Abstract
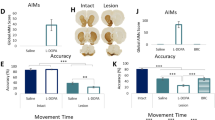
The mechanisms underlying dopamine agonist-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease remain poorly understood. Similar to patients, rats with severe nigrostriatal degeneration induced by 6-hydroxydopamine are more likely to show dyskinesia during chronic treatment with unselective dopamine receptor agonists than with D2 agonists, suggesting that D1 receptor stimulation alone or in conjunction with D2 receptor stimulation increases the chances of experiencing dyskinesia. As a first step towards disclosing drug-induced brain activation in dyskinesia, we examined the effects of dopamine agonists on behavior and blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) signal in the striatum and motor cortex of rats with unilateral nigrostriatal lesions. Rats were rendered dyskinetic before pharmacologic functional magnetic resonance imaging by means of a repeated treatment regime with dopamine agonists. The unselective agonist apomorphine and the selective D1/D5 agonist SKF-81297 induced strong forelimb dyskinesia (FD) and axial dystonia and increased BOLD signal in the denervated striatum. Besides, SKF-81297 produced a significant but smaller BOLD increase in the intact striatum and a symmetric bilateral increase in the motor cortex. The D2 family agonist quinpirole, which induced mild dyskinesia on chronic treatment, did not produce BOLD changes in the striatum or motor cortex. Further evidence to support an association between BOLD changes and dyskinesia comes from a direct correlation between scores of FD and magnitude of drug-induced BOLD increases in the denervated striatum and motor cortex. Our results suggest that striatal and cortical activation induced by stimulation of D1/D5 receptors has a primary role in the induction of peak dose dyskinesia in parkinsonism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aubert I, Guigoni C, Hakansson K, Li Q, Dovero S, Barthe N et al (2005). Increased D1 dopamine receptor signaling in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol 57: 17–26.
Bedard PJ, Boucher R (1989). Effect of D1 receptor stimulation in normal and MPTP monkeys. Neurosci Lett 104: 223–228.
Bezard E, Brotchie JM, Gross CE (2001). Pathophysiology of levodopa-induced dyskinesia: potential for new therapies. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 577–588.
Blanchet PJ, Grondin R, Bedard PJ (1996). Dyskinesia and wearing-off following dopamine D1 agonist treatment in drug-naive 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-lesioned primates. Movement Disord 11: 91–94.
Blandini F, Fancellu R, Orzi F, Conti G, Greco R, Tassorelli C et al (2003). Selective stimulation of striatal dopamine receptors of the D1- or D2-class causes opposite changes of fos expression in the rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Neurosci 17: 763–770.
Brooks DJ, Piccini P, Turjanski N, Samuel M (2000). Neuroimaging of dyskinesia. Ann Neurol 47 (Suppl 1): S154–S158; discussion S158–S159.
Buhmann C, Glauche V, Sturenburg HJ, Oechsner M, Weiller C, Buchel C (2003). Pharmacologically modulated fMRI—cortical responsiveness to levodopa in drug-naive hemiparkinsonian patients. Brain 126: 451–461.
Cenci MA, Lee CS, Björklund A (1998). -DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the rat is associated with striatal overexpression of prodynorphin- and glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA. Eur J Neurosci 10: 2694–2706.
Cenci MA, Whishaw IQ, Schallert T (2002). Animal models of neurological deficits: how relevant is the rat? Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 574–579.
Chen Q, Andersen GK, Zhang Z, Ovadia A, Cass WA, Gash DM et al (1999). Functional MRI of basal ganglia responsiveness to levodopa in parkinsonian rhesus monkeys. Exp Neurol 158: 63–75.
Chen YCI, Galpern WR, Brownell AL, Matthews RT, Bogdanov M, Isacson O et al (1997). Detection of dopaminergic neurotransmitter activity using pharmacologic MRI: correlation with PET, microdyalisis and behavioral data. Magnet Reson Med 38: 389–398.
Crossman AR (1990). A hypothesis on the pathophysiological mechanisms that underlie levodopa- or dopamine agonist-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease: implications for future strategies in treatment. Movement Disord 5: 100–108.
Delfino MA, Stefano AV, Ferrario JE, Taravini IR, Murer MG, Gershanik OS (2004). Behavioral sensitization to different dopamine agonists in a parkinsonian rodent model of drug-induced dyskinesias. Behav Brain Res 152: 297–306.
Donoghue JP, Wise SP (1982). The motor cortex of the rat: cytoarchitecture and microstimulation mapping. J Comp Neurol 212: 76–88.
Filion M, Tremblay L, Bedard PJ (1991). Effects of dopamine agonists on the spontaneous activity of globus pallidus neurons in monkeys with MPTP-induced parkinsonism. Brain Res 547: 152–161.
Fiorentini C, Rizzetti MC, Busi C, Bontempi S, Collo G, Spano P et al (2006). Loss of synaptic D1 dopamine/N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor complexes in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the rat. Mol Pharmacol 69: 805–812.
Gerfen CR, Miyachi S, Paletzki R, Brown P (2002). D1 dopamine receptor supersensitivity in the dopamine-depleted striatum results from a switch in the regulation of ERK1/2/MAP kinase. J Neurosci 22: 5042–5054.
Gnanalingham KK, Erol DD, Hunter AJ, Smith LA, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1995). Differential anti-parkinsonian effects of benzazepine D1 dopamine agonists with varying efficacies in the MPTP-treated common marmoset. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 117: 275–286.
Goulet M, Madras BK (2000). D(1) dopamine receptor agonists are more effective in alleviating advanced than mild parkinsonism in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292: 714–724.
Grillner S, Hellgren J, Menard A, Saitoh K, Wikstrom MA (2005). Mechanisms for selection of basic motor programs—roles for the striatum and pallidum. Trends Neurosci 28: 364–370.
Ireland MD, Lowe AS, Reavill C, James MF, Leslie RA, Williams SC (2005). Mapping the effects of the selective dopamine D2/D3 receptor agonist quinelorane using pharmacological magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroscience 133: 315–326.
Kalisch R, Delfino M, Murer MG, Auer DP (2005). The phenylephrine blood pressure clamp in pharmacologic magnetic resonance imaging: reduction of systemic confounds and improved detectability of drug-induced BOLD signal changes. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 180: 774–780.
Kalisch R, Elbel GK, Gossl C, Czisch M, Auer DP (2001). Blood pressure changes induced by arterial blood withdrawal influence BOLD signal in anesthesized rats at 7 Tesla: implications for pharmacologic MRI. Neuroimage 14: 891–898.
Keefe KA, Gerfen CR (1995). D1–D2 dopamine receptor synergy in striatum: effects of intrastriatal infusions of dopamine agonists and antagonists on immediate early gene expression. Neuroscience 66: 903–913.
LaHoste GJ, Yu J, Marshall JF (1993). Striatal Fos expression is indicative of dopamine D1/D2 synergism and receptor supersensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 7451–7455.
Lundblad M, Andersson M, Winkler C, Kirik D, Wierup N, Cenci MA (2002). Pharmacological validation of behavioral measures of akinesia and dyskinesia in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurosci 151: 120–132.
Meissner W, Ravenscroft P, Reese R, Harnack D, Morgenstern R, Kupsch A et al (2006). Increased slow oscillatory activity in substantia nigra pars reticulata triggers abnormal involuntary movements in the 6-OHDA-lesioned rat in the presence of excessive extracellular striatal dopamine. Neurobiol Dis 22: 586–598.
Metz GA, Whishaw IQ (2002). Drug-induced rotation intensity in unilateral dopamine-depleted rats is not correlated with end point or qualitative measures of forelimb or hindlimb motor performance. Neuroscience 111: 325–336.
Mitchell IJ, Boyce S, Sambrook MA, Crossman AR (1992). A 2-deoxyglucose study of the effects of dopamine agonists on the parkinsonian primate brain. Implications for the neural mechanisms that mediate dopamine agonist-induced dyskinesia. Brain 115: 809–824.
Monville C, Torres EM, Dunnett SB (2005). Validation of the l-dopa-induced dyskinesia in the 6-OHDA model and evaluation of the effects of selective dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists. Brain Res Bull 68: 16–23.
Morelli M, Fenu S, Garau L, Di Chiara G (1989). Time and dose dependence of the priming of the expression of dopamine receptor supersensitivity. Eur J Pharmacol 162: 329–335.
Murer MG, Dziewczapolski G, Menalled L, Garcia MC, Agid Y, Gershanik O et al (1998). Chronic levodopa is not toxic for remaining dopaminergic neurons, but instead promotes their recovery, in rats with moderate nigrostriatal lesions. Ann Neurol 43: 561–575.
Nagaoka T, Harel N, Zhao F, Wang P, Kim SG (2002). Critical threshold for arterial blood pressure for BOLD response to visual stimulation in anesthetized cats. Annual Meeting of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM) Abstract 1367.
Neafsey EJ, Bold EL, Haas G, Hurley-Gius KM, Quirk G, Sievert CF et al (1986). The organization of the rat motor cortex: a microstimulation mapping study. Brain Res Rev 396: 77–96.
Nguyen TV, Brownell AL, Iris Chen YC, Livni E, Coyle JT, Rosen BR et al (2000). Detection of the effects of dopamine receptor supersensitivity using pharmacological MRI and correlations with PET. Synapse 36: 57–65.
Nutt JG (2000). Clinical pharmacology of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol 47 (Suppl 1): S160–S164; discussion S164–S166.
Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Rodriguez M, DeLong MR, Olanow CW (2000). Pathophysiology of levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease: problems with the current model. Ann Neurol 47 (Suppl 1): S22–S32; discussion S32–S34.
Olsson M, Nikkhah G, Bentlage C, Bjorklund A (1995). Forelimb akinesia in the rat Parkinson model: differential effects of dopamine agonists and nigral transplants as assessed by a new stepping test. J Neurosci 15: 3863–3875.
Paul ML, Graybiel AM, David JC, Robertson HA (1992). D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptors synergistically activate rotation and c-fos expression in the dopamine-depleted striatum in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci 12: 3729–3742.
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press: Sidney.
Pearce RK, Jackson M, Britton DR, Shiosaki K, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1999). Actions of the D1 agonists A-77636 and A-86929 on locomotion and dyskinesia in MPTP-treated L-dopa-primed common marmosets. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 142: 51–60.
Rascol O, Nutt JG, Blin O, Goetz CG, Trugman JM, Soubrouillard C et al (2001). Induction by dopamine D1 receptor agonist ABT-431 of dyskinesia similar to levodopa in patients with Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 58: 249–254.
Rascol O, Sabatini U, Brefel C, Fabre N, Rai S, Senard JM et al (1998). Cortical motor overactivation in parkinsonian patients with L-dopa-induced peak-dose dyskinesia. Brain 121: 527–533.
Robertson HA, Peterson MR, Murphy K, Robertson GS (1989). D1-dopamine receptor agonists selectively activate striatal c-fos independent of rotational behaviour. Brain Res 503: 346–349.
Salin P, Dziewczapolski G, Gershanik OS, Nieoullon A, Raisman-Vozari R (1997). Differential regional effects of long-term L-DOPA treatment on preproenkephalin and preprotachykinin gene expression in the striatum of 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 47: 311–321.
Steward CA, Marsden CA, Prior MJ, Morris PG, Shah YB (2005). Methodological considerations in rat brain BOLD contrast pharmacological MRI. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 80: 687–704.
Taymans JM, Kia HK, Groenewegen HJ, Leysen JE, Langlois X (2005). Bilateral control of brain activity by dopamine D1 receptors: evidence from induction patterns of regulator of G protein signaling 2 and c-fos mRNA in D1-challenged hemiparkinsonian rats. Neuroscience 134: 643–656.
Trugman JM, Wooten GF (1987). Selective D1 and D2 dopamine agonists differentially alter basal ganglia glucose utilization in rats with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine substantia nigra lesions. J Neurosci 7: 2927–2935.
Tuor UI, McKenzie E, Tomanek B (2002). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of tonic pain and vasopressor effects in rats. Magnet Reson Imaging 20: 707–712.
Ungerstedt U (1976). 6-hydroxydopamine-induced degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway: the turning syndrome. Pharmacol Ther 2: 37–40.
Waddington JL, Daly SA, Downes RP, Deveney AM, McCauley PG, O'Boyle KM (1995). Behavioural pharmacology of ‘D-1-like’ dopamine receptors: further subtyping, new pharmacological probes and interactions with ‘D-2-like’ receptors. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 19: 811–831.
Wang R, Foniok T, Wamsteeker JI, Qiao M, Tomanek B, Vivanco RA et al (2006). Transient blood pressure changes affect the functional magnetic resonance imaging detection of cerebral activation. Neuroimage 31: 1–11.
Winkler C, Kirik D, Bjorklund A, Cenci MA (2002). L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson's disease: relation to motor and cellular parameters of nigrostriatal function. Neurobiol Dis 10: 165–186.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by DAAD and Argentine Agency for the Promotion of Science (PROALAR99-66 and PICT-05-11063), National Parkinson Foundation (USA), Argentine National Research Council (CONICET) and University of Buenos Aires. We thank Dr Valeria Della Maggiore for helpful comments on an earlier version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delfino, M., Kalisch, R., Czisch, M. et al. Mapping the Effects of Three Dopamine Agonists with Different Dyskinetogenic Potential and Receptor Selectivity Using Pharmacological Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Neuropsychopharmacol 32, 1911–1921 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301329
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301329
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Kinase Fyn As a Novel Intermediate in l-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson’s Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
-
The striatal cholinergic system in l-dopa-induced dyskinesias
Journal of Neural Transmission (2018)
-
The role of beta-arrestin2 in shaping fMRI BOLD responses to dopaminergic stimulation
Psychopharmacology (2017)
-
The effects of BMY-14802 against l-DOPA- and dopamine agonist-induced dyskinesia in the hemiparkinsonian rat
Psychopharmacology (2013)
-
Postsynaptic nigrostriatal dopamine receptors and their role in movement regulation
Journal of Neural Transmission (2010)