Abstract
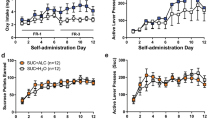
We have recently shown that priming injections of alcohol and footshock stress reinstate alcohol seeking in drug-free rats. Here we tested whether naltrexone and fluoxetine, two drugs used in the treatment of alcohol dependence, would affect reinstatement of alcohol seeking induced by these events. We also determined the effects of these drugs on alcohol self-administration during the maintenance phase. Rats were trained to press a lever for a 12% w/v alcohol solution. After stable drug-taking behavior was obtained, lever pressing for alcohol was extinguished. Reinstatement of drug seeking was then determined after priming injections of alcohol (0.24–0.96 g/kg) or exposure to intermittent footshock (5 and 15 min). Rats were pretreated with naltrexone (0.2–0.4 mg/kg) or fluoxetine (2.5–5 mg/kg) during maintenance or during tests for reinstatement. Both naltrexone and fluoxetine decreased lever presses for alcohol during the maintenance phase. Naltrexone blocked alcohol-induced, but not stress-induced reinstatement. In contrast, fluoxetine blocked stress-induced reinstatement, while its effect on alcohol-induced reinstatement was less consistent. The implications of these data to the understanding of relapse to alcohol are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abe M, Nakai H, Tabata R, Saito K, Egawa M . (1998): Effect of 5-[3-[((2S)-1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylmethyl)amino]propoxy]-1,3-benzodioxole HCl (MKC-242), a novel 5-HT1A-receptor agonist, on aggressive behavior and marble burying behavior in mice. Jpn J Phrmacol 76: 297–304
Aggleton JP . (1992): The amygdala: neurobiological aspects of emotion, memory, and mental dysfunction. New York, Wiley-Liss
Akil H, Madden J, Patrick RL, Barchas JD . (1976): Stress-induced increase in endogenous opiate peptides: Concurrent analgesia and its partial reversal by naloxone. In Kosterlits HW (ed), Opiates and Endogenous Opioid Peptides. Amsterdam, The Netherlands, Elsevier, pp 63–70
Akunne HC, Soliman KF . (1994): Serotonin modulation of pain responsiveness in the aged rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 48: 411–416
Amit Z, Galina H . (1986): Stress-induced analgesia: Adaptive pain suppression. Physiol Rev 66: 1091–1120
Amit Z, Smith BR, Gill K . (1991): Serotonin uptake inhibitors: Effects on motivated consummatory behaviors. J Clin Psychiatry 52(suppl):55–60
Bigelow GE, Griffiths RR, Liebson IA . (1977): Pharmacological influences upon human ethanol self-administration. In: Gross MM (ed), Alcohol intoxication and withdrawal. New York, Plenum Press, pp 523–538
Bliss EL, Thatcher W, Ailion J . (1972): Relationship of stress to brain and serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. J Psychiatry Res 9: 71–80
Bodnoff SR, Suranyi-Cadotte B, Quirion R, Meaney MJ . (1989): A comparison of the effects of diazepam versus several typical and atypical anti-depressant drugs in an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharmacology 97: 277–279
Brown SA, Vik PW, Patterson TL, Grant I, Schuckit MA . (1995): Stress, vulnerability and adult alcohol relapse. J Stud Alcohol 56: 538–545
Cannon WB . (1935): Stresses and strains of homeostasis. Am J Med Sci 189: 1–14
Carroll ME, Comer SD . (1996): Animal models of relapse. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 4: 11–18
Chaouloff F . (1993): Physiopharamcological interactions between stress hormones and central serotonergic systems. Brain Res Rev 18: 1–32
Cooper ML, Russell M, Skinner JB, Frone MR, Mudar P . (1992): Stress and alcohol use: Moderating effects of gender, coping and alcohol expectancies. J Abnorm Psychol 101: 139–152
de Wit H . (1996): Priming effects with drugs and other reinforcers. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 4: 5–10
de Wit H, Chutuape MA . (1993): Increased ethanol choice in social drinkers following ethanol preload. Behav Pharmacol 4: 29–36
De Vry J, Benz U, Schreiber R, Traber J . (1993): Shock-induced ultrasonic vocalization in young adult rats: A model for testing putative anti-anxiety drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 16: 331–339
Erb S, Shaham Y, Stewart J . (1996): Stress reinstates cocaine-seeking behavior after prolonged extinction and drug-free periods. Psychopharmacology 128: 408–412
Erb S, Mueller D, Shaham Y, Leung S, Stewart J . (1998a): Effect of clonidine on stress- and drug induced relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking. Soc Neurosci Abstr 24: 498
Erb S, Shaham Y, Stewart J . (1998b): The role of corticotropin-releasing factor and corticosterone in stress- and cocaine-induced relapse to cocaine seeking in rats. J Neurosci 14: 5529–5536
Fuller RW . (1994): Uptake inhibitors increase extracellular serotonin concentration measured by brain microdialysis. Life Sci 55: 163–167
Fuller RW, Snoody HD . (1990): Serotonin receptors subtypes involved in the elevation of serum corticosterone concentration in rats by direct- and indirect serotonin agonists. Neuroendocrinology 52: 206–211
Gonzales RA, Weiss F . (1998): Suppression of ethanol-reinforced behavior by naltrexone is associated with atenuation of ethanol-induced increase in dialysate dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 18: 10663–10671
Grignaschi G, Samanin R . (1992): Role of serotonin and catecholaines in brain in the feeding suppressant effect of fluoxetine. Neuropharmacology 31: 445–449
Griebel G, Blanchard DC, Agnes RS, Blanchard RJ . (1995): Differential modulation of antipredator defensive behavior in Swiss-Webster mice following acute and chronic administration of imipramine and fluoxetine. Psychopharmacology 120: 57–66
Griebel G, Rodgers RJ, Perrault G, Sanger DJ . (1997): Risk assessment behaviour: evaluation of utility in the study of 5-HT-related drugs in the rat elevated plus-maze test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 57: 817–827
Haraguchi M, Samson HH, Tolliver GA . (1990): Reduction in oral ethanol self-administration in the rat by the 5-HT uptake blocker fluoxetine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35: 259–262
Herz A . (1997): Endogenous opioid systems and alcohol addiction. Psychopharmacology 129: 99–111
Hodgson R, Rankin H, Strickwell T . (1979): Alcohol dependence and the priming effect. Behav Res Ther 17: 379–387
Hore BD . (1971): Factors in alcoholic relapse. Brit J Addict 66: 89–96
Hyytia P, Sinclair JD . (1993): Responding for oral ethanol after naltrexone treatment by alcohol-preferring AA rats. Alcoholis: Clin Exp Res 17: 631–636
Kirby LG, Allen AR, Lucki I . (1995): Regional differences in the effects of forced swimming on extracellular levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. Brain Res 682: 189–196
Kirby LG, Lucki I . (1997): Interaction between the forced swimming test and fluoxetine treatment on extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282: 967–976
Lê AD, Tomkins DM, Sellers EM . (1996): Uses of serotonin and opiate based drugs in the pharmacotherapy of alcohol dependence: An overview of the preclinical data. Alcohol Alcoholism 31: 27–32
Lê AD, Quan B, Juzystch W, Fletcher PJ, Joharchi N, Shaham Y . (1998): Reinstatement of alcohol-seeking by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress in rats. Psychopharmacology 135: 169–174
Linseman MA . (1987): Alcohol consumption in free feeding rats: Procedure, genetic and pharmacokinetic factors. Psychopharmacology 92: 254–261
Ludwig AM, Wikler A, Stark LH . (1974): The first drink. Psychobiological aspects of craving. Arch Gen Psychiatry 30: 539–547
Messing RB, Phebus L, Fisher LA, Lytle LD . (1975): Analgesic effect of fluoxetine hydrochloride (Lilly 110140), a specific inhibitor of serotonin uptake. Psychopharmacol Commun 1: 511–521
Murphy JM, Waller MB, Gatto GJ, McBride WJ, Lumeng L, Li TK . (1988): Effects of fluoxetine on the intragastric self-administration of ethanol in the alcohol preferring P line of rats. Alcohol 5: 283–286
Naranjo CA, Sellers EM . (1989): Serotonin uptake inhibitors attenuate ethanol intake in problem drinkers. Recent Dev Alcohol 7: 255–266
Nelson CJ, Jordan WP, Bohan RT . (1997): Daily fluoxetine administration impairs avoidance learning in the rat without altering sensory thresholds. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 21: 1043–1057
O'Malley SS, Jaffe JH, Chang G, Schottenfeld RS, Meyer RE, Rounsaville BJ . (1992): Naltrexone and coping skills therapy for alcohol dependence: A controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49: 881–887
Rueter LE, Fornal CA, Jacobs BL . (1997): A critical review of 5-HT brain microdialysis and behavior. Rev Neurosci 8: 117–137
Sanchez C, Meier E . (1997): Behavioral profiles of SSRIs in animal models of depression, anxiety and aggression. Are they all alike? Psychopharmacology 129: 197–205
Sanger DJ, Blackman DE . (1976): Rate-dependent effects of drugs: A review of the literature. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 4: 73–83
Schwarz-Stevens KS, Files FJ, Samson HH . (1992): Effects of morphine and naloxone on ethanol- and sucrose-reinforced responding in non-deprived rats. Alcoholism: Clin Exp Res 16: 822–832
Sellers EM, Higgins GA, Sobell MB . (1992): 5-HT and alcohol abuse. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13: 69–75
Selye H . (1956): The stress of life. New York, McGraw-Hill
Shaham Y . (1996): Effect of stress on opioid-seeking behavior: Evidence from studies with rats. Annal Behav Med 18: 255–263
Shaham Y, Stewart J . (1995): Stress reinstates heroin self-administration behavior in drug-free animals: An effect mimicking heroin, not withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 119: 334–341
Shaham Y, Stewart J . (1996): Effects of opioid and dopamine receptor anatgonist on relapse induced by stress and re-exposure to heroin in rats. Psychopharmacology 125: 385–391
Shaham Y, Rajabi H, Stewart J . (1996): Relapse to heroin-seeking under opioid maintenance: the effects of opioid withdrawal, heroin priming and stress. J Neurosci 16: 1957–1963
Shaham Y, Funk D, Erb S, Brown TJ, Walker CD, Stewart J . (1997): Corticotropin-releasing factor, but not cortico sterone, is involved in stress-induced relapse to heroin-seeking in rats. J Neurosci 17: 2605–2614
Shaham Y, Erb S, Leung S, Buczek Y, Stewart J . (1998a): CP-154,526, a selective, non peptide antagonist of the corticotropin-releasing factor type 1 receptor attenuates stress-induced relapse to drug seeking in cocaine-and heroin-trained rats. Psychopharmacology 137: 184–190
Shaham Y, Leung S, McDonald RJ, Stewart J . (1998b): Disruption of inhibitory processes may be involved in stress-induced relapse to heroin. Soc Neurosci Abstr 24: 498
Sinclair JD, Senter RJ . (1967): Increased preference for ethanol in rats following alcohol deprivation. Psychonom Sci 8: 11–16
Stewart J . (1984): Reinstatement of heroin and cocaine self-administration behavior in the rat by intracerebral application of morphine in the ventral tegmental area. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20: 917–923
Stewart J, de Wit H . (1987): Reinstatement of drug-taking behavior as a method of assessing incentive motivational properties of drugs. In Bozarth MA (ed), Methods of assessing the reinforcing properties of abused drugs. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 211–227
Tricklebank MD, Hutson PH, Curzon G . (1982): Analgesia induced by brief footshock is inhibited by 5-hydroxytryptamine but unaffected by antagonists of 5-hydroxytryptamine or by naloxone. Neuropharmacology 21: 51–56
Ulm RR, Volpicelli JR, Volpicelli LA . (1995): Opiates and alcohol self-administration in animals. J Clin Psychiatry 56(suppl 7):5–14
Volpicelli JR, Anterman AI, Hayashida M, O'Brien CP . (1992): Naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49: 876–880
Volpicelli JR, Rhines KC, Rhines JS, Volpicelli LA, Alterman AI, O'Brien CP . (1997): Naltrexone and alcohol dependence: role of subject compliance. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54: 737–742
Weiss F, Mitchiner M, Bloom FE, Koob GF . (1990): Free-choice responding for ethanol versus water in alcohol prefering (P) and unselected Wistar rats is differentially modified by naloxone, bromocriptine and methysergide. Psychopharmacology 101: 178–186
Zernig G, Fabisch K, Fabisch H . (1997): Pharmacotherapy for alcohol dependence. Trends Pharmacol Sci 18: 229–231
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Addiction Research Foundation (AD Lê) and the MRC of Canada (YS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lê, A., Poulos, C., Harding, S. et al. Effects of Naltrexone and Fluoxetine on Alcohol Self-Administration and Reinstatement of Alcohol Seeking Induced by Priming Injections of Alcohol and Exposure to Stress. Neuropsychopharmacol 21, 435–444 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00024-X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00024-X
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Blocking μ-opioid receptors attenuates reinstatement of responding to an alcohol-predictive conditioned stimulus through actions in the ventral hippocampus
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Reinstatement of Pavlovian responses to alcohol cues by stress
Psychopharmacology (2023)
-
CRF-5-HT interactions in the dorsal raphe nucleus and motivation for stress-induced opioid reinstatement
Psychopharmacology (2021)
-
Naloxone effects on extinction of ethanol- and cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in mice
Psychopharmacology (2017)
-
Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Drug Seeking: 20 Years of Progress
Neuropsychopharmacology (2016)