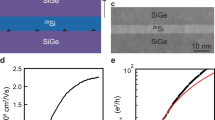
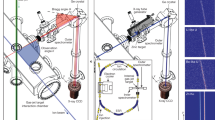
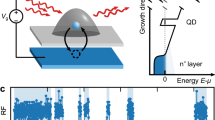
Abstract
C. N. SMYTH1 has shown that the space-charge between anode and cathode in the cut-off region of a diode gives rise to a large input conductance 1/R at ultra-high frequencies. He has also put forward arguments that the space-charge behaves as an additional source of noise at ultra-high frequencies. Hence it might be worth while to measure the 'equivalent noise temperature' Te of the conductance l/R, Te being defined by in which denotes the mean square noise current in a frequency interval Î"ν and k is Boltzmann's constant.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smyth, C. N., Nature, 157, 841 (1946).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VAN DER ZIEL, A., VERSNEL, A. Total Emission Noise in Diodes. Nature 159, 640–641 (1947). https://doi.org/10.1038/159640b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/159640b0
This article is cited by
-
Total Emission Damping
Nature (1948)