in the activity of antidepressants in the mouse forced swimming test. Eur J Pharmacol 325: 129–135.
Richards JB, Seiden LS (1991). A quantitative interresponse time analysis of DRL performance differentiates similar effects of the antidepressant desipramine and the novel anxiolytic gepirone. J Exp Anal Behav 56: 173–192.
Schmidt CJ, Fox CB, Harms JF, Wylie P, Seegar TF, Guanowsky V et al (2001). CP-646,781: a potent dual SSRI/5-HT2A receptor agonist. Socr Neurosci Abstr 27: Program no. 665-17.
Schotte A, Janssen PFM, Gommeren W, Luyten WH, Van Gompel P, Lesage AS et al (1996). Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding. Psychopharmacology 124: 57–73.
Schreiber R, Brocco M, Audinot V, Gobert A, Veiga S, Millan MJ (1995). 1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4 iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane)-induced head-twitches in the rat are mediated by 5-hydroxytryptamine(5-HT)2A receptors: modulation by novel 5-HT2A/2C antagonists, D1 antagonists and 5-HT1A agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273: 101–112.
Seiden LS, Dahms JL, Shaughnessy RA (1985). Behavioral screen for antidepressants: the effects of drugs and electroconvulsive shock on performance under a differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate schedule. Psychopharmacology 86: 55–60.
Shelton RC, Tollefson GD, Tohen M, Stahl S, Gannon KS, Jacobs TG et al (2001). A novel augmentation strategy for treating resistant major depression. Am J Psychiatry 158: 131–134.
Sokolowski JD, Seiden LS (1999). The behavioral effects of sertraline, fluoxetine, and paroxetine differ on the differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate 72-second operant schedule in the rat. Psychopharmacology 147: 153–161.
Stockmeier CA, Dilley GE, Shapiro LA, Overholser JC, Thompson PA, Meltzer HY (1997). Serotonin receptors in suicide victims with major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 16: 162–173.
Tanaka E, North RA (1993). Actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine on neurons of the rat cingulate cortex. J Neurophysiol 69: 1749–1757.
Tohen M, Vieta E, Calabrese J, Ketter TA, Sachs G, Bowden C et al (2003). Efficacy of olanzapine and olanzapine–fluoxetine combination in the treatment of bipolar I depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60: 1079–1088.
Willins DL, Deutch AY, Roth BL (1997). Serotonin 5-HT2A receptors are expressed on pyramidal cells and interneurons in the rat cortex. Synapse 27: 79–82.
Zhang W, Perry KW, Wong DT, Potts BD, Bao J, Tollefson GD et al (2000). Synergistic effects of olanzapine and other antipsychotic agents in combination with fluoxetine on norepinephrine and dopamine release in rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 23: 250–262.
Zhou F-M, Hablitz JJ (1999). Activation of serotonin receptors modulates synaptic transmission in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol 82: 2989–2999.
Acknowledgements
This work was previously presented at the 2001 Society for Neuroscience meeting (San Diego, CA) and the 2001 meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology (San Juan, Puerto Rico). This study was supported by PHS Grants K08 MH01551, R01 MH62186, a NARSAD Young Investigator Award (1999 Fairfax Investigator Award), the state of Connecticut (GJM), and National Institutes of Health Grants FIS 01/1147 and SAF2001-2133 (FA) We appreciate Dr Younglim Lee's review of the manuscript. We thank Nigel Henry, Sara Heron, Andrew Kwak, Megan Lennon, Boting Zhang, and Leticia Campa for technical assistance. We also thank Leslie Rosello for secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marek, G., Martin-Ruiz, R., Abo, A. et al. The Selective 5-HT2A Receptor Antagonist M100907 Enhances Antidepressant-Like Behavioral Effects of the SSRI Fluoxetine. Neuropsychopharmacol 30, 2205–2215 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300762
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300762
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
5-HT 2A and 5-HT 2C receptor antagonism differentially modulate reinforcement learning and cognitive flexibility: behavioural and computational evidence
Psychopharmacology (2024)
-
Effect of psilocybin on marble burying in ICR mice: role of 5-HT1A receptors and implications for the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
-
High-throughput brain activity mapping and machine learning as a foundation for systems neuropharmacology
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Premature responses in the five-choice serial reaction time task reflect rodents’ temporal strategies: evidence from no-light and pharmacological challenges
Psychopharmacology (2016)
-
Increased Serotonin Transporter Expression Reduces Fear and Recruitment of Parvalbumin Interneurons of the Amygdala
Neuropsychopharmacology (2015)