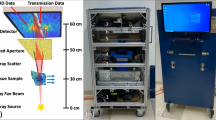
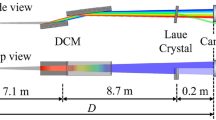
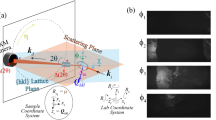
Abstract
A STANDARD method of X-ray analysis consists in measuring the strength of the diffracted beams corresponding to a series of reflections around a crystal zone (for example, the reflections with indices hol around the b axis), and then forming a double Fourier series with the amplitudes F as coefficients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Krist., 69, 168 (1928).
Z. Krist., 70, 475 (1929).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BRAGG, W. A New Type of ‘X-Ray Microscope’. Nature 143, 678 (1939). https://doi.org/10.1038/143678a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/143678a0
This article is cited by
-
DNA: hardware and software of life
Journal of Computational Electronics (2014)
-
Holograms of atoms
Nature (2001)
-
Optical Fourier Synthesis for Non-centrosymmetric Projections of Crystal Structures
Nature (1962)
-
A Simple Version of Bragg's X-ray Microscope
Nature (1955)